ESS 230 Midterm
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Mechanical Weathering Processes (PEWTS)
Pressure release (Exfoliation); Water freeze/thaw cycles; Thermal Expansion; Salt crystallization
Chemical Weathering Processes (HHOOS)
Hydration, Hydrolysis, Oxidation, Organic activity, Solution
Mechanical Weathering
No change in chemical composition; material breaks down into smaller pieces
Rates of Weathering Influenced by
Moisture, Surface Area, Temperature
Factors in Eroding Landscape Rates (CVLLT)
Climate-precipitation, Topography, Vegetation, Lithology, Land Use
Soil Creep
Gradual downslope movement of weathered material by gravity
Overland Flow
When enough flow accumulates to overcome erosion resistance of ground surface- Precipitation rate>infiltration rate
Landslides
downslope movement of soil/rock due to gravity; can be slow or rapid
Debris Flows
Type of landslide, high water content, rapid
Glacier Erosion
scours bedrock, picks up sediment and moves it; rapid, depends on glacier size, precipitation rate
~10mm/yr
River Incision
Carve into bedrock, slow erosion process
<.01 mm - 1 mm yr
Bank Erosion
recycles materials stored on valley bottom, typically in floodplain, delivered by other erosion processes
Joint
Crack in rock
Fault
Crack in earth
Soil
solid earth material weathered by physical, chemical, and organic processes, so it can support plant life
Mainstem
Main, thickest river
Hillslope
Unchannelized land surface
Discharge
All water moving thru cross section of river in given amount of time: width x av depth x velocity, m3/s
Factors of Soil Formation (COPTT)
Climate, Organisms, Parent Material, Topography, Time
Humic acids
Produced by plants and animals; effective chemical weathering agent
Elluviation
leaching by infiltrating water
Illuviation
deposition and accumulation of materials from higher levels of soil
O layer
humus
A layer
zone of leaching soluble salts
Weathering
The disintegration or breakdown of rock materials
Chemical Weathering
Breakdown as a result of chemical reactions
Bicarbonate Ion
dominant ion in surface runoff
Biological Weathering
Weathering by plant/animals, can be mechanical or chemical
B layer
zone of accumulation of salts
C layer
Weathered parent material
Aridisols
arid zone soil; physically weathered rock- not much plant life
Mollisols
grassland soils; decomposed organic material and soil material
Oxisols
tropical soils; oxidized
Continental Crust
thick, granite, not so dense
Oceanic Crust
thin, basalt, dense
Continental plate collison
high mountain ranges form
Oceanic plate collision
island arc and submarine trench form
Oceanic-continental plate collision
mountains and trench form
Subduction
when ocean crust is carried down into mantle following collision; sediment and basalt heated to form magma
Mid Ocean Ridges
underwater mountain ranges, 2k-4k m deep

Abyssal Basins
4k-6k m deep, include abyssal hills and plains
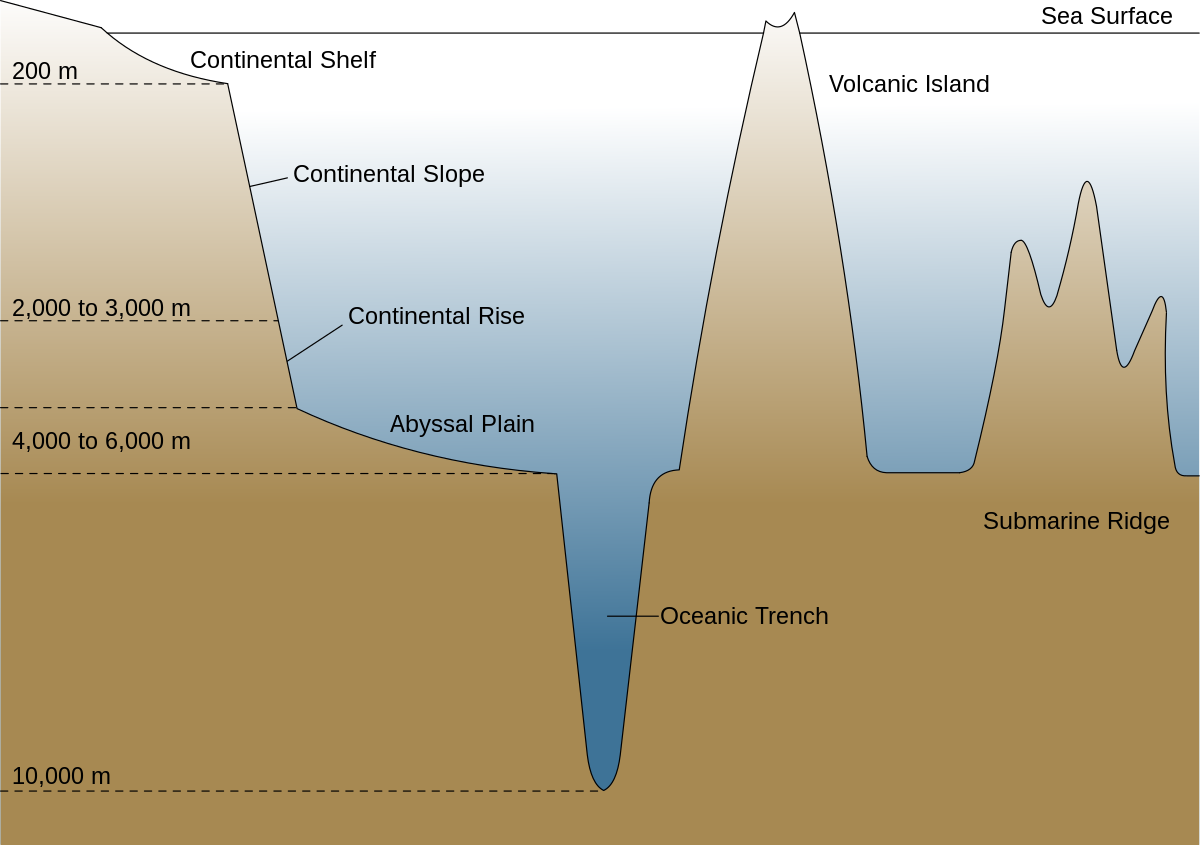
Continental Margin
created by sediment from land that builds into ocean basins when rifting occurs, 10% of land
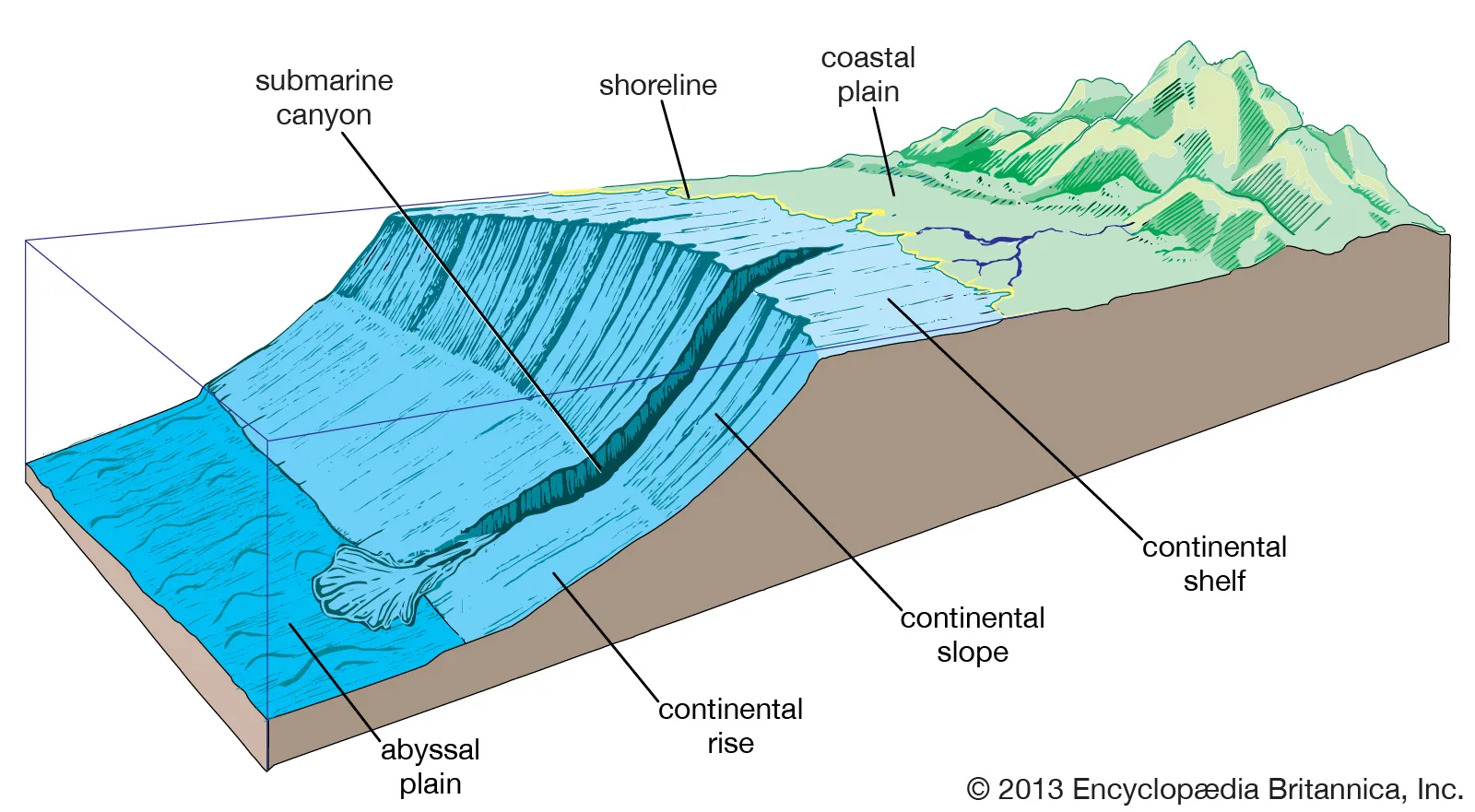
Continental Shelf
gently dipping, land surface when tide is out, glacial ice melted and flooded this portion of land
Continental Slope
steep, edge of continental crust, eroded by sediment, has underwater canyons
Continental Rise
gentle gradient, sediment from land piled onto ocean crust. 10% of ocean floor. between slope & plain
Submarine Fan
formed thru sediment accumulating at base of submarine canyon
Trailing Edge (passive) Margin
same direction of both plates, coastal plane, broad shelf, slope, and rise
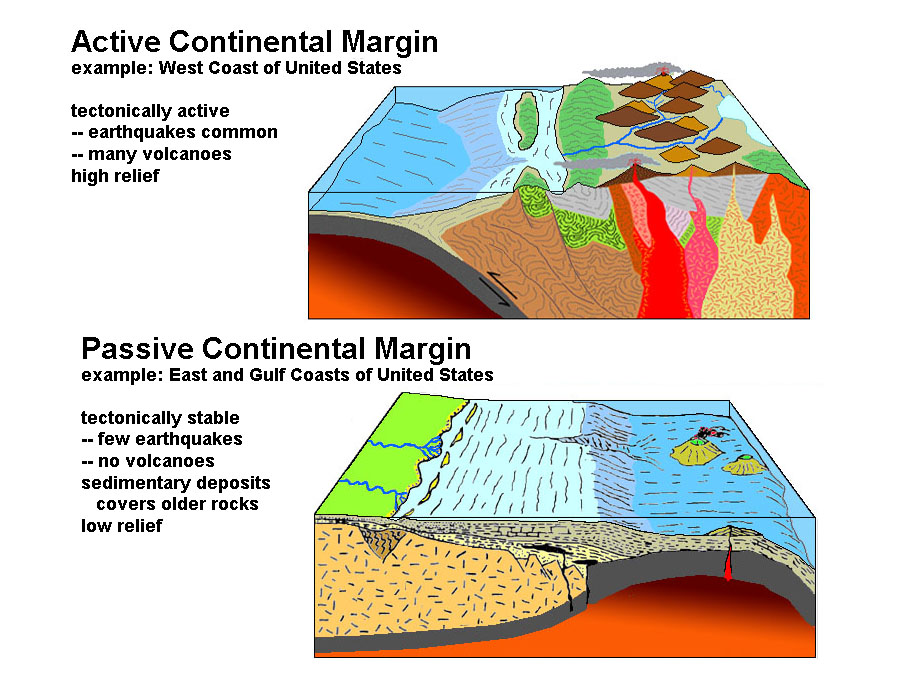
Collision (active) Margin
oceanic-continental plates collide, coastal mountain range/volcanoes, earthquakes, steep shelf, slope, and submarine trench
Lithogenic Sediment
from disintegration of rock on land, dominant near continental shelf slope & rise
Biogenic Sediment
Dissolved materials become solid, causing biogenic oozes; made up of microscopic single celled plants and animals; include calcium carbonate (limestone) and silicon dioxide (opal)
Authigenic Sediment
dissolved inorganic materials become sediment, sea water supersaturated with some chemicals (magnese nodules, red clay)
Cosmogenic Sediment
From outside earth (meteorites)
Milankovitch cycles- earth orbits
main reason for sea level changes over thousands of years
Glacial Rebound
inc in sea level resulting from continental crust rising after weight of glacier disappears after melting
Delta Subsidence
changes in sea level; when delta falls below sea level due to lack of sediment
Turbidity Currents
occur during low sea level; underwater landslide, earthquake triggers, moving sediment down continental slope and creating underwater canyons thru erosion
Transgressive sand layer
relic deposits of old sand beach
Sedimentation during high sea level
estuaries/fjords filled and deltas formed, sediment can only escape to shelf, or to slope if on collision margin
World water in rivers
.0001%, 3% of water on land
Runoff
Precipitation - (evaporation +infiltration)
Watershed/drainage basin
portion of landmass where runoff goes into a specific stream, separated by drainage divides, usually mountain ridges
Drainage Divide
separates watersheds
Tributaries
Any smaller stream that feed larger streams w/in watershed
Base Level
physical lower limit to river incision (gradient of 0)
If base level goes up, caused by deposition
down, caused by erosion/incision
River
flows downslope along a clearly defined passageway, transporting a load of sediment
Channel
Passageway that river runs down
Gradient units
m/km
Cross Sectional Area
wxd, m2- all increase with downstream evolution as opposed to the slope
Load units
kg/m3
Downstream evolution
Inc in: discharge, velocity, width, depth; Dec in: slope
Flood
Discharge so great that it exceeds capacity of channel and overflows banks
Dissolved load
dissolved ions, finest clay particles & depends on rocks being weathered into river
Suspended load
sediment fine enough to remain in suspension: silt and clay; size depends on velocity + turbulence
Occurs when turbulent upward currents exceed the “settling” velocity of silt and clay particles
Bed Load
Sediment rolling and bouncing along riverbed, 5-20% of sediment; sand, gravel, and boulders
Saltation
Series of short, intermittent jumps by bedload
Estuary
semi-enclosed coastal environment where saltwater and freshwater mix
Delta
sedimentary deposit at mouth of a river causes coastline to protrude into ocean
evolve from estuaries
more sediment supply than removal
Little Sediment supply
estuaries and fjord filling, trapping mechanisms important
Moderate Supply
some estuaries fill, sediment leaks into shelf
Large Sediment supply
Deltas built seaward (Mississippi)
Coastal plain estuary
drowned river valley
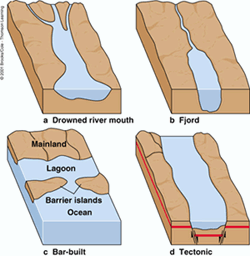
Fjord
estuary w/ glacial origin, deep w/ shallow sill near mouth
Bar-built Estuary
sand spit or barrier island encloses embayment
Tectonic Estuary
dropped down basin, near ocean, seawater floods basin (Sao Fran)
Consolidation
How much water has been removed from between particles
Salt Wedge
landward bottom current of salt water in esturine circulation
saltwater moving inward to replace saltwater being expelled
Halocline
freshwater-saltwater boundary (denser saltwater is underneath)
Fjord Circulation
Sill causes little circulation: little oxygen present and marine life dies
Flocculation
formation of aggregates from individual silt and clay particles
Turbidity
sediment in suspension
Turbidity Maximum
when fluvial and esturine suspended particles meet at halocline, where most particles are deposited into bed
To Form a Delta, Sediment Supply must overcome (STECH)
Slow sea level rise, tectonic subsidence, erosion, consolidation, human removal of ground water
Most common location for Delta
Where sediment enters protected body of water
Topset
Freshwater swamps, brackish water marshes
Sediment accumulation is controlled by rise of sea level
Land surface sinks from consolidation of mud underlying
Lobe of Maximum Sedimentation
depression filled w/ sediment, river switches to another location
Sill
shallow area separating basins of two bodies of water
Central basin
largest volume
Southern basin
largest shoreline
Whidbey Basin
largest tidelands
River Salinity
0 ppt