Silverstein and Hopper Chapter 187: Viscoelastic Monitoring
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What do viscoelastic tests measure?
Kinetics of clot formation (time needed for the clot to form)
Mechanical properties of the clot (tensile strength)
Time to dissolution of the clot (fibrinolysis)
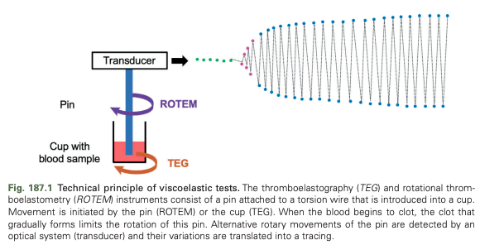
How do TEG and ROTEM instruments work?
Consist of a pin attached to a torsion wire that is introduced into a cup
The blood sample is incubated with an activator and a specific temperature in a cup above which is an axis connected to an optical detection system
Movement causes low shear conditions
As long as the blood remains in a liquid state, the pin rotates freely
Fibrin strands that are forming gradually limit the rotation of this pin
The firmer the clot (increase in its viscoelastic properties), the more the resistance increases, and the more the pin's rotation is hampered
Alternative rotary movement of the pin are detected by an optical system and their variations are translated into a tracing in which the amplitude of the wire oscillation is on the y-axis and the time is on the x-axis
Amplitude is directly converted to physical units that represent the strength of the formed clot
Angle of Rotation in ROTEM
4.75 degrees
Angle of Rotation in TEG
4.45 degrees
What initiates the rotary movement in ROTEM?
The pin
What initiates the rotary movement in TEG?
The cup
PROVETS Recommendations
Results from various analyzers are not directly comparable and extrapolation of the results from one machine to the other should be avoided
Recommended that each site create their own site specific reference values for each machine
Jugular venipuncture recommended but samples from IVCs can be used if there is easy withdrawal of blood
Evacuated blood tubes and 21 gauge needles or larger suggested
Collect blood samples in a tube with 3.2% buffered sodium citrate in a strict 1:9 ratio of citrate to blood and then held at room temperature for 30 minutes prior to analysis
For clinical practice, conduct tests long enough to obtain all relevant values
For research, conduct all tests long enough to obtain the values of the fibrinolysis parameters
All four standard TEG and ROTEM variables should be universally reported and the reporting of shear elastic modulus (G) is encouraged
Contemporary values for hematocrit, fibrinogen concentration, and platelet count should be reported in addition to the TEG/ROTEM results
What is the diagram produced by ROTEM called?
Thromboelastomer
What is the diagram produced by TEG called?
Thromboelastogram
Draw the TEG/ROTEM Diagram
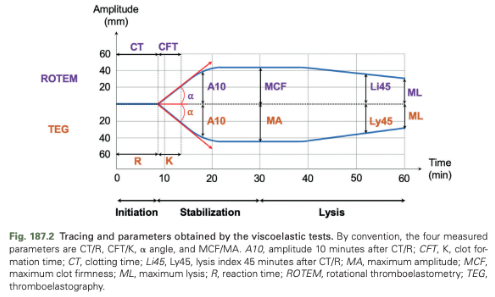
Initiation Phase of TEG/ROTEM
Corresponds to the time between the beginning of the analysis and the formation of the first strands of fibrin; the end of this phase is characterized by the divergence of the plot into two curves
Stabilization Phase of TEG/ROTEM
Corresponds to the time between the end of initiation and the maximum separation of the two curves; represents the formation of the clot
Lysis Phase of TEG/ROTEM
Corresponds to the progressive convergence time of the two curves until the end of the test or the complete convergence of the two curves; describes fibrinolysis
Time from Activation of the Test to a Clot Firmness of 2 mm
CT (coagulation time) - ROTEM
R (reaction time) - TEG
What does CT/R correspond with in ROTEM/TEG?
Corresponds to the initiation phase of coagulation until the appearance of the first fibrin filaments and activated platelets
What are the factors that most contribute to CT/R in ROTEM/TEG?
Hematocrit and plasma concentrations of factors, V, VII, IX, and X
Time from End of CT or R until a Clot Firmness of 20 mm point has been reached
CFT (clot formation time) - ROTEM
K - TEG
What does CFT/K indicate in ROTEM/TEG?
The speed of appearance of fibrin and the connection of fibrin filaments within the clot
Represents the speed of clot formation
What are the most significant contributing factors to CFT/K in ROTEM/TEG?
Hematocrit, platelet count, and plasma fibrinogen and factor V concentrations
Alpha Angle (a Angle)
Expressed in degrees
The angle formed between the baseline and a tangential line to the ROTEM at CT or the TEG at R (2 mm amplitude)
What does the alpha angle describe?
The kinetics of clot formation
What are the factors that contribute most to the alpha angle?
Hematocrit, platelet count, and the plasma concentrations of fibrinogen, factor V, and factor IX
Maximum Amplitude of the Clot
Maximum clot firmness (MCF) - ROTEM
Maximum amplitude (MA) -TEG
What does MCF/MA measure in ROTEM/TEG?
The final strength of the clot and is the expression of its ultimate viscoelastic properties
What is MCF/MA primarily determined by in ROTEM/TEG?
Hematocrit, platelet count, and plasma fibrinogen concentration
What do amplitudes at 5, 10, 15, and 20 minutes (A5, A10, A15, A20) represent?
The firmness of the clot 5, 10, 15, and 20 minutes after the end of CT/R
What are A5, A10, A15, and A20 used to predict?
MCF/MA at an earlier stage
Seldom reported in veterinary medicine
Lysis Indices at 30, 45, and 60 Minutes
Li30, Li45, Li60 - ROTEM
Ly30, Ly45, Ly60 - TEG
Ratio between the value of the amplitude of the clot measure at 30, 45, and 60. minutes after the end of CT/R to that of the MCF/MA
What do the Li30, Li45, Li60/Ly30, Ly45, Ly60 describe?
The progression of fibrinolysis detected during the analysis
Maximum Lysis (ML)
Maximum fibrinolysis detected during the analysis
Defined as the ratio between the lowest amplitude after reaching the MCF/MA and the MCF/MA
Maximum Clot Elasticity (MCE) Formulas
ROTEM: (100 x MCF):(100-MCF)
TEG: (100 x MA): (100-MA)
Shear Elastic Modulus Strength (G) Equations
50 x MCE
ROTEM: (500 x MCF): (100- MCF)
TEG: (5000 x MA): (100-MA)
Thrombodynamic Potential Index (TPI) Equations
ROTEM: MCE:CFT
TEG: MCE:K
Coagulation Index (CI) Equations
TEG: 0.1227 x R + 0.0092 x CFT + 0.1655 X MA - 0.0241 x a - 5.0220
Clot Elasticity (CE) Equation
CE = (100 x A):(100 -A)
A - amplitude of the clot
What does a CI greater than 4 suggest?
A hypercoagulable profile
What does a CI less than -4 suggest?
A hypocoagulable profile
What is the activator added to evaluate the extrinsic pathway with ROTEM/TEG?
Tissue factor (exTEM for ROTEM)
What is the activator added to evaluate the intrinsic pathway with ROTEM/TEG?
Activator is ellagic acid (inTEM for ROTEM) and kaolin or ellagic acid (for TEG)
Characterized by an elongation of the CT or R compared with the assays evaluating the extrinsic pathway
Fibrinogen Function (fibTEM)
Evaluates fibrinogen function by adding tissue factor and cytochalazine D, a powerful inhibitor of platelet aggregation
Characterized by lower amplitudes and MCF compared with the exTEM assay
Heparinase-Based TEM (hepTEM)
Evaluates hemostasis by initiating the intrinsic pathway (activation by ellagic acid) while inhibiting the activity of heparins by adding heparinase
Aprotinin-Based TEM (apTEM)
Evaluates fibinolysis (activation of hemostasis by tissue factor) by adding an antifibrinolytic, aprotinin
VCM-VET
Uses fresh, nonanticoagulated blood that is tested immediately after sampling
Relies on viscoelastic properties of whole blood
Does not routinely utilize activators
Test cartridges are preheated to 37*C on the heating plate
Blood is placed in the cup associated with the cartridge and the cartridge is placed inside the machine
Cartridge has two flexible arms, one of which is moved by the motor of the analyzer and the other is unattached, both have a built-in glass plate
Blood flows in between the glass plates and as blood clots and fibrin forms the glass plates adhere to each other and the arms start moving together
Info transmitted into a graphic form
Values are the same as those of ROTEM
VCM-VET Clotting Time
Time from test initiation until amplitude of 1% is achieved
VCM-VET Clot Formation Time
Time between the 1% amplitude and 10% amplitude of the clotting signal
VCM-VET Alpha Angle
The angle between the middle axis and the tangent to the clotting curve through the 1% amplitude point
VCM-VET Maximum Clot Firmness
Maximum amplitude of the VCM graph
VCM-VET Lysis Index at 30 Min
Fibrinolysis 30 minutes after CT; measured as the relation of the amplitude to the maximum clot firmness (% remaining clot firmness)
What changes on ROTEM/TEG are consistent with hypercoagulability?
Shortened CT/R or CFT/K or increased a angle or MCF/MA
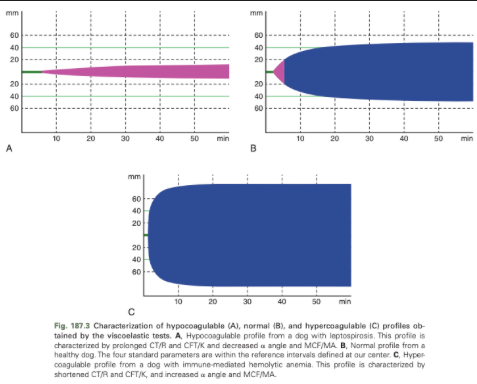
What changes on ROTEM/TEG are consistent with hypocoagulability?
Prolonged CT/R or CFT/K or decreased a angle or MCF/MA
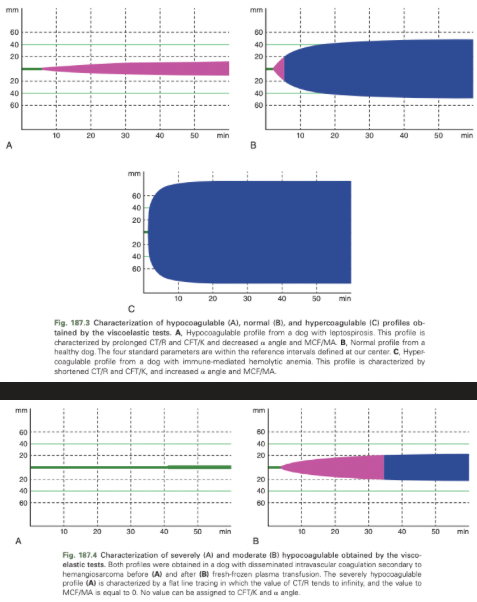
Hypocoagulable TEG/ROTEM
Normal TEG/ROTEM
Hypercoagulable TEG/ROTEM
Hypercoagulable/Hypocoagulable Profile vs State
Viscoelastic tests can only exhibit a hypercoagulable or hypocoagulable profile and not a hyper/hypocoagulable state
Hyper/hypocoagulable state = hypercoagulable/hypocoagulable profile associated with clinical and/or biological signs of thrombosis/hemorrhagic diathesis
What are some factors that can affect ROTEM and TEG Profiles?
Anemia can cause artifactual hypercoagulable profile
Increased hematocrit can cause TEG variables indicative of hypocoagulability
Decreased fibrinogen and platelet count will caused decreased clot strength
Detection of Hyperfibrinolysis with TEG
Depending on the methodology, there may be an increase or decrease in lysis calculation
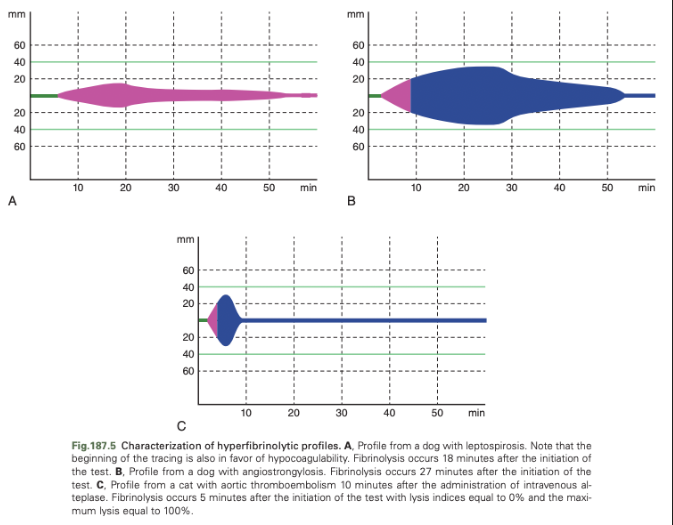
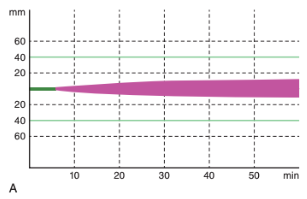
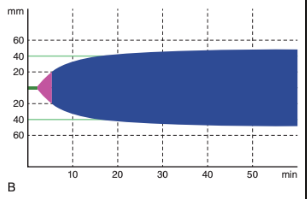
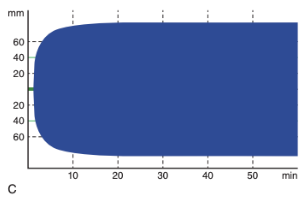
Detection of Hypofibrinolysis with TEG/ROTEM
Standard TEG/ROTEM assays may be unable to detect hypofibrinolysis in dogs and cats
Using ROTEM/TEG to Monitor Antithrombotic Therapy
Gold standard for monitoring the effect of heparin on coagulability is anti-factor Xa activity but his isn't readily available
Can use viscoelastic tests for this purpose
Use of unfractionated heparin was associated with hypocoagulability in healthy cats and dogs
The use of LMWH was not associated with significant alterations of ROTEM and TEG parameters in healthy cats and healthy dogs unless supraphysiological doses were used in healthy dogs
Limitations of ROTEM/TEG
Major limitation remains the interpretation of results
Second limitation is price of systems
Third, systems require long technical time and rigorous machine maintenance
Fundamental difference in the use of viscoelastic tests between human and veterinary medicine
In human medicine, they appear to be an aid in the therapeutic management of critically ill patients due to publications
In veterinary medicine, they remain confined only to the observation of hemostatic changes present in a patient