Health Psychology Unit 1
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What is health?
Health means feeling good physically, mentally, and socially — not just being free from sickness.
Determinants (factors) of health
Biology & Genetics
Individual Behavior
Social Factors
Physical Environment
Health Services
Policy
The world health org (WHO) defines health as
a state of complete, physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
The Biomedical Model
A way of understanding health and illness that focuses only on the biological and physical aspects of disease.
such as age, gender, and genetics
It sees illness as something wrong with the body (like infection, injury, or chemical imbalance).
It doesn’t really consider social, psychological, or environmental factors.
The goal is to diagnose, treat, and cure the disease, usually with medicine, surgery, or other medical procedures.
Biological components
genes
race/ethnicity
biological age
biological sex/gender
physiological sensitivity
immune response
infection agents
environmental toxins (interacts w your gene expression)
Psychological components
Behavior (adaption & maintenance)
Emotional (feelings)
Cognition (thoughts, beliefs, and attitude)
Personality (characteristic ways of thinking and feeling)
Stress
Social components
Family relationships
Culture influences
Generational differences
Education (includes health education)
Social support
Medical care
Pollution control
Biopsychosocial Model
Looks at body, mind, and social factors together.
such as stress, economic satus, and cultural influences
Illness = mix of physical, mental, and social causes.
Treatment focuses on the whole person, not just the body.
Critical thinking
a questioning approach to all information and arguements
doesn’t blindly accept conclusions
examines all underlying assumptions
evaluates evidence
questions sources and possible ulterior motives
considers alternative explanations
Scientific method
used to explore the relationship between variables
A Theory
A detailed explanation that has been tested many times and never shown to be false
It causes testable predictions (hypotheses)
Testable Hypotheses
more than educated guess
A precise testable prediction about the relationship between two variables
Research
a test collecting data to support or refute a hypothesis
systematic
having a plan before the investigation starts
precision
Data collected carefully
Unbiased/objective
Look at the results without letting personal opinions get in the way. Only use what the data shows.
“lets the facts speak for themselves”
unscientific thinking
leaping to untested conclusions
faulty reasoning
ignoring alternative explanations in the face of our own expectation
belief bias
judging an argument based on what you already believe, not on logic
example: “I believe all natural foods are safe, so this new herbal supplement must be safe,” even without proof
confirmation bias
only noticing information that supports what you believe
Example: Thinking your team is the best, so you only read good news about them
Epidemiology
The study of how diseases spread, who they affect, and how to control or prevent them
Epidemiologist
Informs public about origins of disease
determines impact on prior generations
determines potential risk of disease to current and future populations
Morality (death)
the number of cases a specific disease, illness, or disability in a given group of people at a given time
Morbidity (sickness)
the number of people that are living with a disease or health problem
Incidence
the new number of cases of a disease or condition that occurs in a specific population with in a defined time interval
ex: rapid increase od HIV cases in siberia
Prevalence
The total number (old and new) of diagnosed cases of a disease or condition that exist at a given time
ex: total number of HIV cases in siberia
Retrospective study
when researchers look back at past data to find patterns or connections
Prospective study
a longitudinal study that follows people into the future to see what happens
Descriptive study
A type of research that simply describes what is happening in a group without trying to test cause and effect
answers questions like “what, who, where, and when but not why”
examples case studies, surveys, interviews, and naturalistic observations
Correlational studies
examines the relationship between two variables
can not show cause and effect
correlation coefficient (r)
r= +1 → perfect positive correlation
r = -1 → perfect negative correlation
r = 0 → no correlation
Numbers closer to 1 or -1 mean a stronger relationship.
Numbers closer to 0 mean a weaker relationship.
Experimental study
when researchers test cause and effect between x and y
disadvantages: cost and many variables can not be experimentally manipulated
Null hypothesis
the idea that there is no effect or no difference in an experiment or study
Independent variable (x)
The thing the researcher changes or controls
Dependent variable (y)
The thing that is measured
Experimental group
The group that gets the treatment or change
Control group
The group that does not get the treatment and stays normal
random sample
how researchers choose people from a larger population
everyone has equal chance of being picked
Purpose: to make sure the study group represents the population
example: Picking 100 students at random from a whole school to survey
Random Assignment
Happens after you already have your sample
How researchers put participants into groups
Everyone had an equal chance of being in any group
Purpose: to make sure groups are fair and balanced
Quasi Experiments
A study where the groups are already different at the start.
Groups are not randomly assigned
Example:
Class A has mostly high-achieving students.
Class B has mostly average students.
If you test a new teaching method, Class A might do better not because of the method, but because the students were already stronger to start with.
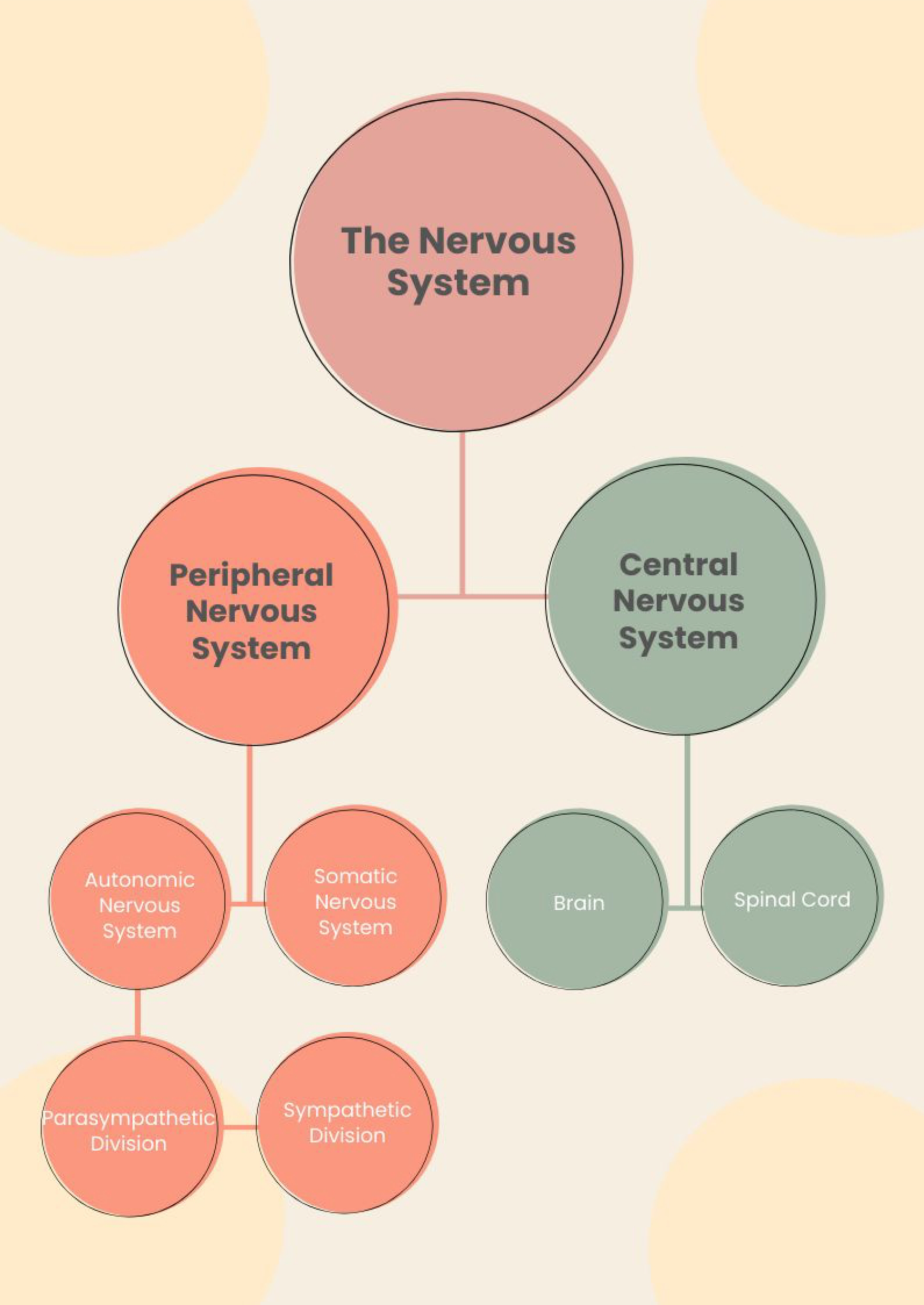
Central NS
The brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
The sensory/motor nerve fibers that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
Somatic NS
links the CNS with skeletal muscles
voluntary muscles such as jumping, walking, and chewing
Autonomic NS
Links the CNS with internal organs
Involuntary organs such as heart, reflexes, and hiccups
Sympathetic nervous system
division of the autonomic NS
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Parasympathetic NS
division of the autonomic NS
calms the body, conserving its energy
The nervous system
The body’s speed, electrochemical communication system
Network of interconnected nerve cells/ nerve fibers
Sensory
input to the brain/ spinal cord
motor
output from the brain/spinal cord to muscles and organs
Interneurons
transmit impulses between other neurons
The brain
is made up of 86 - 100 billion nerve cells (called neurons)
ten times as many support cells (called glia)
Neurons three task
Receive information from other neurons
Carries information down its length
Passes information to next neuron in line
Brain communication = Electrochemical
Electrical: Messages travel through neurons as tiny electrical signals.
Chemical: Neurons pass messages to each other using chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Chart
Brain chemistry
Neurons are separated by a space (synapse)
Neurotransmitter
a chemical messenger in the brain.
It carries signals from one nerve cell to another, helping control things like mood, movement, and memory.
The brain
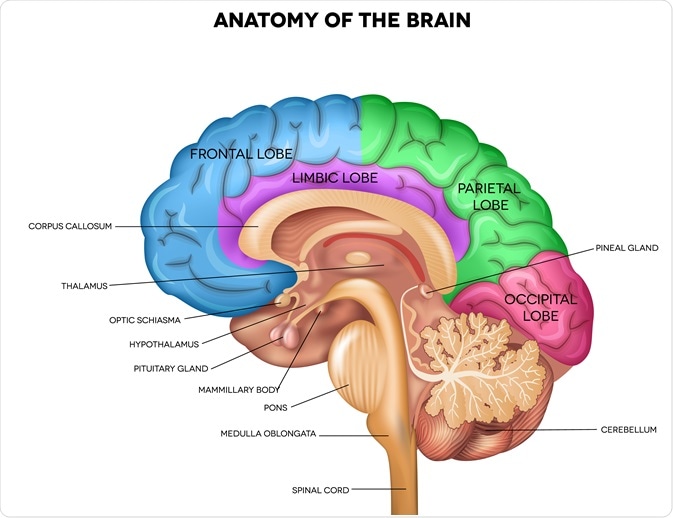
Hindbrain
cerebellum
medulla
pons
Cerebellum
Helps coordinate voluntary muscle movements
maintenance of balance
involved in emotional control, communication of sensory info
Medulla
controls heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
Pons
Link between the hindbrain and the midbrain
helps control breathing
controls the sleep wake cycle
The midbrain
pathway between hindbrain and forebrain
coordination of visual and auditory reflexes
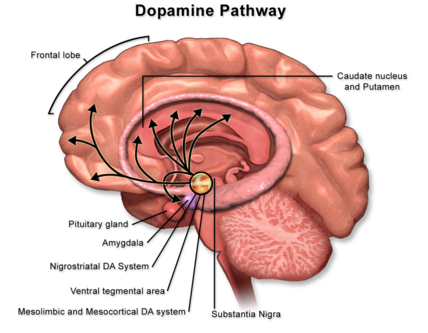
substantia nigra
in the midbrain
neuroransmitter dopamine
attention, memory, and problem solving
Superior colliculus
in the midbrain
receives input from the retina and the visual cortex
Limbic System (forebrain)
Neural structures at the border of the brainstem (hindbrain & midbrain) and cerebral hemispheres
associated with emotions like fear and aggravation
controls certain drives like food and sex
Amygdala (LS)
neural clusters that are components of the limbic system
linked to emotions
emotional memories
Hippocampus (LS)
Involved in cognitive processes such as
spatial orientation (where)
learning
new memory
you would remember if you seen a hippo on campus
Hypothalamus (LS)
neural structure lying below the thalamus
directs several maintenance activities
eating
drinking
body temperature
helps govern the endocrine system and the pituitary gland
is linked to the brains reward system
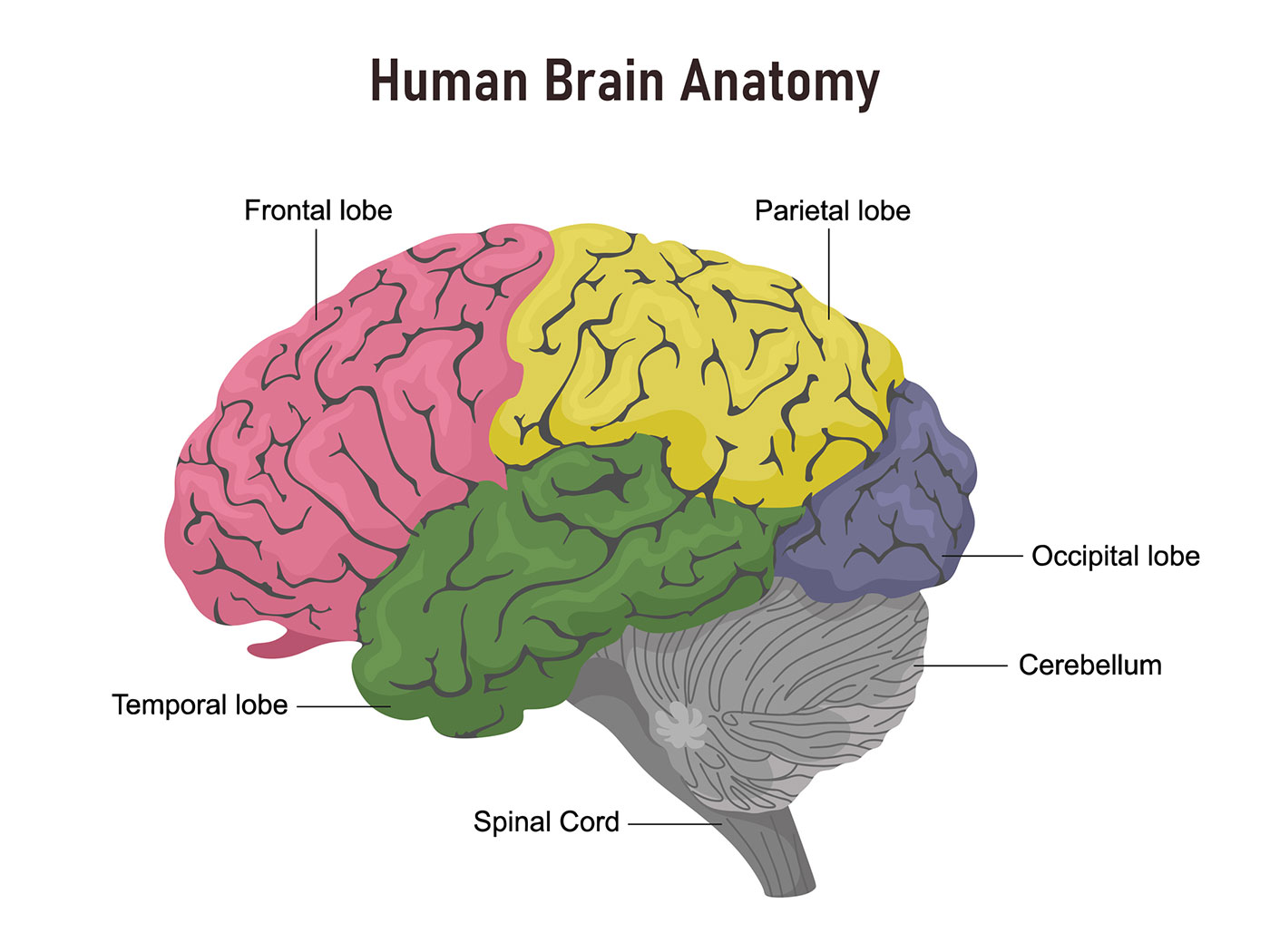
The cerebral cortex
Fabric of interconnected neural cells that cover the cerebral hemisphere
the body’s ultimate control and information processing center
divided into 4 lobes
Frontal lobes
making plans and judgements
contains the motor cortex
muscle movements
speech production
parietal lobes
includes the sensory cortex
receives information from skin and body
involved in representing space/your relationship in it
Occipital lobe
Includes the visual areas which receive visual information from the opposite visual field
Temporal lobe
Includes the auditory areas
retention of visual memories
major role in speech comprehension
The endocrine system (master control system)
slow chemical communication system
a set of glands → secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Hormones
chemical messengers
produced:
by the the endocrine glands
in one tissue and affect another
Adrenal glands
located above the kidneys
adrenal medulla: secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
norepinephrine helps to arouse the body in times of stress
adrenal cortex: secretes cortisol and helps to reduce swelling/inflammation
Cortisol
helps the body recover by repairing damage and reducing inflammation
works with the parasympathetic NS to restore homeostasis
chronic cortisol release
when your body keeps pumping out the stress hormone cortisol for a long time
weakens immune system
can cause cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer,, pain, fatigue, and depression
can also affect cognitive functioning, including memory
pituitary gland
under the influence of the hypothalamus
regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
Hypothalamus
controls hormones and basic body functions
Pituitary gland secretes ACTH (adrenocortitropic hormone)
ACTH binds the adrenal cortex to make cortisol
Thyroid gland
produces thyroxin
helps regulate growth and metabolism
hormones secreted by parathyroid glands regulate level or calcium in the body
Pancreas
glycogen increases the concentration of glucose in the body
insulin controls the conversion if sugar and carbohydrates into energy = decrease sugar levels
Cushing’s syndrome
A condition caused by too much cortisol in the body.
Symptoms:
Weight gain (especially belly/face)
High blood pressure
Weak muscles
Fragile skin / easy bruising
Mood changes (anxiety/depression)
High blood sugar
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1:
Body can’t make insulin (autoimmune)
Usually starts in childhood/teen years
Needs insulin shots
Type 2:
Body can’t use insulin properly (insulin resistance)
Usually starts in adults
Can often be managed with diet, exercise, and meds
Osteoporosis
A condition where bones become weak and brittle.
Causes/Risk Factors:
Low calcium or vitamin D
Aging (especially in postmenopausal women)
Certain medications or medical conditions
Effects:
Higher risk of fractures
Loss of height or posture changes
Cells
smallest building blocks of life
Tissues
groups of cells working together
organs
groups of tissues working together
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid makes too little hormone.
Body slows down.
Symptoms: Tired, weight gain, feeling cold, slow heart rate.
Hyperthyroidism
Thyroid makes too much hormone.
Body speeds up.
Symptoms: Nervousness, weight loss, feeling hot, fast heart rate.
Similarities between norepinephrine and epinephrine
Both are hormones & neurotransmitters.
Both are released during stress (“fight or flight”).
Both increase heart rate, blood pressure, and alertness.
Differences between norepinephrine and epinephrine
Epinephrine (Adrenaline):
Stronger effect on the heart (increases heart rate, blood flow).
Released mostly from the adrenal glands into the bloodstream.
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline):
Stronger effect on blood vessels (tightens them, raises blood pressure).
Works more as a neurotransmitter in the brain, keeping you alert.
cytokine
a tiny protein that helps cells in your immune system talk to each other.
They act like messenger signals: telling immune cells when to start fighting germs, calm down, or heal.
Different cytokines can cause inflammation, fever, or healing responses.