Excretion
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Waste products of plants
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Water/water vapour
Excretion
The removal of waste substances of metabollic reactions
Metabolic waste produced by the human body
Carbon dioxide and water
Urea
Substances in excess
Organs for excretion
Kidneys- Urea
Lungs- Carbon Dioxide
Skin- Water, excess mineral ions, some urea (Sweating)
Functions of the kidney
Regulate water content of the blood
They excrete the toxic waste products of metabolism
Osmoregulation
The process of maintaining the water and salt concentrations
Importance of osmoregulation
Maintaining water levels
Too much water- Cells swell up and can burst
To little water- Cells loose water and can die
Key features of the urinary system
To filter waste products from the blood and expel it from the body as urine
To control water levels of the body
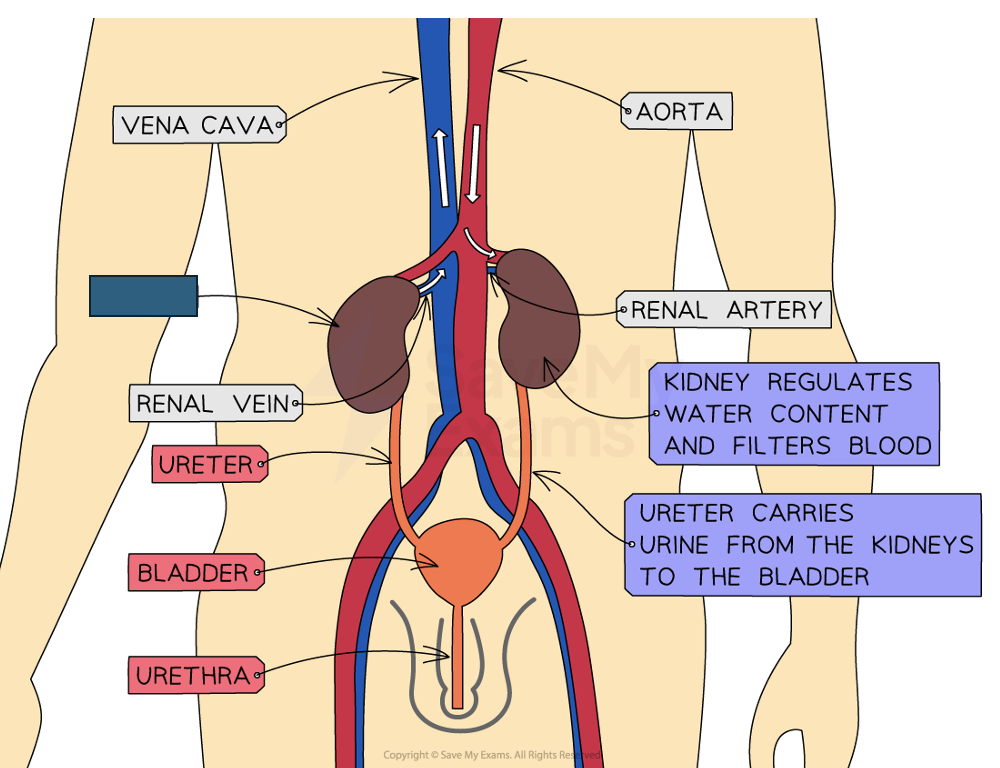
Label the structure and its function
Kidney
Filters the blood
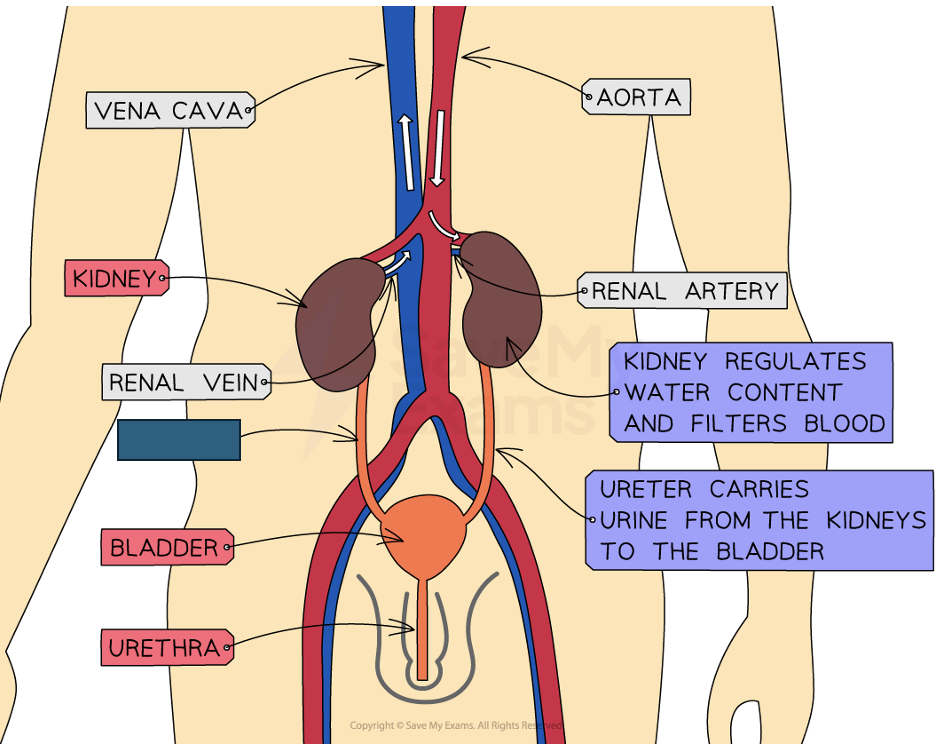
Label the structure and its function
Ureter
Tube connecting the kidney and the bladder
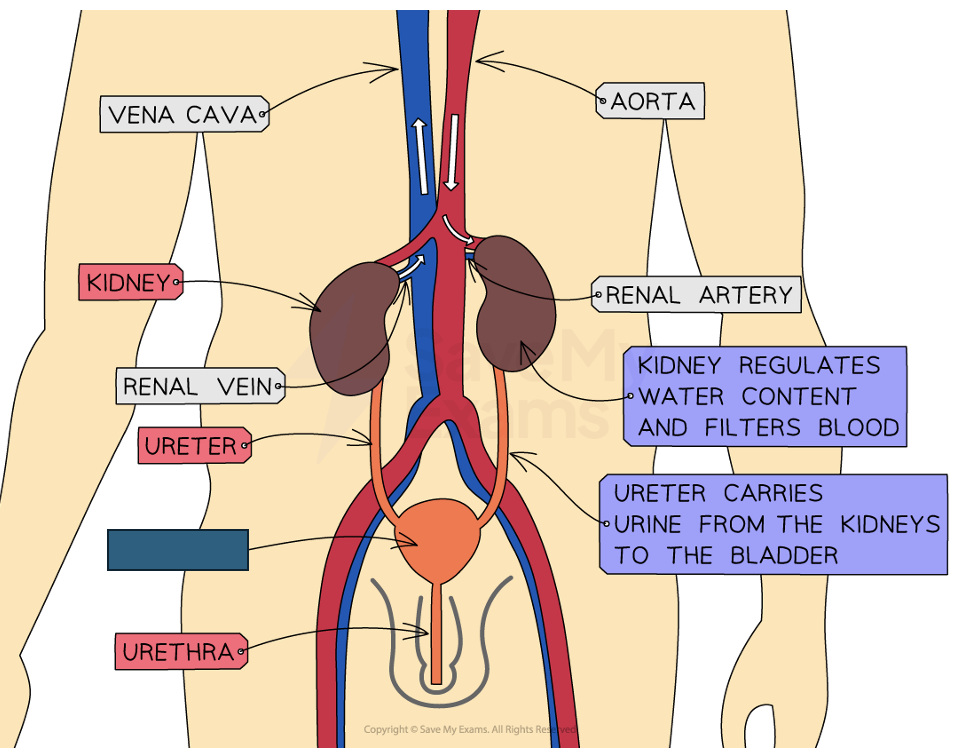
Label the structure and its function
Bladder
Organ that stores urine as it is produced by the kidney
Label the structure and its function
Urethra
Tube that connects the bladder to the exterior, where urine is released
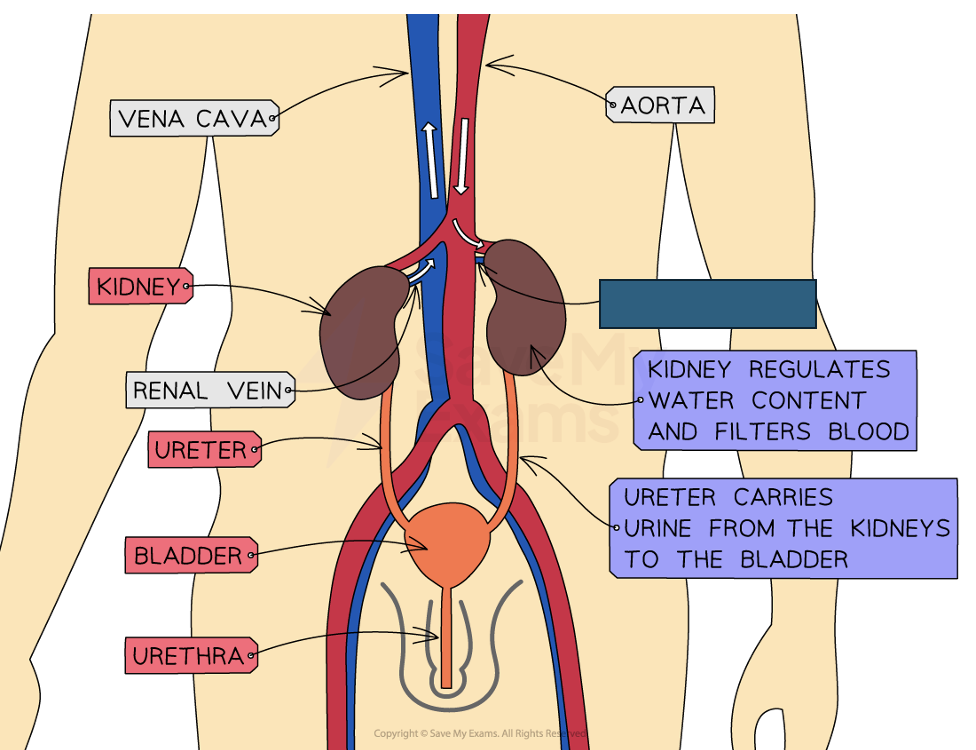
Label the structure and its function
Renal artery
Comes from the aorta delivers oxygenated blood to the kidney
3 main sections of the kidney
Cortex
Medula
Renal Pelvis
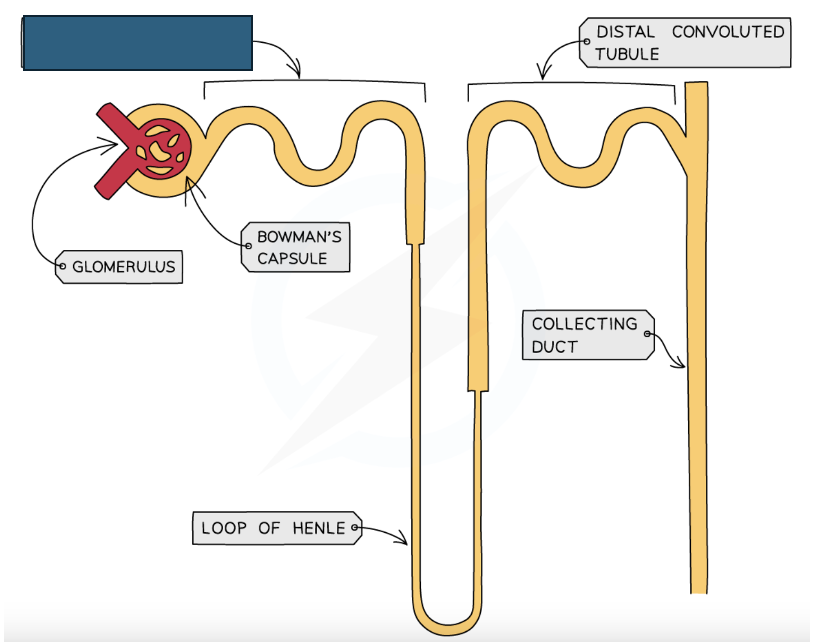
Label the structure
Proximal convoluted tubule
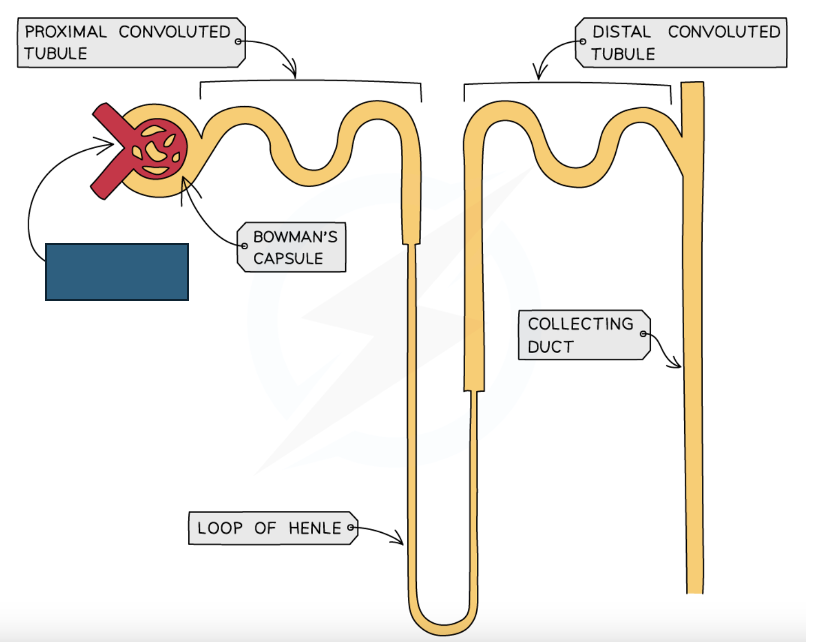
Label the structure
Glomerulus
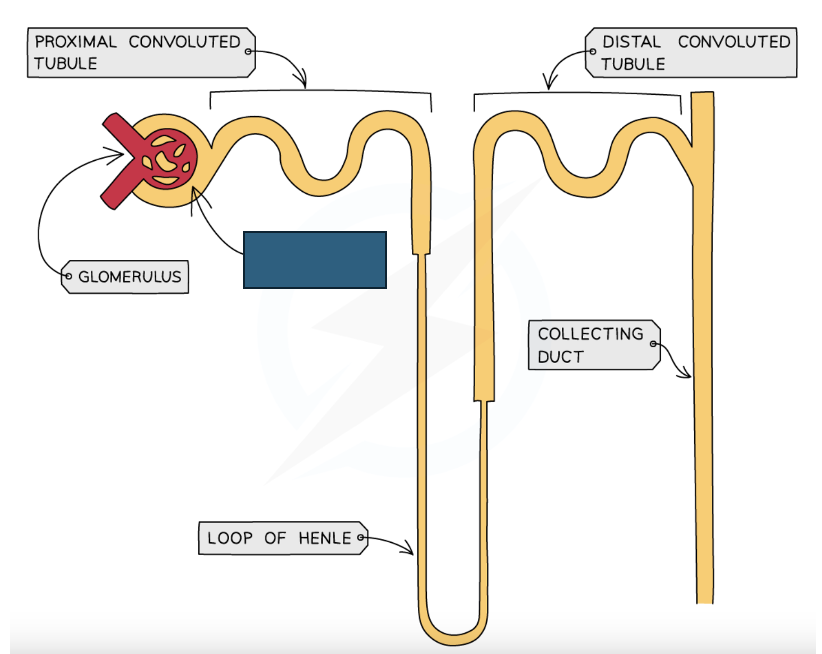
Label the structure
Bowman’s capsule
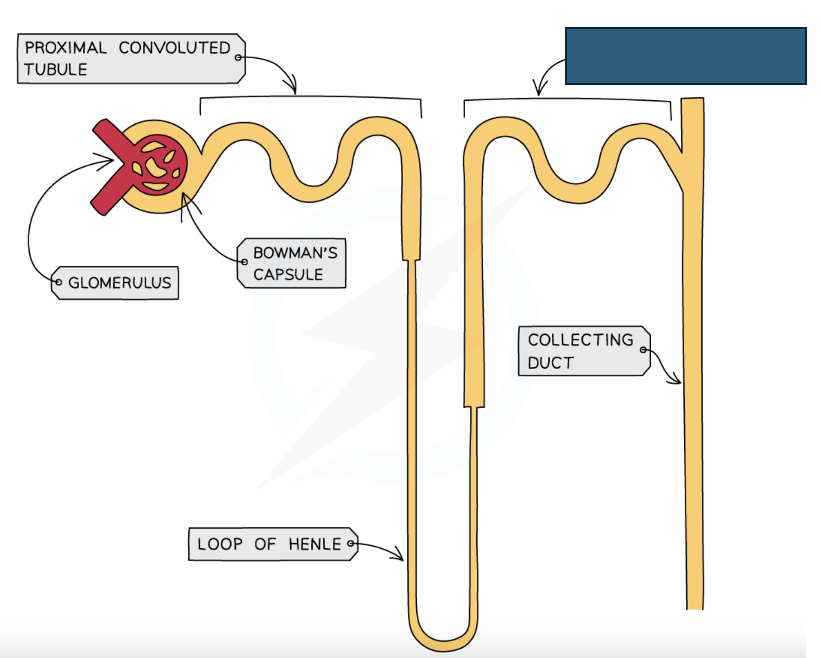
Label the structure
Distal convoluted tubule
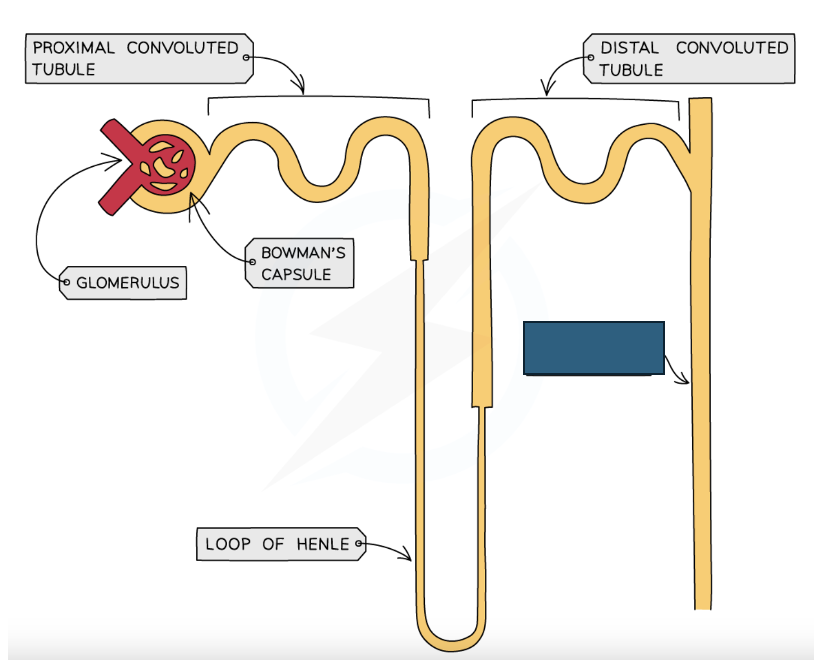
Label the structure
Collecting duct
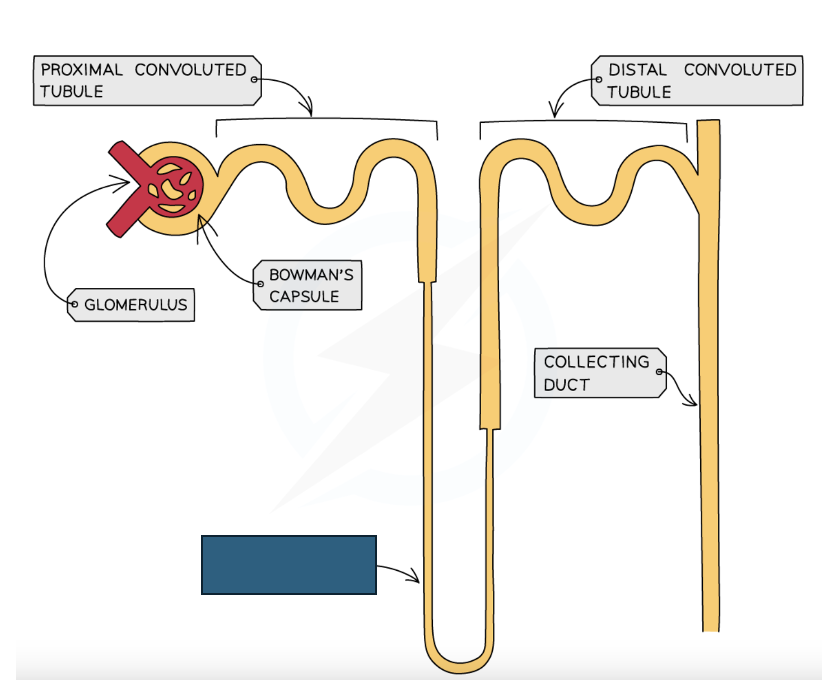
Label the structure
Loop of henle
Ultrafiltration process
Arterioles branch off the renal artery and lead to each nephron, forming a glomerulus inside the Bowman’s capsule.
The capillaries narrow, increasing blood pressure and forcing small molecules out of the blood into the Bowman’s capsule, forming glomerular filtrate.
Components of glomerular filterate
Urea
Water
Glucose
Salts
Why can’t proteins and red blood cells be filtered during ultrafiltration
They are too large
Selective reabsorption
Occurs in the nephron, primarily at the proximal convoluted tubule.
Glucose, some salts, and most water are reabsorbed back into the blood.
Active transport is used for glucose reabsorption, requiring mitochondria for energy.
How is water absorbed
Osmosis
How are salts absorbed
Active transport
Why do people with diabetes have glucose in their urine
Their blood glucose levels are too high for complete reabsorption.
Adaptation of the nephron
Contains a lot of mitochondria which provides energy for active transport of glucose molecules
Role of ADH
Controls water reabsorption
Affects the permeability of the collecting duct
Maintains water levels by negative feedback
Gland that releases ADH
Pituitary gland in the hypothalamus
High water content
The hypothalamus detects high water levels
Less ADH is released → Collecting duct is less permeable
Less water is reabsorbed
Large volume of dilute urine
Low water content
Hypothalamus detects low water content
More ADH is released → collecting duct is more permeable
More water is reabsorbed
Small volume of concentrated urine
Composition of urine
Excess water
Excess mineral ions
Urea
Factors affecting urine
Exercise
Water intake
Temperature
Effect of high water intake on urine
More water removed
Large volume of dilute, pale urine.
Effect on low water intake on urine
Less water removed
Small volume of concentrated, dark urine
Effect of high temperature on urine
More water lost in sweat
Less water in urine
Small volume of concentrated, dark urine
Effect of exercise on urine
More water lost in sweat
Less water in urine
Small volume of concentrated, dark urine