KNES 259 Physiology - Highlight Reel
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What is Cell Physiology?
The study of body functions and how body systems work together
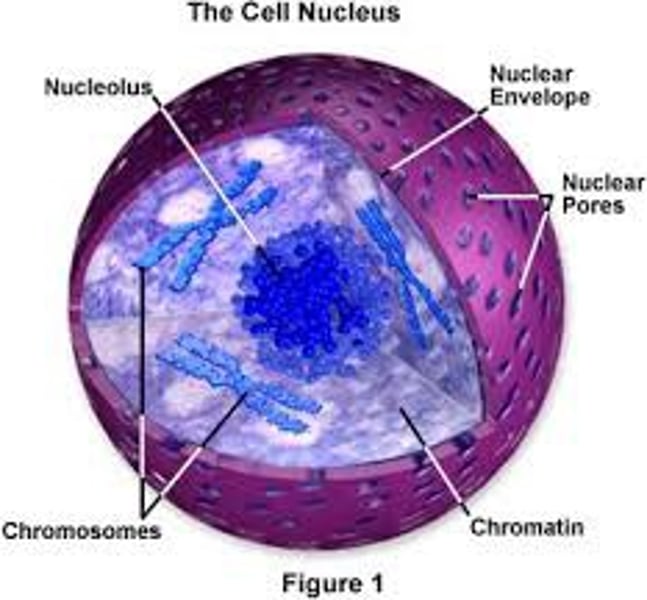
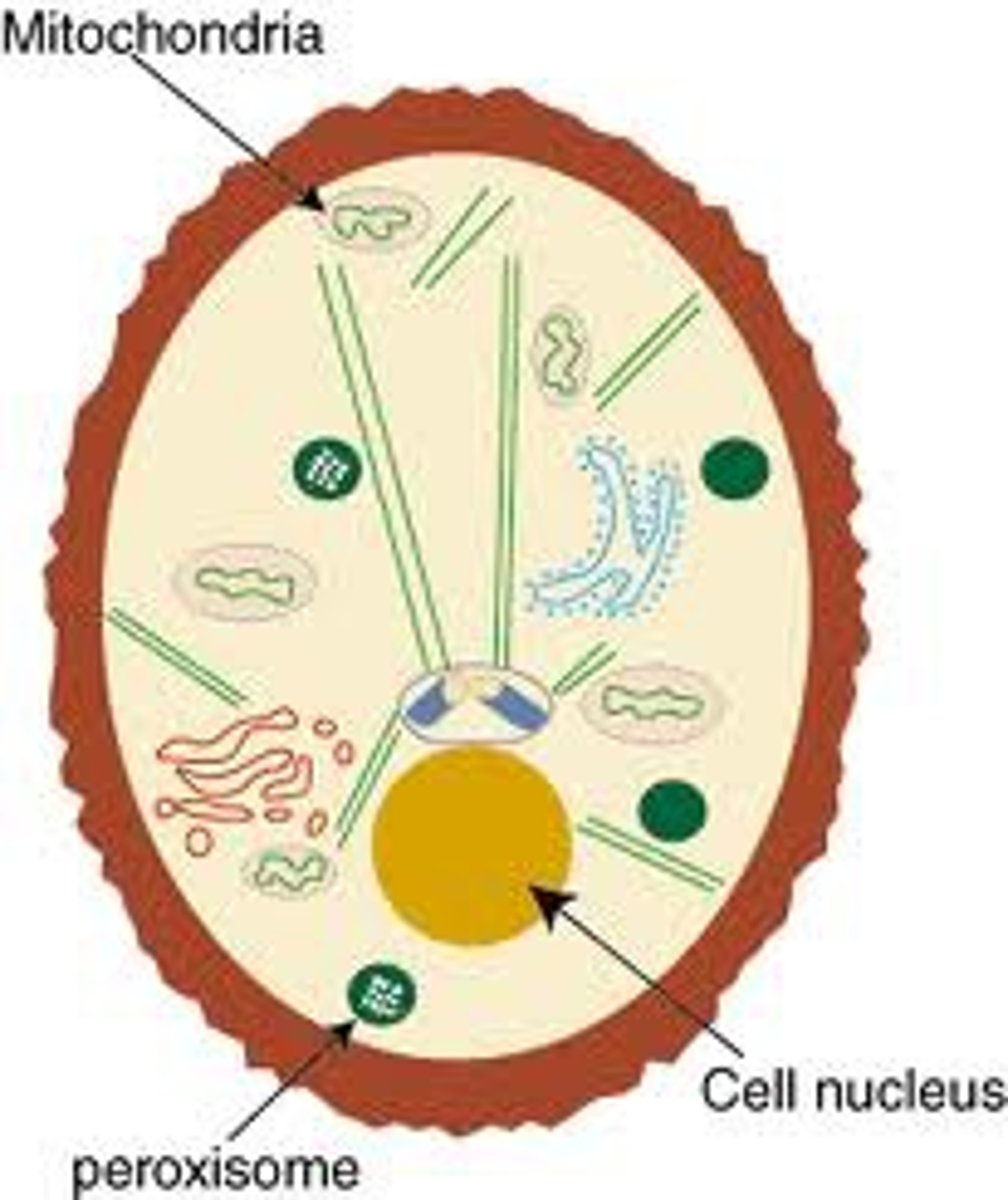
The Cell - Nucleus
Responsible for: cell replication and repair. (normally 1 per cell;) EXCEPTIONS: RBC: no nucleus . MUSCLE: mulitnulceated
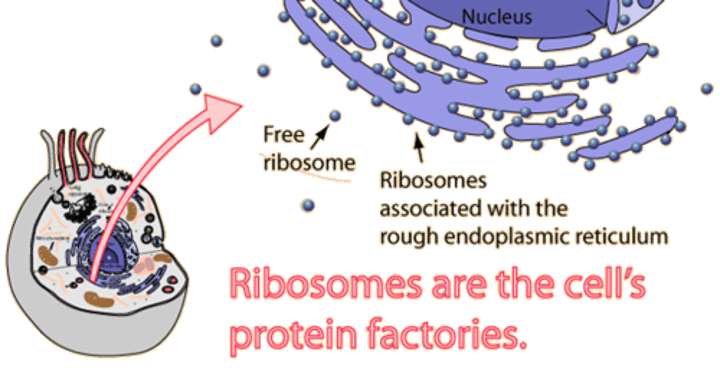
The Cell - Ribosomes
Makes proteins. Free (makes portions for the cell) --> ex)muscle, or attached
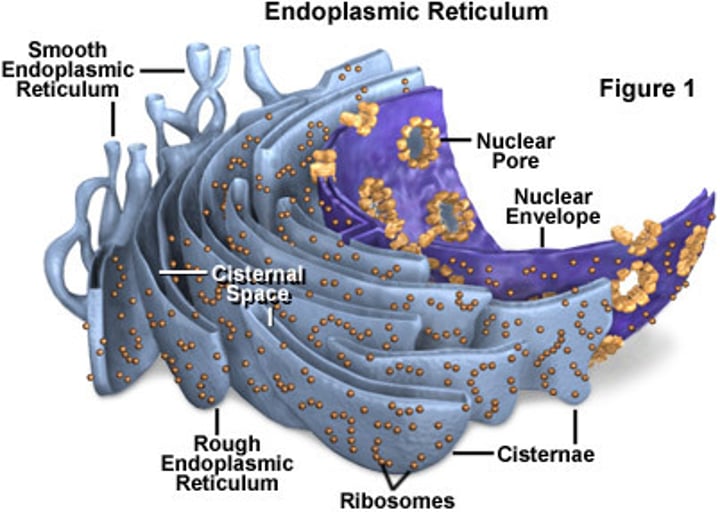
The Cell - Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
SMOOTH ER: calcium storage (skeletal, muscle), de-toxification (liver), steroid production (ovaries, testes). ROUGH ER: ribosomes attached, makes organelles, protein production for export, ex) pancreas
The Cell - Golgi Complex
Re-packages RER portions into a vesicle that can leave the cell (different membrane from the cell so it can leave) ex) pancreas

The Cell - Peroxisomes
OXIDATIVE ENZYMES: Metabolism - beta oxidation, lipid synthesis. Detoxify various waste products - makes hydrogen peroxide (coverts water with a catalase). ex) liver hepatocytes
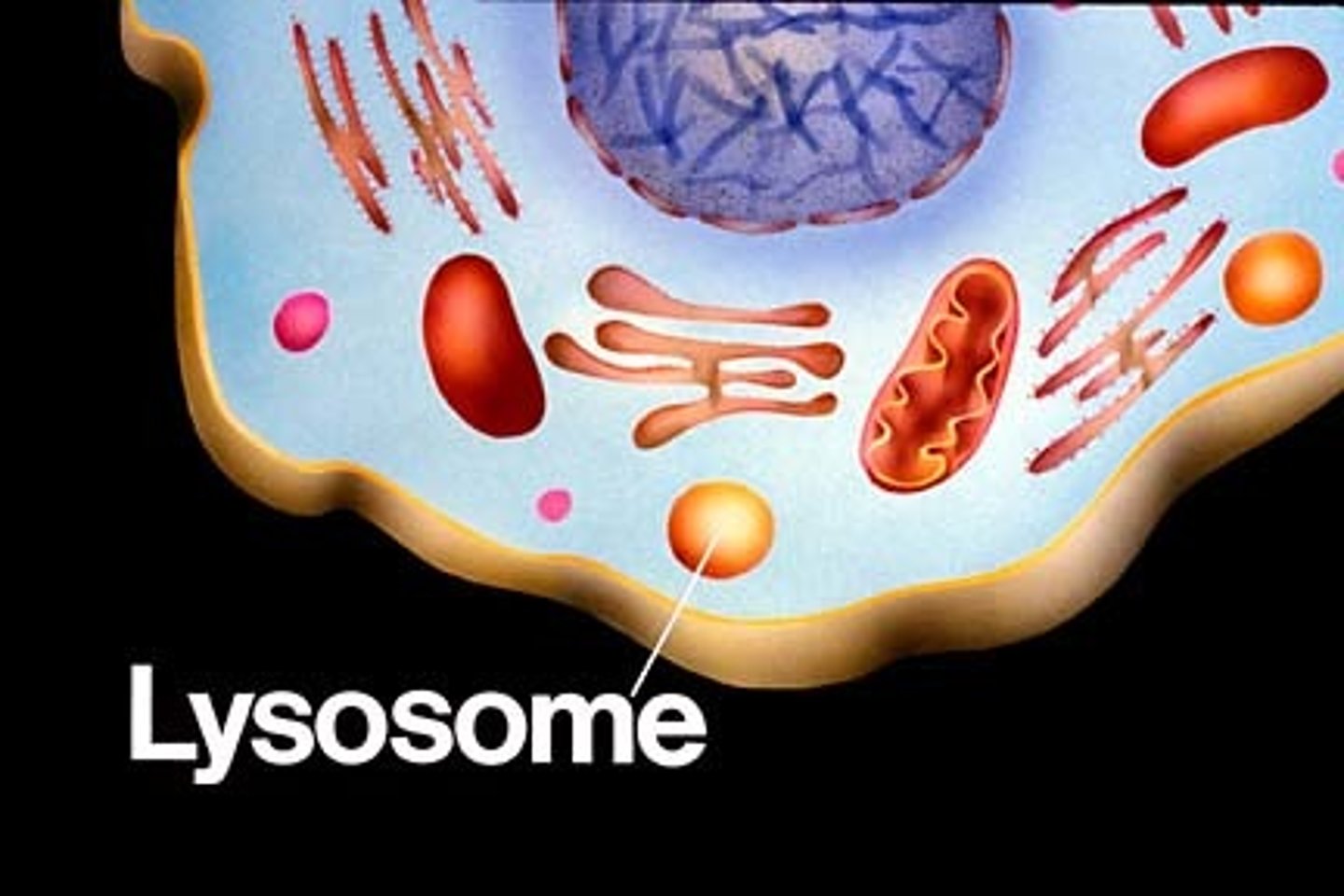
The Cell - Lysosomes
Sac of digestive enzymes. Used for repair and removal of foreign matter (immune response). ex) WBC's - killer cells
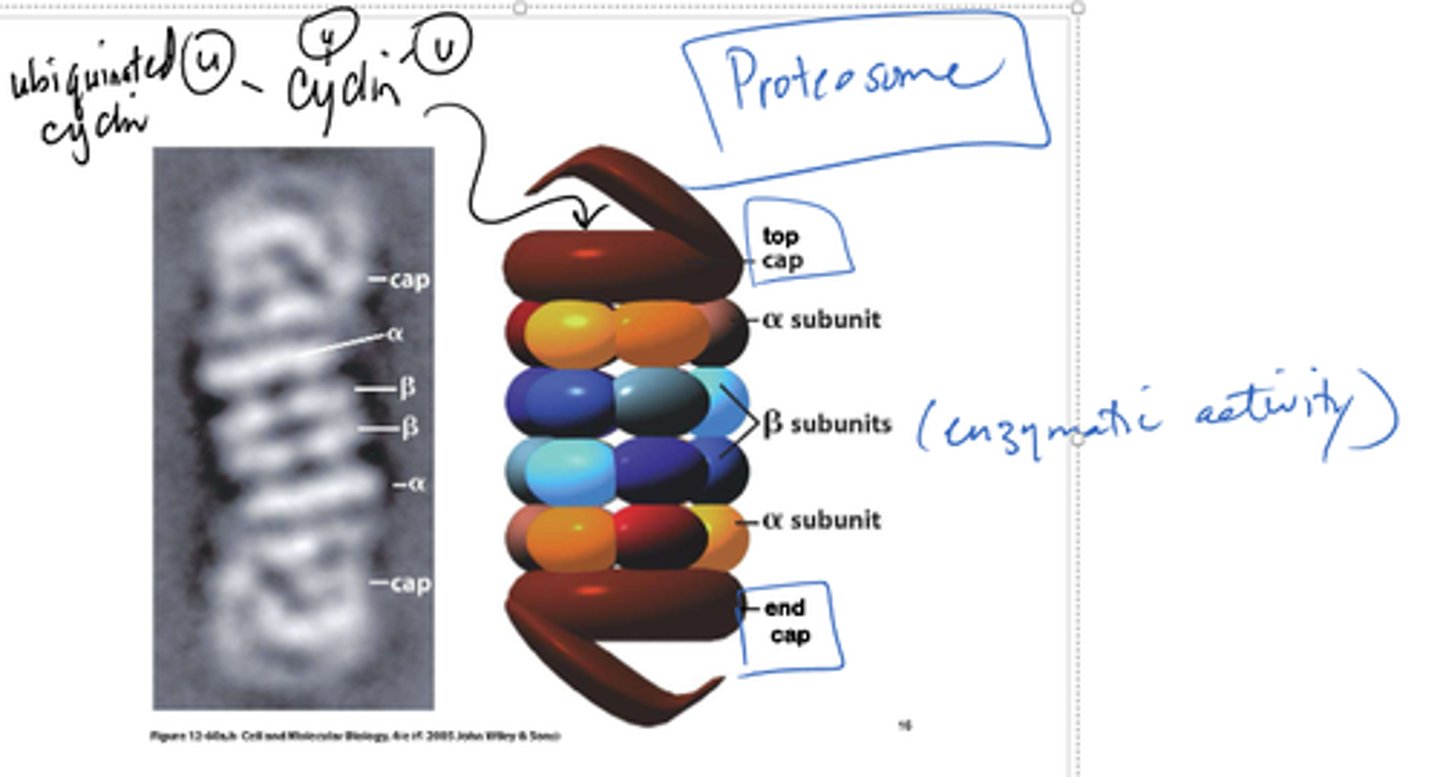
The Cell - Proteosomes
LARGE PROTIEN COMPLEXES. Protein digesting organelles - digest tagged proteins (damaged or no longer needed). Quality assurance. With age, may be unable to normally remove proteins - causes build up of bad proteins.
The Cell - Cytoskeleton
COMPLEX PROTEIN NETWORK. Acts as "bone and muscle" of the cell. 3 elements - Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments.
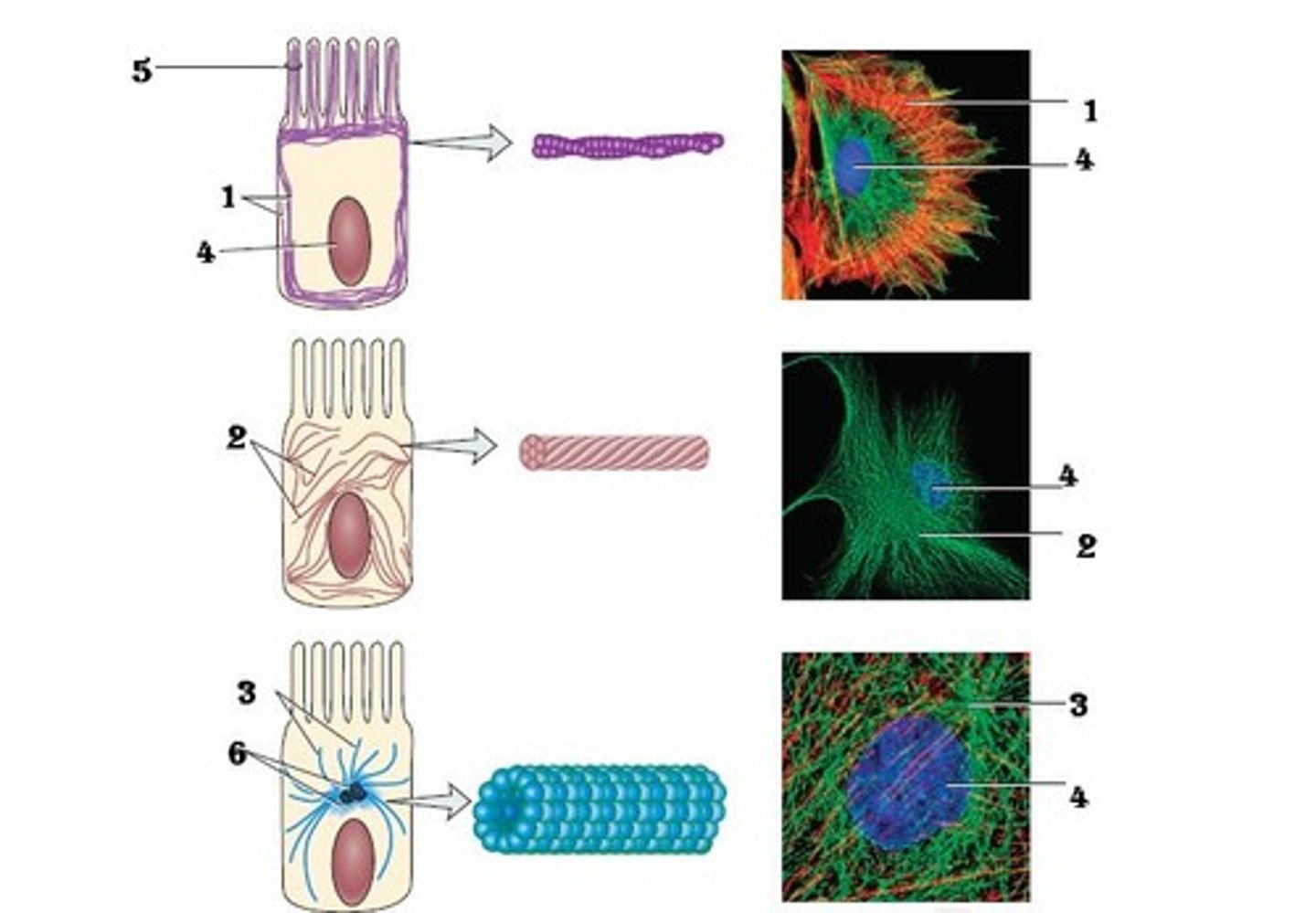
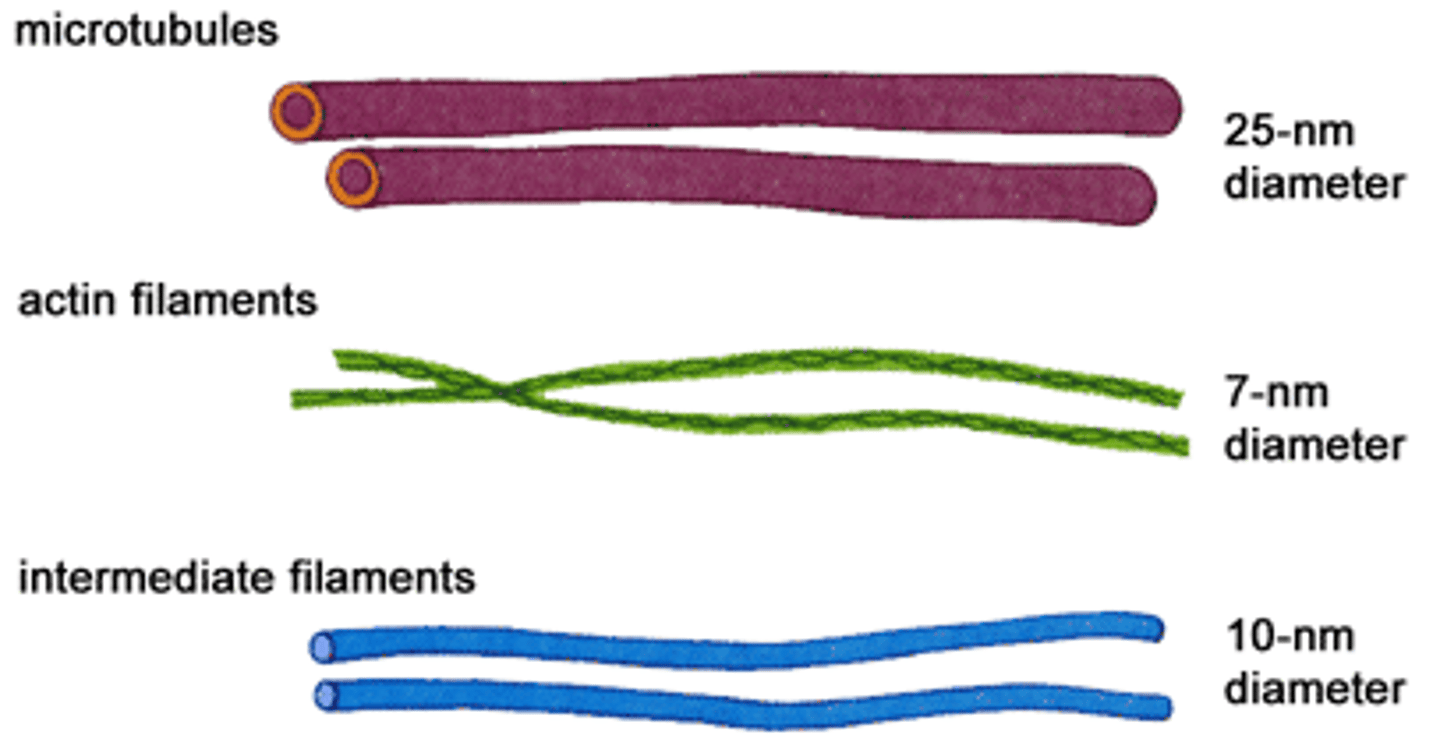
Cytoskeleton - Microtubules
Transport secretory vesicles. Form mitotic spindle during cell division - form + break down quickly. (thin) ex) tubulin.
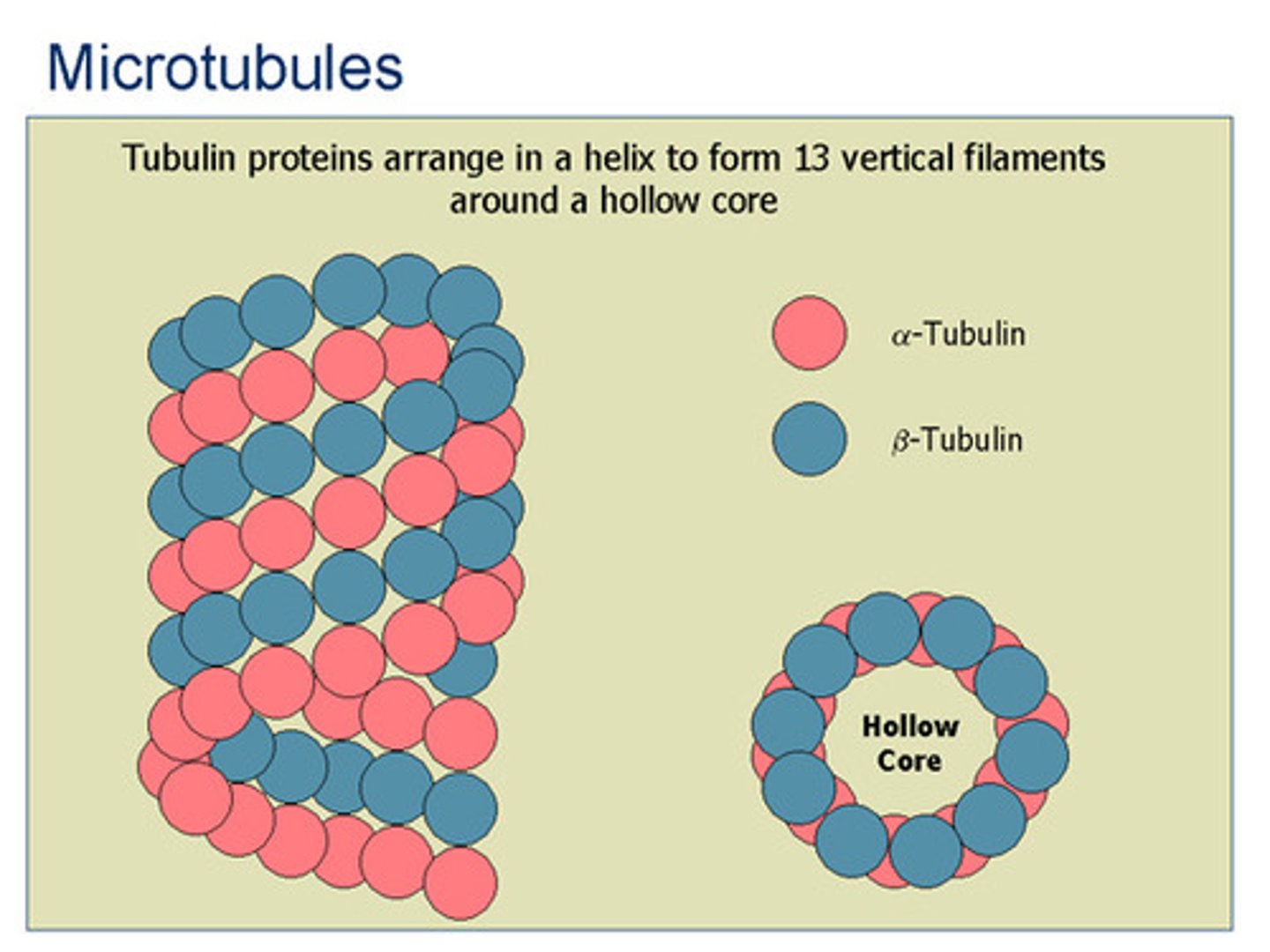
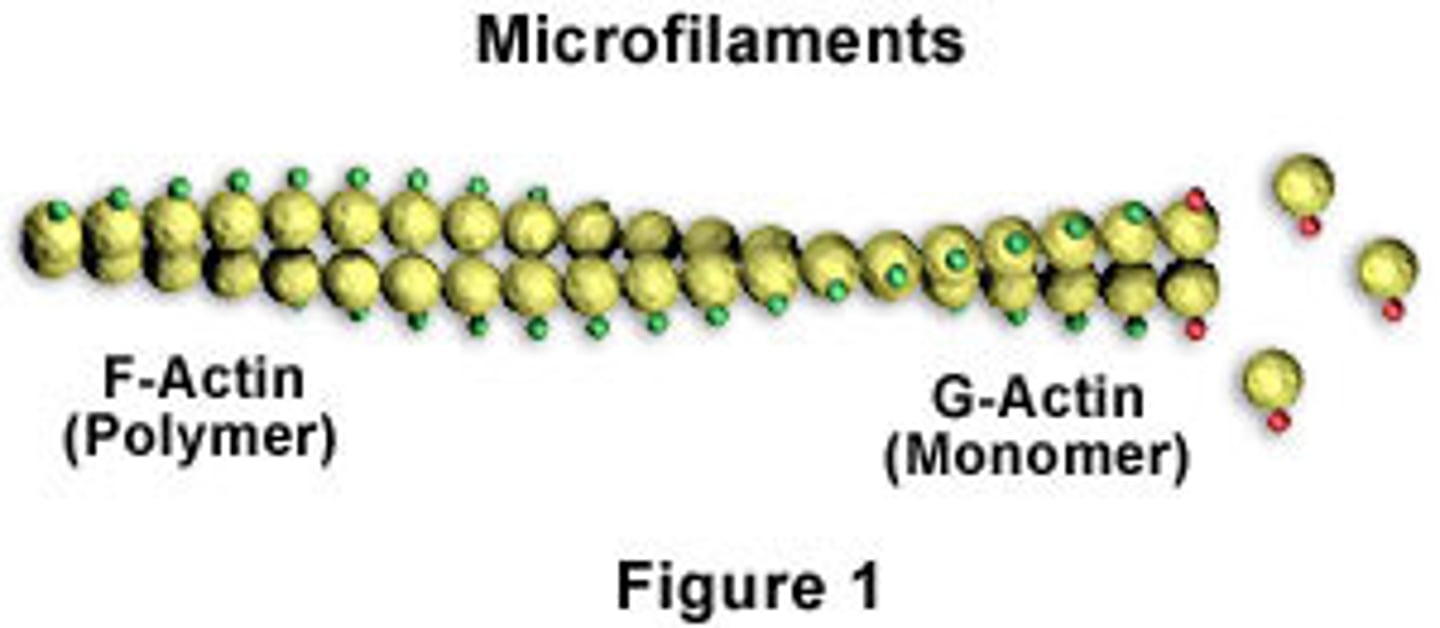
Cytoskeleton - Microfilaments
Contractile systems. Muscle. Mechanical stiffeners. (fatter) ex) actin and myosin.
Cytoskeleton - Intermediate Filaments
Help resist mechanical stress. Hair, skin - collagen. (most complex) ex)keratin
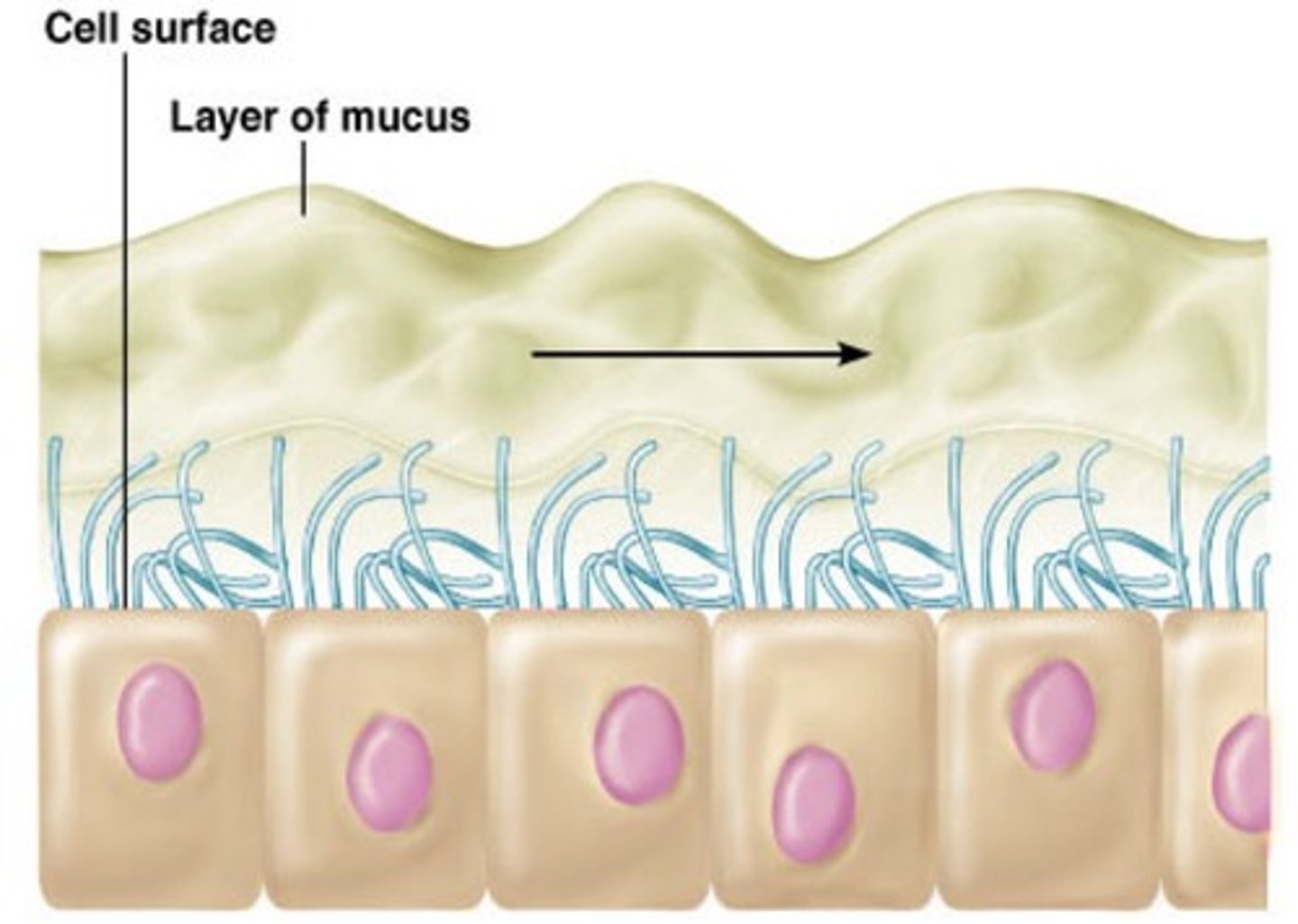
The Cell - Cilia
Directional movement of particles. Beat upwards in lungs. ex) trachea, uterine tubes
The Cell - Flagella
On moving cell. ex) sperm
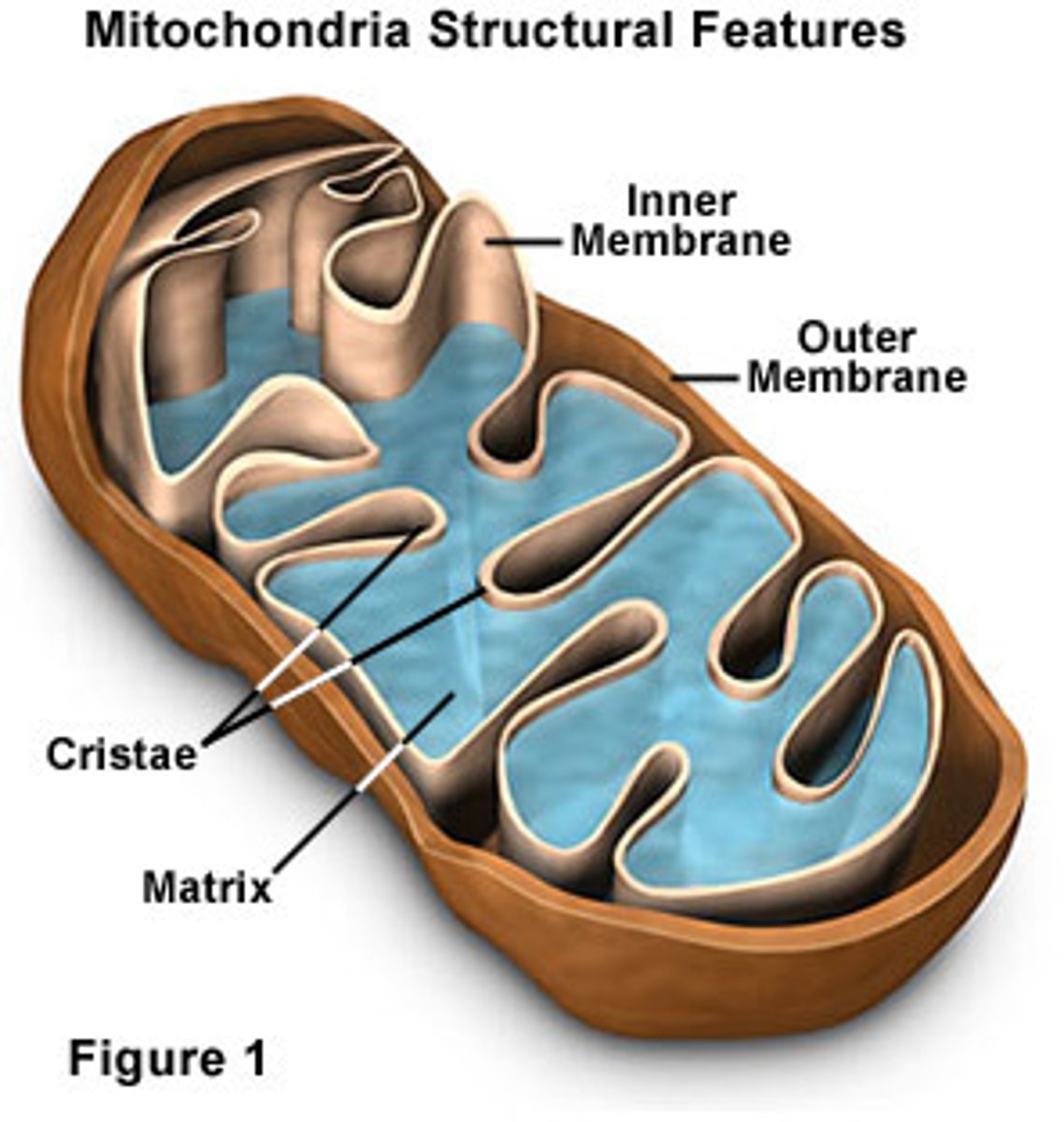
The Cell - Mitochondria
ENERGY ORGANELLE. Site of ATP production. Enzymes for TCA (tricarboxylic acid) and ETC (electronic transport chain). Powerhouse.
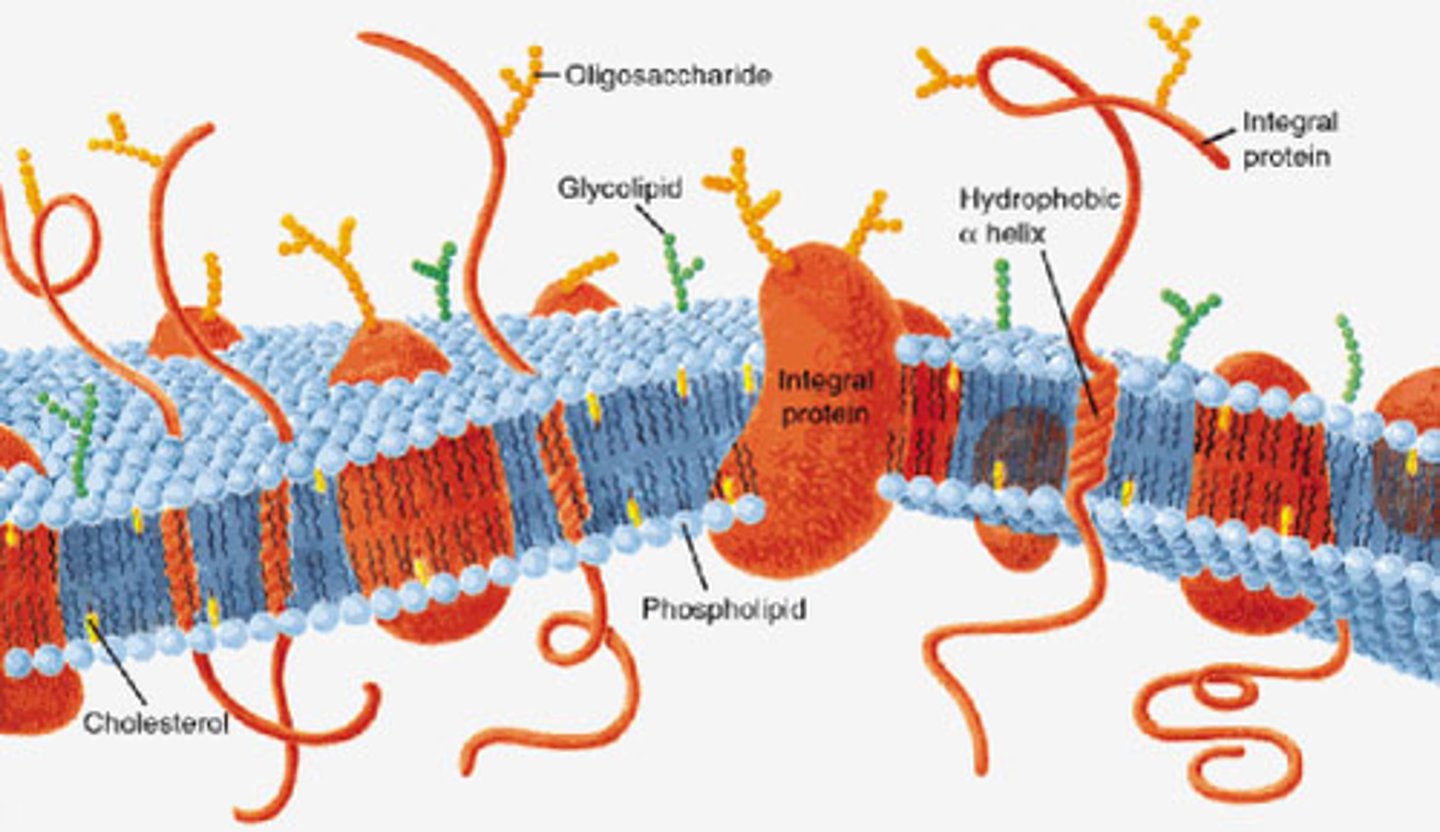
Plasma Membrane Structure
Physical barrier --> gateway for exchange --> communication --> cell structure
Cell Membrane Structure
Phospholipids and Cholesterol
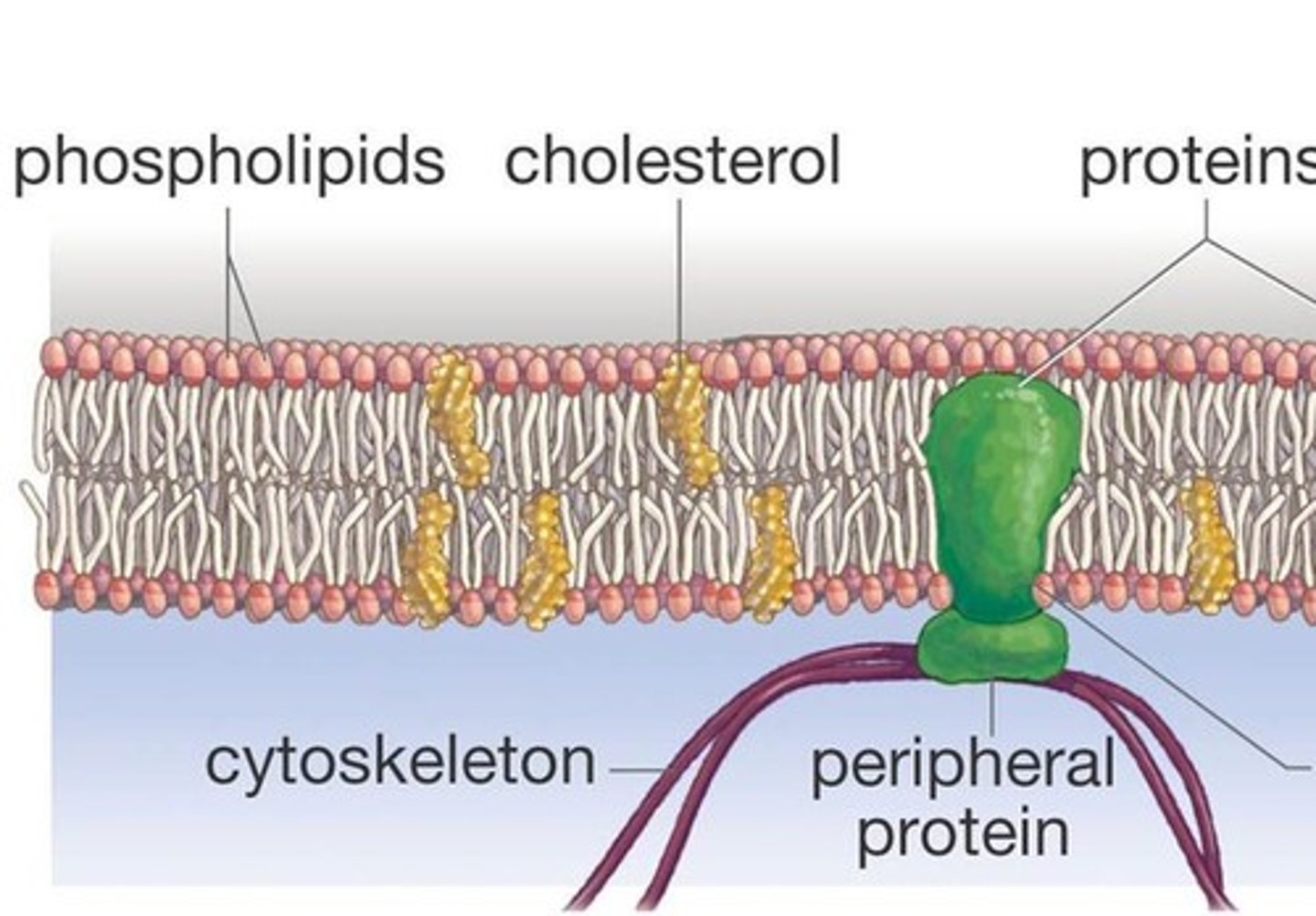
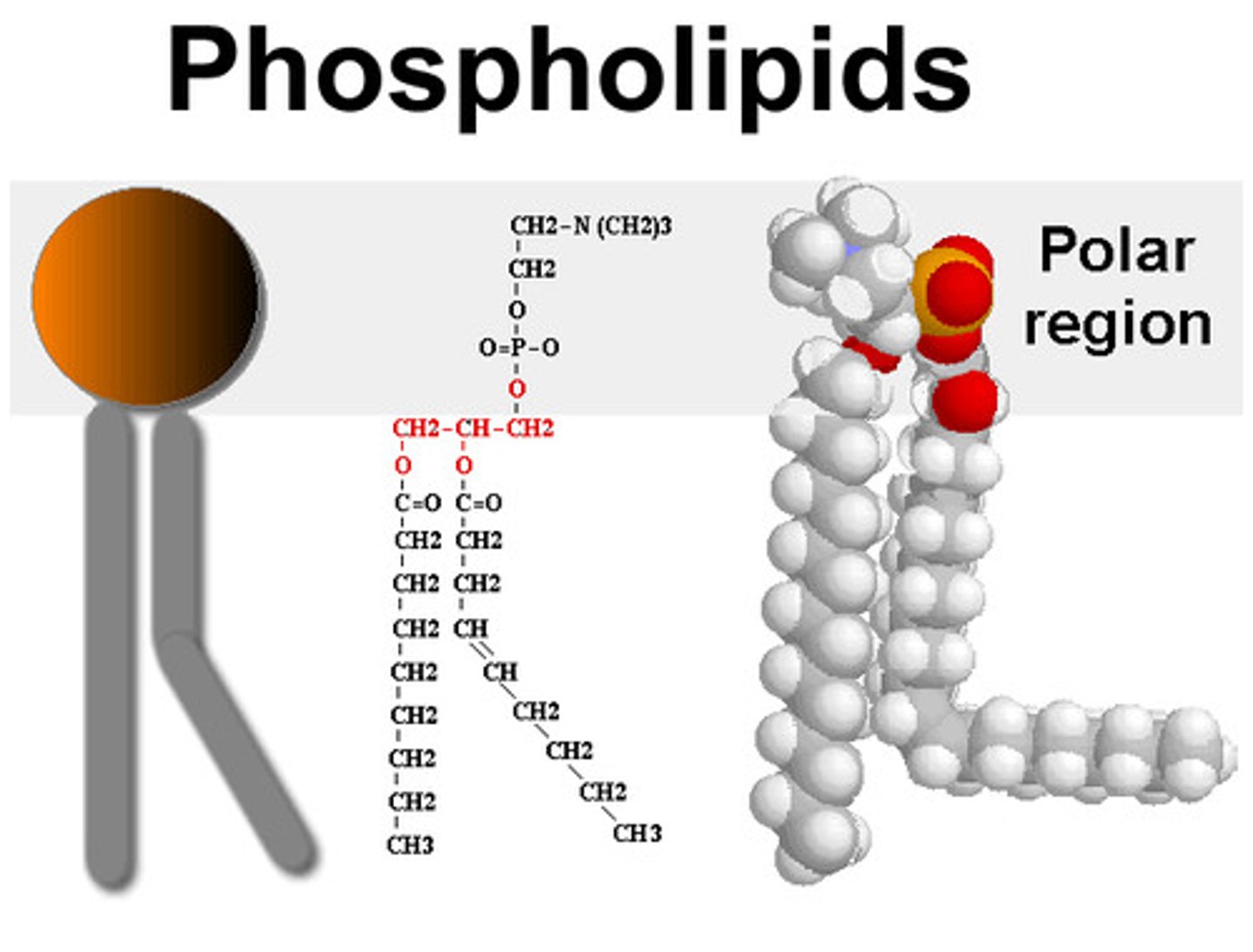
Phospholipids
Choline head - polar: water soluble. Fatty acid tails - non-polar, creates barrier for flow.
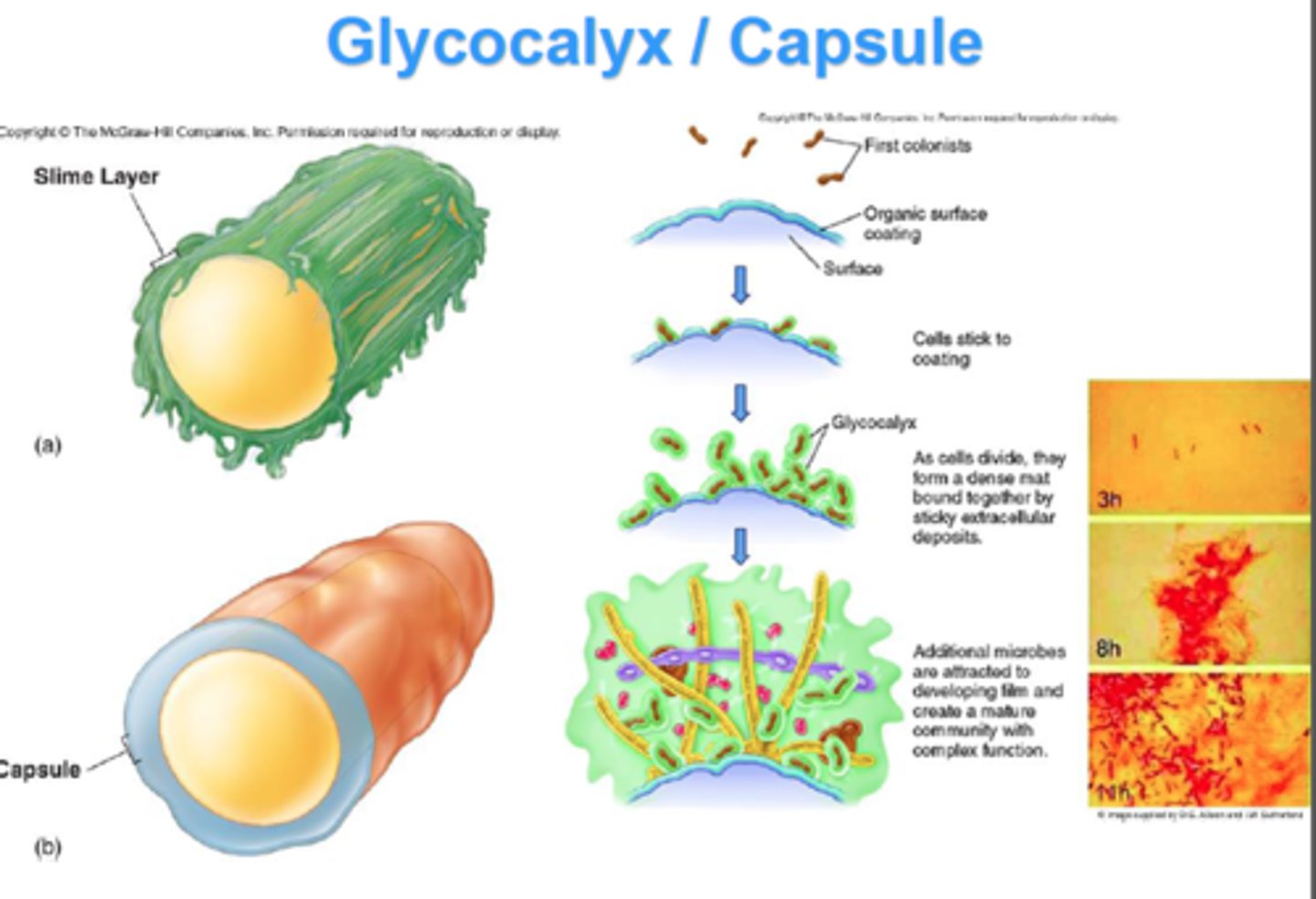
Glycocalyx
Glycoprotiens and glycolipids on surface of cell - cell identity, and cell orientation. Helps cell align, cell identification, creates room for cell to move.
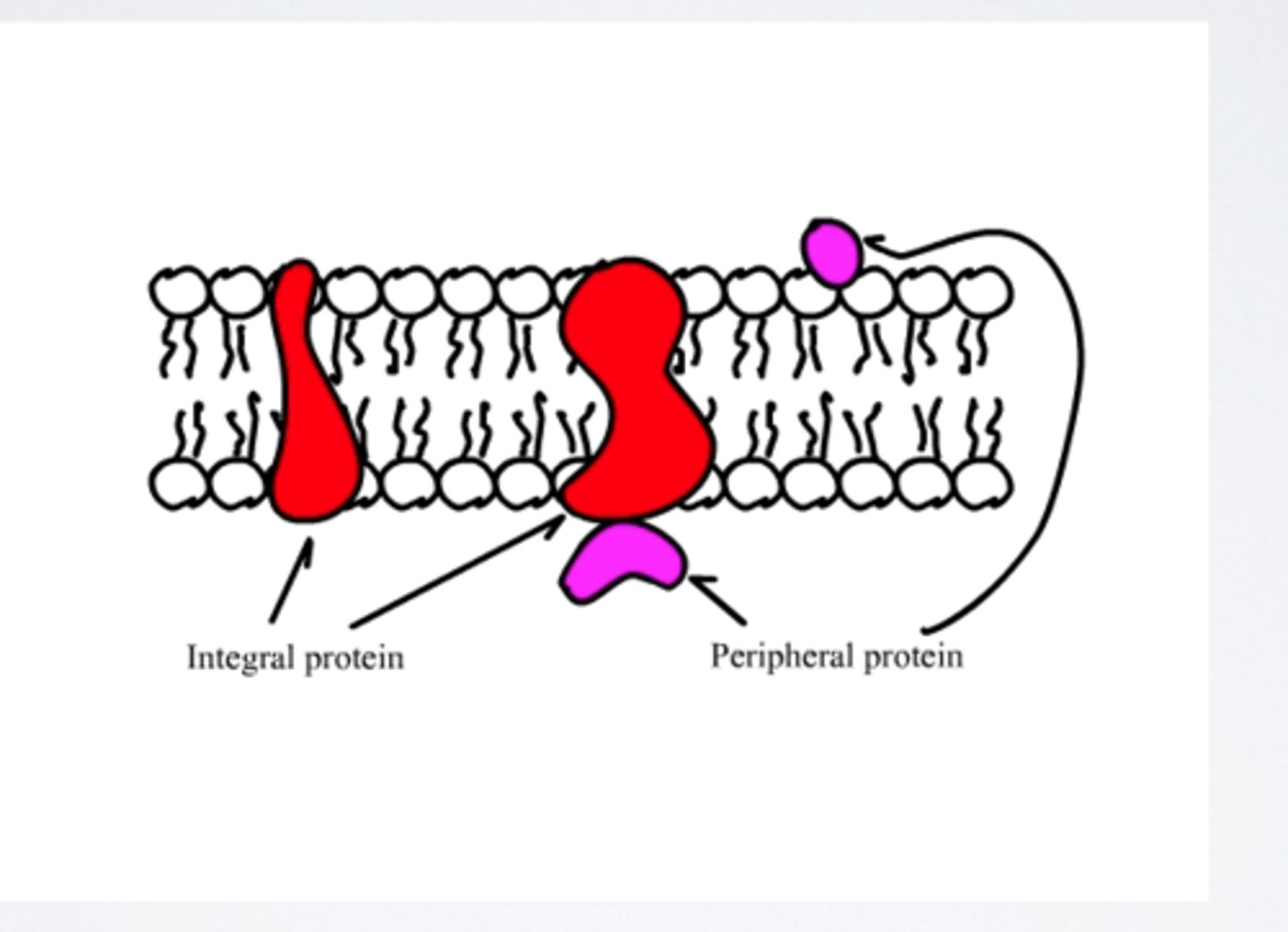
What are the Two Type of Membrane Proteins?
Integral (transmembrane) Proteins
Peripheral Proteins
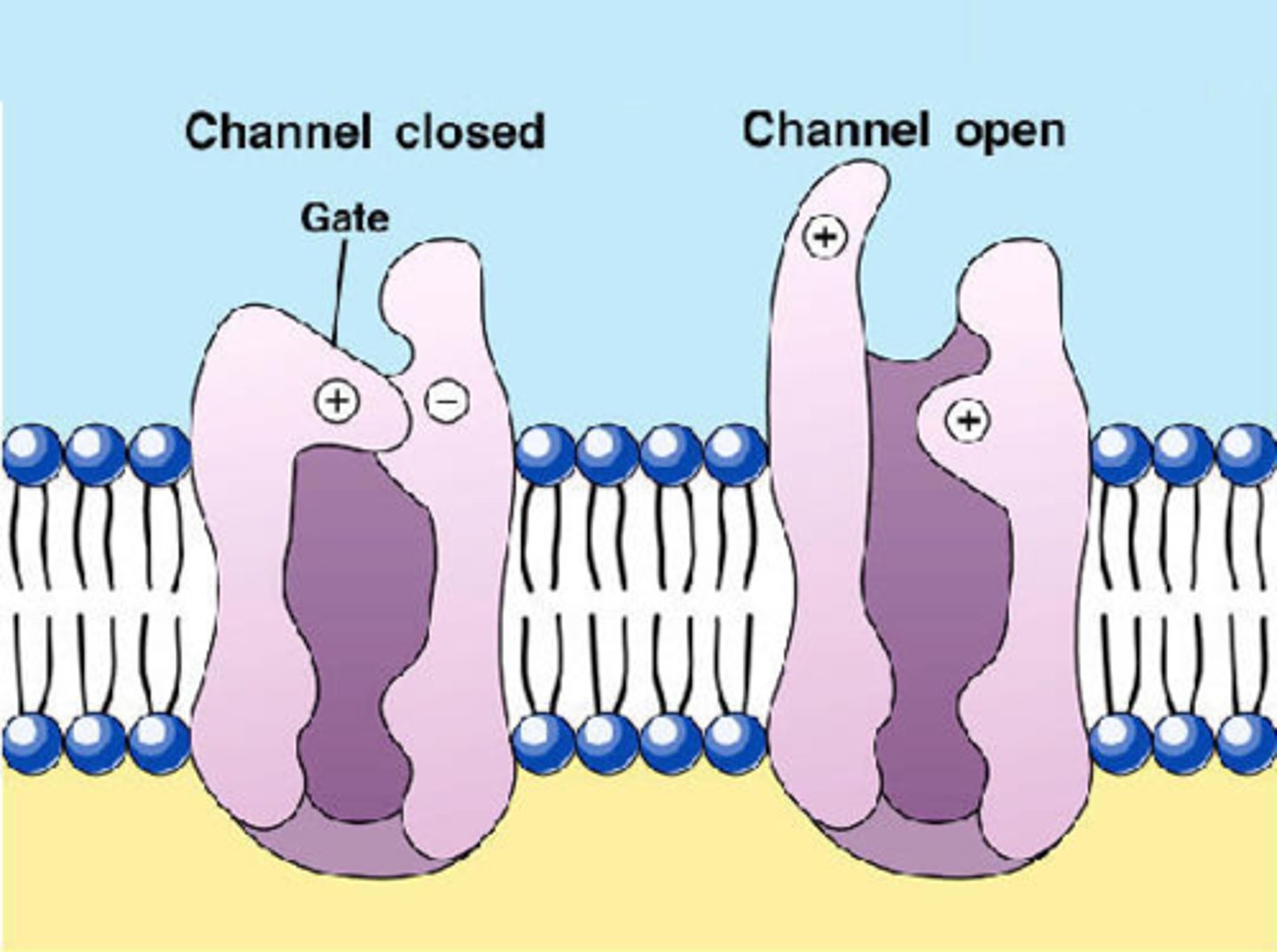
Membrane Proteins - Ion Channels
Forms a pore though which a specific ion can flow to get across membrane. We can't open or close it. INTEGRAL
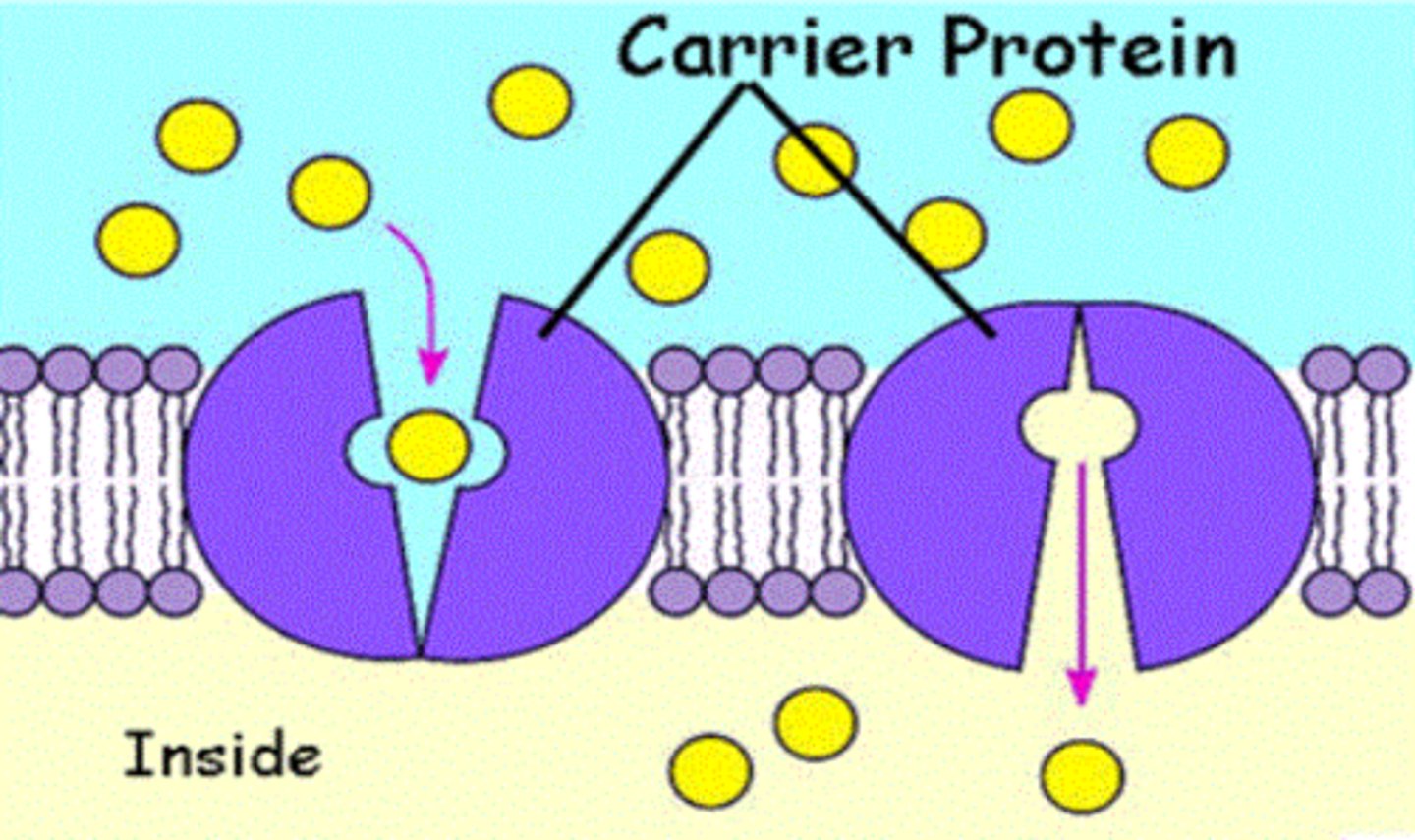
Membrane Proteins - Carriers
Transports a specific substance across membrane by undergoing a change in shape. INTEGRAL
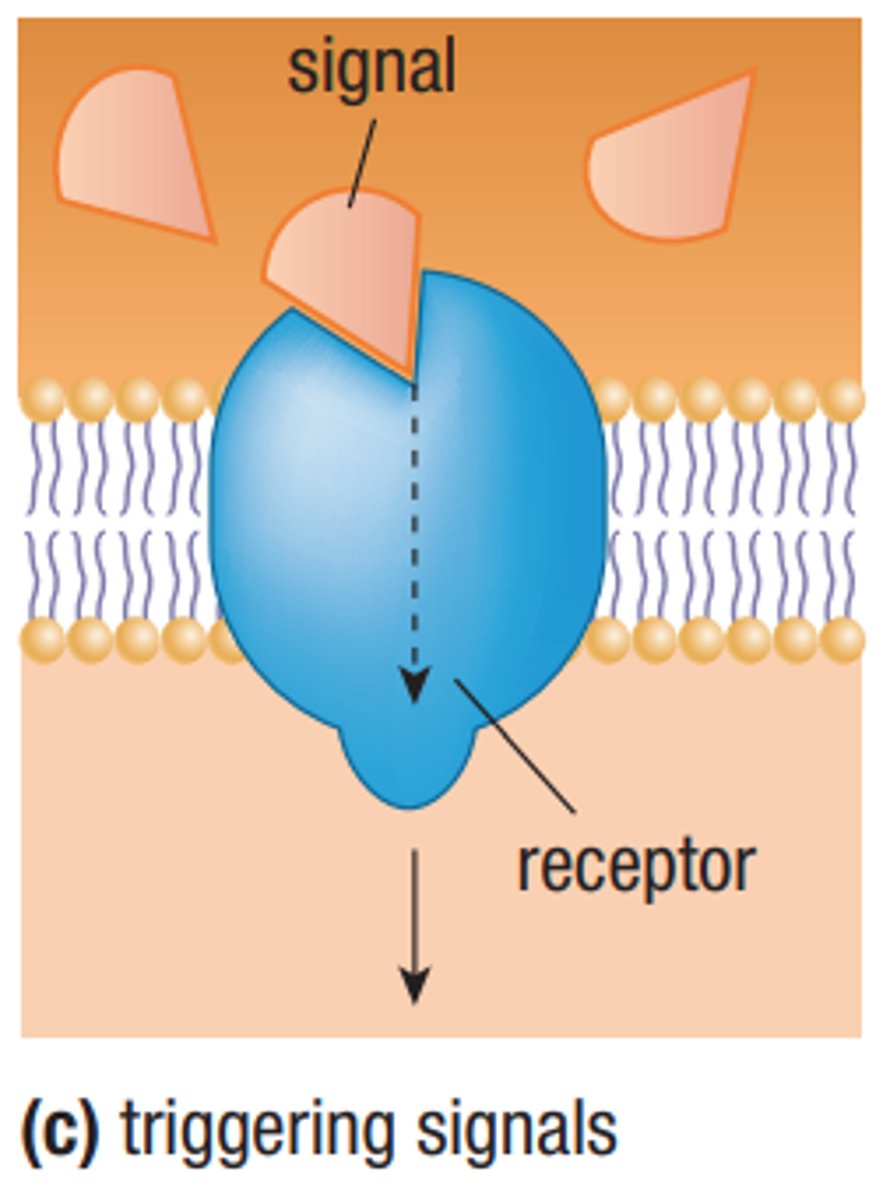
Membrane Proteins - Receptor Sites
Recognizes specific ligand and alters cell's function in some way. Tells cells to do same things. INTEGRAL
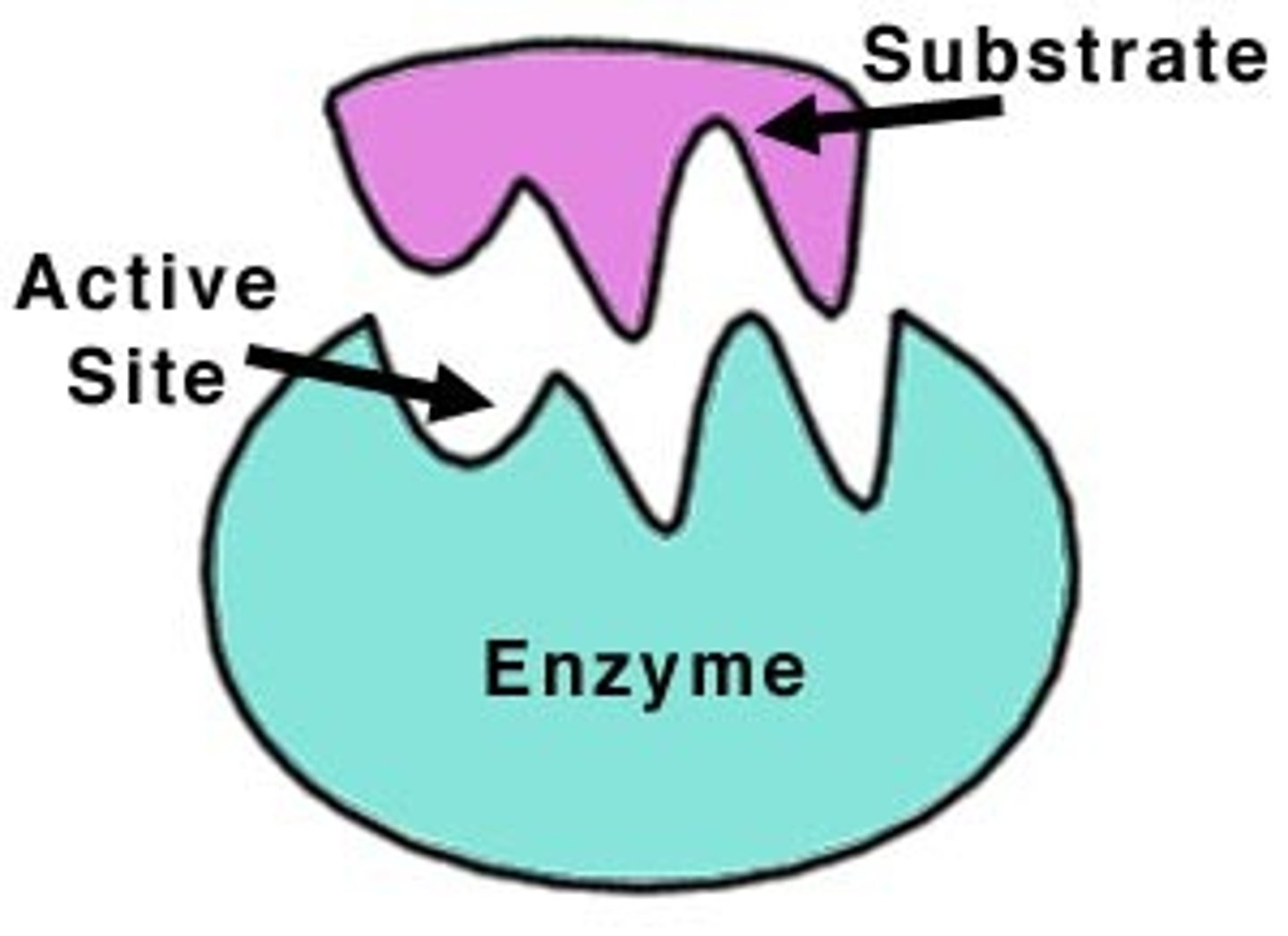
Membrane Proteins - Enzymes
Catalyzes a reaction inside or outside cell (depending on which direction the active site faces). INTEGRAL AND PERIPHERAL
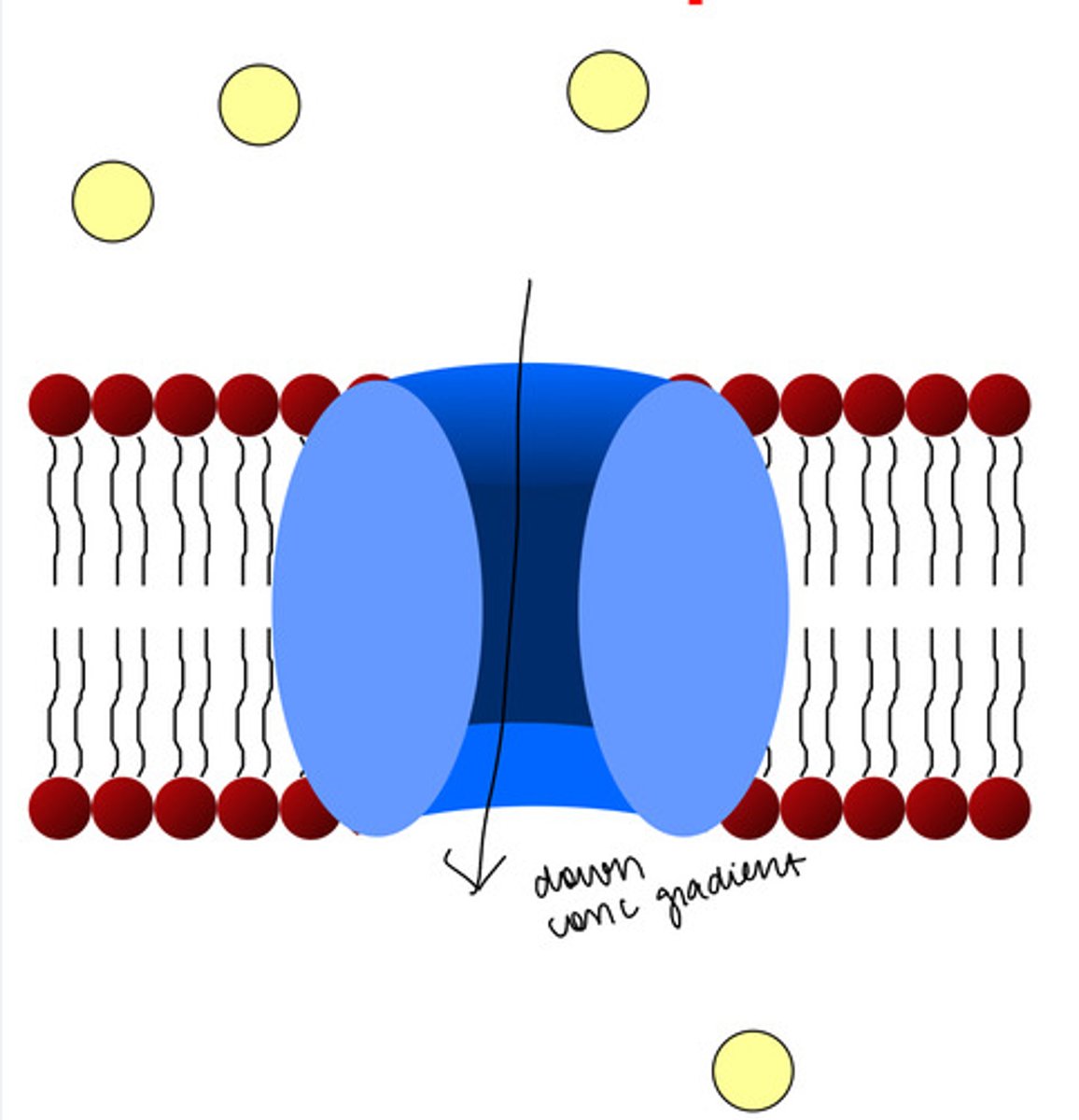
Membrane Proteins - Pores
Open up channels through them. Specific to H2O. INTEGRAL
Membrane Proteins - Structural
Shapes the structure and skeleton of cell. INTEGRAL
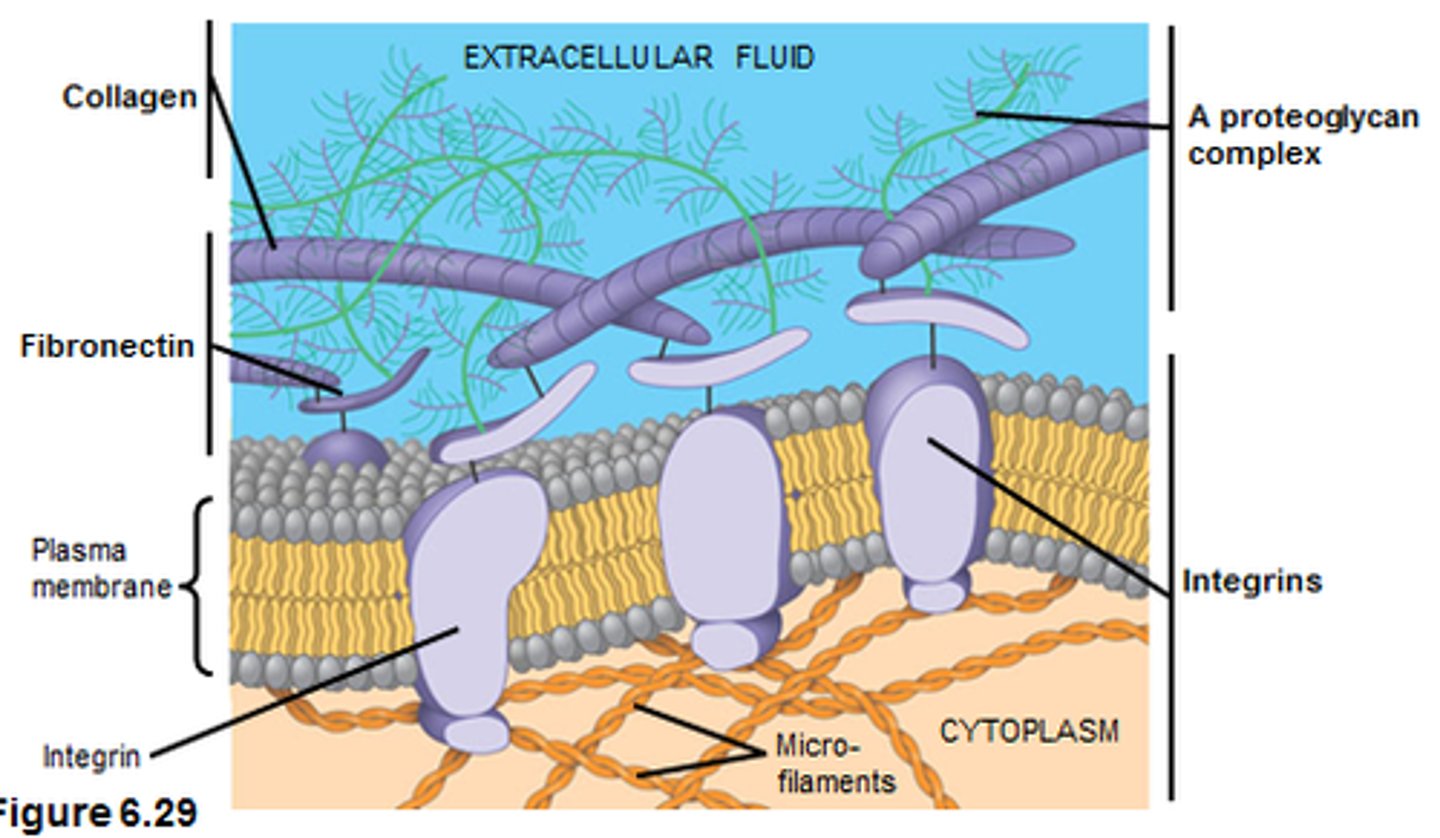
Membrane Proteins - Cell Adhesion (Cell Junctions)
Anchors filaments inside and outside the plasma membrane, providing structural stability and shape for the cell. INTEGRAL AND PERIPHERAL
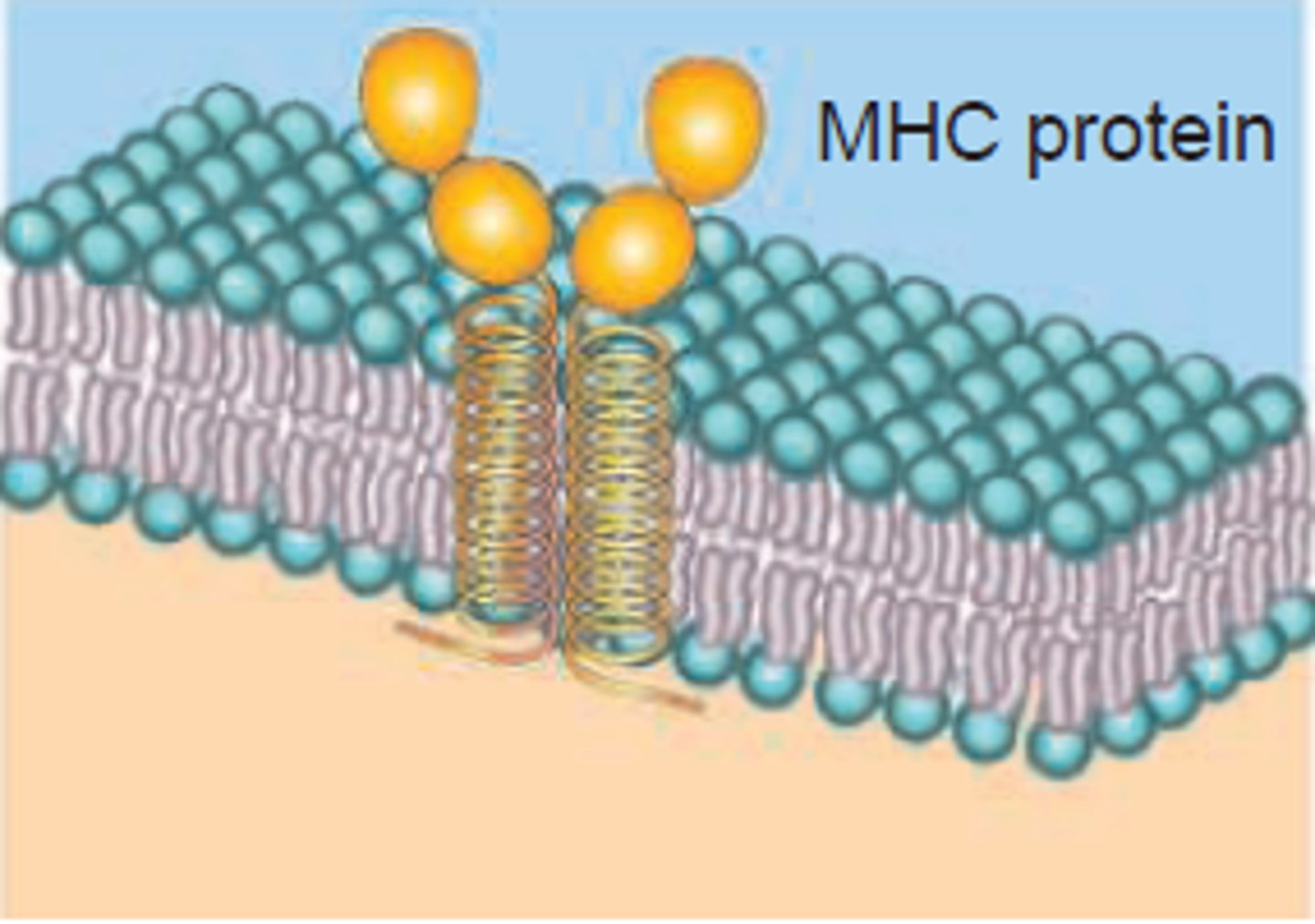
Membrane Proteins - Cell Identity Marker
Distinguishes your cells from anyone else's (except for identical twins). GLYCOPROTEIN
What are Membrane Gradients?
Power movement without ATP
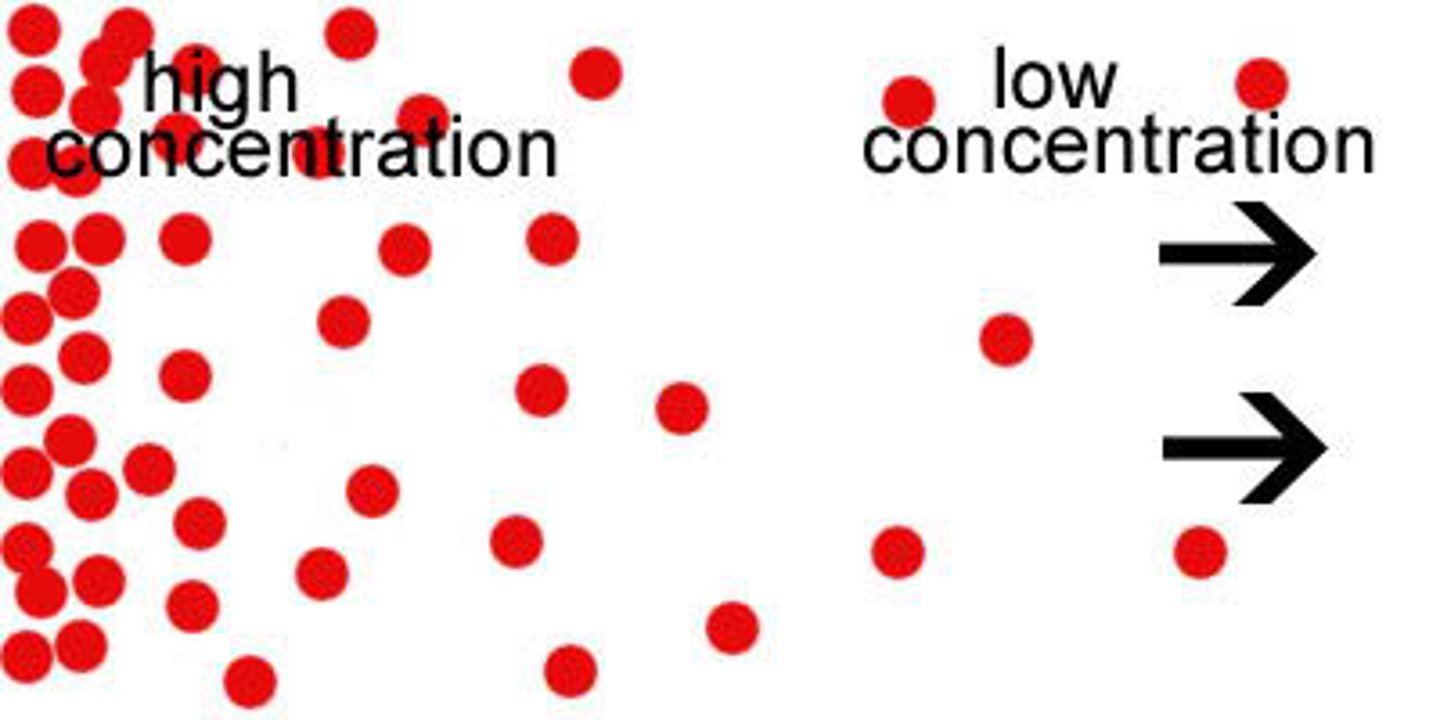
Membrane Gradients - Concentration Gradient
Difference in substance concentration across a membrane
Membrane Gradients - Electrical Gradient
Difference in charge (conc. of ions)
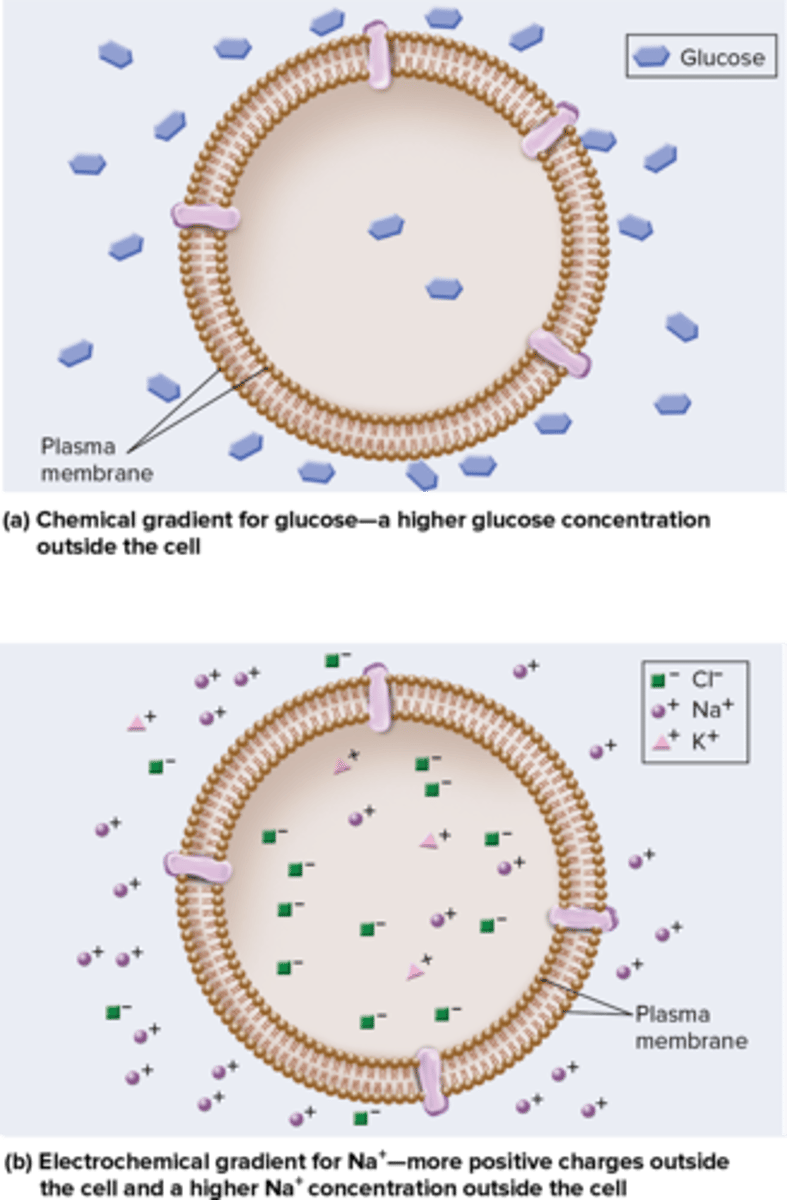
Membrane Gradients - Electrochemical Gradient
Combination of both
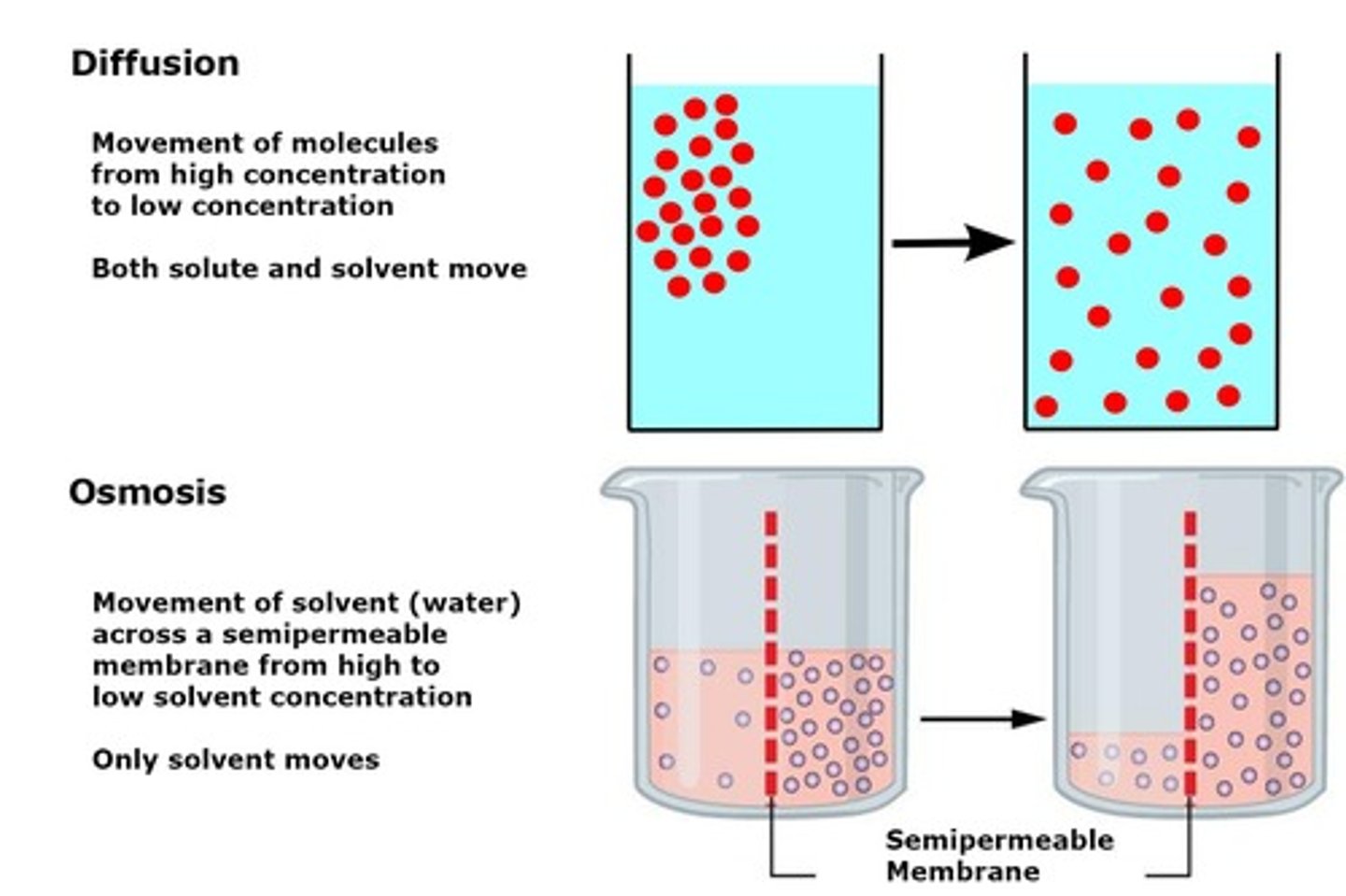
What is Diffusion?
Two - way movement. Consider net movement.
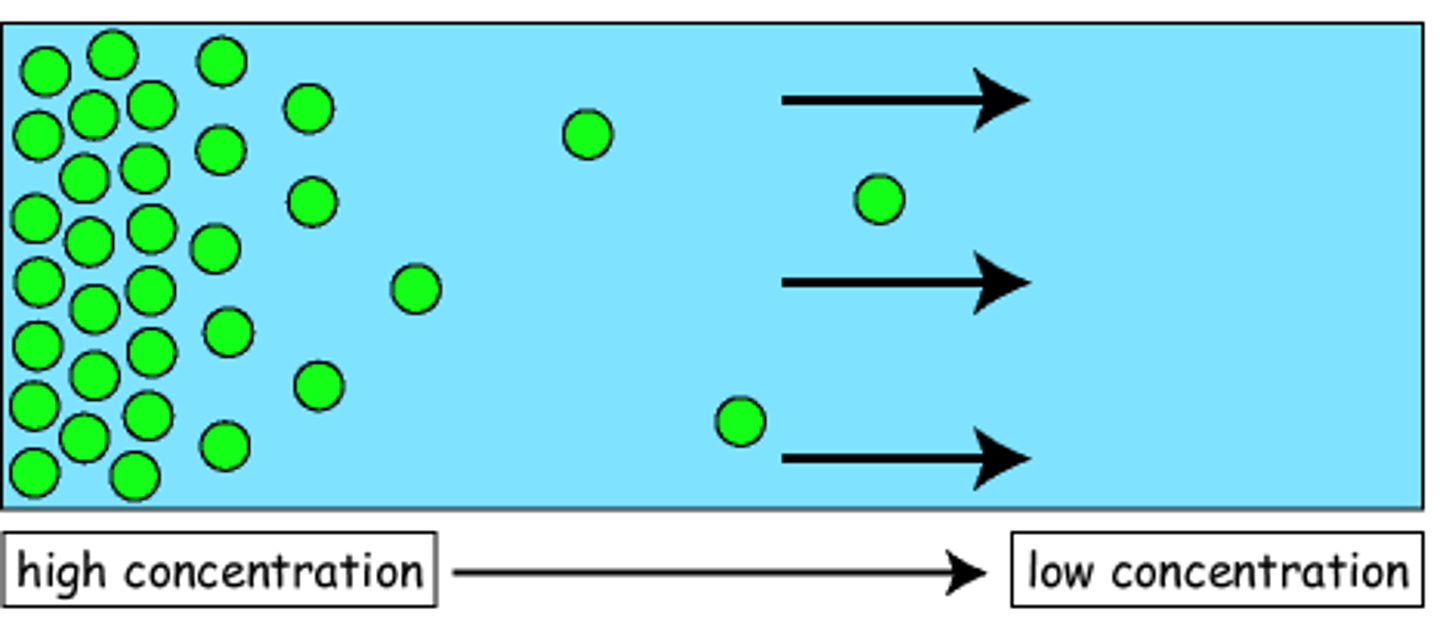
Membrane Transport - Simple Diffusion
Net diffusion from high to low concentration (due to particles random collisions). Small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide), steroids.
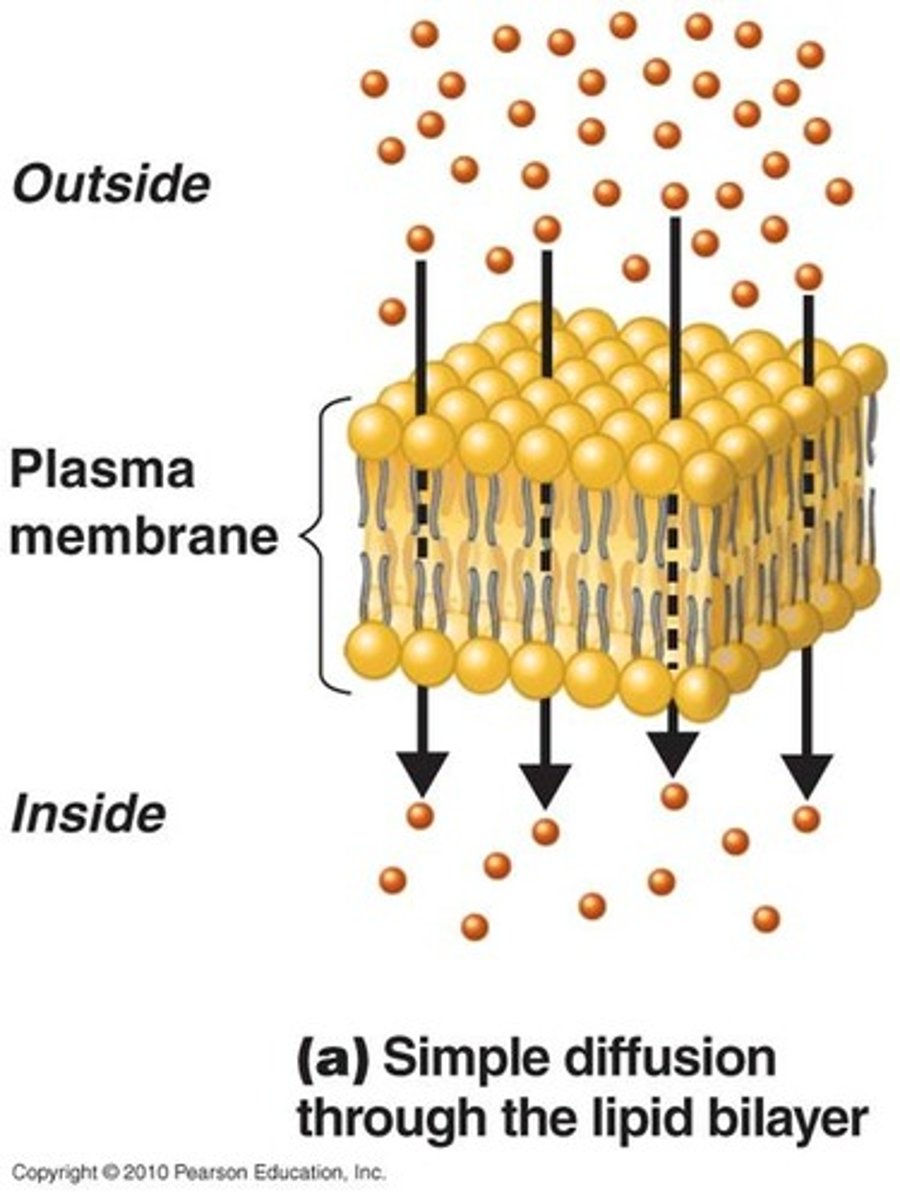
What does the rate of diffusion depend on?
- Temperature
- Concentration gradients
- Diffusion distance
- Mass of diffusion substance

Diffusion Across a Membrane (and what it depends on)
Particle must be permeable
- Permeability
- Surface area
- Gradient
- Temperature
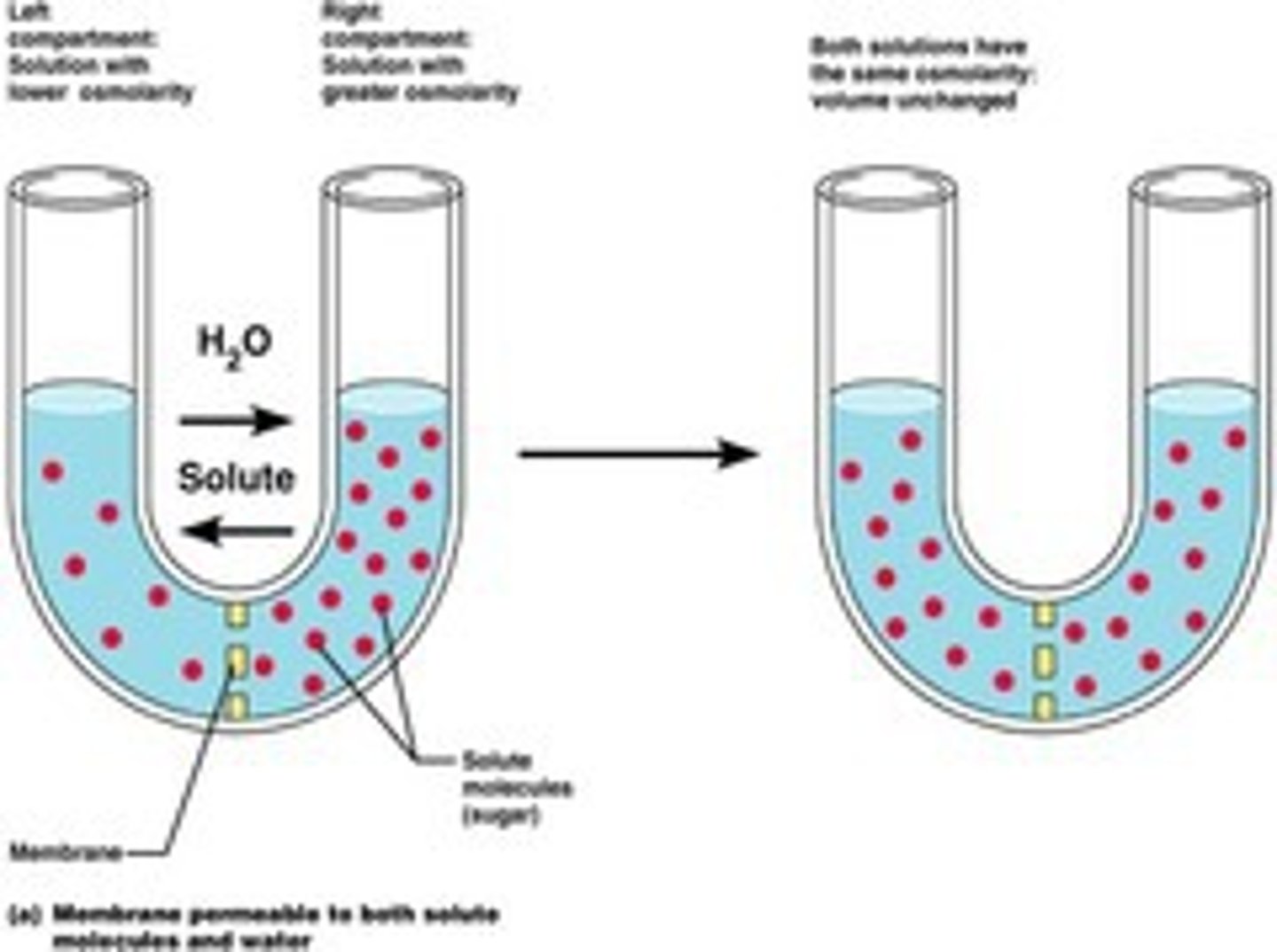
Membrane Transport - Osmosis
Net diffusion of water down its own concentration gradient. "Pulled" by non-diffusible particles.
Whats the Difference Between Osmosis and Diffusion?
Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion specifically for water molecules moving across a semi-permeable membrane
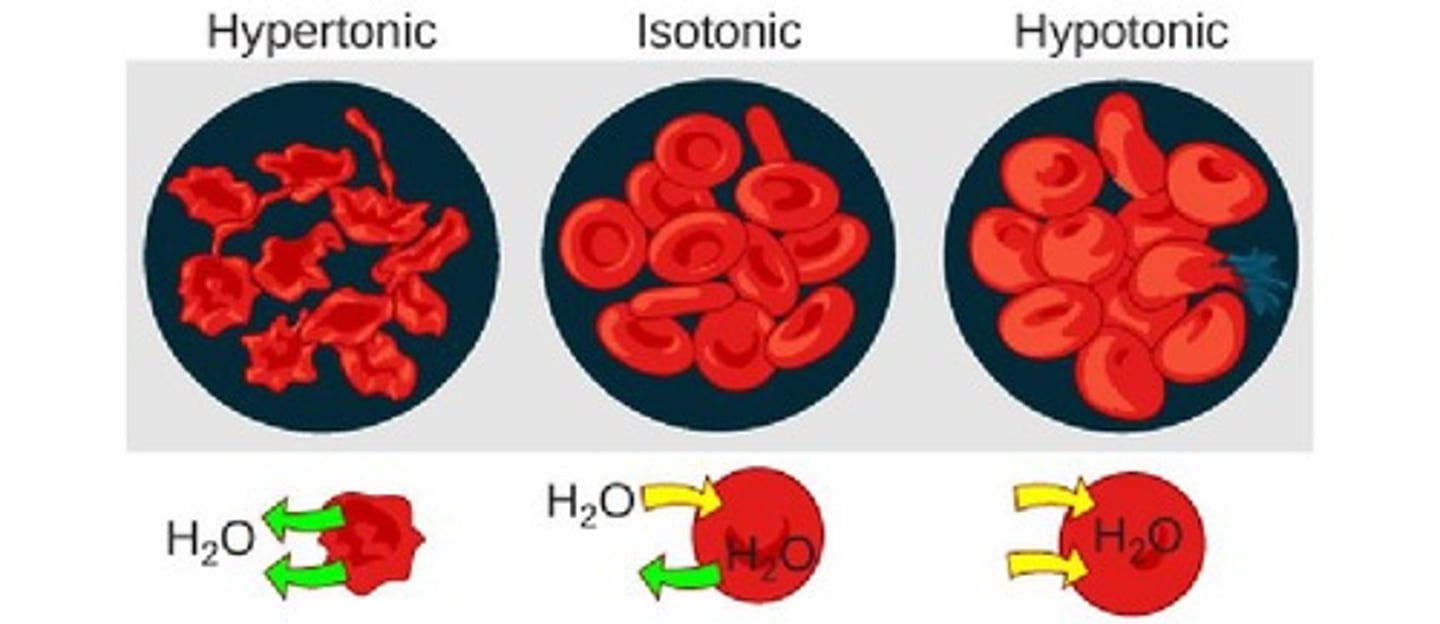
What is Tonicity?
It determines osmosis. Tonicity: # go non-diffusible particles. "Water magnets"
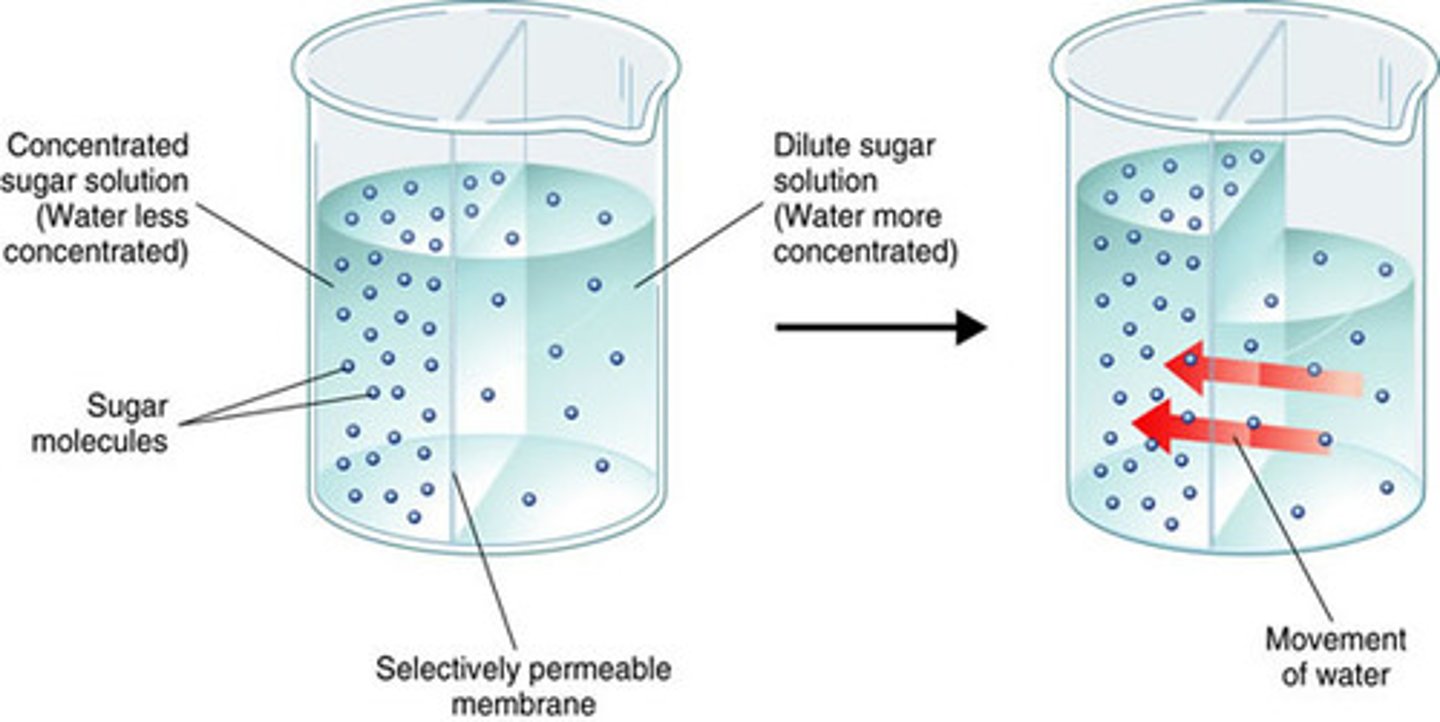
What are the types of Tonicity?
ISOTONIC: solutions are the same / no net osmosis
HYPOTONIC: fewer non-diffusible particles - cells swell
HYPERTONIC: more non-diffusible particles - cells shrink
Water moves from hypotonic to hypertonic.
Facilitated Membrane Transport Diffusion
Role of plasma proteins - pores, channels (protein is channel only) , carriers. Movement can only occur if channels is open. Substance moves in though con. gradient. CHANNEL MEDIATED OR CARRIER MEDIATED.
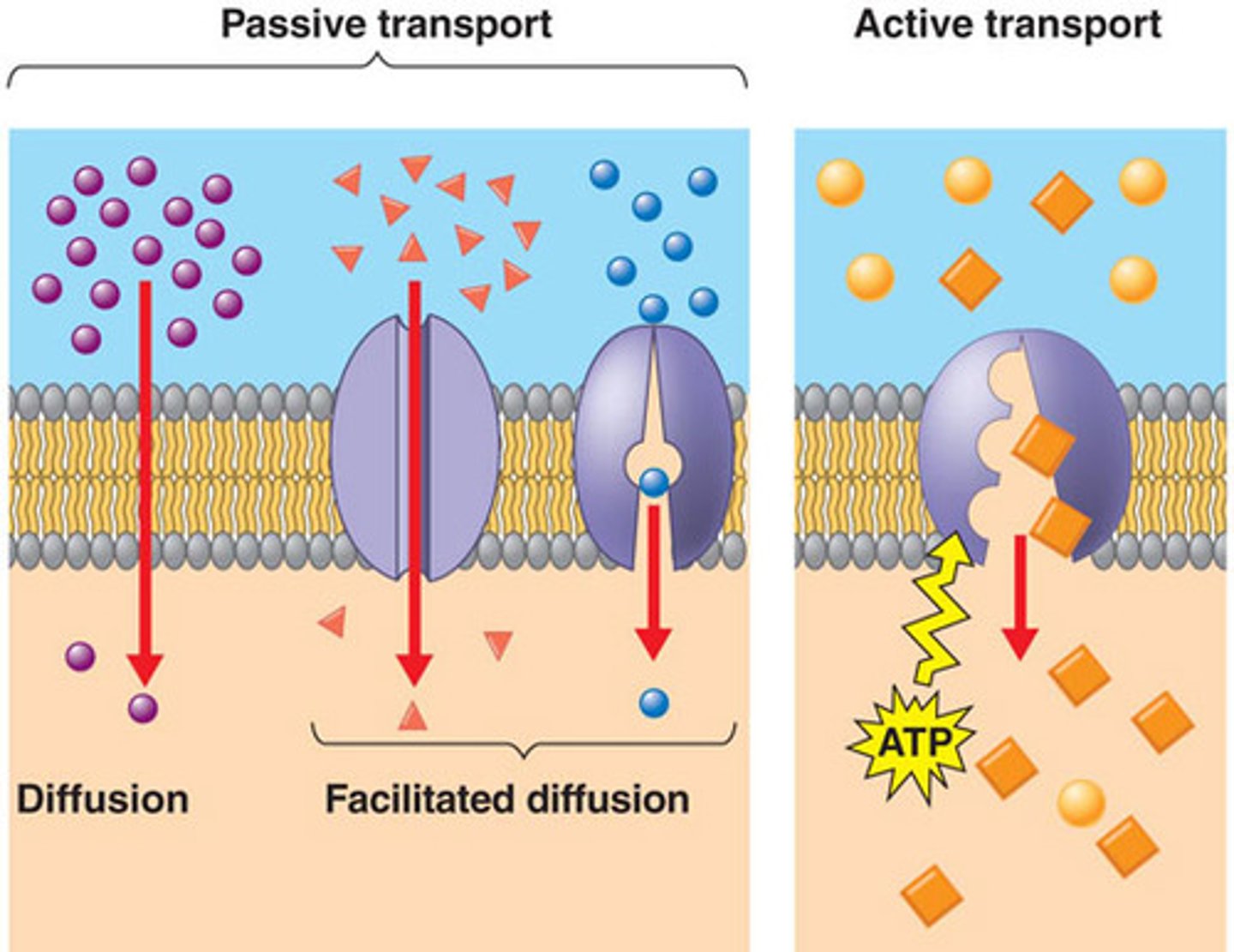
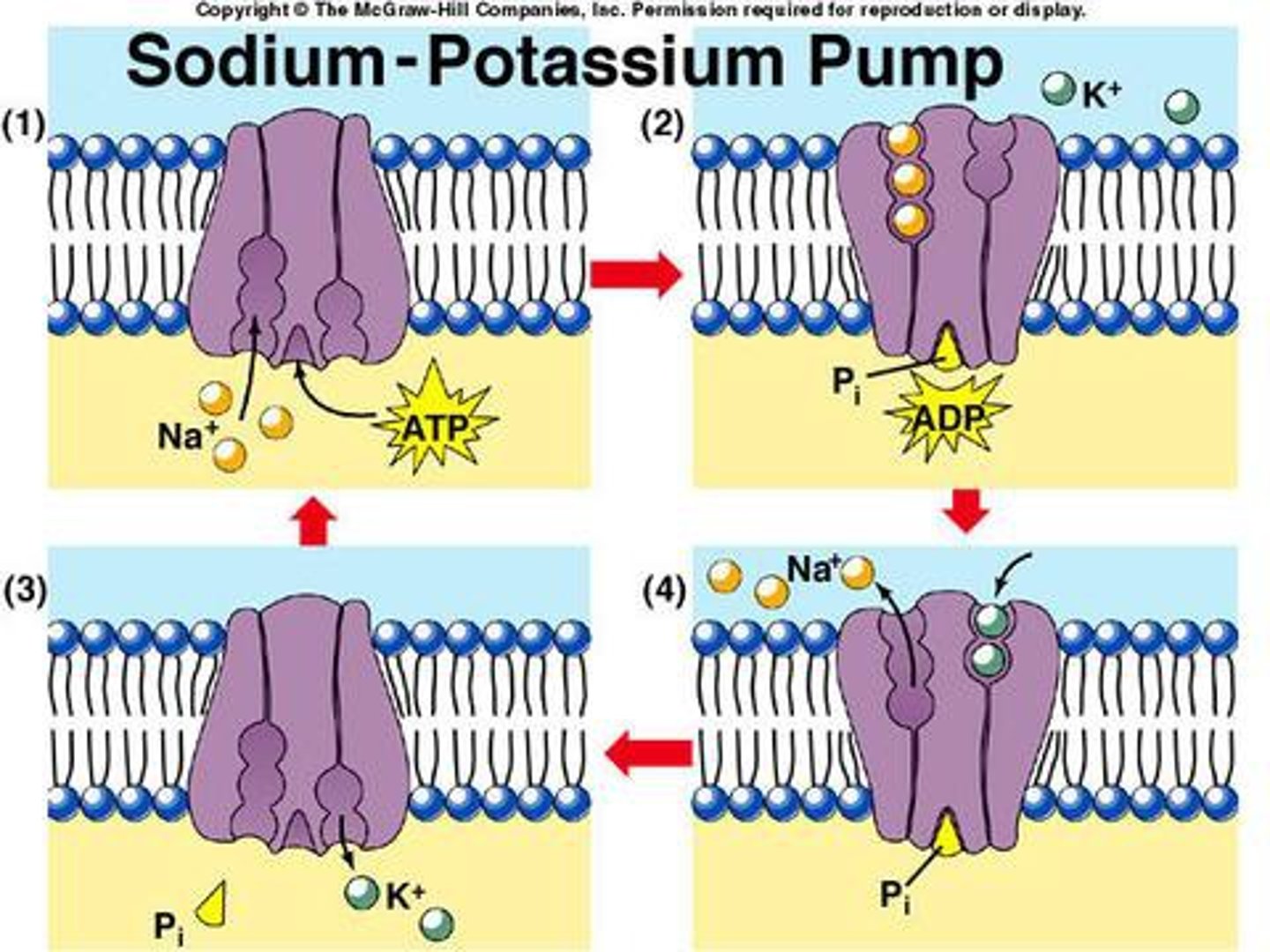
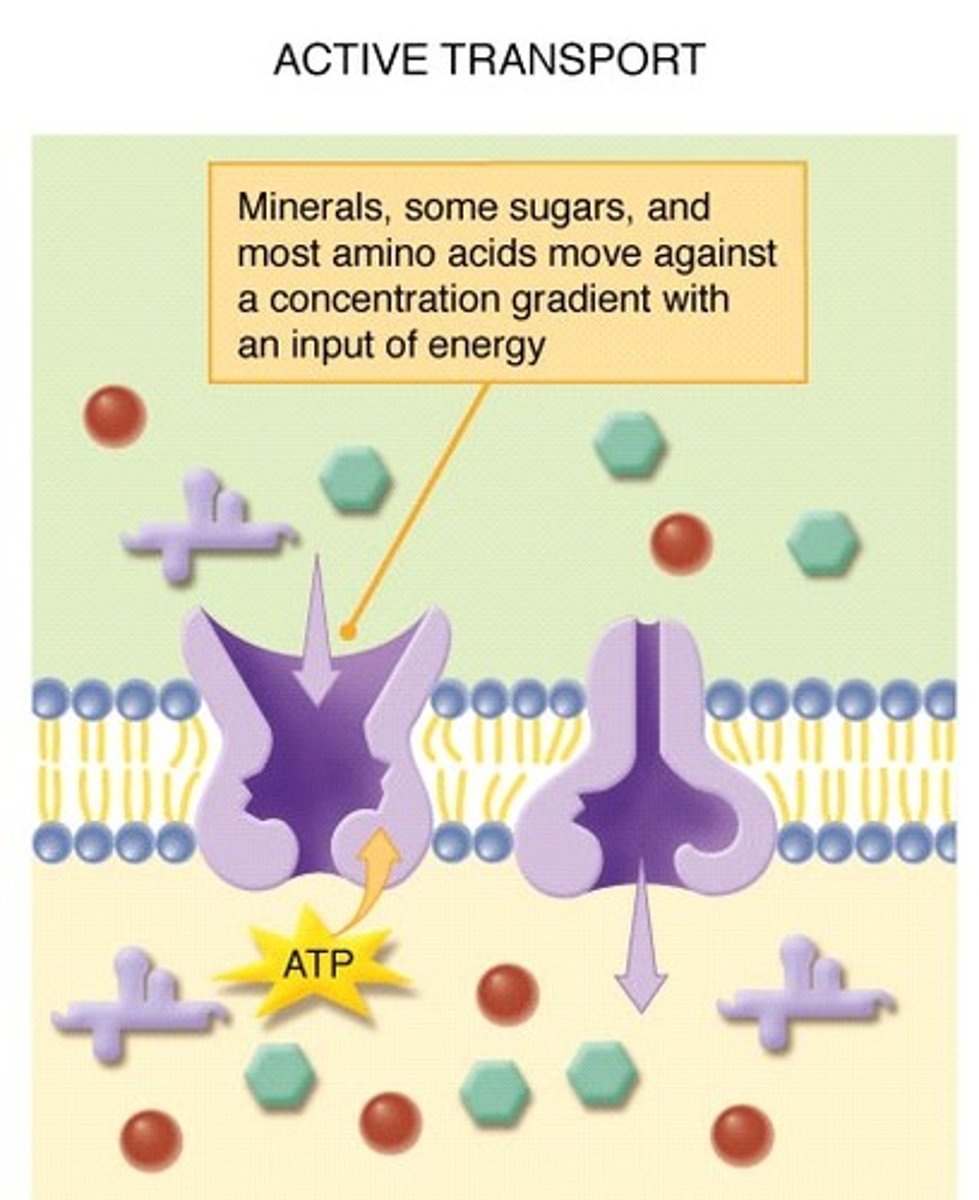
Active Transport
Against gradient - requires energy (ATP). MUST USE CARRIER. Na K Pump.
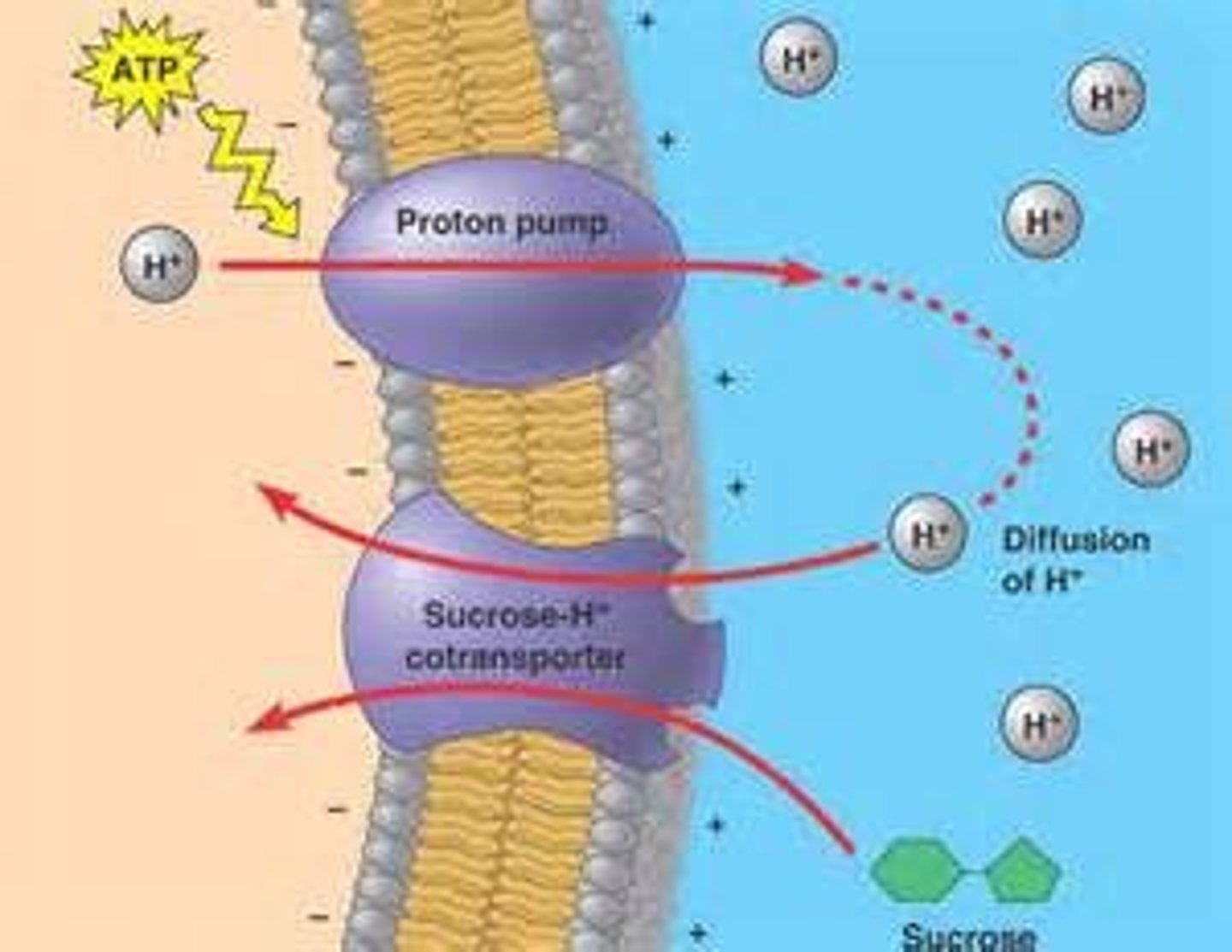
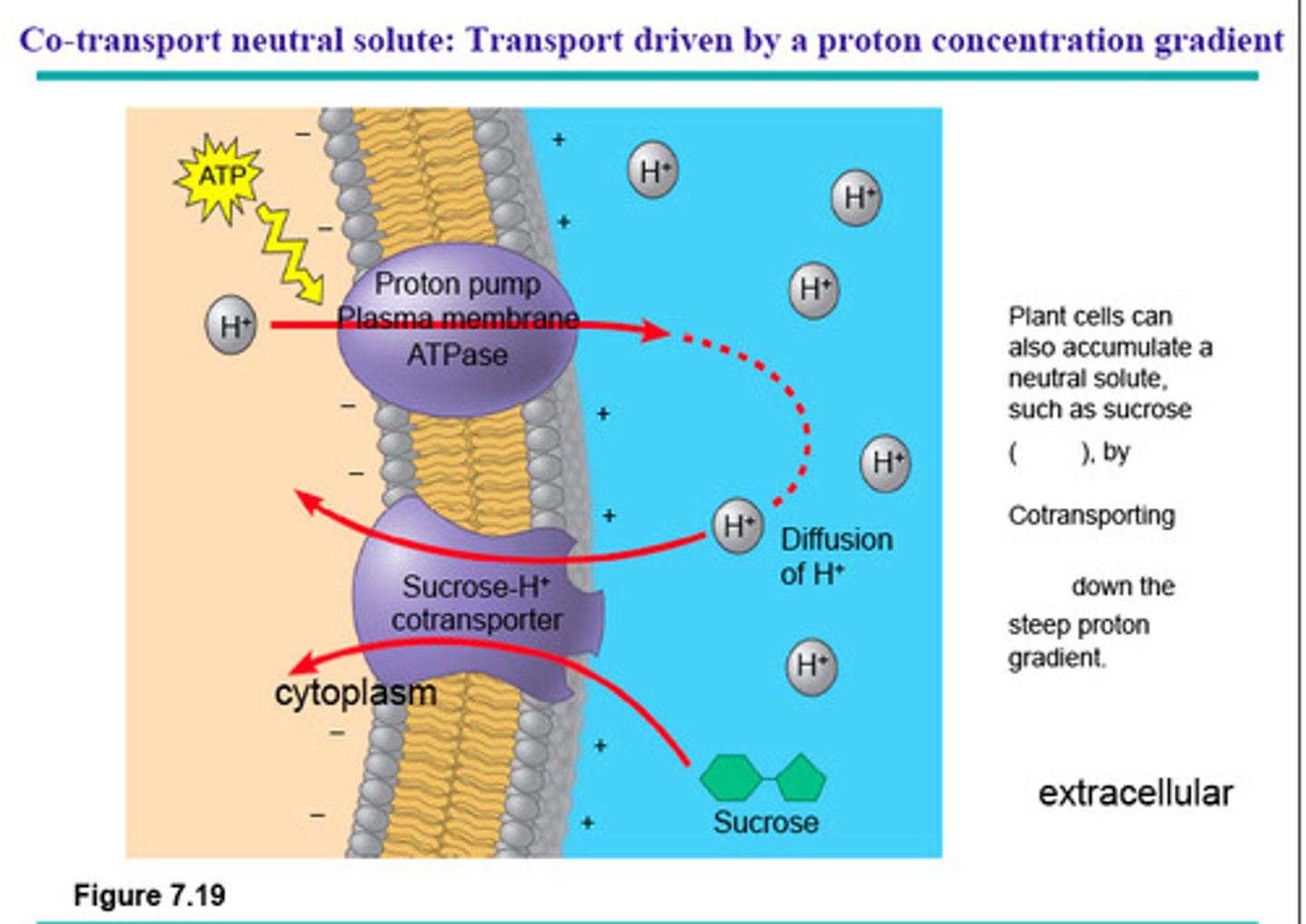
Co-Transport
Secondary active transport. Powered by ( ) gradient of one solute. Moves 2nd solute against gradient. AKA symporter
Counter Transport
Similar to co-transport, but each molecule moves in opposite directions. AKA anti-porter
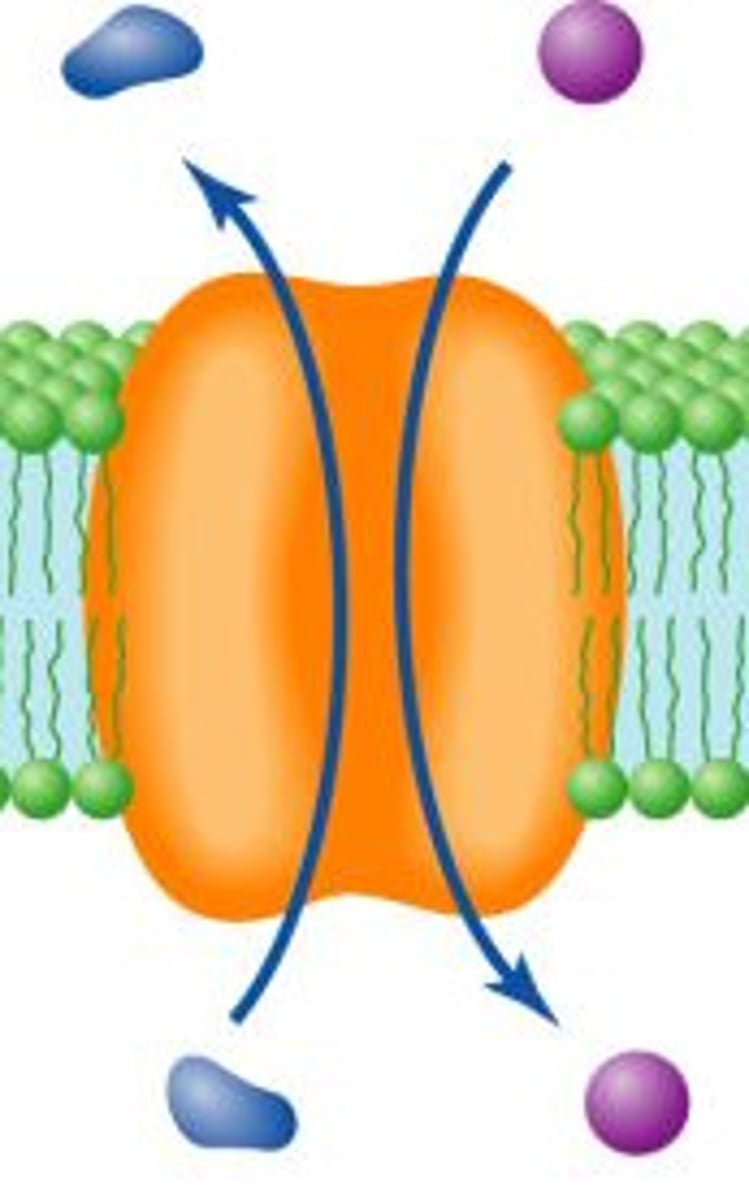
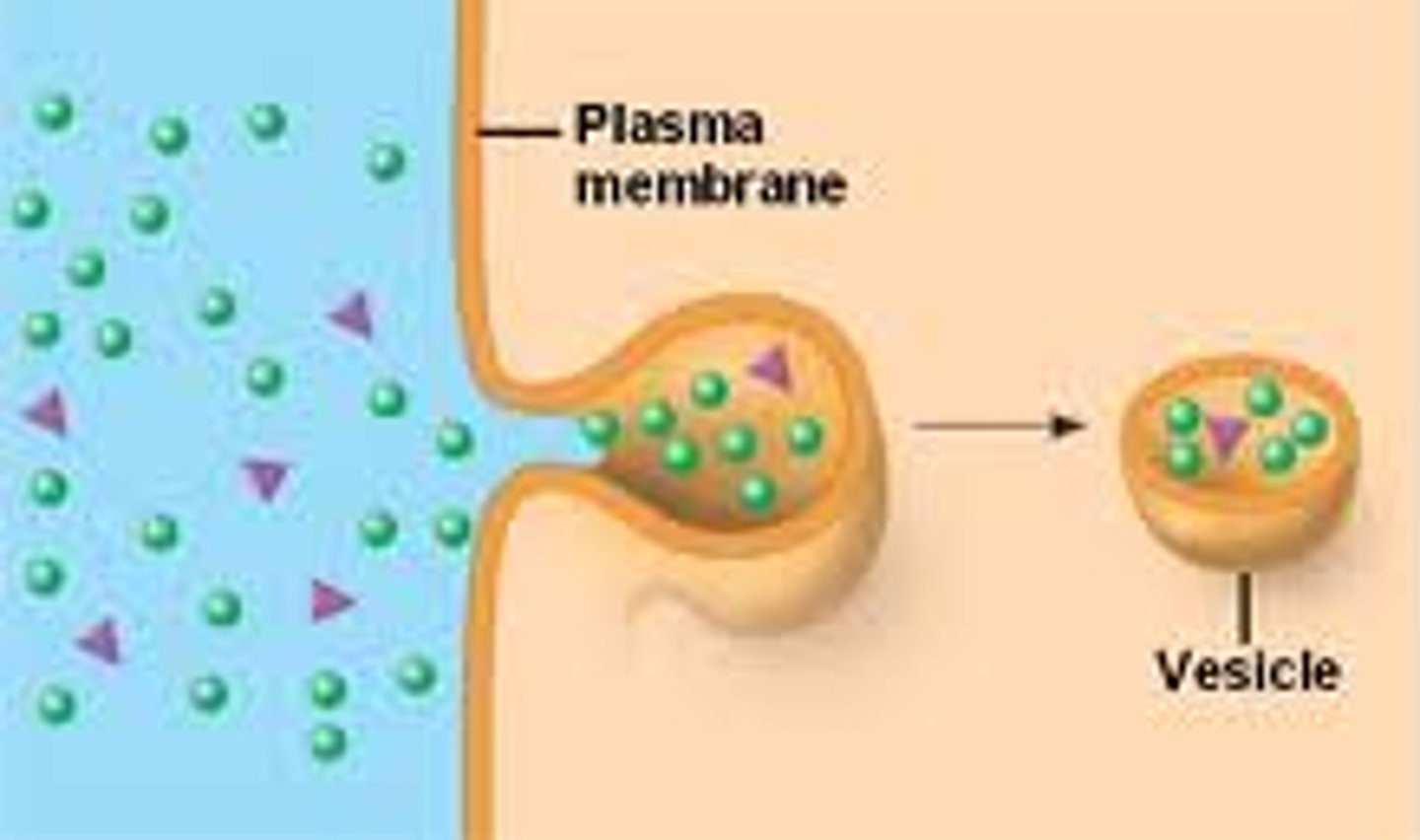
Vesicle Transport
Endocytosis (enter) Exocytosis (exit)
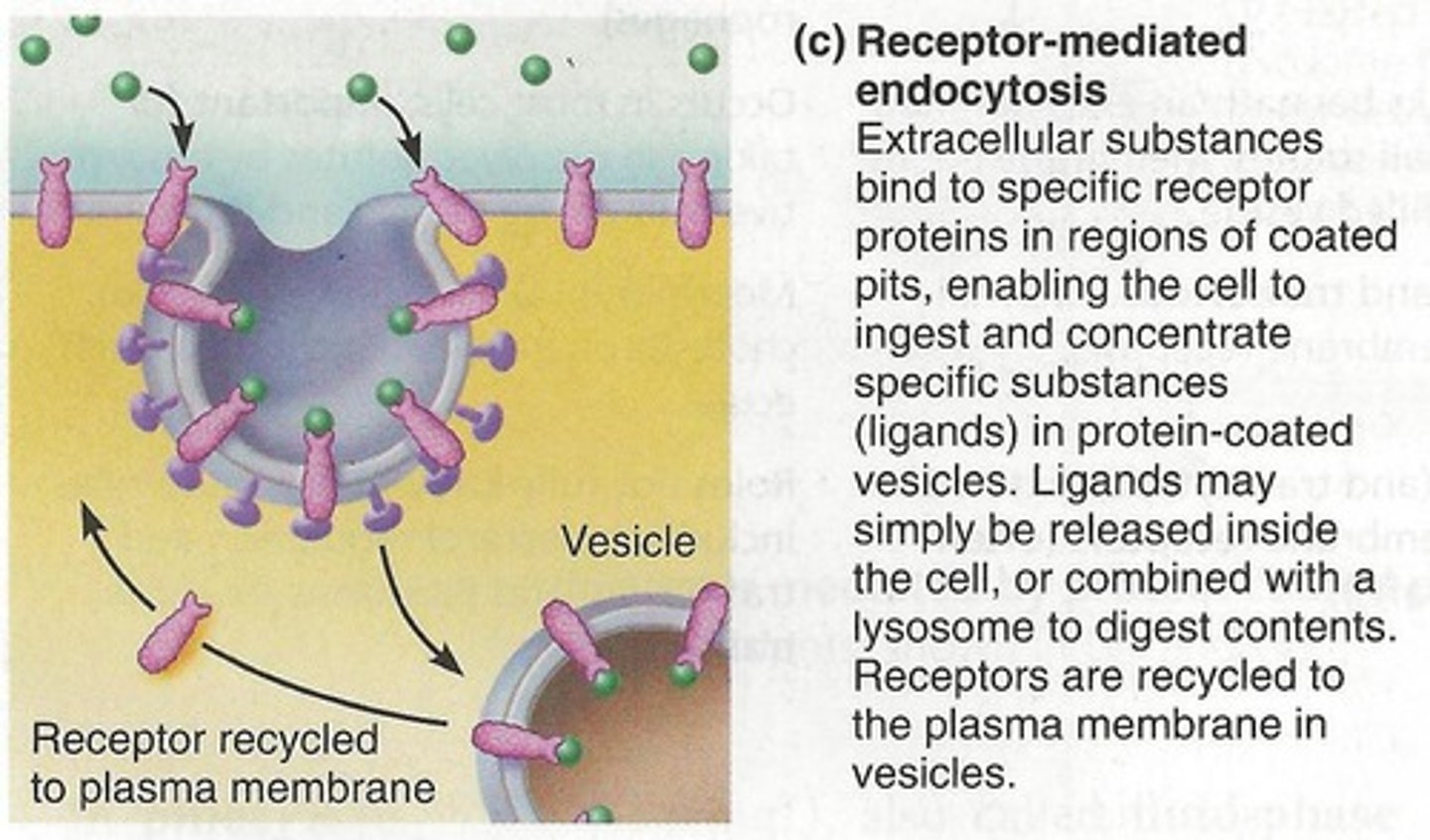
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Binds molecules and then takes in as vesicle. BINDS then takes out.
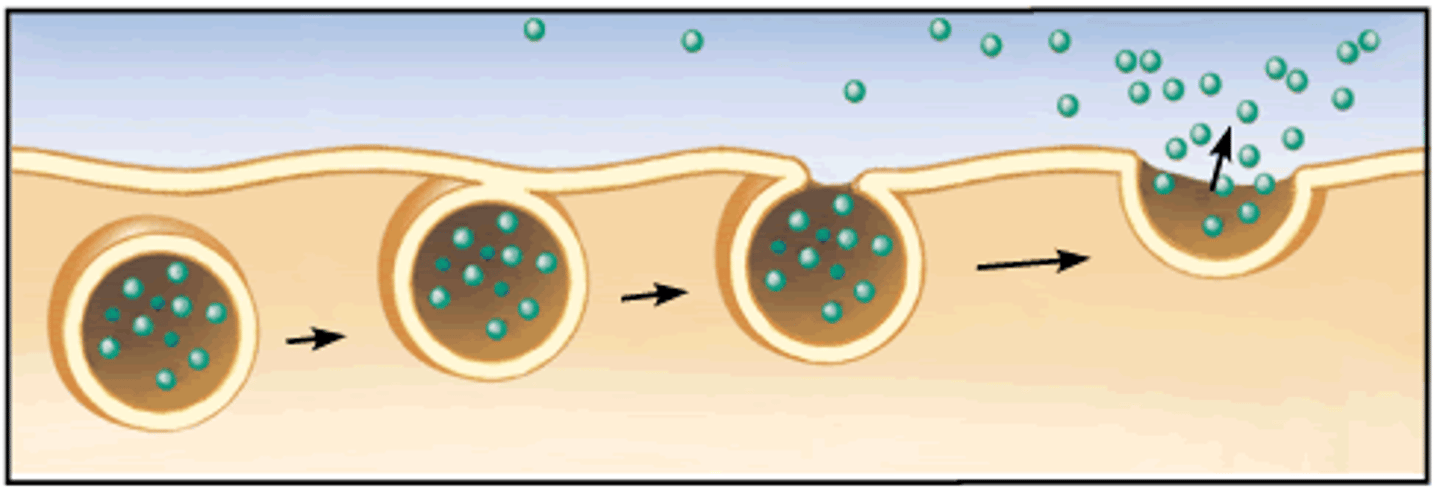
Phagocytosis
Breaking down. Immune response in WBCs. Still engulfing - focuses more on breaking down.
Pinocytosis
Most cells can move water into the cell in bulk flow. In our out. Uses a vesicle.
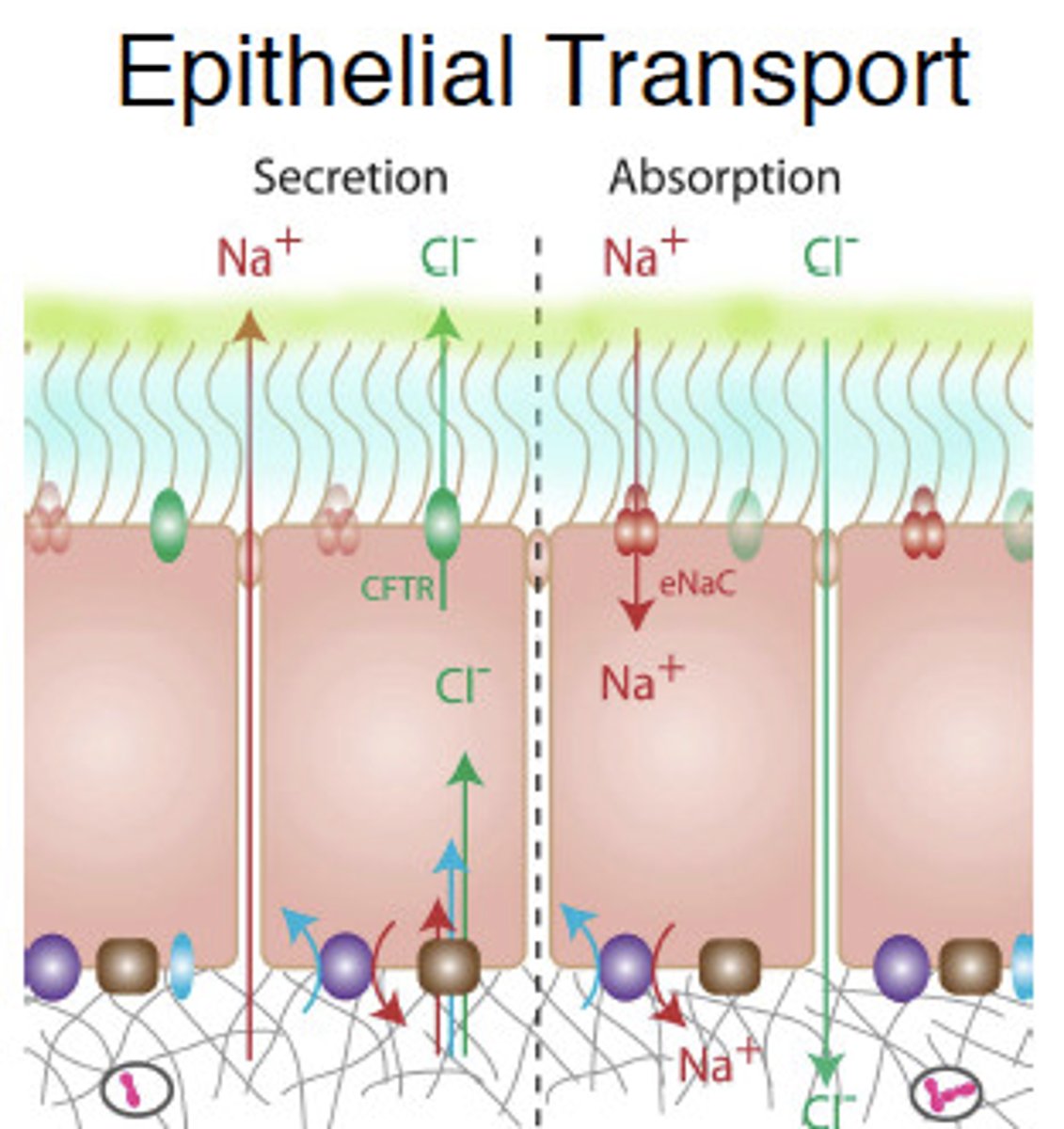
Epithelial Transport
Combines both diffusion and active transport for movement. (not on midterm)
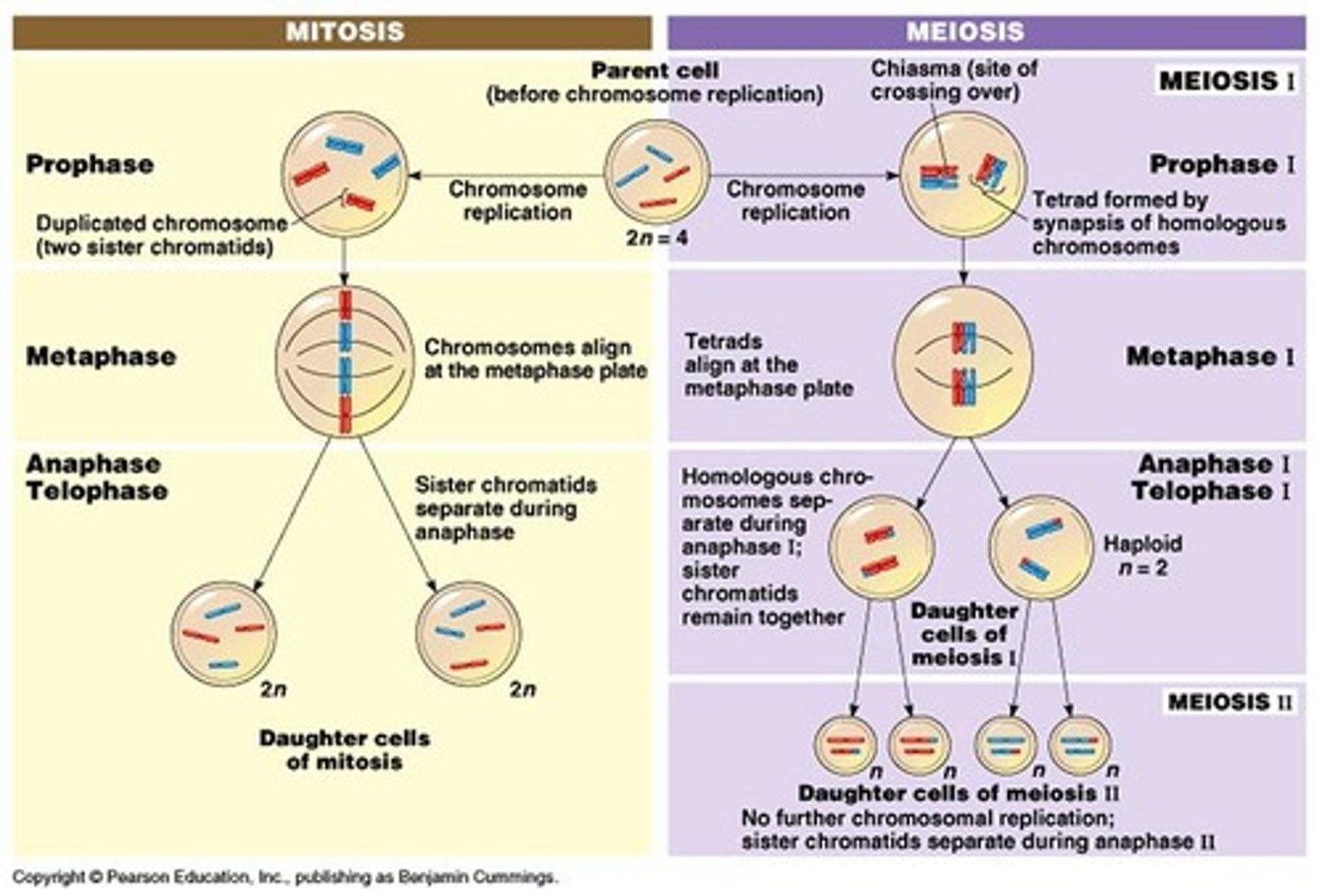
Mitosis Phases
Interphase (before mitosis), Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase and Cytokinesis
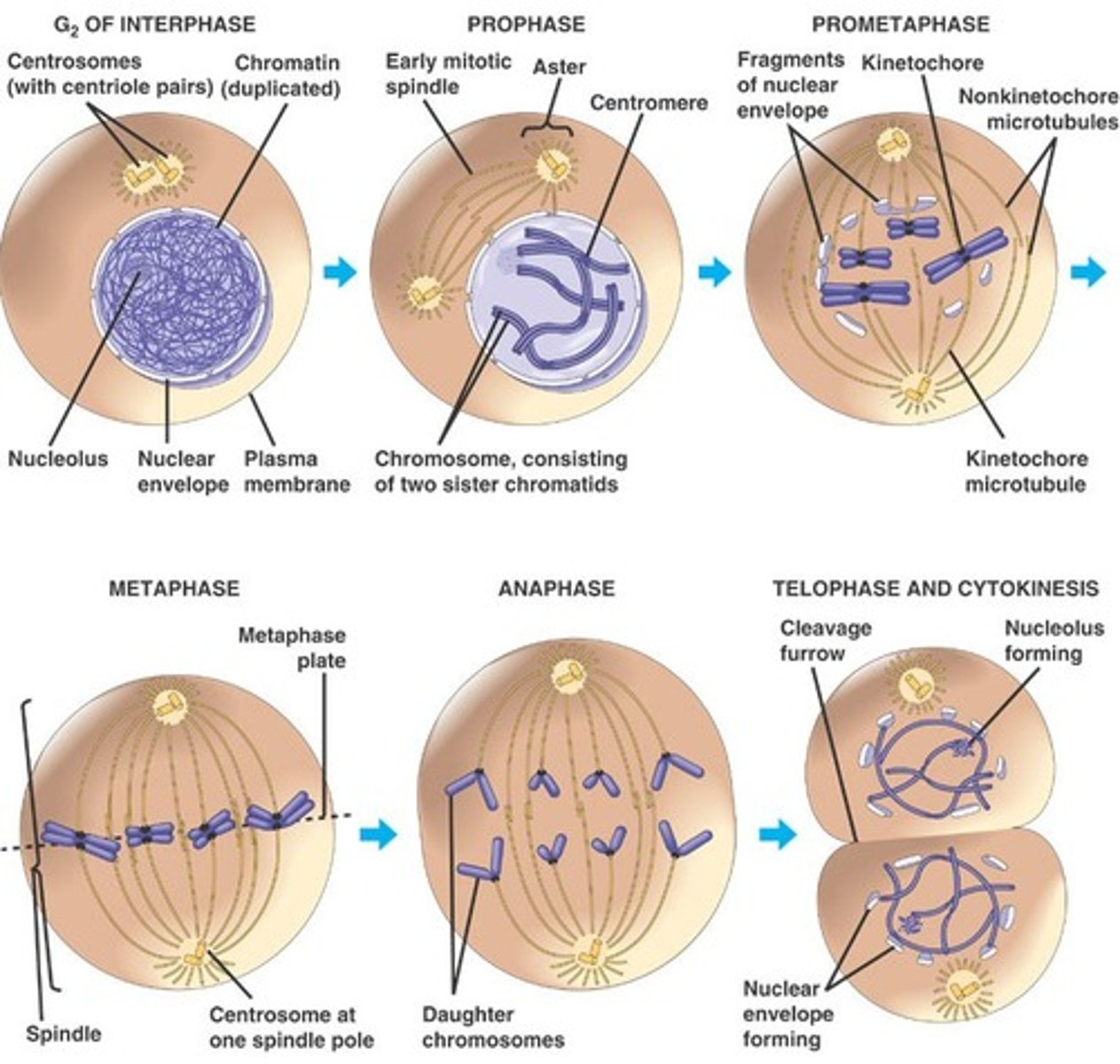
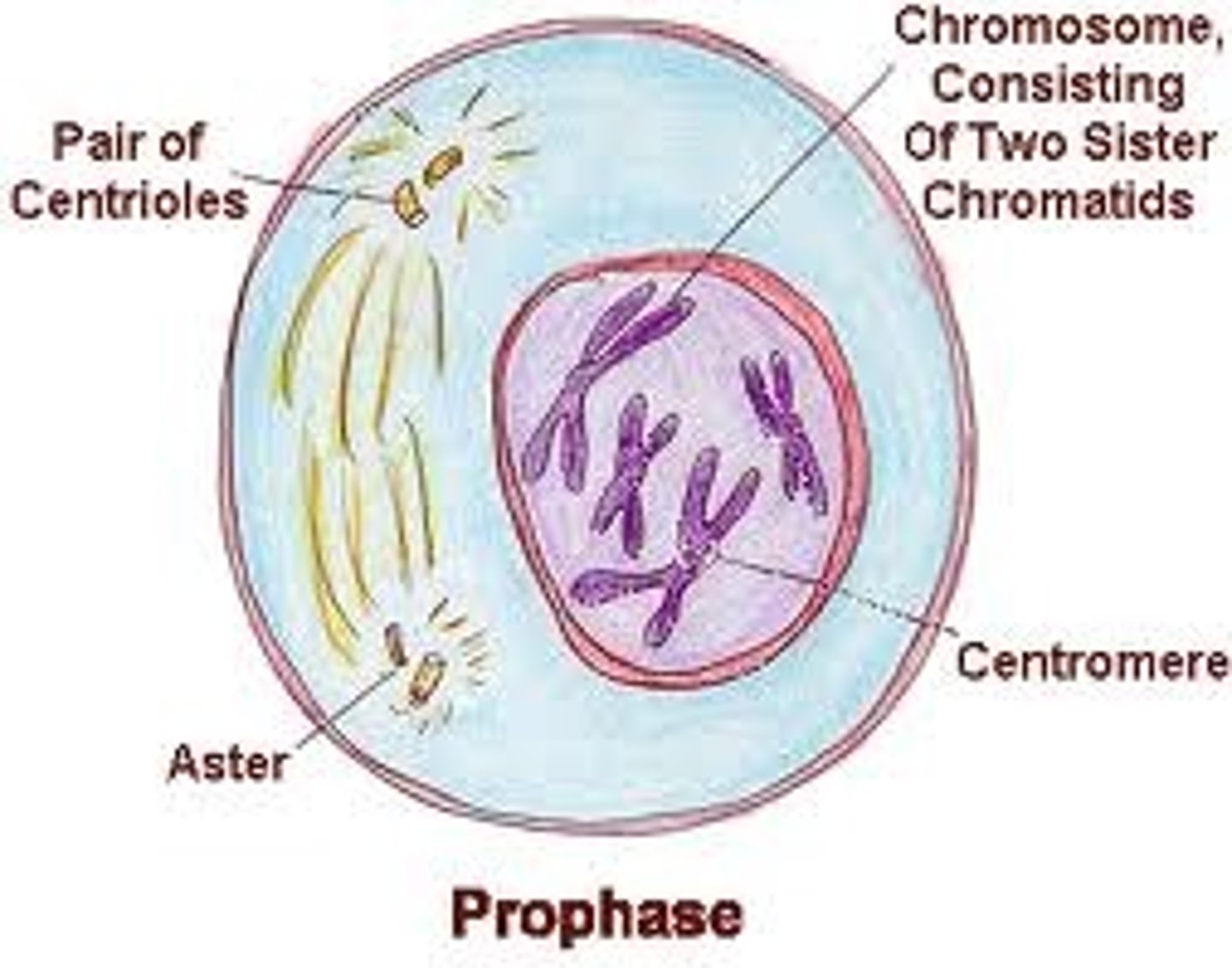
Mitosis - Prophase
Chromatin in nucleus condenses into chromosomes. Nuclear wall degenerates. Centrosomes start to move apart. (get rid of nuclear membrane so it can divide)
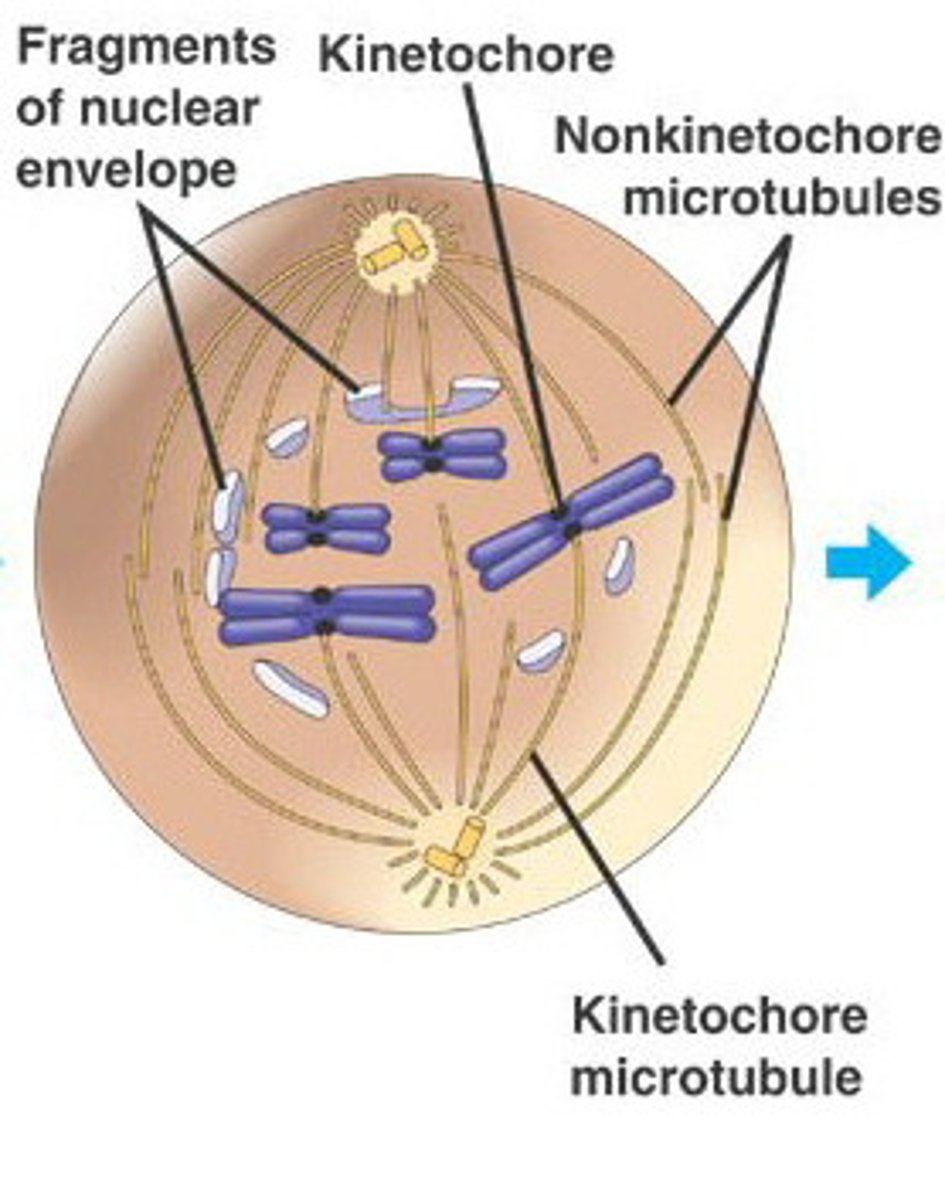
Mitosis - Pro-metaphase
Nuclear envelope disappears. Spindles form chromatic to centrosomes. Kinetochore proteins appear (become visible)
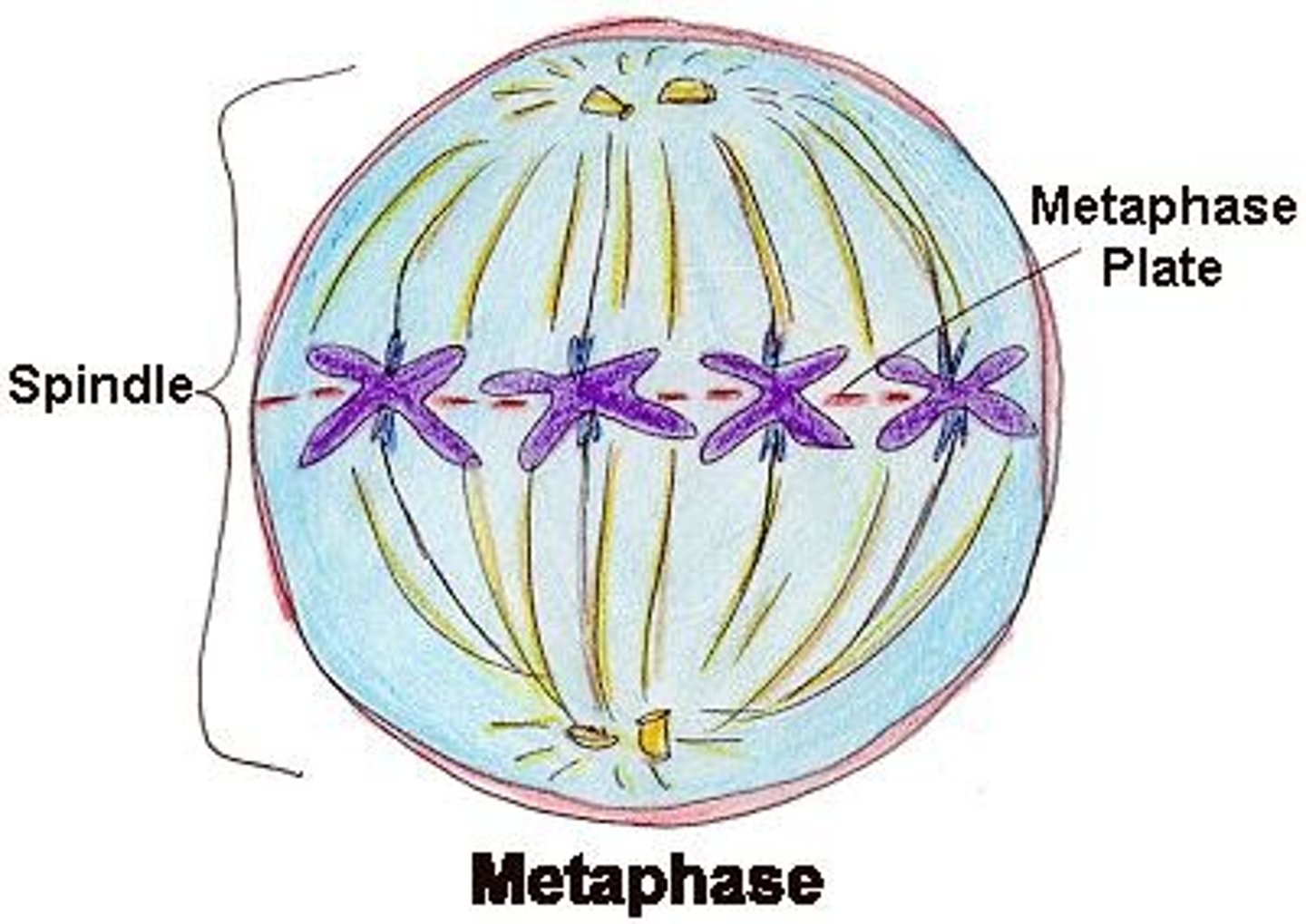
Mitosis - Metaphase
(middle) Centromeres of chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate. Mitotic spindles start to form - ready to pull apart.
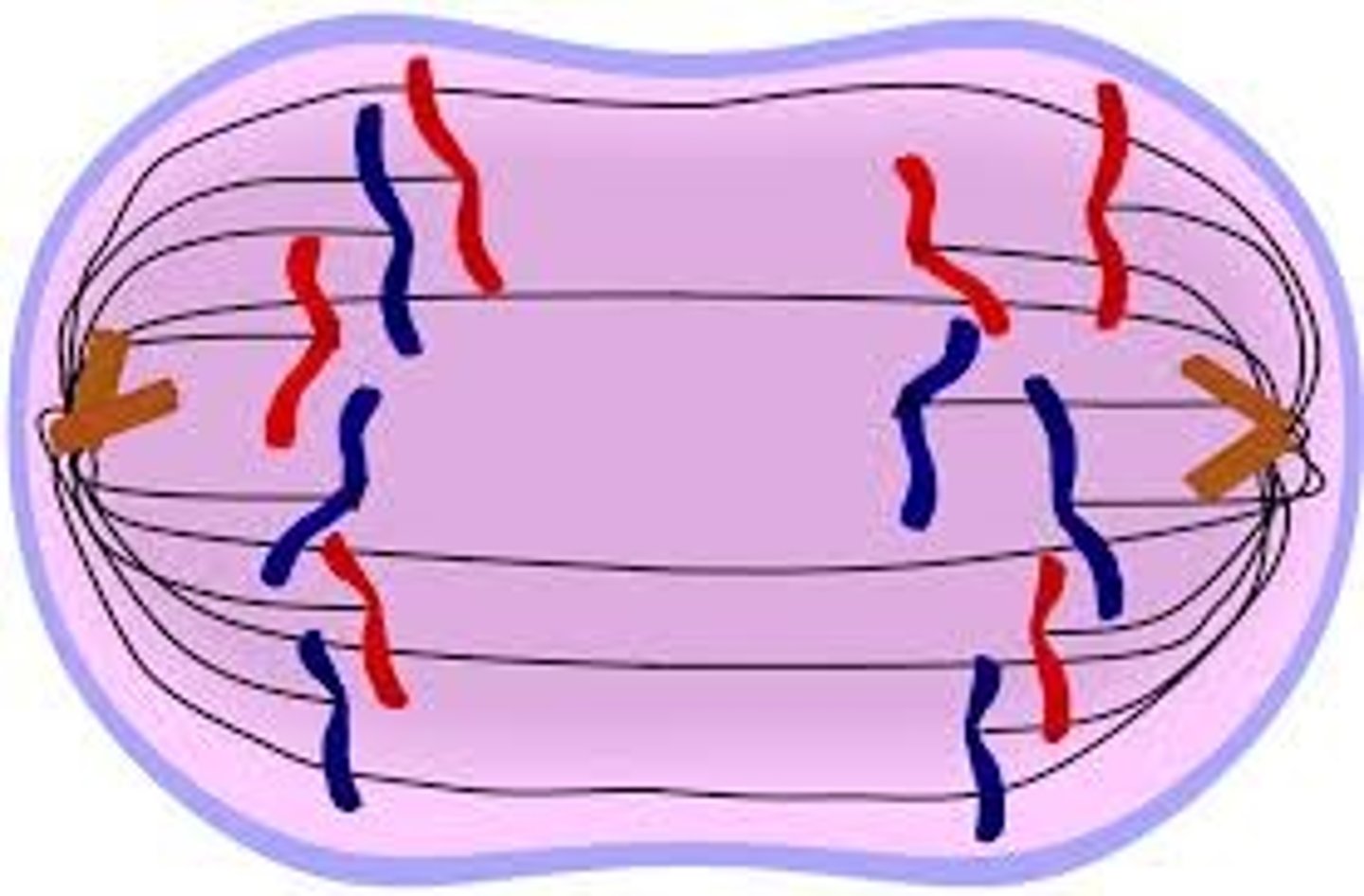
Mitosis: Anaphase
Centromeres of chromosomes split. Kinetichore microtubules sister chromatids move toward opposite poles of the cell (pulled apart). Ones pulling get shorter. Non-Kinetochore microtubule - overlap and push against each other, elongating the cell.
Mitosis - Telophase
Mitotic spindles dissolve. Chromosomes becomes chromatin. New nuclear membrane forms (undoing prophase)
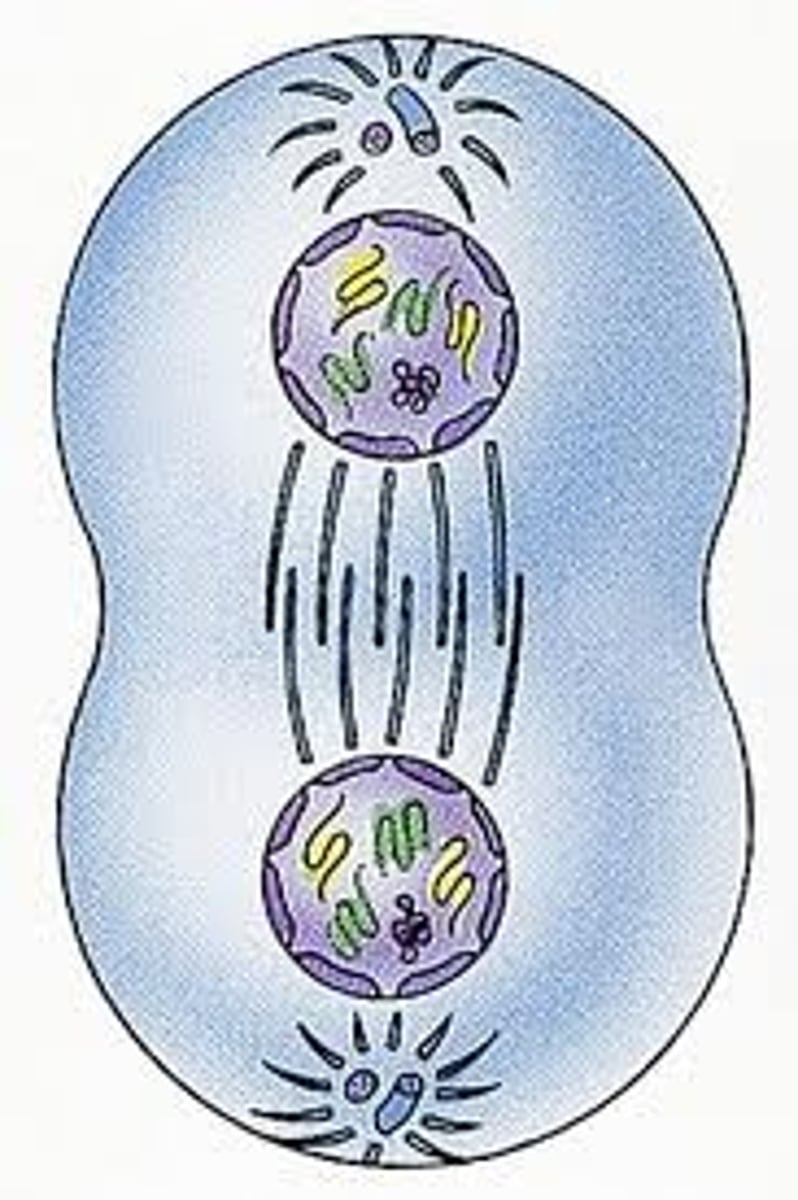
Mitosis - Cytokinesis
Division of cytoplasm. Occurs with telophase. Cleavage furrow pinches cell in two (actual division into 2 daughter cells). After this, new cells enter interphase.
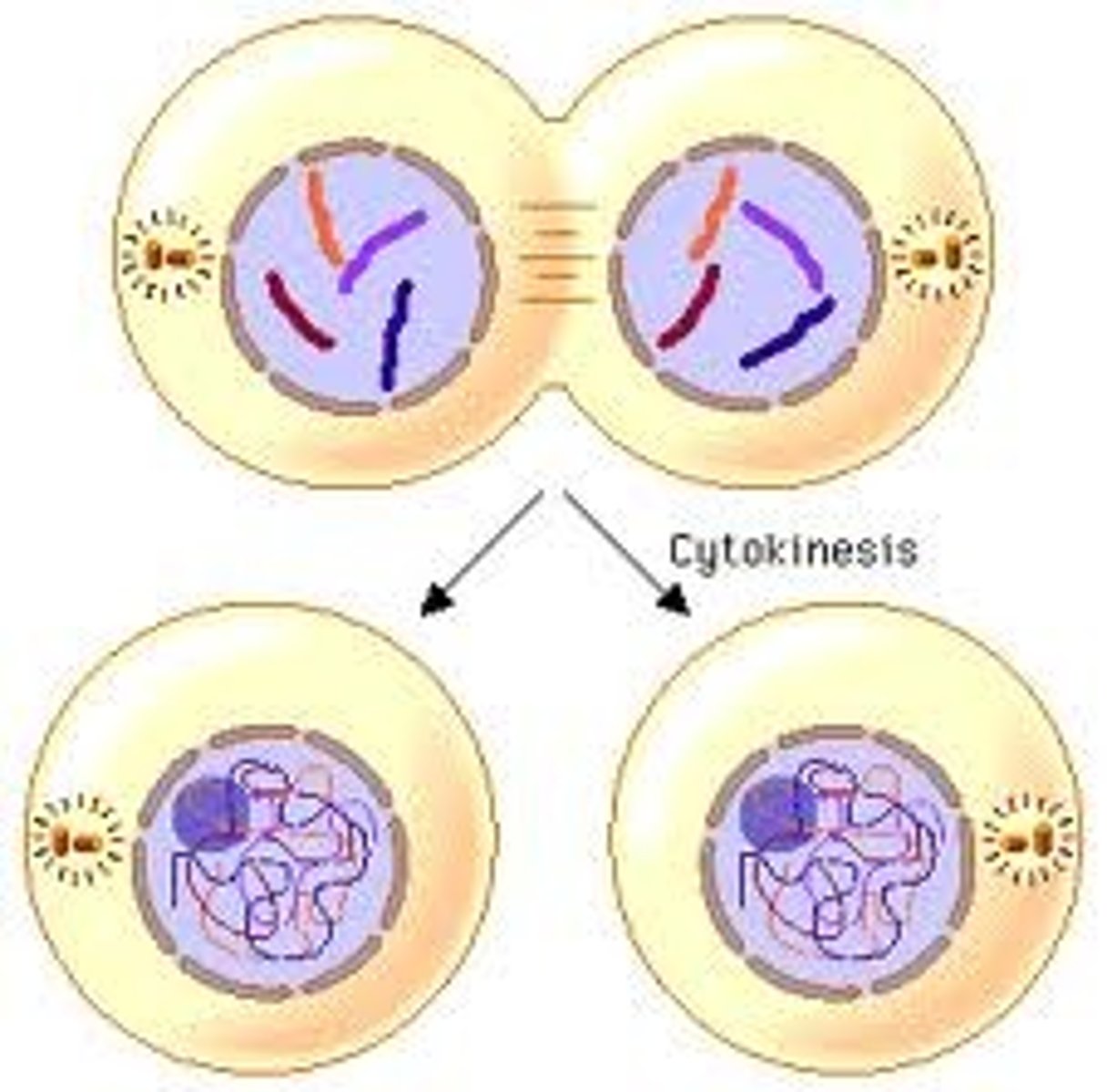
What is Meiosis?
Sexual reproduction. Produces a haploid set of chromosomes (eggs and sperm). Chromosomes replicate once. 2 cell divisions - Meiosis 1, Meiosis 2.
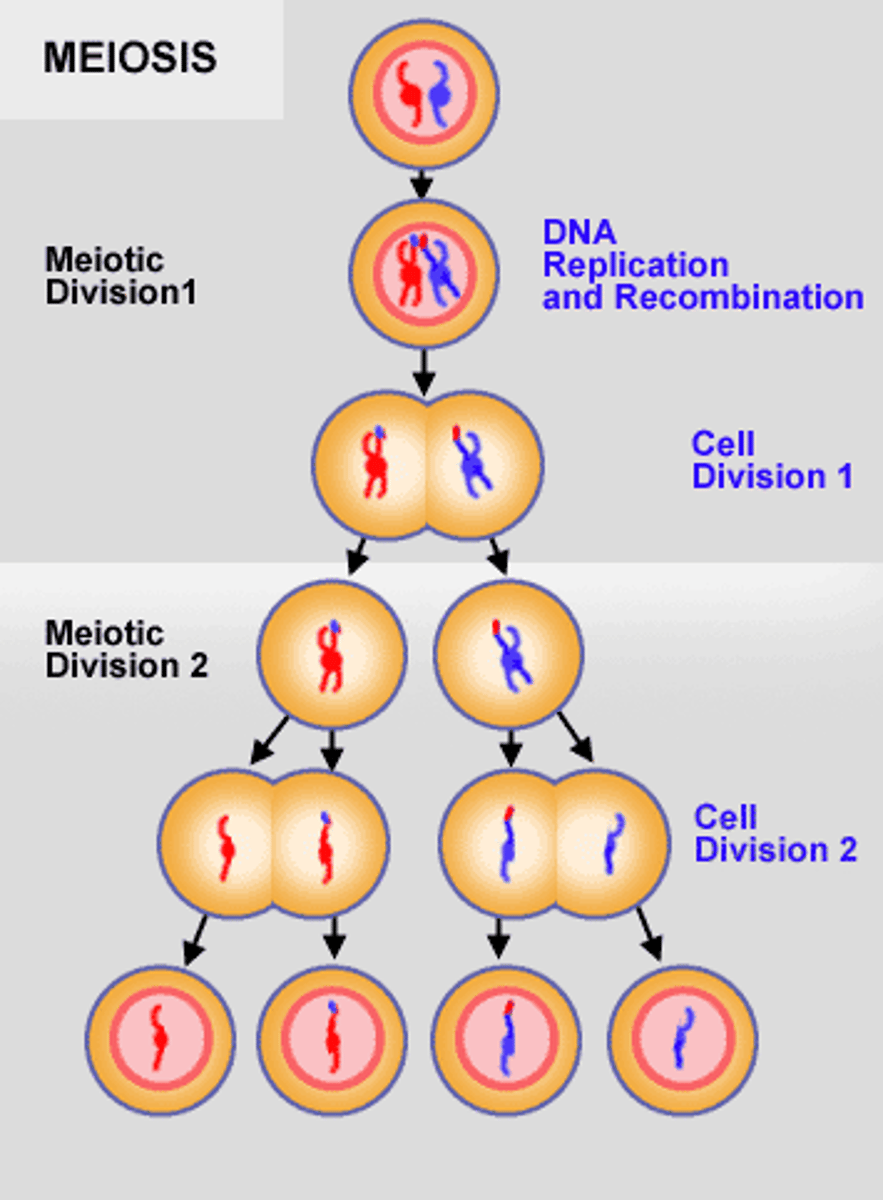
Meiosis 1 vs 2
1 - reduces chromosomes from diploid to haploid. 2 - produces 4 haploid daughter cells.
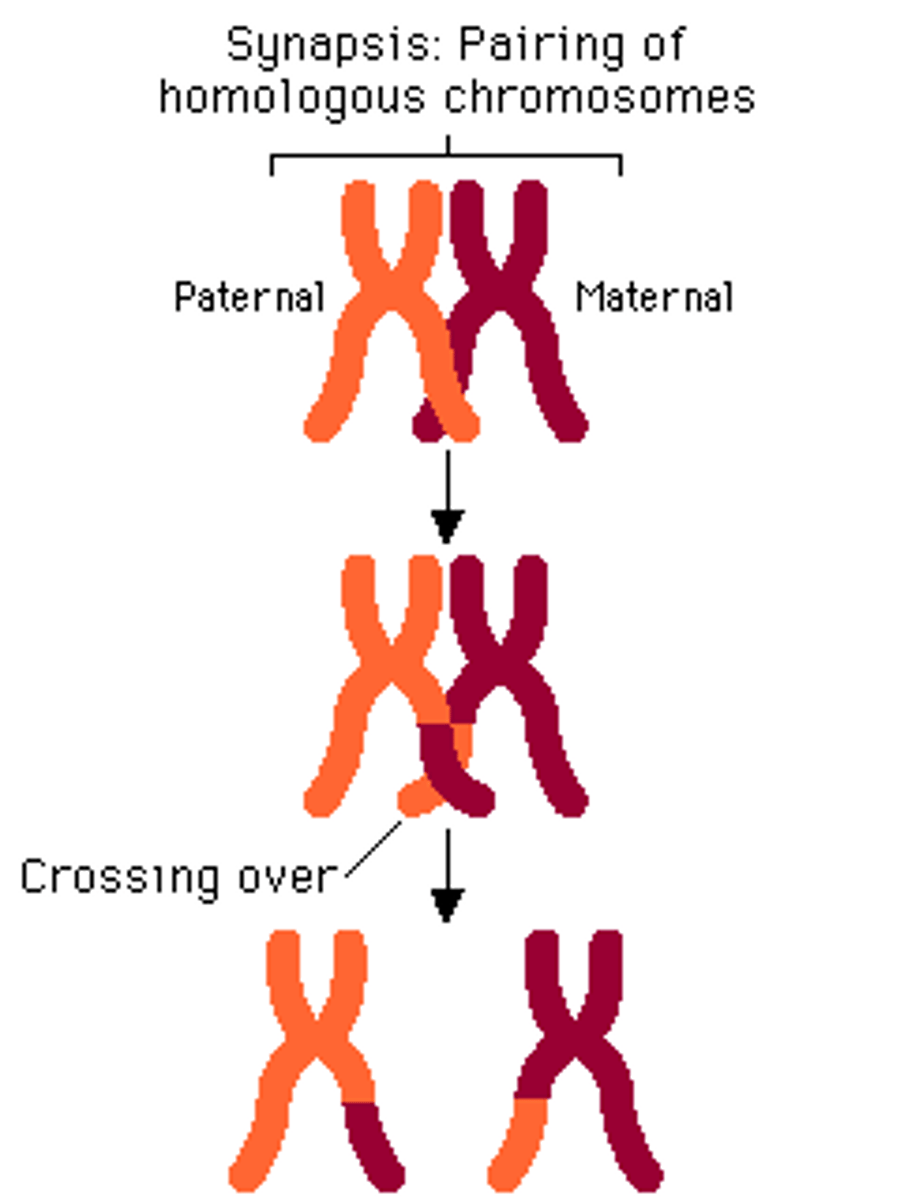
Meiosis - Crossing Over
Prophase 1 (split over the metaphase line before this). Increases genetic variability. Produces chromosomes that carry genes from 2 different parents.
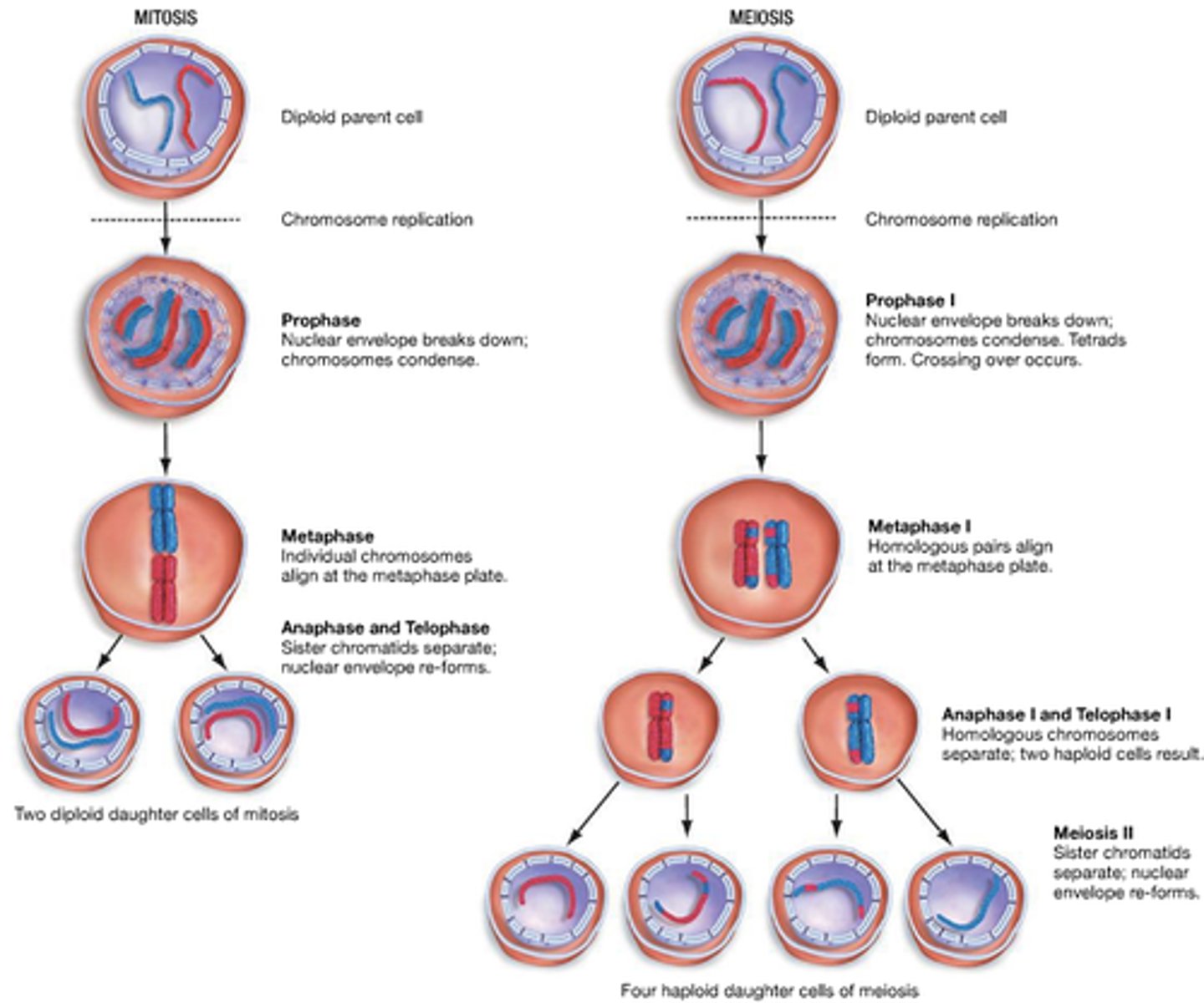
Meiosis vs Mitosis
Meiosis - 23 pairs (all look the same). Mitosis - 46 singles (all unique - new).
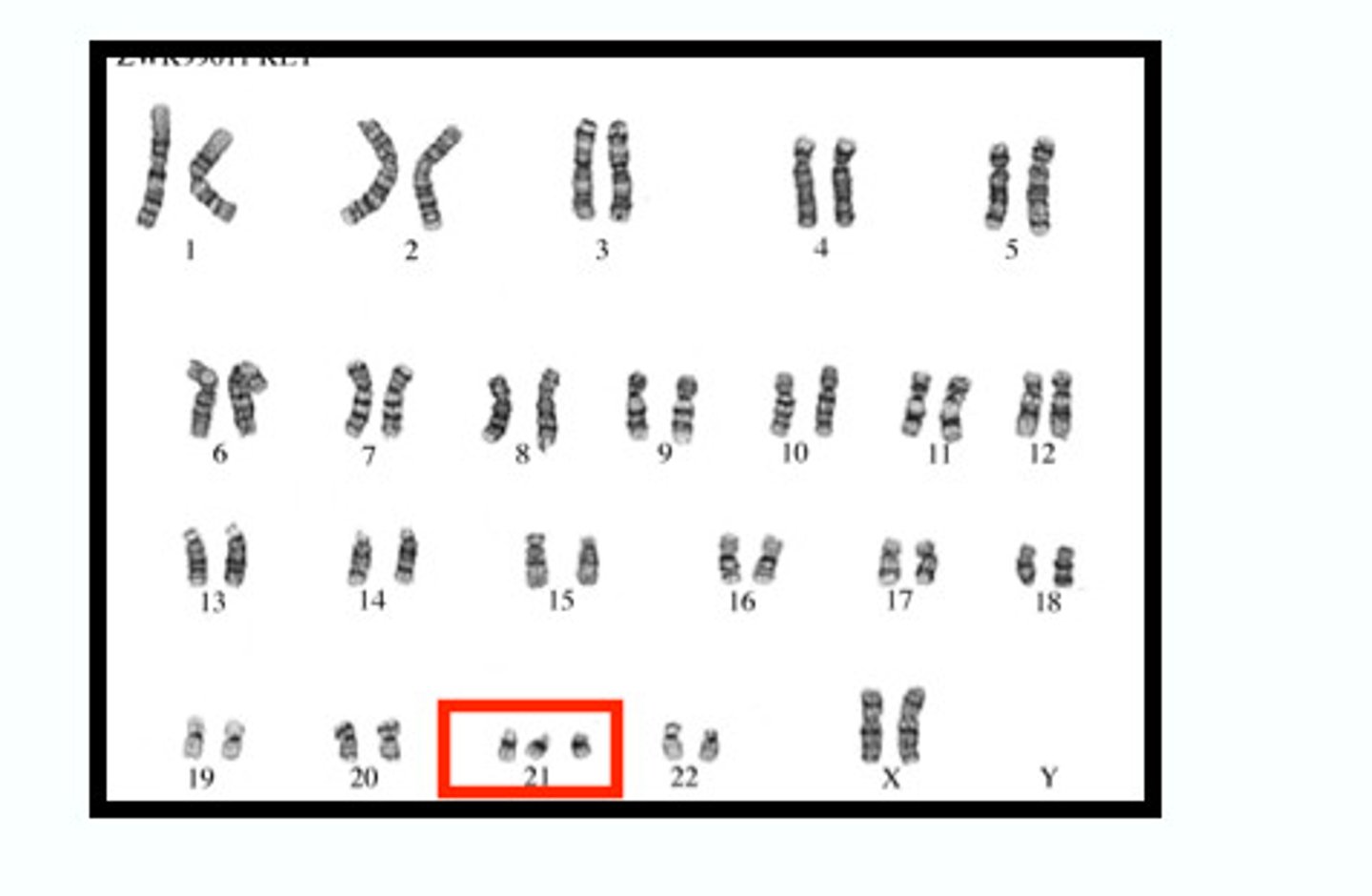
What causes Down syndrome?
trisomy 21, extra copy of chromosome 21
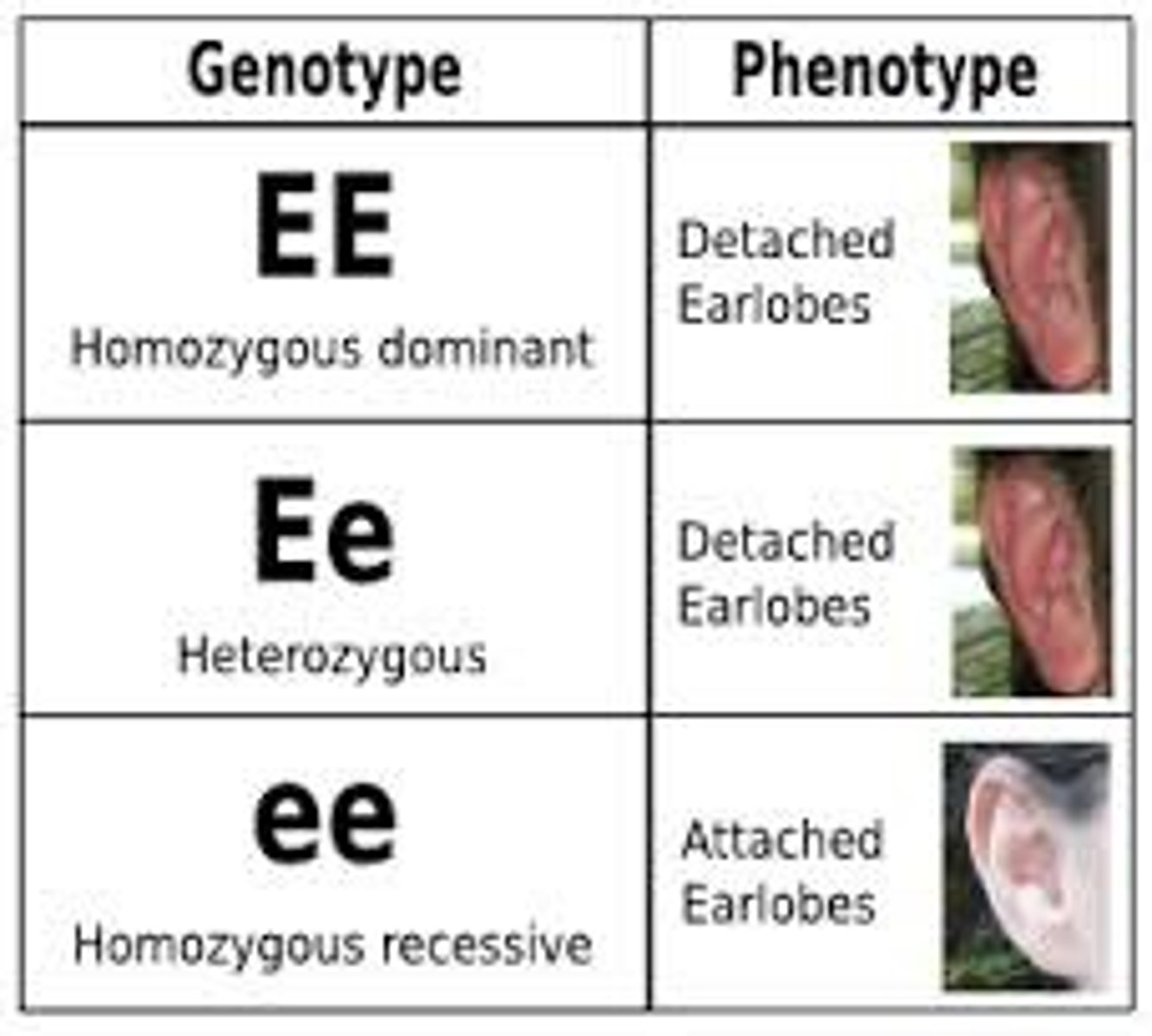
Genetics - Phenotype
Its physical appearance of a specific character
Genetics - Genotype
The genetic makeup (alleles) that determine the physical appearance
Genetics - Character
A heritable feature, such as eye colour or hair colour
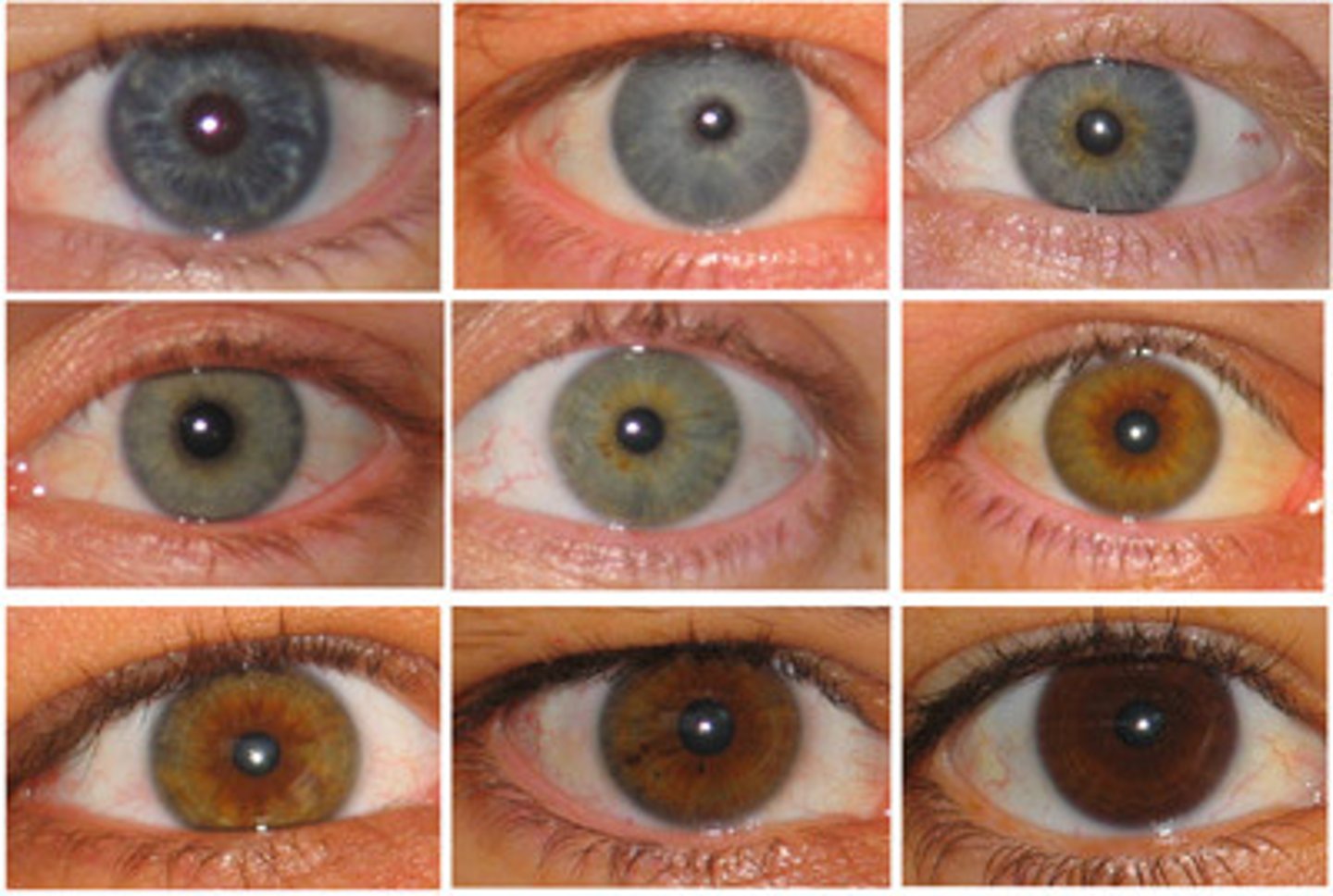
Genetics - Trait
A variant of a character, such a blue eyes or brown eyes
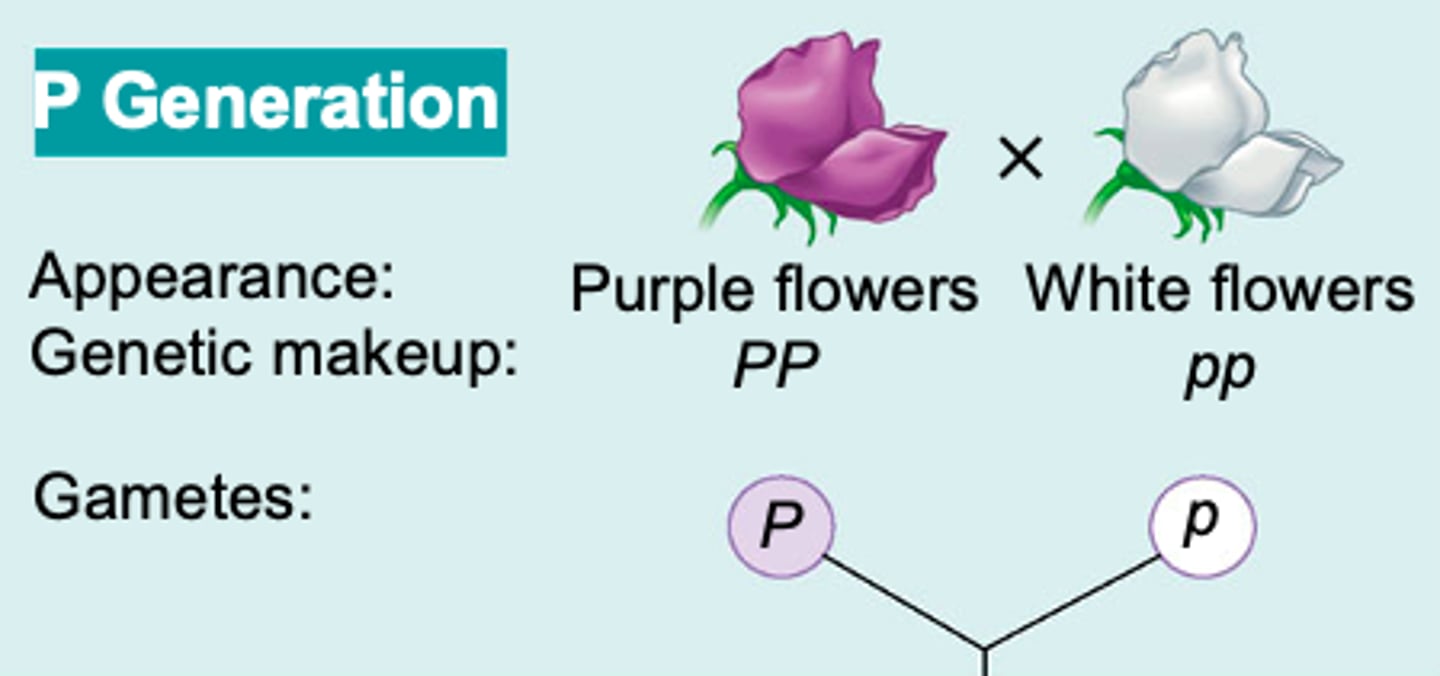
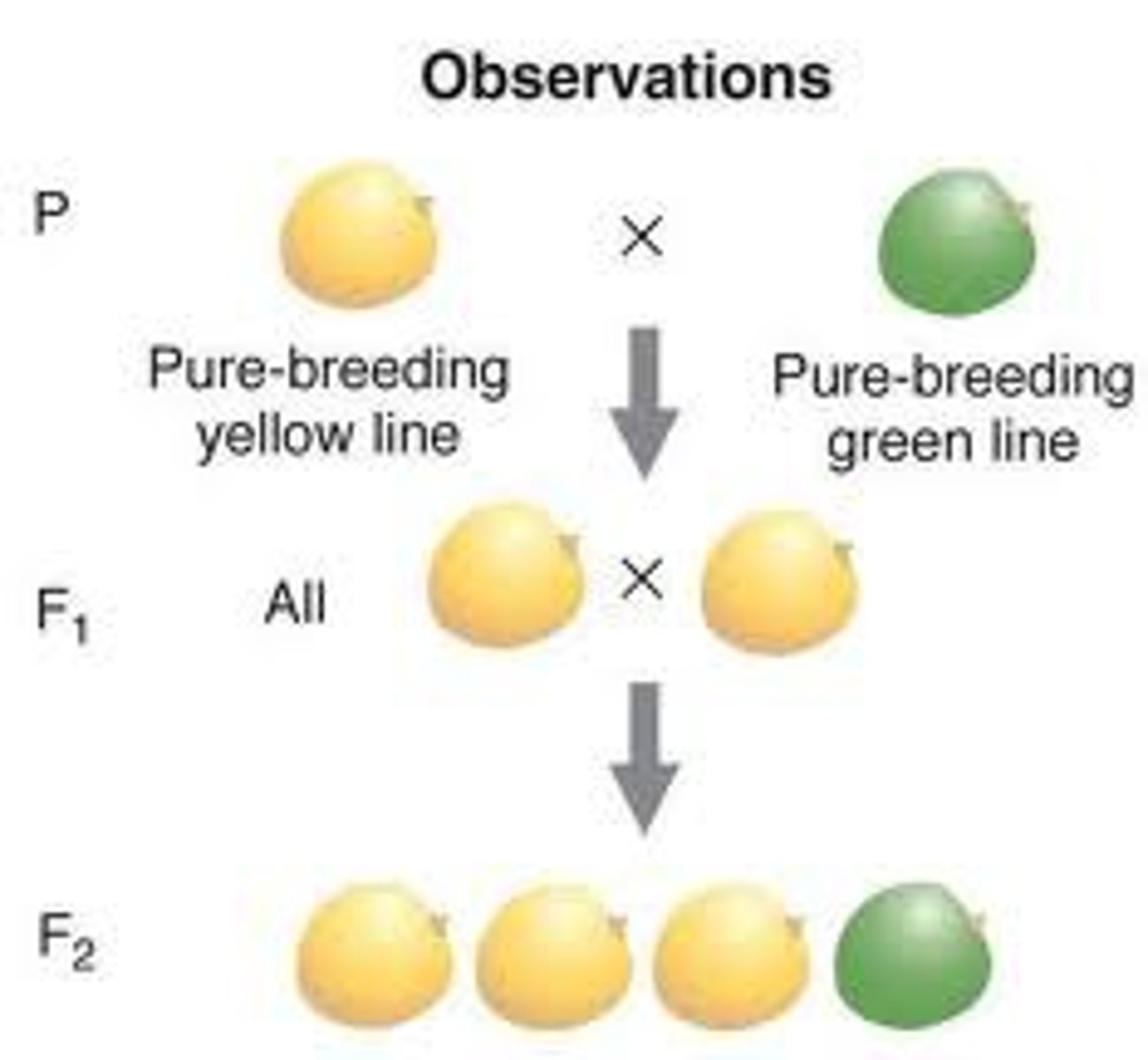
Genetics - P Generation
The true breeding parents
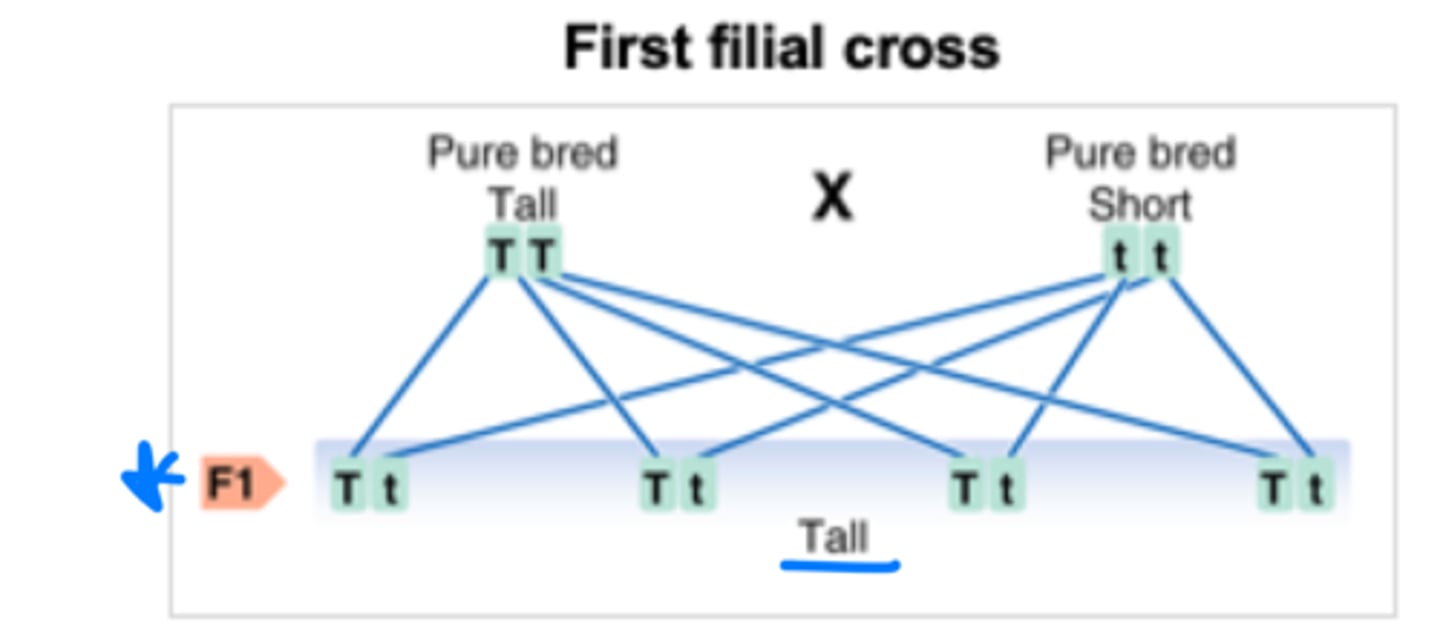
Genetics - F1 Generation
Hybrid offspring of the P generation
Genetics - F2 Generation
When F1 individuals self - pollinate
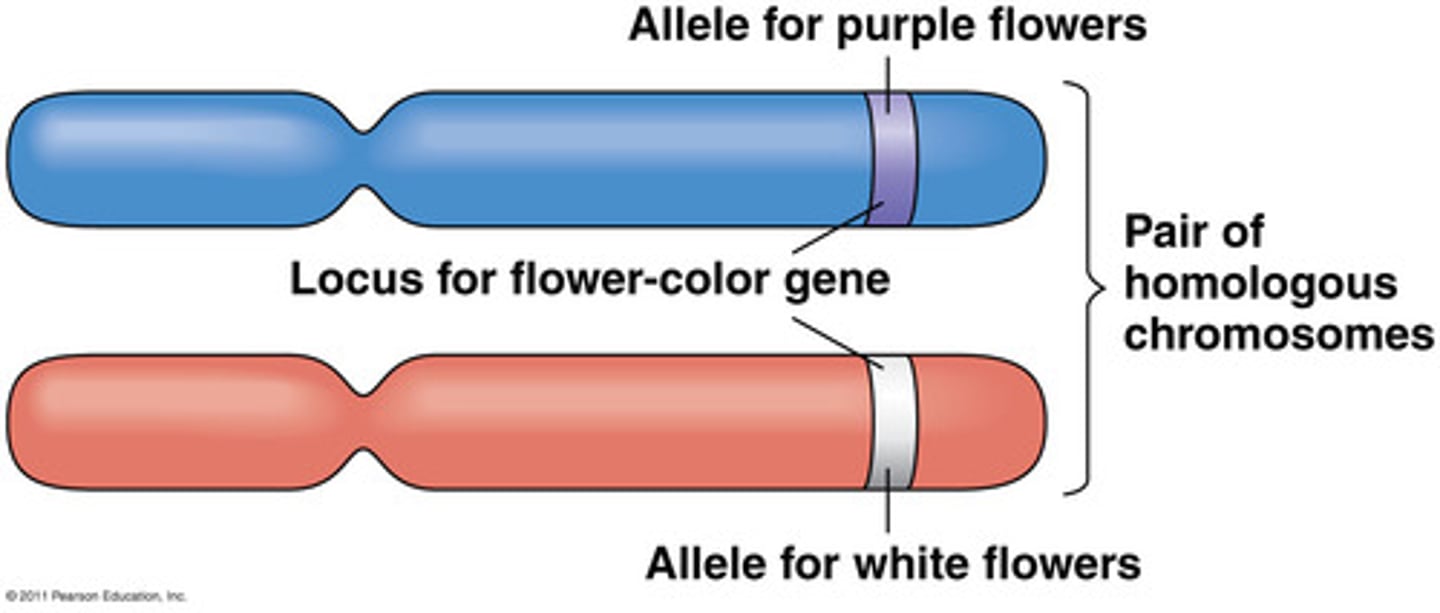
Genetics - Alleles
Inherited characteristics on the genes (get on from each parent)
Genetics - Dominant Allele
Determines the organisms appearance
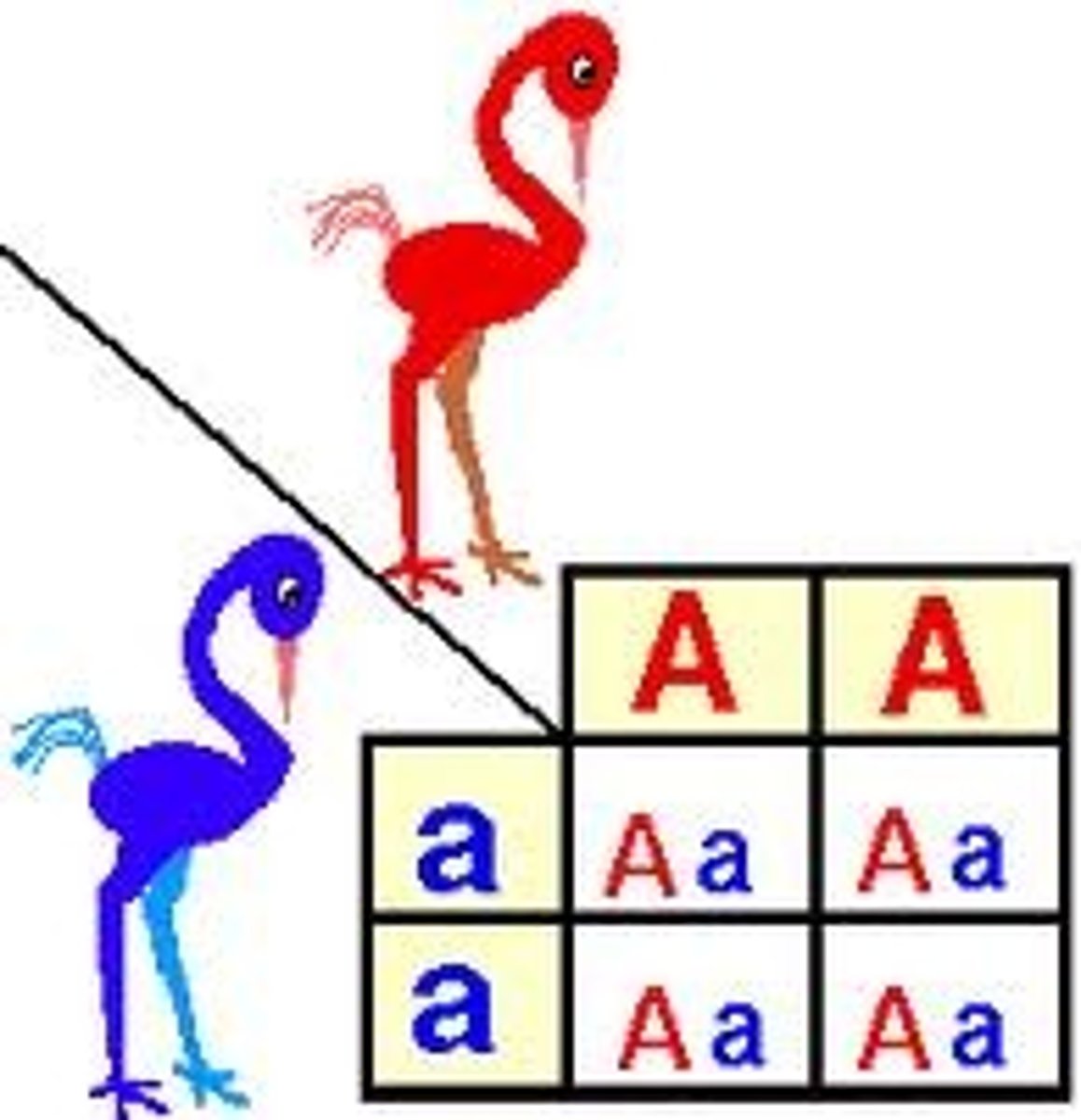
Genetics - Recessive Allele
Has no noticeable effect on the organisms appearance
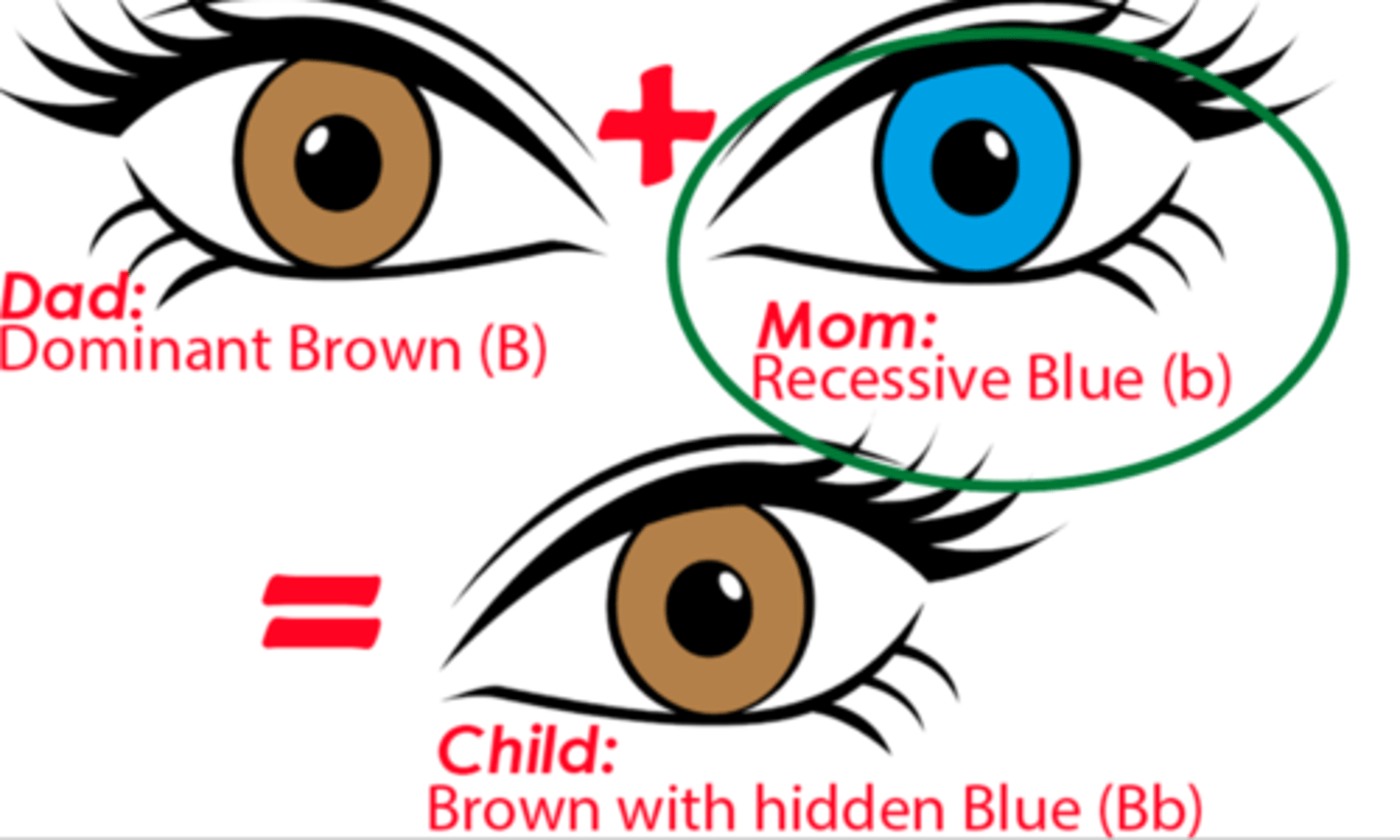
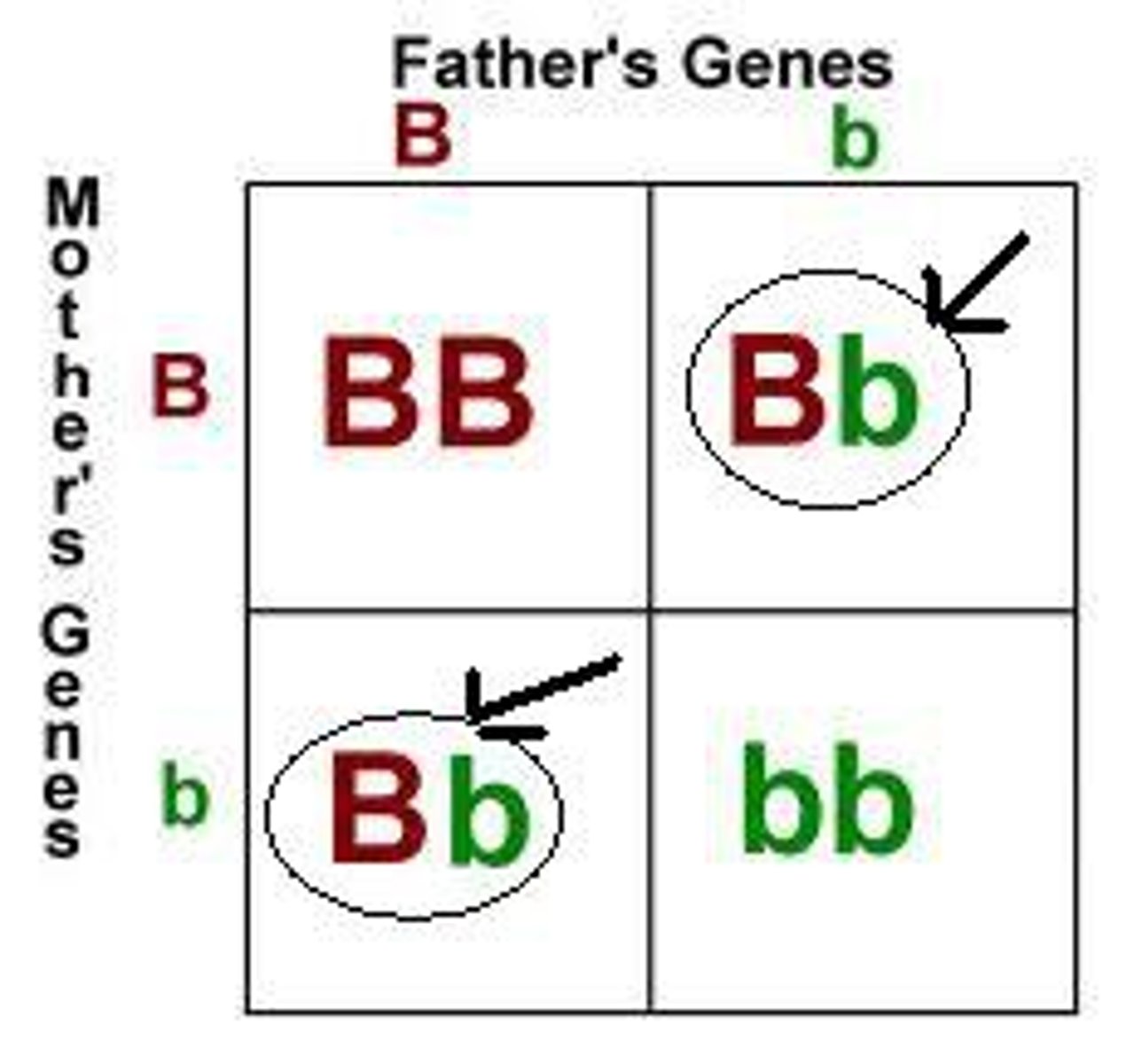
Genetics - Homozygous
Has a pair of identical alleles for that gene. Either dominant or recessive.

Genetics - Heterozygous
Has a pair of alleles that are different for that gene
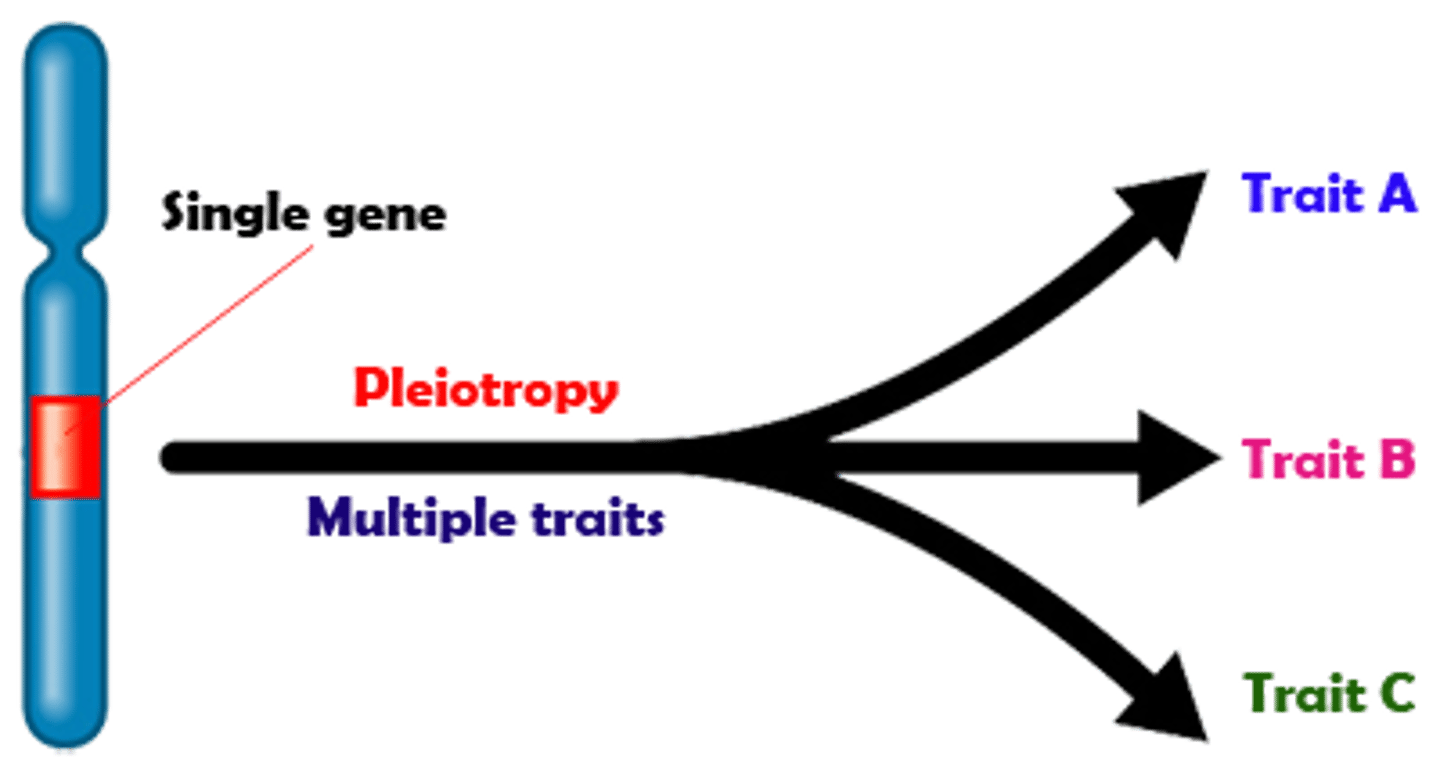
Genetics - Pleiotropy
One gene, many effects
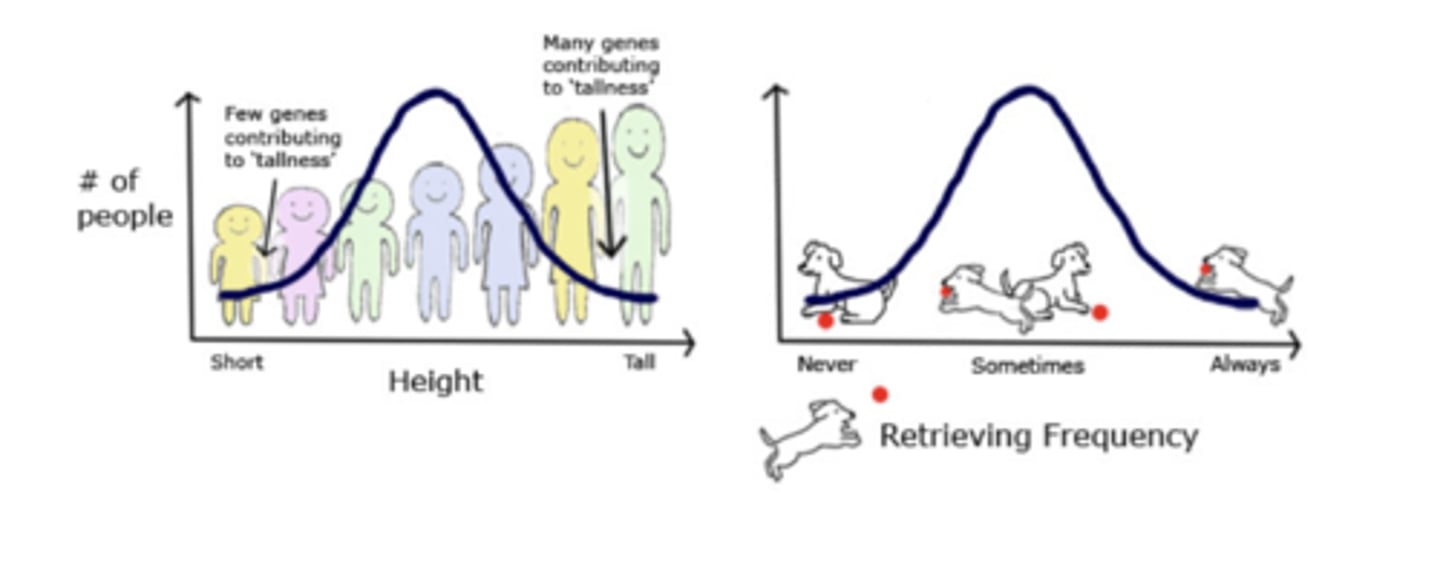
Genetics - Polygeny
Many genes affecting one trait
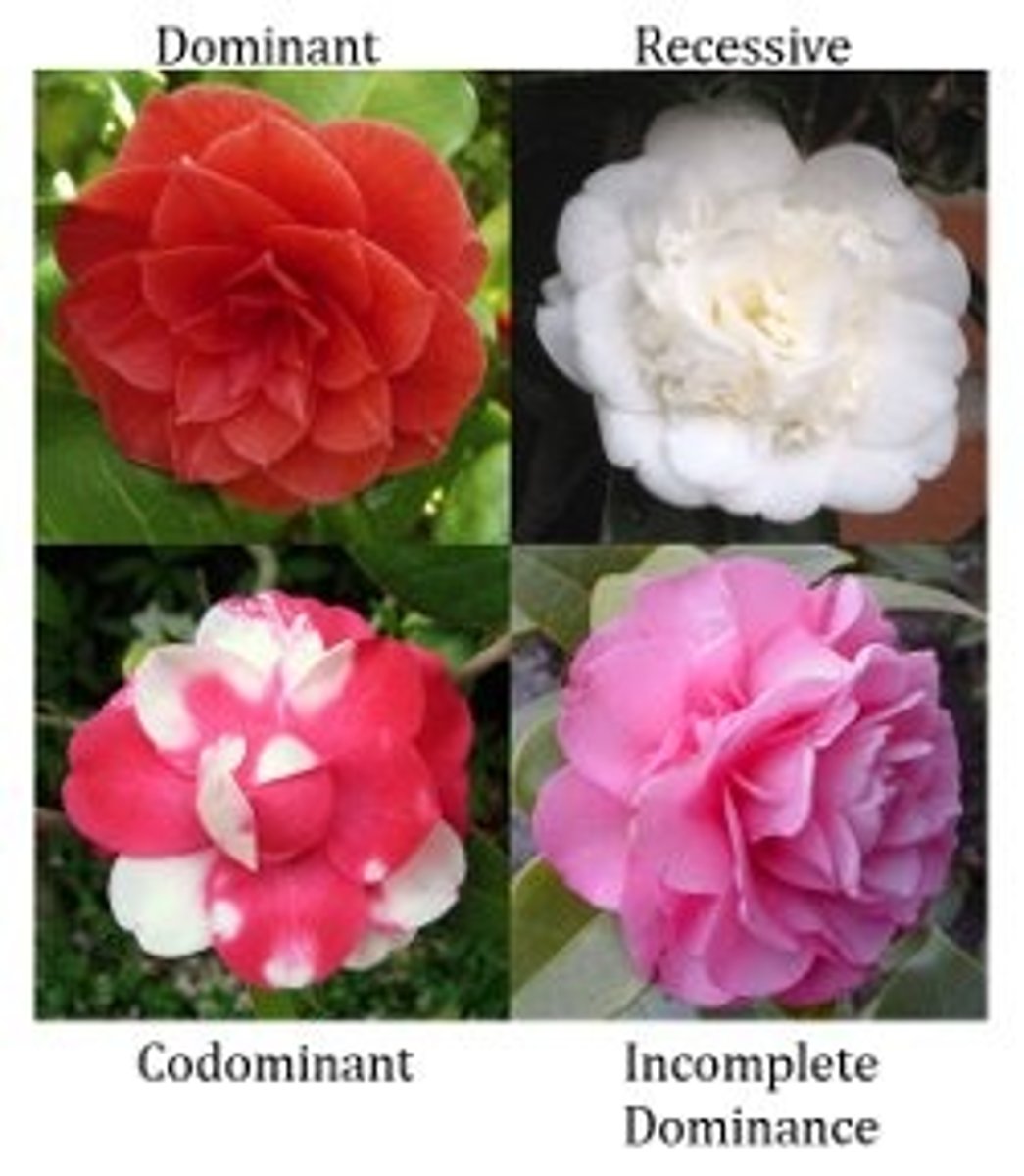
Genetics - Co-dominance
More than one dominant gene can be displayed
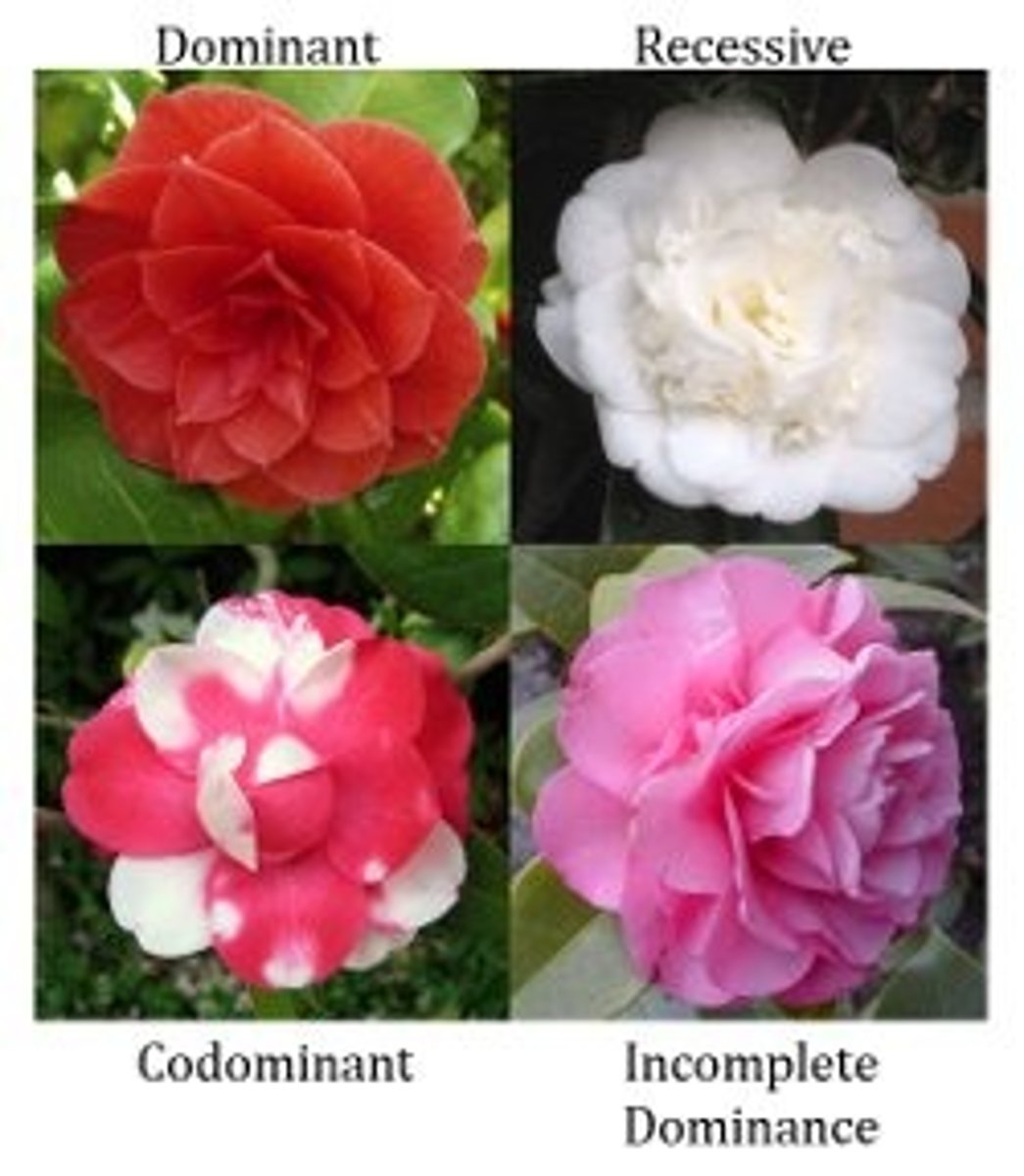

Genetics - Incomplete Dominance
Intermediate trait is seen with heterozygous genotypes

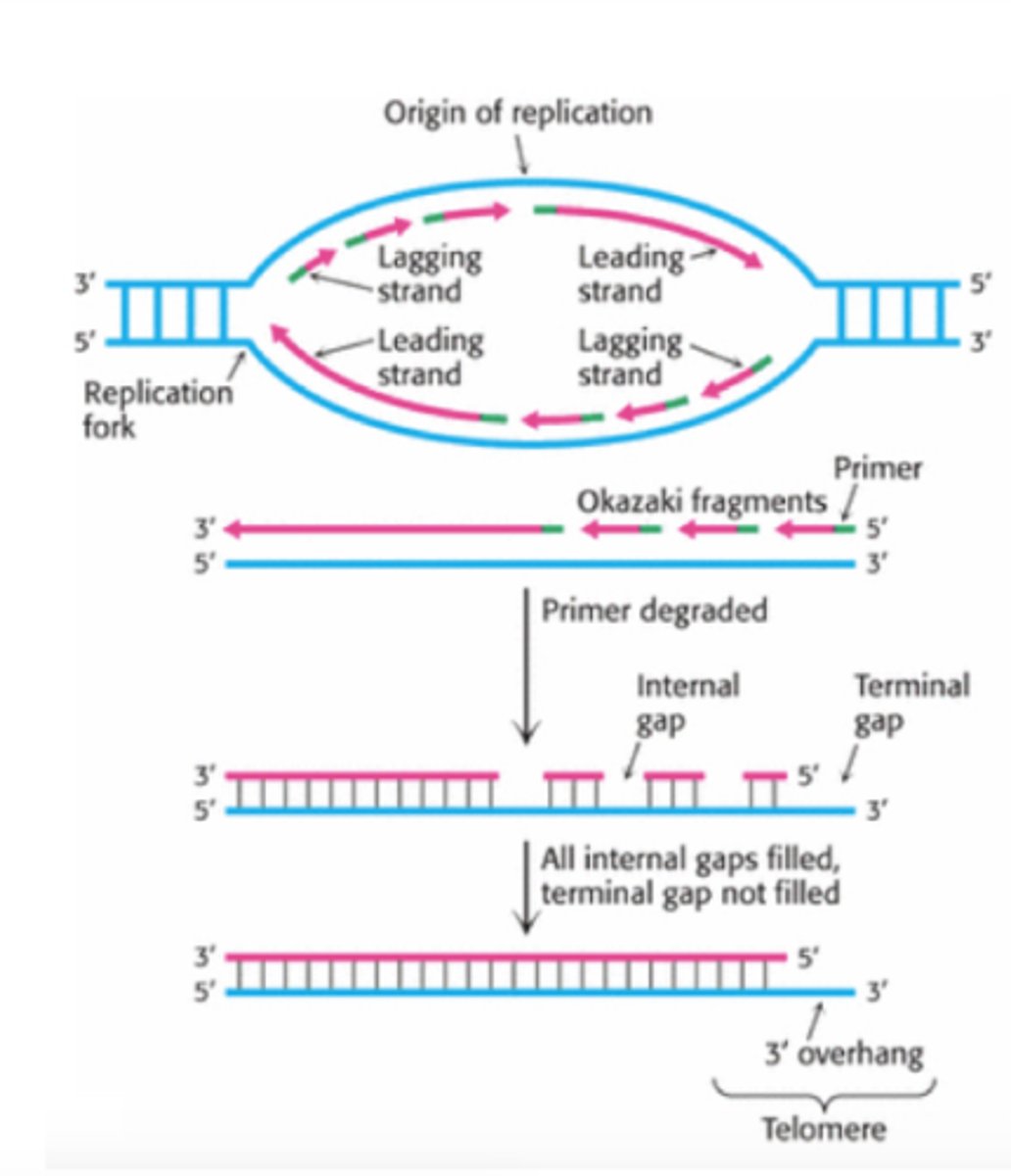
What is DNA Replication?
Each strand acts as a template for building a new strand. Parent unwinds - two daughter built. Semi-conservative: each daughter has 1 parent cell. Begins at sites of origins.

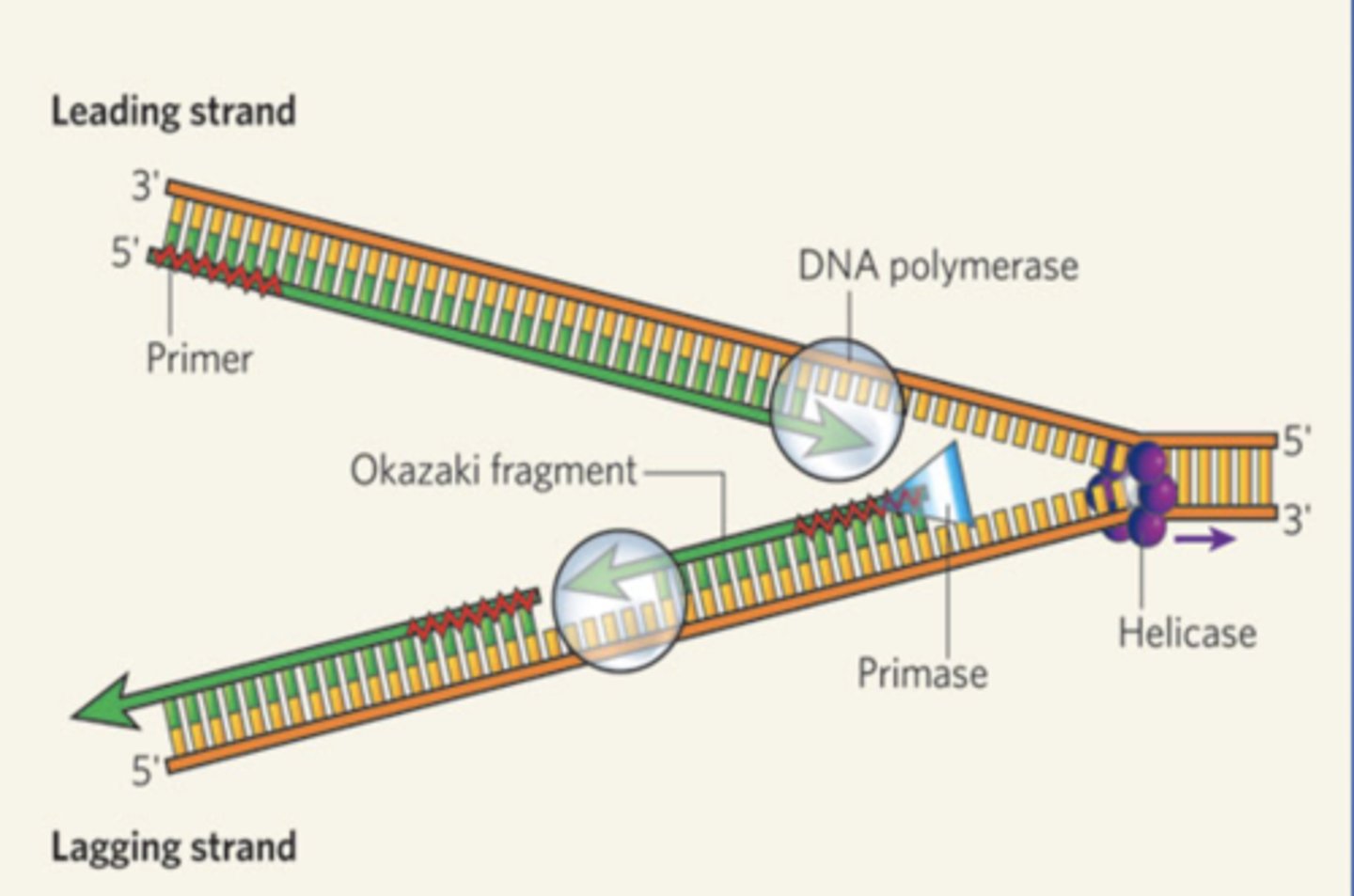
DNA Replication - Helicase
UNWINDS THE HELIX. Binding proteins stabilize template strands. Topoisomerase stabilizes the "over-twist" ahead of helices.
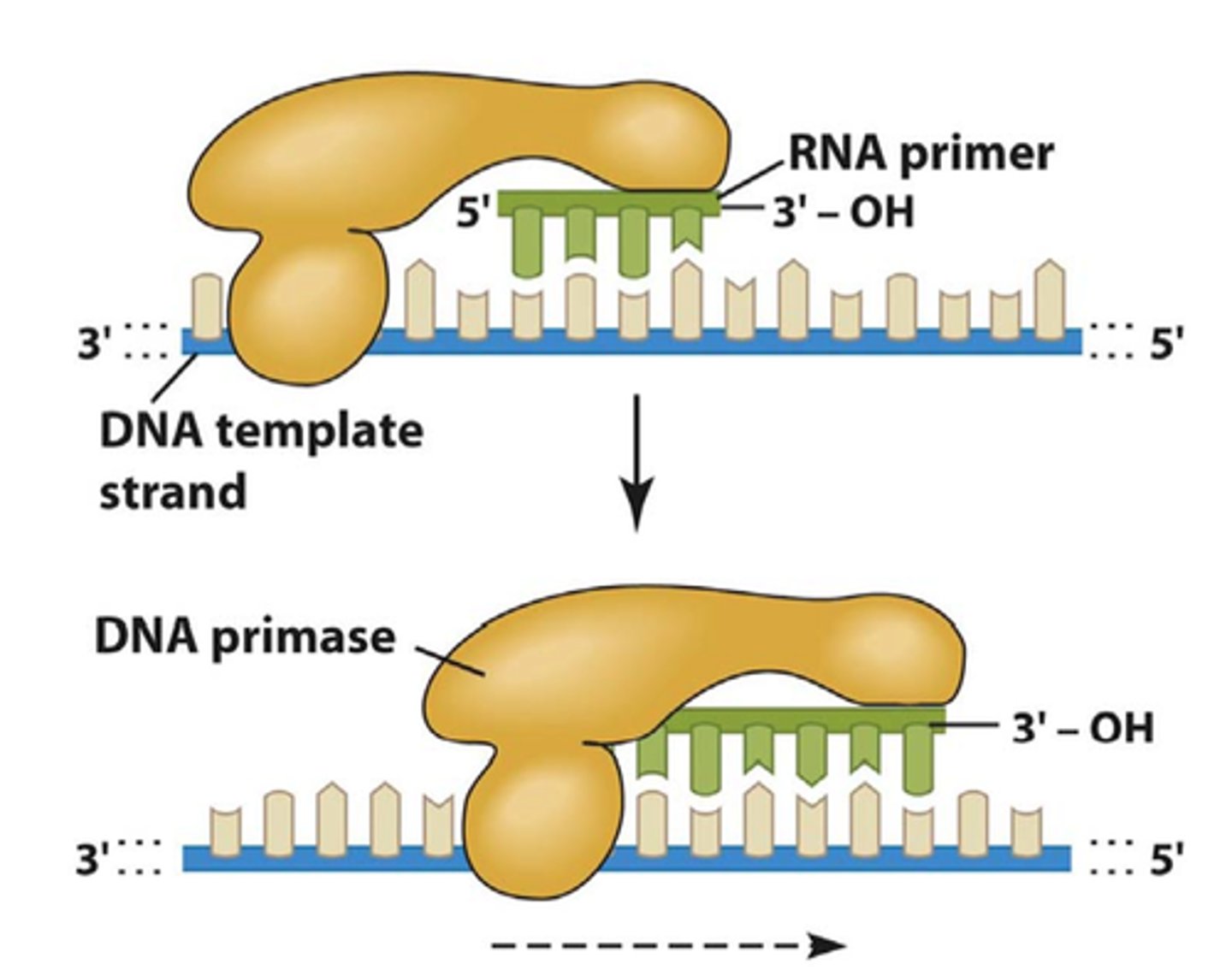
DNA Replication - Primase
"Primes" strands with RNA
DNA Replication - Polymerase 3
Elongates strand - adds nucleotides to 3' end only. Reads parent strand from 3' to 5'. Builds daughter from 5' to 3'.
DNA Replication - Polymerase 1
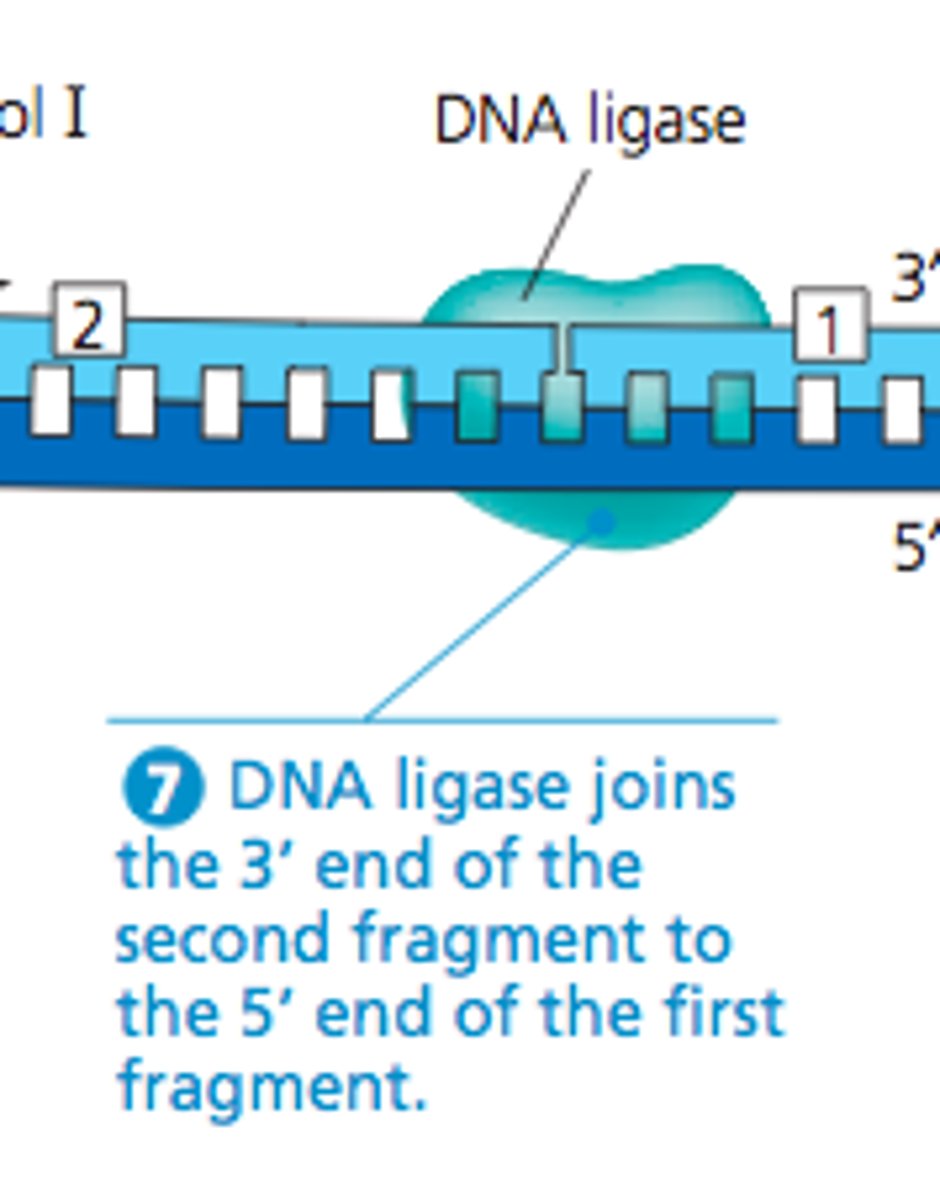
Replaces primer RNA
DNA Replication - Ligase
"Glues" back together
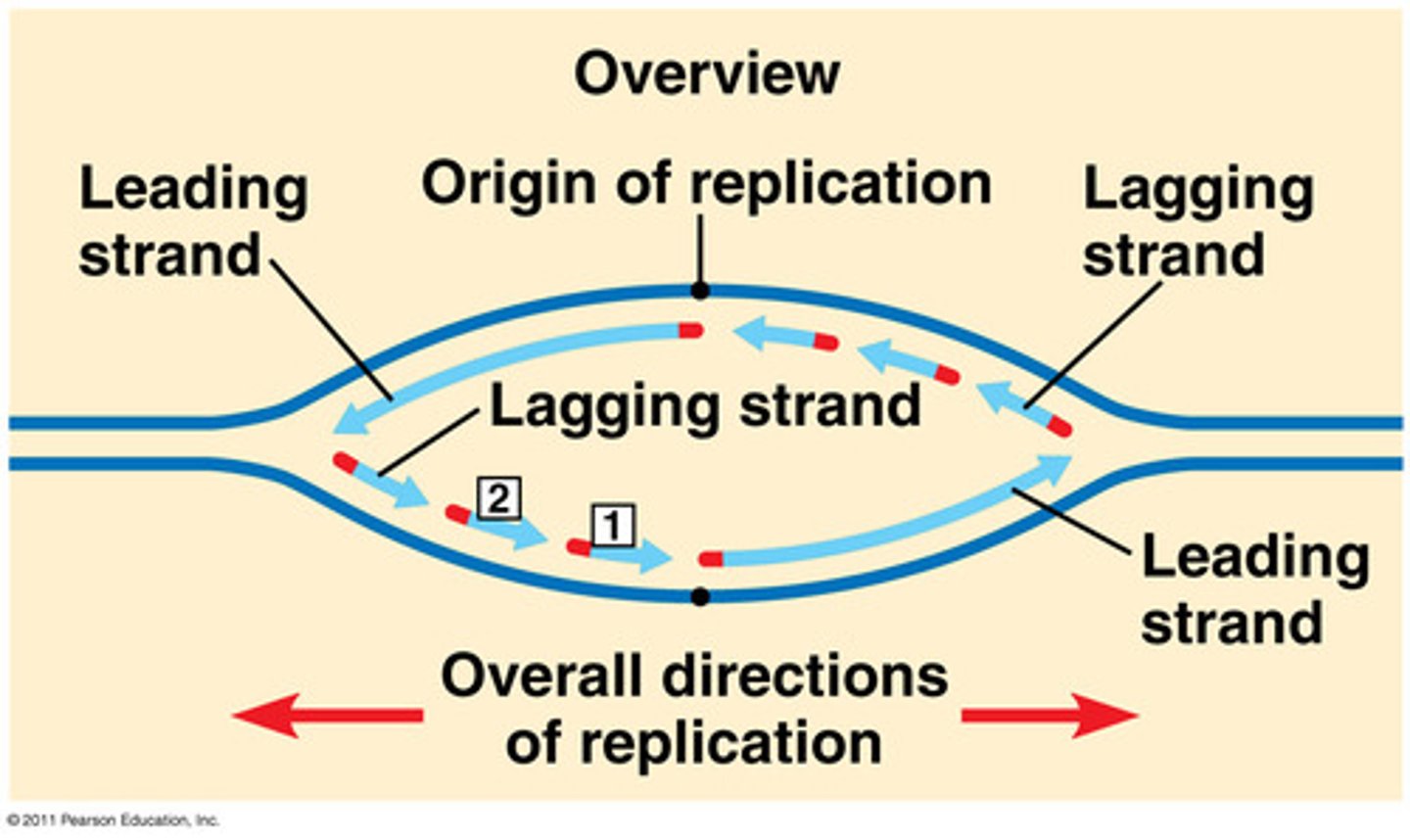
DNA Replication - Leading Strand
Synthesize a complimentary strand continuously - moving towards replication fork. Primase adds RNA primer once --> DNA Poly 3 builds continuously towards fork --> Poly 1 replaces primes --> Ligase binds it to other segment (initial section)
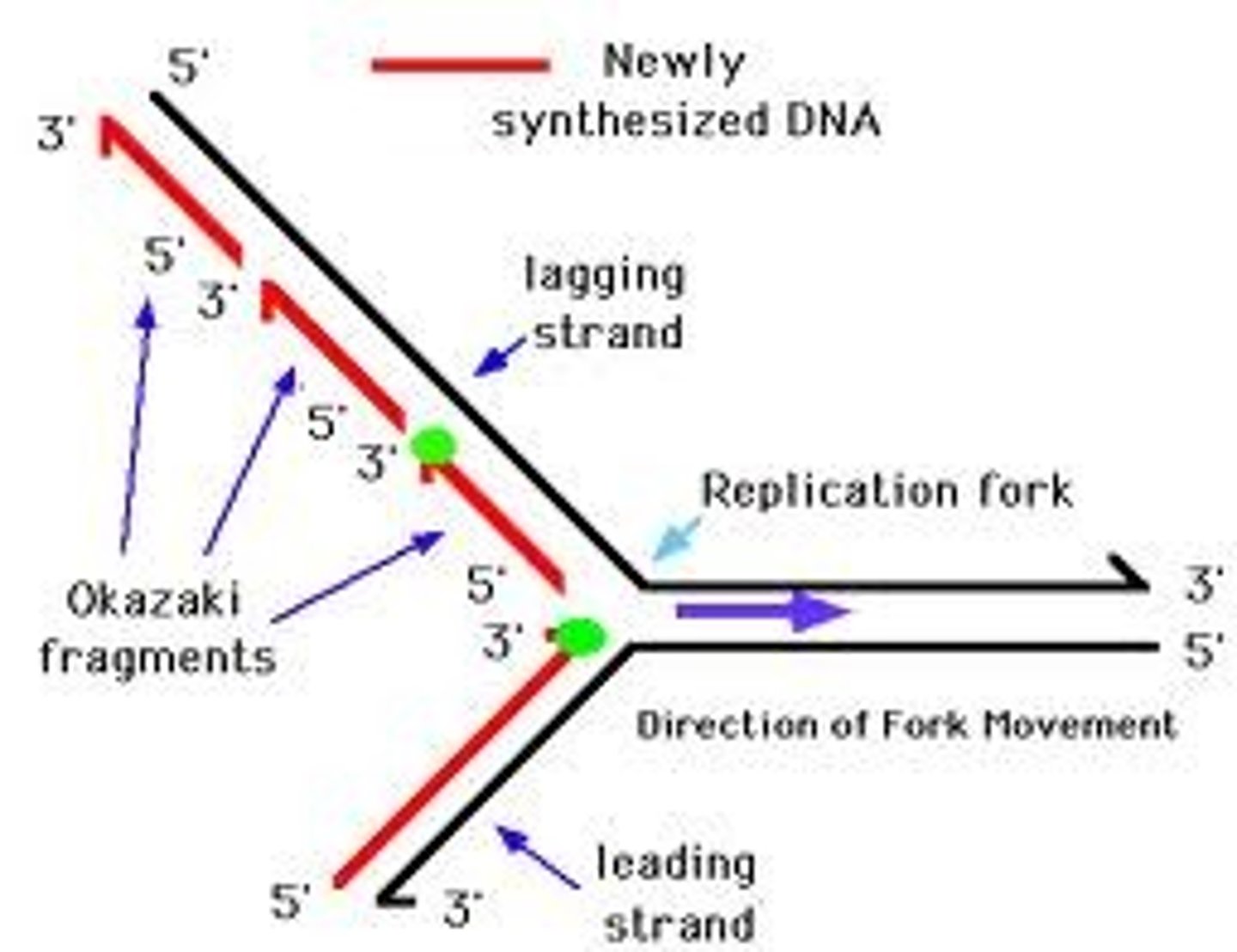
DNA Replication - Lagging Strand
Synthesize as a series of Okazaki fragments (segments) - joined together by ligase. Moves away from fork. Primase adds short primer sequence --> DNA Poly 3 adds nucleotides to 3' end until it reaches next primer - Okazaki fragment --> DNA Poly 1 replaces primer nucleotides with DNA --> Ligase bonds segments together.
Fuel - Glucose
1 glucose yields 38 ATP. Oxygen required for full aerobic process - anaerobic (glycolysis - only yields 2 ATP). Uses about 40% of energy (turned into ATP) stored in glucose - rest is lost as heat. FIRST CHOICE FOR FUELS - QUICK TO BREAK DOWN.
Fuel - Proteins
Amino acids converted to ketoacids (malate, future, citrate). Lowest overall ATP yield. LAST RESORT FOR ENERGY (ex) starvation, high protein intake)
Fuel- Fat
Uses beta oxidation (slow as start - not used initially) to form Acetyl CoA - then enters TSA cycle. High energy yield (ATP). Most efficient storage of energy.
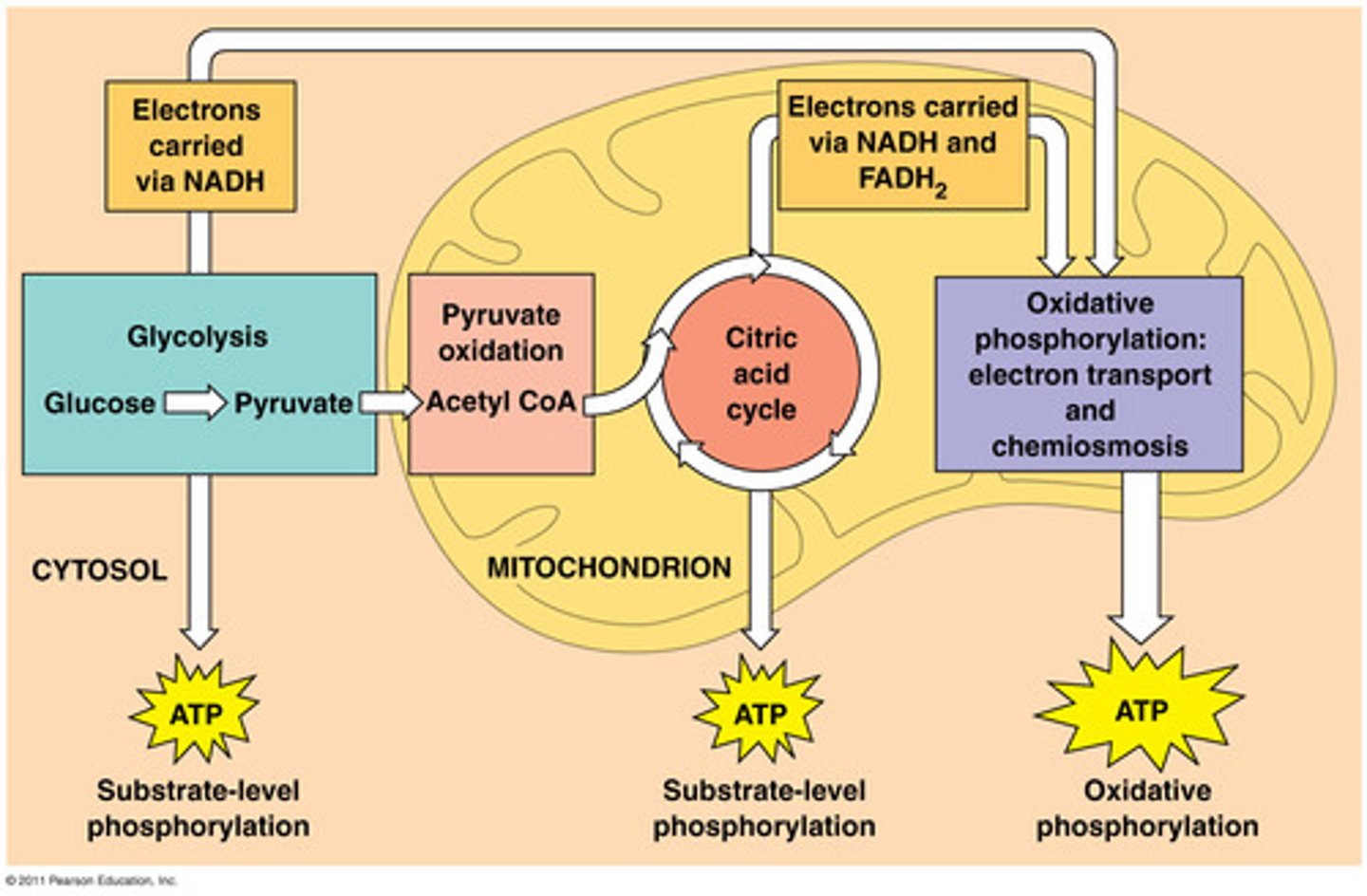
Cellular Respiration
Breakdown of glucose or other fuels in the presence of oxygen to yield ATP
FOUR STAGES:
1) Glycolysis: breakdown of sugar
2) Preparatory Step: gets it into mitochondria
3) Citric Acid Cycle: blow apart rest of molecule
4) Electron Transport Chain: ETC ETS
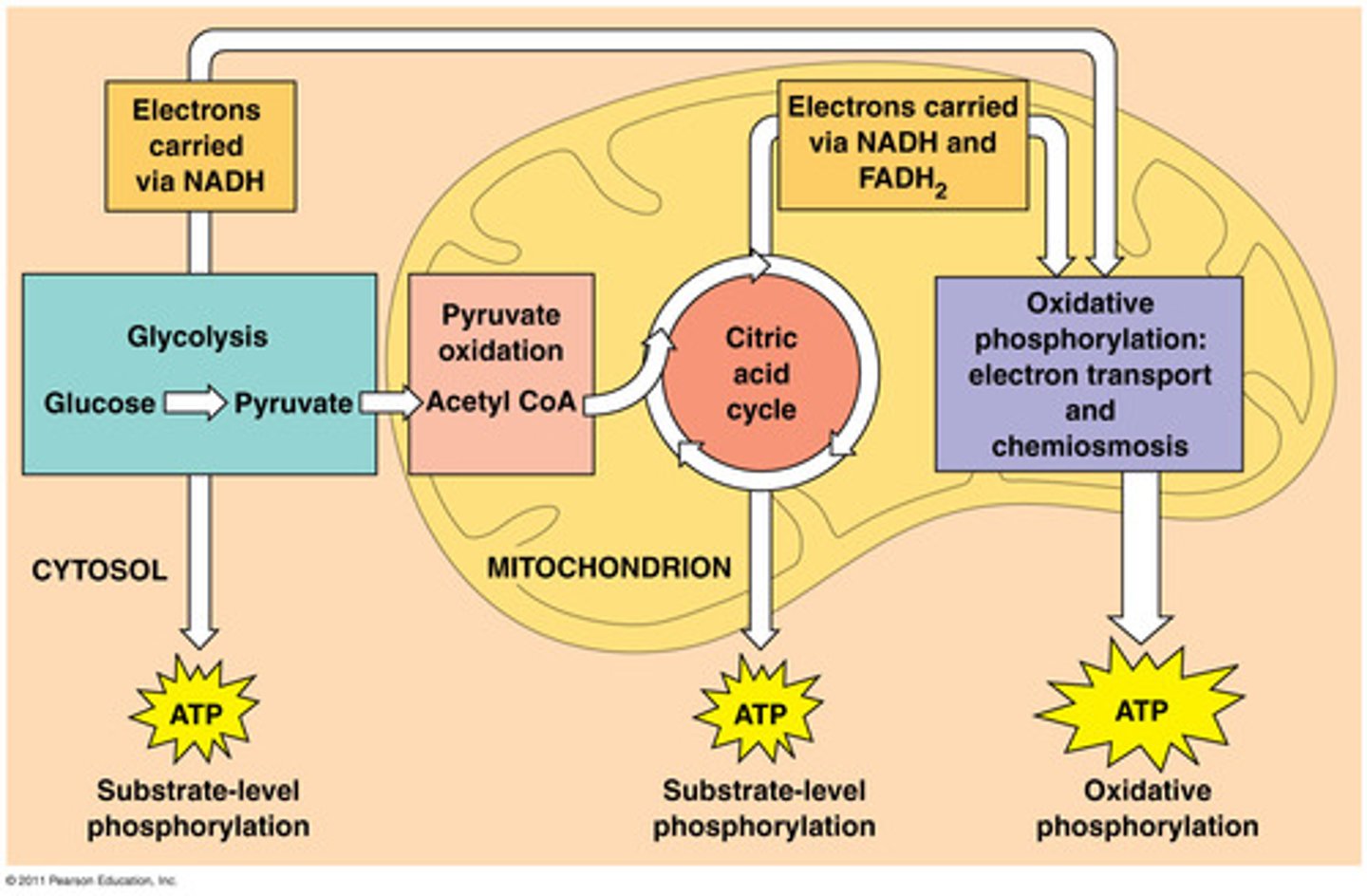
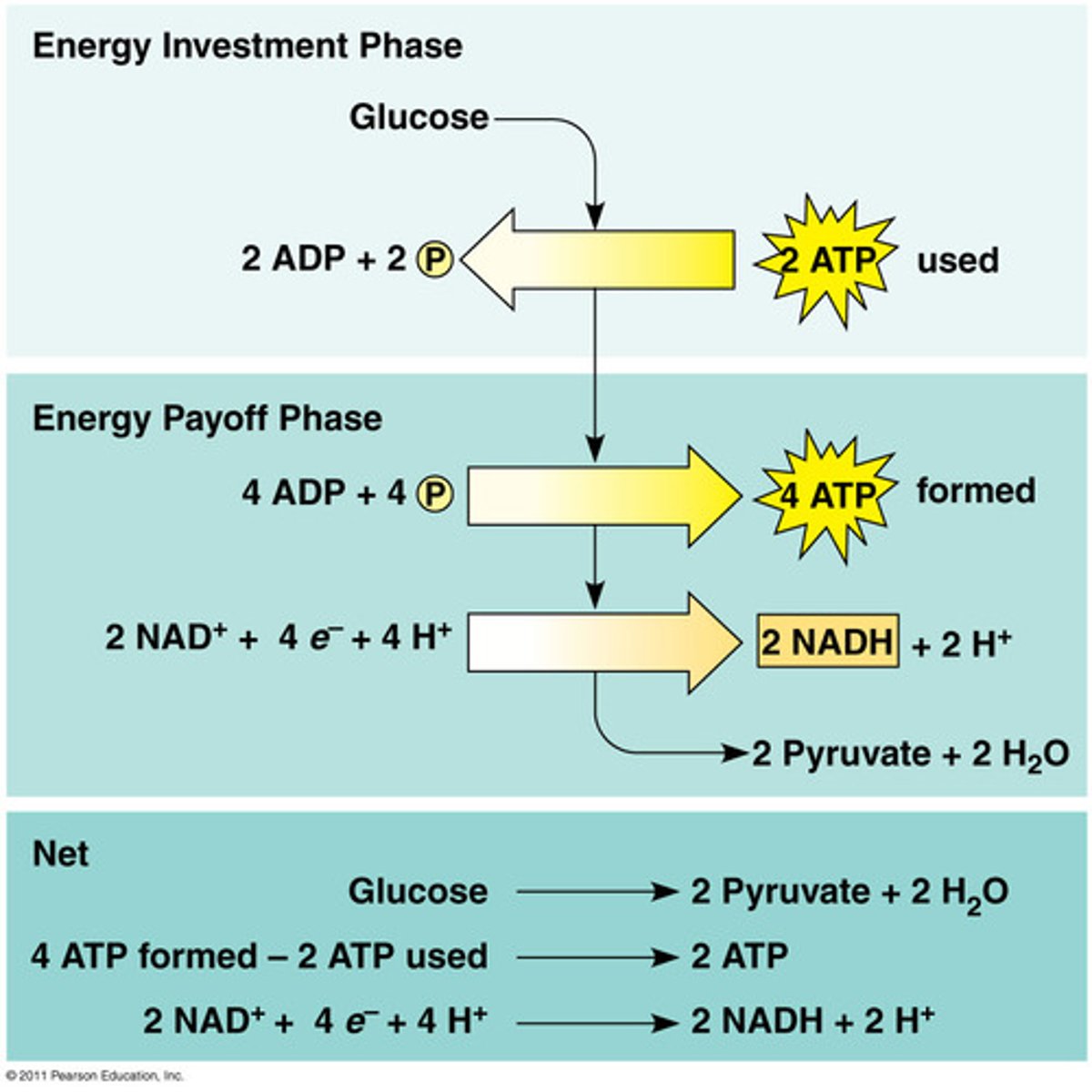
Cell Resp. - Glycolysis
2 ATP in - 1 glucose in. 4 ATP out (but we only GAIN 2). 2 NADH out. 2 pyruvate. Net is 2-2-2. Anaerobic.
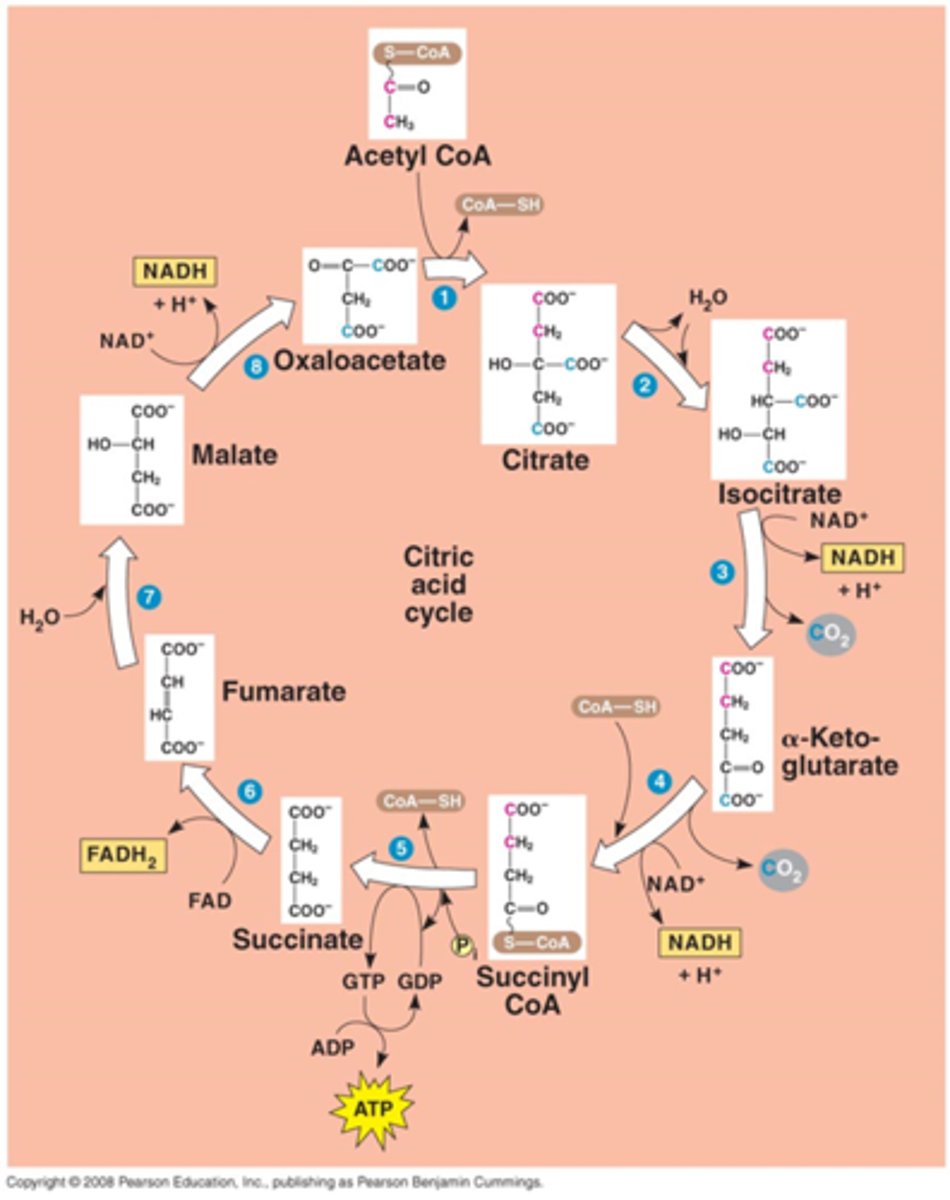
Cell Resp. - Citic Acid Cycle
Loss of CO2. Irreversible. Pyruvate becomes Acetyl CoA.
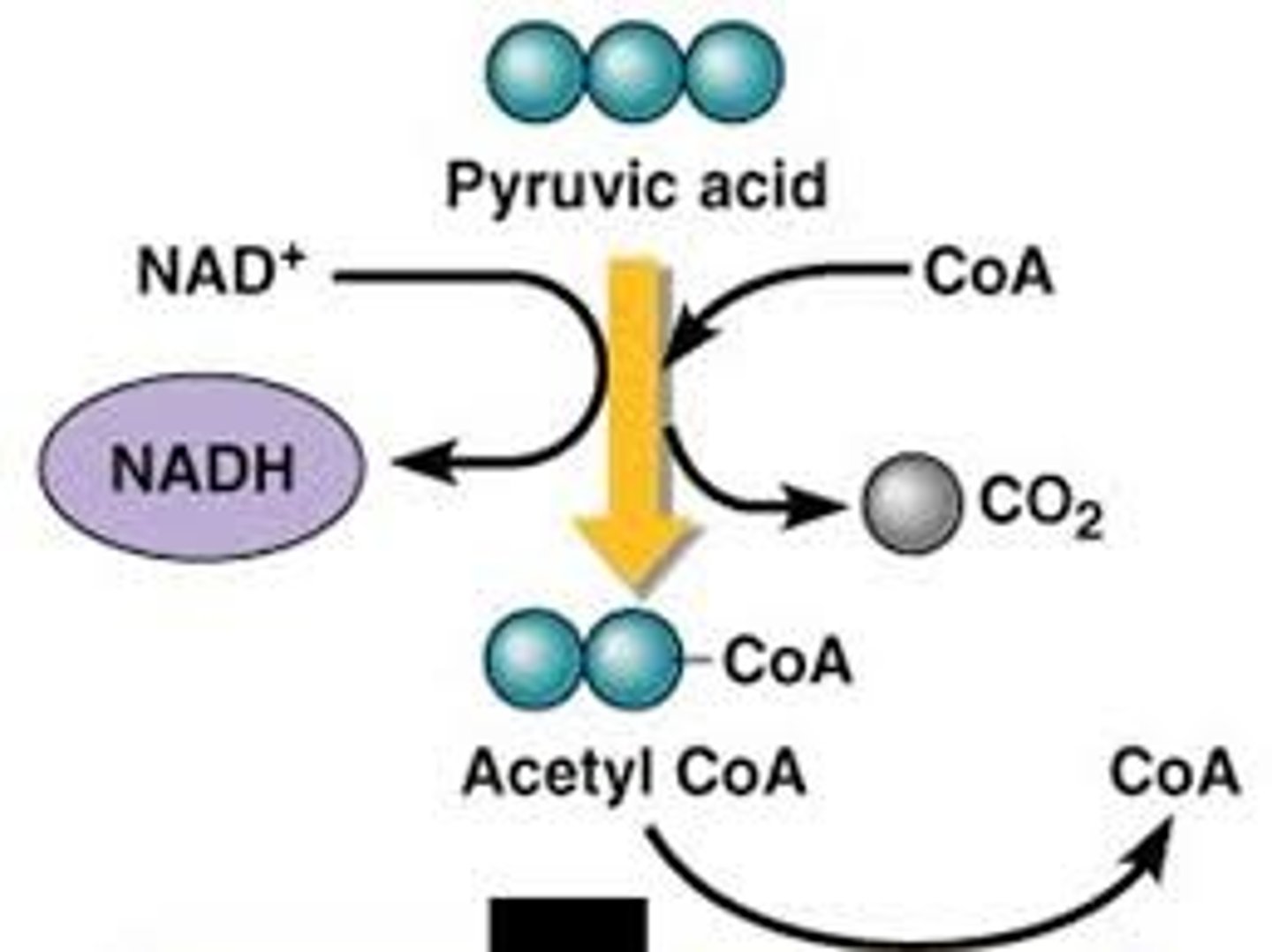
Cell Resp. - Preparatory Step
1 Acetyl CoA in - 3 NADH out, 1 ATP out, 1 FADH out: 2 cycles. 6-2-2.
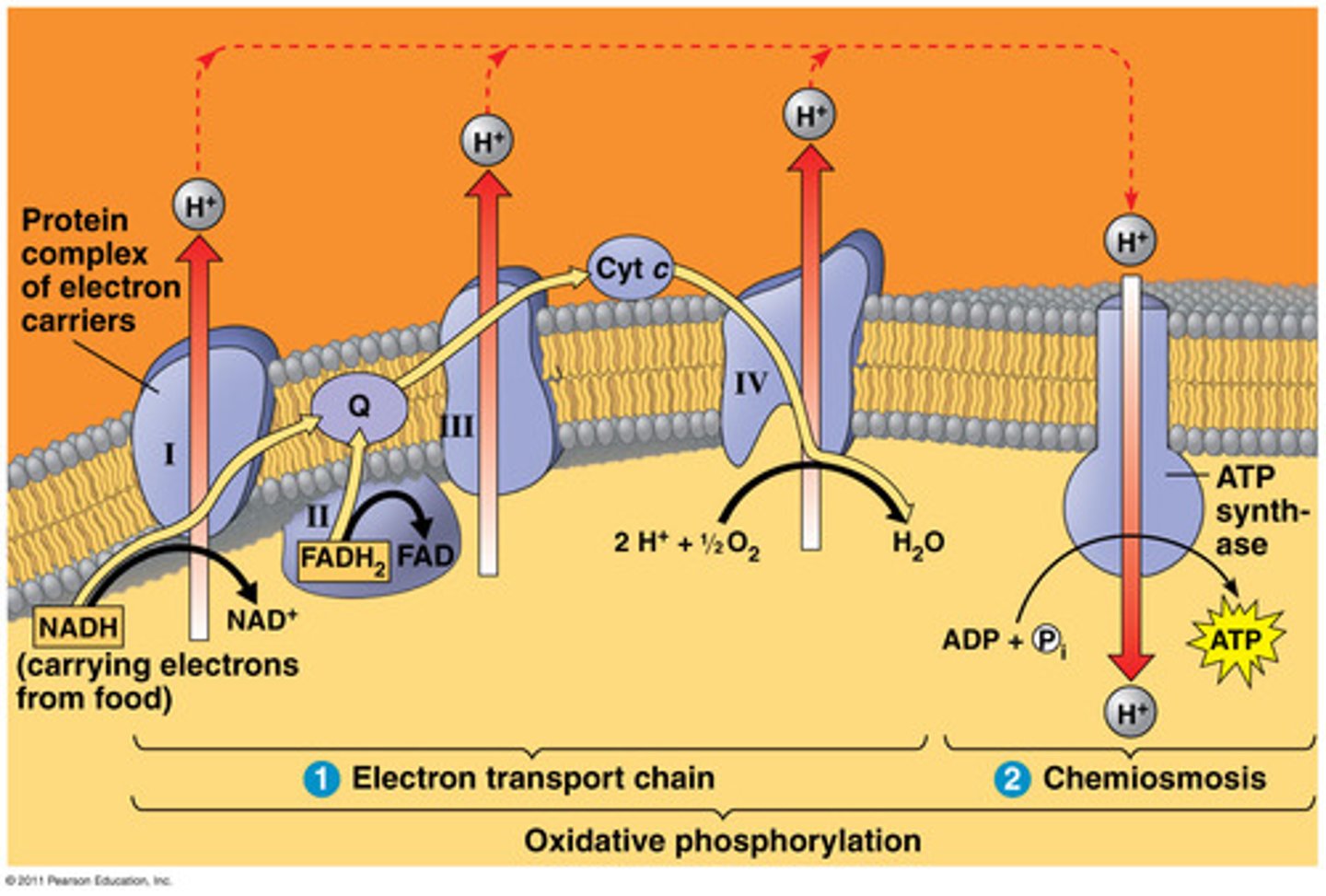
Cell Resp. - ETC
8 NADH in, 2 FADH in. Forms ATP - 32-34 ATP.
Process of Proteins
transporters/carriers
channel/pores
antibodies
storage/structure
hormones/receptors
contractile proteins
enzymes
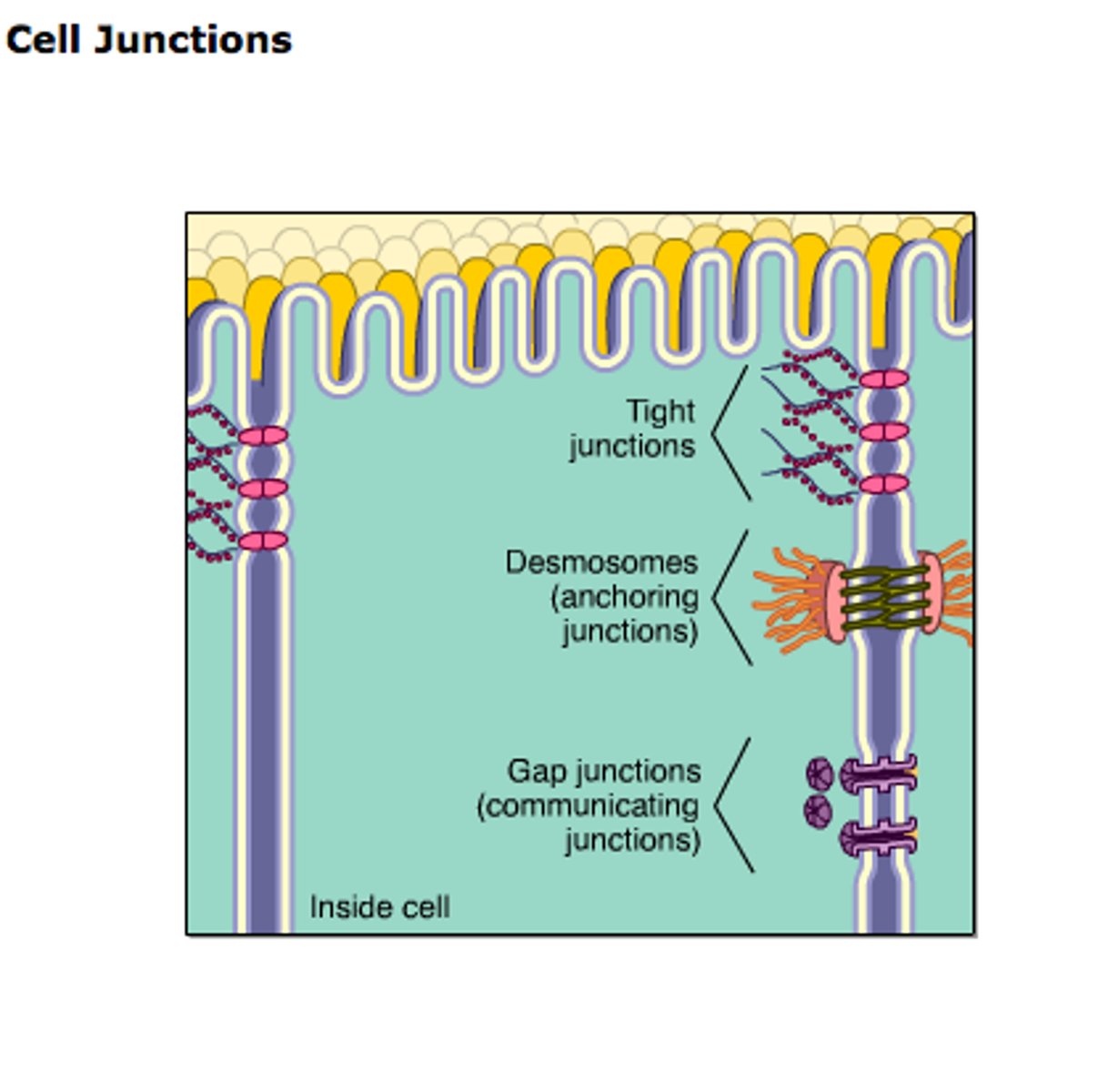
Types of Cell Junctions
Gap Junctions
Tight Junctions
Desmosomes - Adhering Junctions
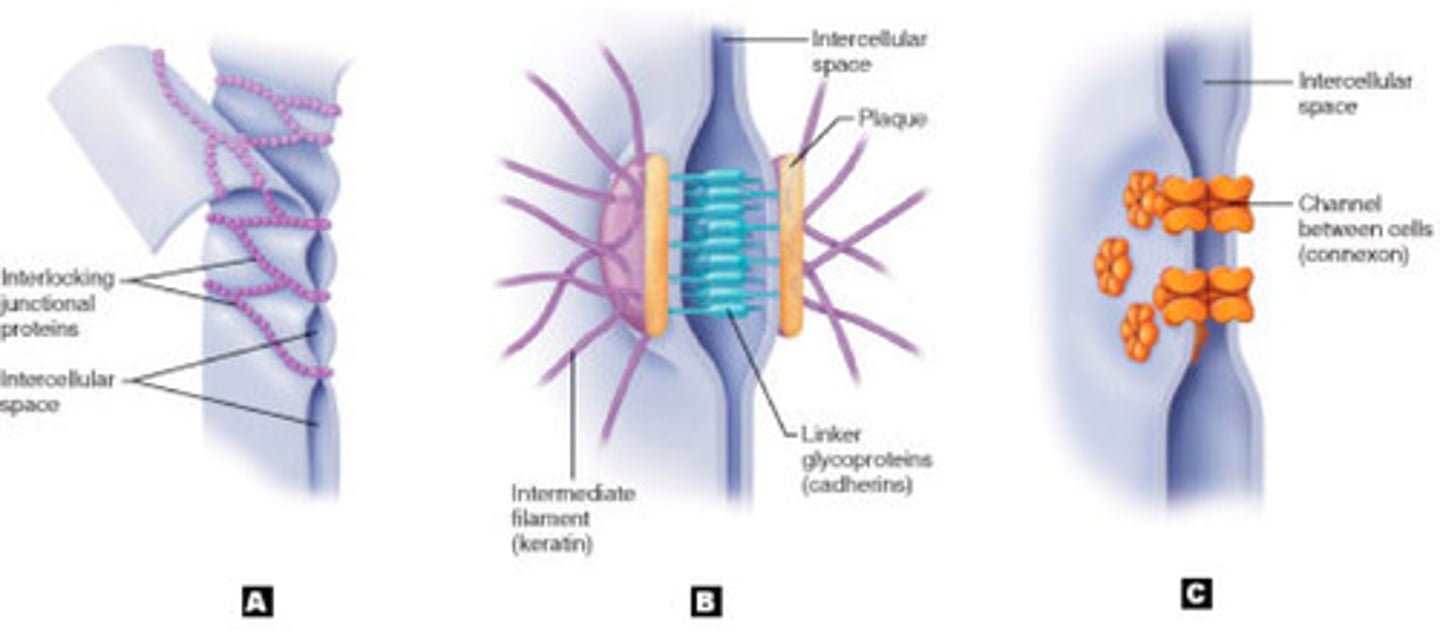
Cell Junctions - Gap Junctions
Allows movement of ions - transmission of charge (electrical impulse) --> small holes (pores)
ex) heart, gut
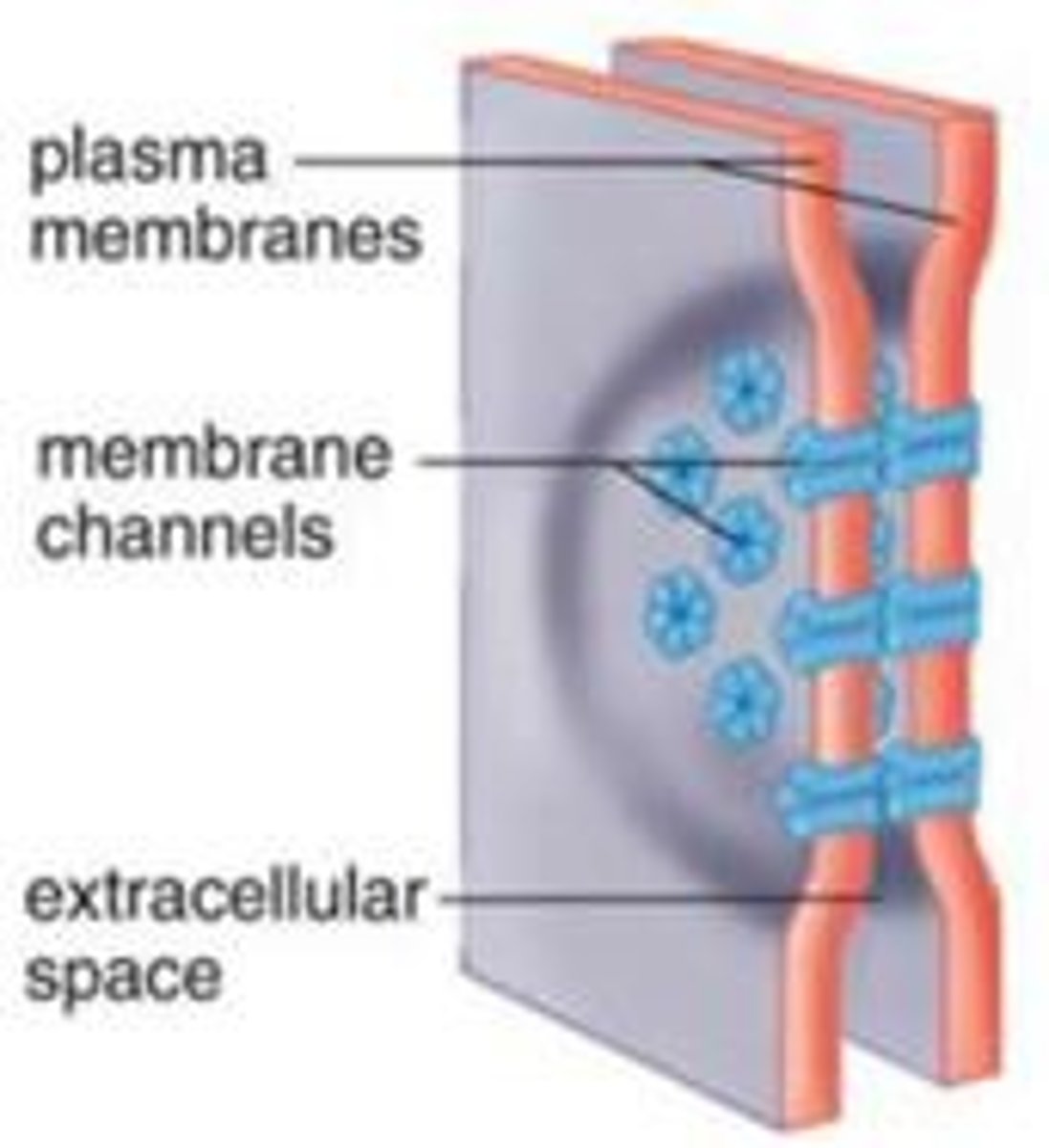
Cell Junctions - Tight Junctions
Allows NO movement between cells - we don't wanna absorb just anything
ex) intestine, blood-brain barrier
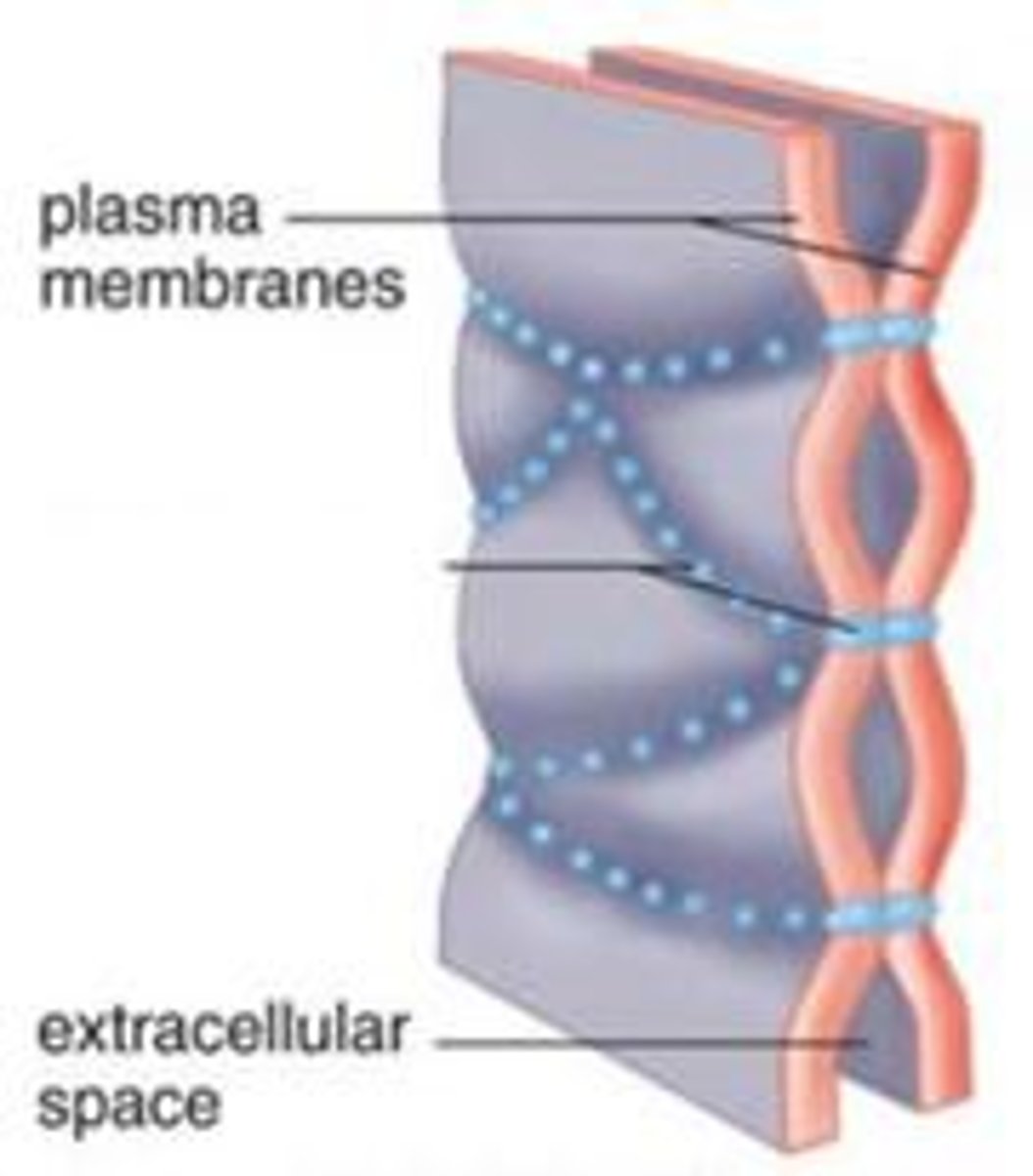
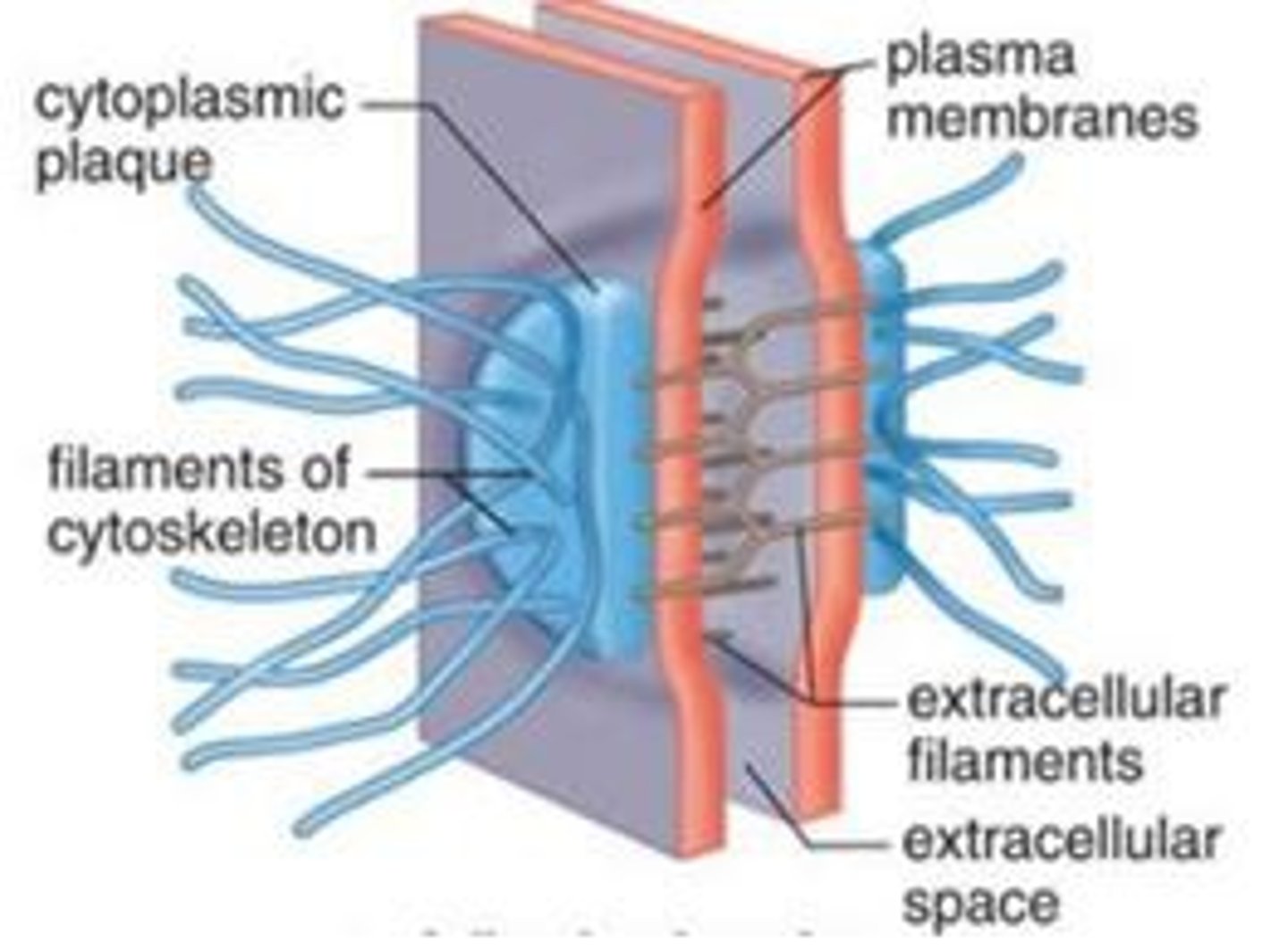
Cell Junctions - Desmosomes
Structural Junction. Withstands stress (growing) - really hard to pull apart.
ex) skin, uterus
What are Tissues?
Cells with similar structure and function
4 TYPES:
1) Epithelial
2) Connective Tissue
3) Nerve
4) Muscle
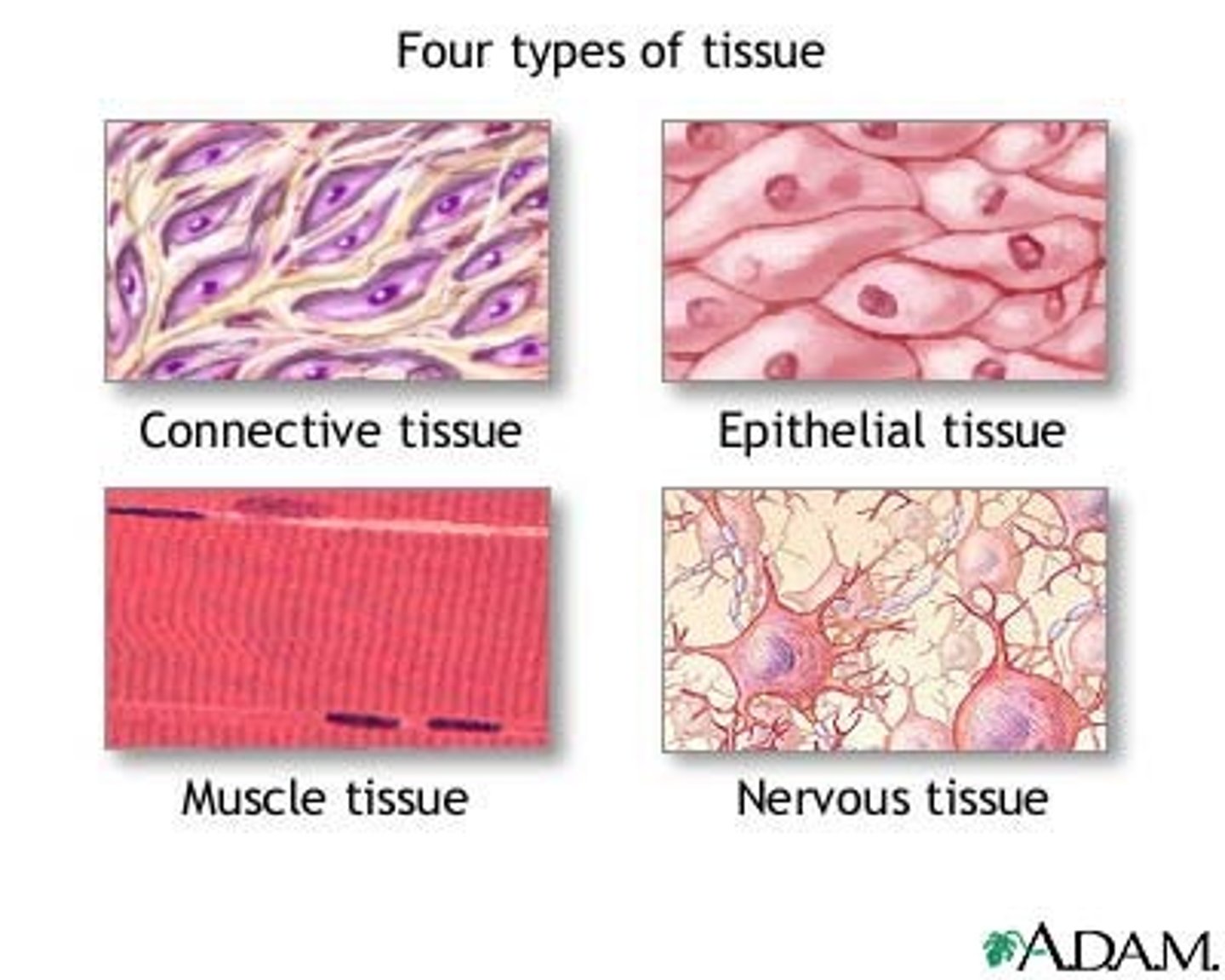
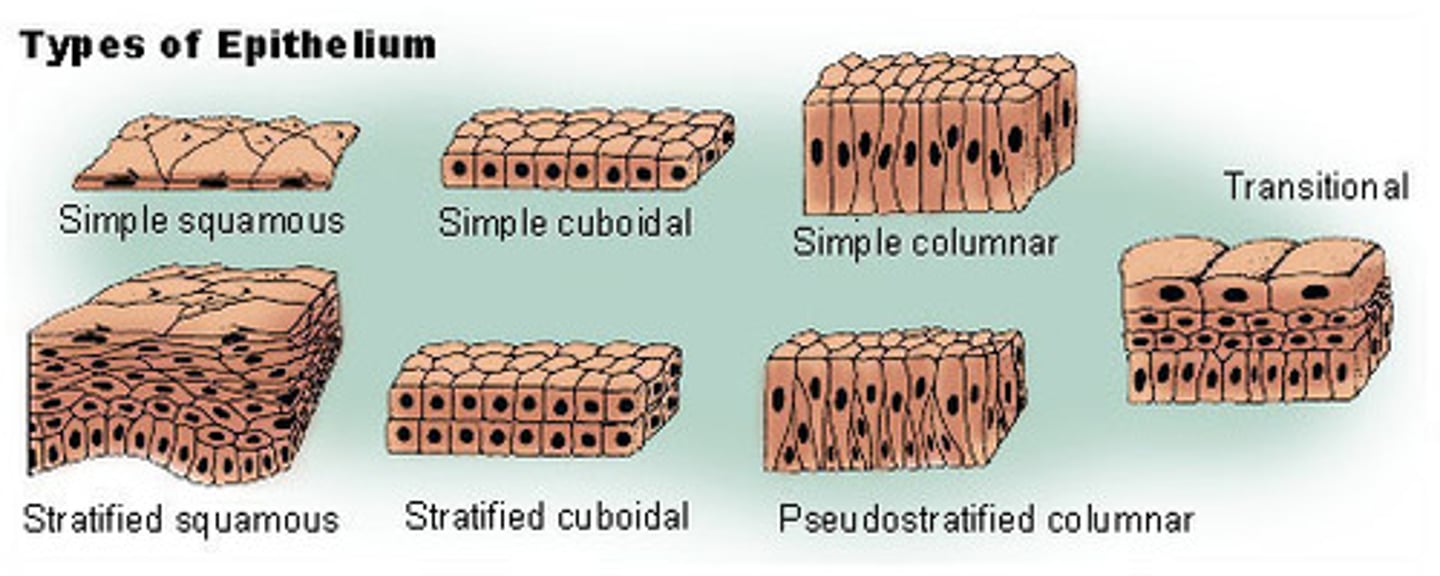
Epithelial Tissue
Covering sheets - covers every single surface everywhere. ex) epithelial lining, skin
GLANDS - exocrine, endocrine. TYPES: SIMPLE, AND STRATIFIED. - Cuboidal, columnar cells, and Squamous cells