Chemistry: chapter 10- Chemical Bonding
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Q/A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
In which of the following compound does the central atom obey the octet rule?
d) SCl2
In the molecule OA = C = OB, the formal charge on OA, C and OB are respectively.
d) 0, 0, 0
Which of the following is electron deficient?
c) BH3
Which of the following molecule contain no π bond?
d) H2O
The ratio of number of sigma (σ) bond and pi (π) bonds in 2 – butynal is
a) 8/3
Which one of the following is the likely bond angles of sulphur tetrafluo-ride molecule?
d) 89°, 117°
Assertion:
Oxygen molecule is paramagnetic.
Reason :
It has two unpaired electron in its bonding molecular orbital
c) assertion is true but reason is false.
According to Valence bond theory, a bond between two atoms is formed when
b) half filled atomic orbitals overlap
In ClF3, NF3 and BF3 molecules the chlorine, nitrogen and boron atoms are
d) sp3d, sp3 and sp hybridised respectively
When one s and three p orbitals hybridise,
b) four equivalent orbitals at 109°28’ to each other will be formed
Which of these represents the correct order of their increasing bond order.
d) O22- < C2+ < O2 < C22-
Hybridisation of central atom in PCl5 involves the mixing of orbitals.
c) s, px, py, pz, dx2 – y2
The correct order of O – O bond length in hydrogen peroxide, ozone and oxygen is
b) O2 > O3 > H2O2
Which one of the following is diamagnetic?
b) O22
Bond order of a species is 2.5 and the number of electrons in its bonding molecular orbital is formed to be 8. The no. of electrons in its antibonding molecular orbital is
a) three
Shape and hybridisation of IF5 are
c) Square pyramidal, sp3d2
Pick out the incorrect statement from the following:
c) All five sp3d hybrid orbitals are not equivalent out of these five sp3d hybrid orbitals, three are at an angle of 120° remaining two are perpendicular to the plane containing the other three
The molecules having same hybridisation, shape and number of lone pairs of electrons are
a) SeF4, XeO2F2
In which of the following molecules / ions BF3, NO2– H20 the central atom is sp2 hybridised?
c) BF3 and NO2–
Some of the following properties of two species, NO3– and H3O+ are described below. Which one of them is correct?
a) dissimilar in hybridisation for the central atom with different structure
The types of hybridisation on the five-carbon atom from right to left in the, 2,3 pentadiene.
a) sp3, sp2, sp, sp2, sp3
XeF2 is isostructural with
d) ICl2–
The percentage of s-character of the hybrid orbitals in methane, ethane, ethene, and ethyne are respectively
a) 25, 25, 33.3, 50
Of the following molecules, which have shape similar to carbondioxide?
c) C2H2
According to VSEPR theory, the repulsion between different parts of electrons obey the order
c) 1. p – 1. p > b. p – 1. p > b. p – b. p
Shape of ClF3 is
c) “T” Shaped
Non – Zero dipole moment is shown by
d) water
Which of the following conditions is not correct for resonating structures?
c) the resonance hybrid should have higher energy than any of the contributing structure.
Among the following, the compound that contains, ionic, covalent, and Coordinate linkage is
a) NH4Cl
CaO and NaCl have the same crystal structure and approximately the same radii. If U is the lattice energy of NaCl, the approximate lattice energy of CaO is
d) 4U
Define Bond order
The number of bonds formed between the two bonded atoms in a molecule is called the bond order.
Define Hybridisation
Hybridisation is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals of the same atom with comparable energy to form an equal number of new equivalent orbitals with the same energy.
Define σ – bond
When two atomic orbitals overlap linearly along the axis, the resultant bond is called a sigma (σ) bond.
What is a pi – bond?
When two atomic orbitals overlap sideways, the resultant covalent bond is called a pi (π) bond. When we consider x-axis as the molecular axis, the py – py and pz – pz overlaps will result in the formation of a π – bond.
What is dipole moment?
The polarity of a covalent bond can be measured in terms of dipole moment which is defined as
μ = q × 2d
Where μ is the dipole moment, q is the charge and 2d is the distance between the two charges. The dipole moment is a vector and the direction of the dipole moment vector points from the negative charge to positive charge.
The unit of dipole moment is coloumb meter (C m). It is usually expressed in Debye unit (d). The conversion factor is 1 Debye = 3.336 × 10-30 C m.
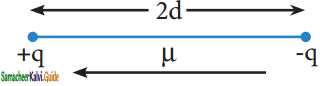
Linear form of carbondioxide molecule has two polar bonds. Yet the molecule has Zero dipole moment. Why?
The linear form of carbon dioxide has zero dipole moment, even though it has two polar bonds. In CO2, the dipole moments of two polar bonds (CO) are equal in magnitude but have opposite direction. Hence, the net dipole moment of the CO2 is,
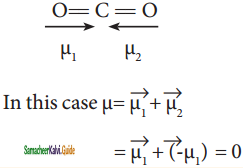
Which bond is stronger σ or π? Why?
1. Sigma bonds (σ) are stronger than Pi bonds (π). Because, sigma bonds are formed from bonding orbitals directly between the nuclei of the bonding atoms, resulting in greater overlap and a strong sigma bond (axial overlapping).
2. π bonds result from the overlap of atomic orbitals that are in contact through two areas of overlap (lateral overlapping). Pi bonds are more diffused bonds than sigma bonds.
Define Bond Energy
The bond enthalpy is defined as the minimum amount of energy required to break one mole of a particular bond in molecules in their gaseous state. The unit of bond enthalpy is kJ mol-1.
considering x-axis as the molecular axis which out of the following will form a sigma bond.
i) 1s and 2py
ii) 2px and 2py
iii) 2px and 2pz
iv) 1s and 2pz
i) 1s and 2py: No sigma bond
ii) 2px and 2py: sigma bond
iii) 2px and 2pz: No sigma bond
iv) 1s and 2pz: No sigma bond
What type of hybridization is possible in the following geometries?
octahedral
tetrahedral
square planar
octahedral: sp3d2
tetrahedral: sp3
square planar: dsp2