Bio307 - Test #3 - Chapter 18 (Gas Exchange)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:13 PM on 11/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
Hypoxia
oxygen deficiency causing a very strong drive to correct the deficiency
2
New cards
hypercapnia
the physical condition of having the presence of an abnormally high level of carbon dioxide in the circulating blood
3
New cards
hypocapnia
a state in which the level of carbon dioxide in the blood is lower than normal; can result from deep or rapid breathing
4
New cards
erythrocyte
aka RBC
5
New cards
hemoglobin
a hemoprotein composed of globin and heme that gives red blood cells their characteristic color, carries oxygen
6
New cards
oxygenated
supplied, treated, enriched with oxygen
7
New cards
deoxygenated
lacking oxygen
8
New cards
affinity (of hemoglobin for O2)
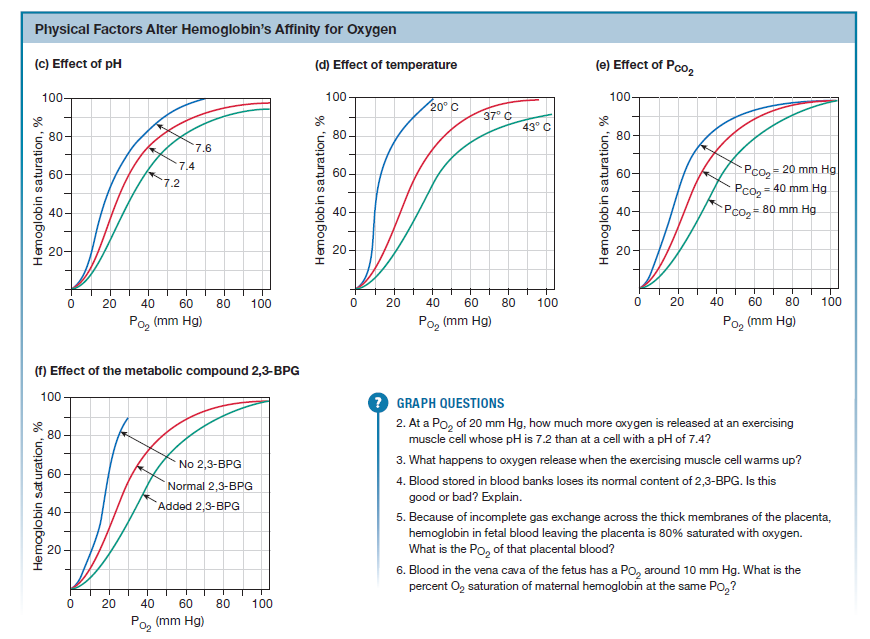
9
New cards
oxyhemoglobin saturation curve
Hemoglobin bound to oxygen
Resting Cell: 75% Saturation
Resting Cell: 75% Saturation
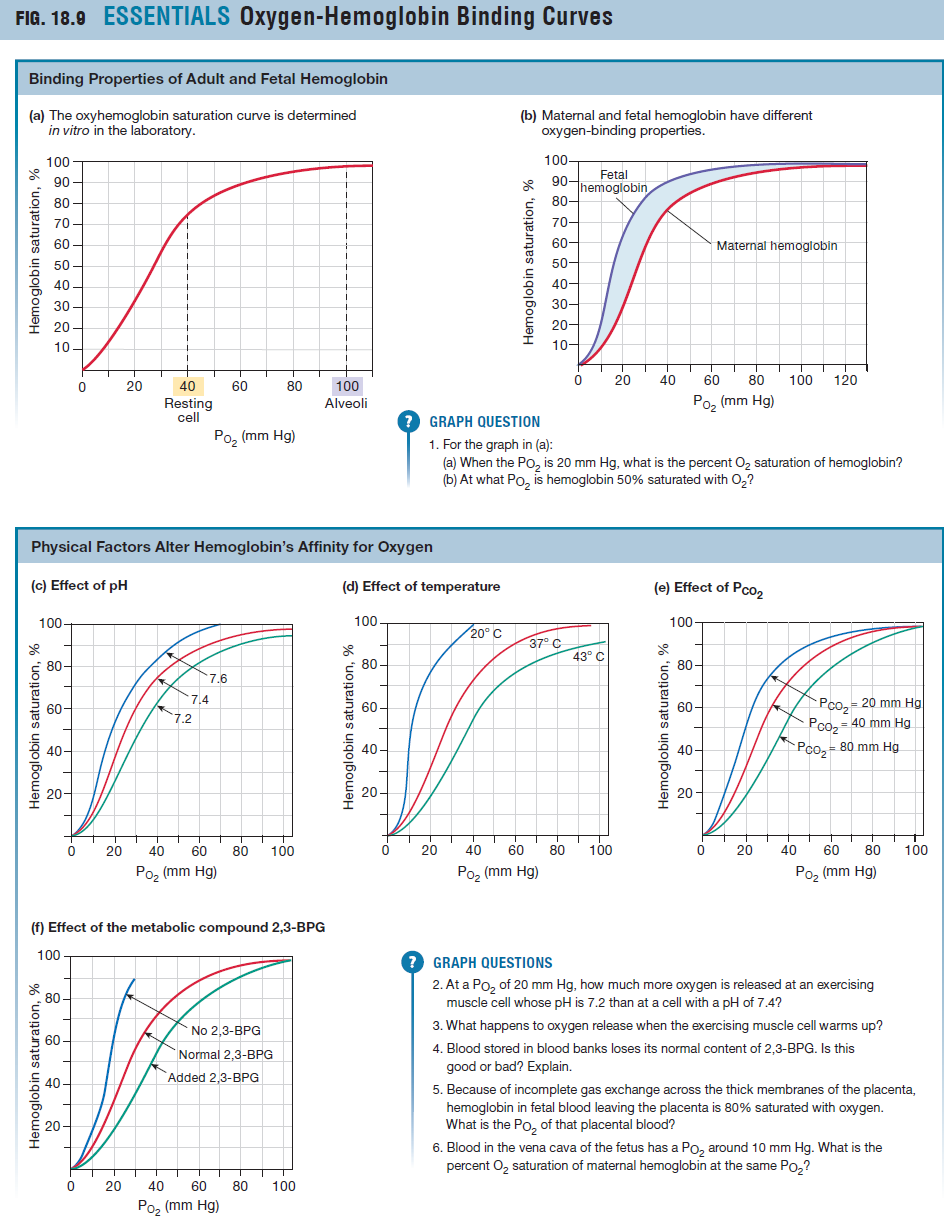
10
New cards
saturated (with respect to hemoglobin)
hemoglobin has adequate oxygen content
11
New cards
Transport of Gases
O2 and CO2 move only by simple diffusion in the body
CO2 can be turned into Bicarbonate (HCO3) to be transported
CO2 can be turned into Bicarbonate (HCO3) to be transported
12
New cards
How do different factors affect the diffusion of O2 and CO2
Emphysema - destroyed alveoli means less surface area for gas exchange
Fibrotic Lung Disease - thick alveolar membrane slows gas exchange
Pulmonary Edema - Fluid in interstitial space increases diffusion distance
Asthma - Increased airway resistance decreases alveolar ventilation
Physical Factors:
- pH
- Temperature
- P(CO2)
- 2,3-BPG
Lung Compliance (lung expandability)
Lung airway resistance
Rate/Depth of breathing
Surface Area (surfactant effect)
Diffusion distance (affected by barrier thickness/fluid amount)
Fibrotic Lung Disease - thick alveolar membrane slows gas exchange
Pulmonary Edema - Fluid in interstitial space increases diffusion distance
Asthma - Increased airway resistance decreases alveolar ventilation
Physical Factors:
- pH
- Temperature
- P(CO2)
- 2,3-BPG
Lung Compliance (lung expandability)
Lung airway resistance
Rate/Depth of breathing
Surface Area (surfactant effect)
Diffusion distance (affected by barrier thickness/fluid amount)
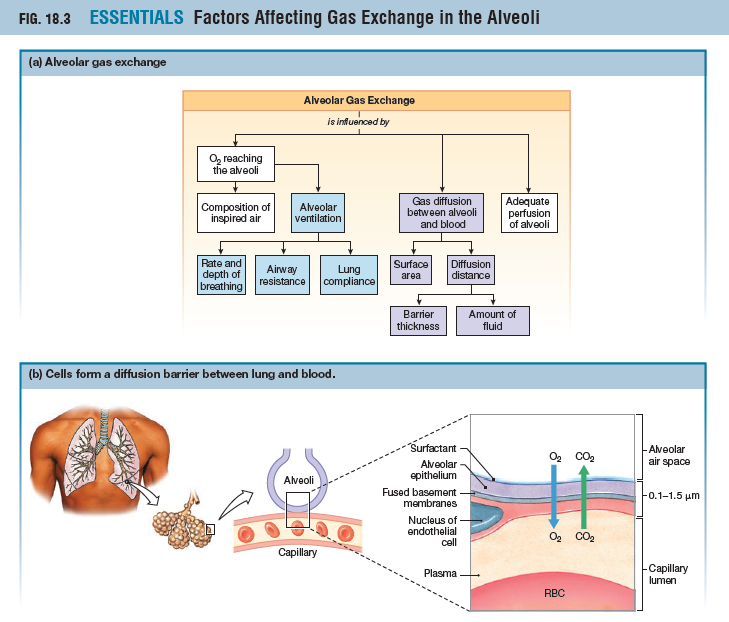
13
New cards
Concentration vs Partial Pressure
Concentration of a molecule dissolved in a water at a certain pressure is the partial pressure of gas in a solution.
Partial pressure of a material depends on the solubility of that gas in that medium
Partial pressure of a material depends on the solubility of that gas in that medium
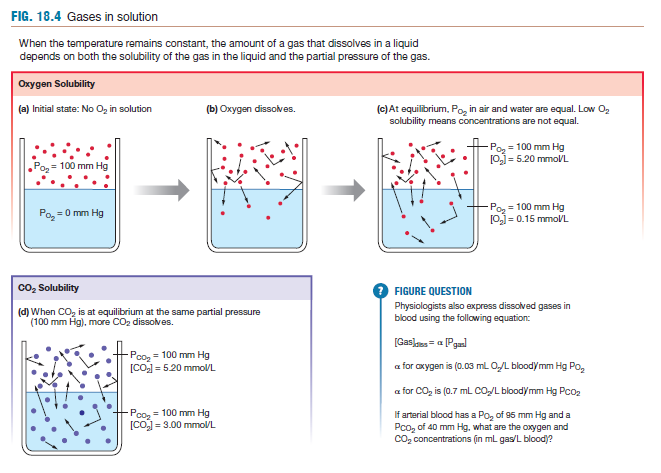
14
New cards
Hemoglobin Purpose + How it Contributes to Ability of Blood to Carry O2
Hemoglobin binds to Oxygen
It increases the ability of blood to carry large amounts of O2
It increases the ability of blood to carry large amounts of O2
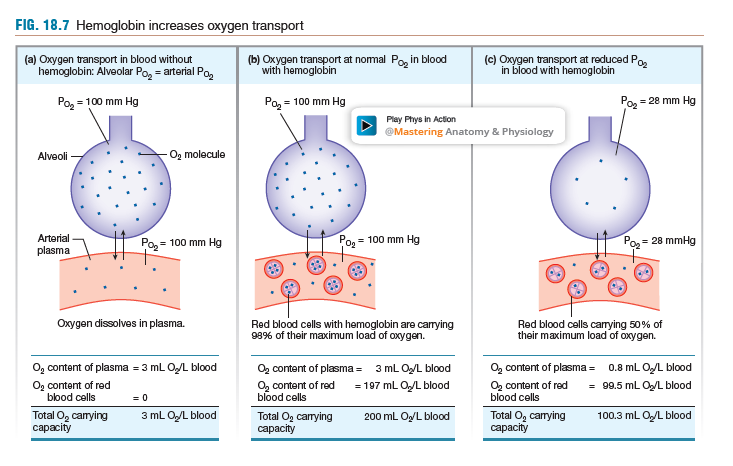
15
New cards
Relationship between tissue's rate of use of O2 and Location on Oxyhemoglobin Saturation Curve
Effect of exercise on O2 delivery
Effect of exercise on O2 delivery
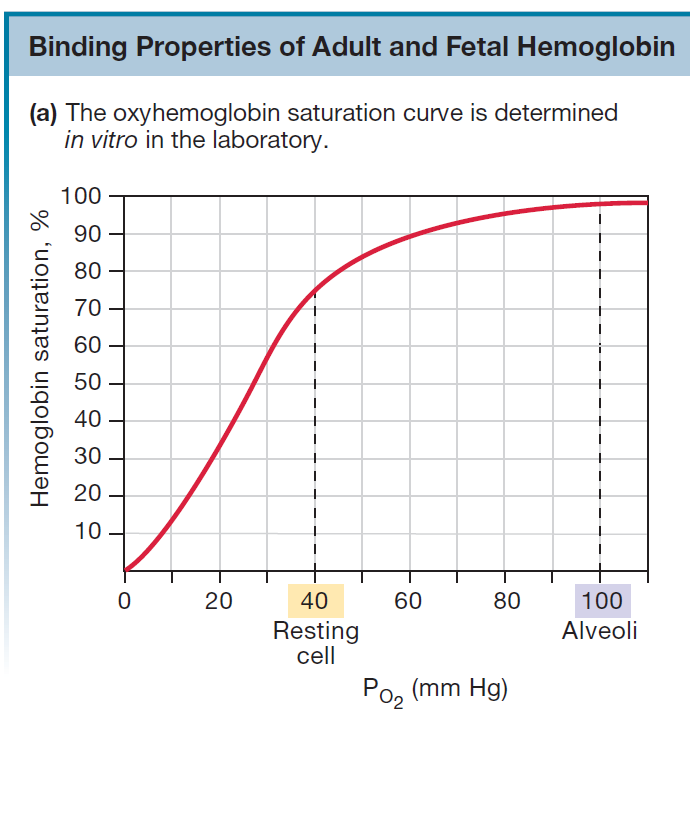
16
New cards
Bohr Effect (what it is? how it happens?)
A shift in the hemoglobin saturation curve that results from a change in pH
as H+ concentrations increase, pH falls, and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen decreases
as H+ concentrations increase, pH falls, and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen decreases
17
New cards
Effect of changes in O2 partial pressure, CO2 partial pressure, pH, temperature on % Saturation of Hemoglobin in that Tissue
^ P(O2): O2 Sat ^
^ P(CO2): O2 Sat v
^ pH = O2 Sat ^
^ temp = O2 Sat v
^ P(CO2): O2 Sat v
^ pH = O2 Sat ^
^ temp = O2 Sat v
18
New cards
How is CO2 transported in the blood (% breakdown)
CO2 is more soluble in body fluid than oxygen is
1) 7% dissolved in Blood Plasma
2) 93% diffuses into RBC (of which 23% binds hemoglobin, 70% converted to bicarbonate)
1) 7% dissolved in Blood Plasma
2) 93% diffuses into RBC (of which 23% binds hemoglobin, 70% converted to bicarbonate)
19
New cards
CO2 + H2O -> H+ + HCO3- Equation Significance
Bicarbonate is more soluble than CO2
1) Provides an additional way to transport CO2 from cells to lungs
2) Helps stabilize the body's pH
Runs forward reaction in systemic tissues (lower partial pressure of HCO3 near systemic tissue), runs backwards in lungs (where there is a lower partial pressure of CO2 as it is dispelled)
1) Provides an additional way to transport CO2 from cells to lungs
2) Helps stabilize the body's pH
Runs forward reaction in systemic tissues (lower partial pressure of HCO3 near systemic tissue), runs backwards in lungs (where there is a lower partial pressure of CO2 as it is dispelled)
20
New cards
How Above Equation Affects Breathing Rate, Kidney Reabsorption of Bicarbonate, metabolic rate of blood pH
^ Respiratory Rate to Remove CO2
Blood reabsorbs more bicarbonate, adding it will shift reaction to left to release CO2 to exhale
^ Metabolic rate = higher CO2 release = increase blood pH
Blood reabsorbs more bicarbonate, adding it will shift reaction to left to release CO2 to exhale
^ Metabolic rate = higher CO2 release = increase blood pH
21
New cards
Location of Motor Neurons that Control Involuntary Breathing
Medulla + Pons
22
New cards
Pathway by which change in partial pressure of CO2 in the blood leads to change in breathing rate and depth
If the blood has a higher p[CO2] then it wants to diffuse more of it through the alveoli to be exhaled, so breaths will be deeper and more frequent
^ CO2 = stimulation of medullary chemoreceptors + carotid/aortic chemoreceptors (influencing afferent sensory neurons) = targeting medulla/pons to cause inspiration/expiration
^ CO2 = stimulation of medullary chemoreceptors + carotid/aortic chemoreceptors (influencing afferent sensory neurons) = targeting medulla/pons to cause inspiration/expiration
![If the blood has a higher p[CO2] then it wants to diffuse more of it through the alveoli to be exhaled, so breaths will be deeper and more frequent
^ CO2 = stimulation of medullary chemoreceptors + carotid/aortic chemoreceptors (influencing afferent sensory neurons) = targeting medulla/pons to cause inspiration/expiration](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/371c14b9622a493384c3b24a82240c4d.jpeg)