A&P Lecture Unit 3: Blood Circulation and Cardio
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Cardiopulmonary disease
#1 cause of death in US: heart disease.
Heart location
Middle of mediastinum
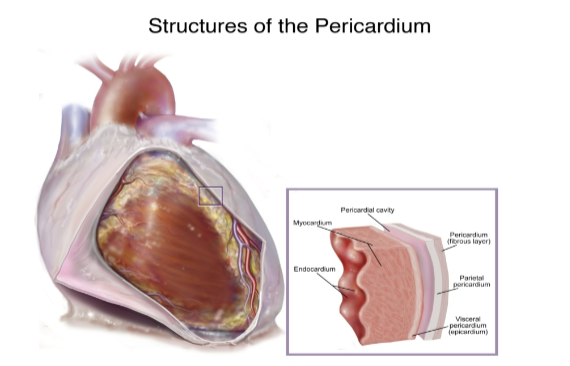
Pericaridum
Fibrous layer
Parietal layer
Space/cavity
Visceral layer (epicardium)
Myocardium (heart muscle)
Endocardium (inner layer, wall of heart chamber)
All Patients Take Meds
Aortic: 2nd intercostal
Pulmonic: 2nd intercostal
Tricuspid: 4th intercostal
Mitral: 5th Intercoastal
Erb’s point
3r intercostal space, left sternal border (good for listening to entire heart)
Which valuve is most gets most damaged most often?
Mitral valve because it must pump to the whole body and needs to use the most force. Sometimes valves open again before ventricles can fully drain
Coronary Circulation
RCA: supplies r atrium, r ventricle, inferior wall L ventricle
LAD: anterior wall L ventricle
LCX: L atrium, lat and post walls of L ventricle
One cardiac cycle
Beginning of contraction to beginning of next contraction
Divided into..
Systole
Diastole
Atrial syatole or diastole
Ventricular systole or diastole
Atria during Systole
At rest: Atria contract and push the final 25-30% of blood from atrium to ventricle (atrial kick)
During Exercise: Atria assume a greater role b/c blood must be pushed to the ventricles more quickly
Therefore, problems with atrial function may emerge during increased exercise
Right ventricle
Only needs to pump blood to lungs
Resistance in pulmonary artery fairly low (15mmHg)
Low pressure/force
Left Ventricle
Must pump blood to entire body
Resistance in aorta fairly high (~100mmHg)
High pressure/force, major work of the heart
End diastolic volume
Ventricles are relativey full (110-120 ml per ventricle)
End-systolic volume
Ventricles have just finished contracting & are relatively empty (40-50 ml)
Stroke Volume
How much blood was pumped out during systole
SV = EDV-ESV
SX = approx. 70 ml
Ejection fraction
EF = (SV/EDV) x 100
EX:
End diastolic volume =115
Stroke volume = 70
Ejection fraction = 70/115 = .61 = 61%
Normal Ejection fraction ~60%
Ejection fraction levels
High: +70%
Normal: 46-70%
Low: 35-45%
Risk: -35%
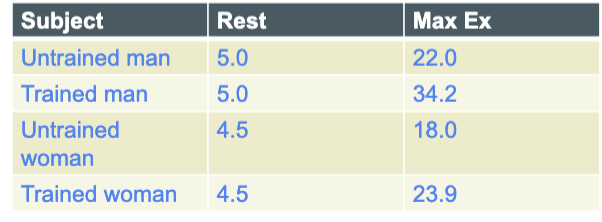
Cardiac Output
Amount of blood pumped per min
Amount leaving either left or right ventricle
Determinants of CO
CO = stroke volume x heart rate
EX: SV = 70 ml/beat and HR = 72 beats/min
CO = 70 ml/beat x 72 beats/min = 5040 ml/min or 5,04 liter/min
Trained heart usually has. lower HR but higher SV
Sympathetic effects on heart
Innervation: SNS neuron innervate entire heart and release norepinerine
Effects:
^ HR (positive chronotropic effect)
^ Contraction force (Positive inotropic effect)
^ Rate of AP conduction (positive dromotropic effect)
Parasympathetic effects on heart
Innervation: Cranial nerve X (vagus) innervates atira and releases acetylcholine
No effect on contraction force bc ventricle no innervated
Circulating catecholamines
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Released from adrenal gland
Released from adrenal gland
Powerful cardiac stimulants
Cardiac “preload”
Volume of blood returning to heart
^ blood return stretches ventricles causes increased SV and CO
Cardiac “afterload”
The forced heart must pump against
^ after causes v CO
Ionic imbalances
^Plasma potassium: slows HR
^Plasma Calcium: Increases HR
Temperature
^Body temp: increase HR
v Body temp: decreases HR
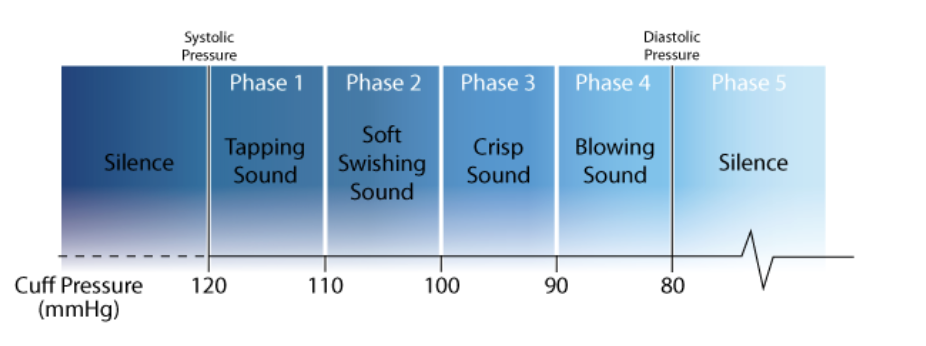
Systolic value (higher number)
Pressure when the heart contracts
Tells us what the heart is doing
S1: lub
Ventricles contracts
Open Semilunar valves
Blood goes to the body
Diastolic value (lower number)
pressure when the heart relaxes
Tells just what the arteries are doing
S2: dub
Ventricles relax
Open AV valves
blood to venrticles
Mean (average) BP
Algebraic (weighted) mean of systolic and diastolic values
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) = (2x diastolic +systolic) /3
Normal MAP ~93.3mmHg
Blood Pressure
BP is a product of..
Cardiac Output
Total peripheral resistance (TPR): The sum of all the resistance in the arterial system
BP = CO x TPR
BP = (SV x HR) x TPR
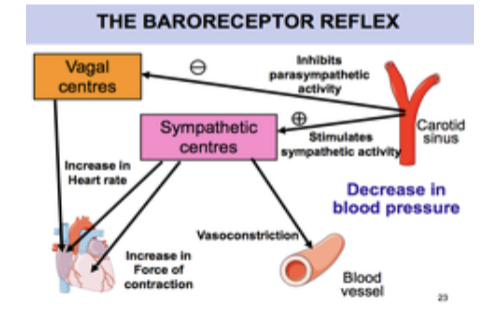
Baroreceptor Reflex
Rapid control of BP (2-3 seconds)
Pressure receptors (baroreceptors) located in large arteries; detect sudden changes in arterial pressure
Baroreceptors send info to CV control center in brainstem (medulla) if BP high or low
CV control alters actives of heart and circulation to bring BP back to normal $
Relatively rapid control of BP (1-2 minutes)
Adrenal Catecholamine: Epinephrine, norepinephrine released from adrenal gland if BP is too low
Renin-angiotensin system: Renin, enzyme from kidneys and Angiotensin, substance in bloodstream controlled by renin
Slow, long-term control of BP (days and weeks)
Kidney
Regulate balance of water and electrolytes (Na+, K+)
If BP is too high → Release fliud from vascular system
If BP is too low → retain fluid in body
Orthostatic hypotension
Stand suddenly and blood rushes to feet and stays there.
SBP >20 mmHg
DBP > 10 mmHg
Predisposing factors
CV disease, meds, elderly, systemic disease/infections, many others
BP Response During Exercise
Normal:
SBP ^ as exercise intensity ^ (^ CO)
DBP unchanged or slight v
Abnormal Response:
SBP unchanged or v as ex: intensity ^
DBP ^ excessively as ex. intensity ^
Resting BP in exercise
Resting BP: SBP > 200 or DBP> 110
Terminate Exercise: SBP > 250 or DBP > 115
P-wave
Atrial depolarization
0.08 to 0.11 sec
QRS Complex
Ventricular Depolarization and Contracting, sending blood out of the heart
<.10 sec
PR segment
0.12 to 0.20 secs
ST Segment
<0.12 sec
T- wave
Ventricle repolarize
< 0.20
QT Interval
<.10sec
Type A
Very common; approximately 41% of US population has this type A
“Contains Type A antigens
Contains Anti- B antibodies
Type B
Contains type B anitgens
Plasma contains anti-A anibodies
Type AB
Contains both A and B antigens
Contains no antibodies in plasma
Type O
Contain no A or B antigens
Contains both A and B antibodies
Blood clotting
Vasuclar spasm: Allows time for next step to occur
When inner wall of vessel is damaged, collagen fiber is exposed
Platelet Plug formation: Loosely knit plug
Platelets in blood attach to damaged site
Attached platelet plug released chemicals that draw more platelets
Coagulation
Platelets secrete serotonin, causing blood vessels to spasm decreasing blood flow to the area
In 15 secs, blood clotting beings
Prothrombin (made by liver with vita. K)→ thrombin → fibrinogen → fibrin
Fibrin forms a net to catch more blood cells and platelets, within 3-6 mins, a clot is created
Cardiac Control
Sinoatrial node: Sets pace for the whole heart at around 70 bpm
AV Node: Delays impulse from SA nodes by about 0.1 second.
a. Allows completion of atrial contraction prior to ventricular contraction
AV bundle: only electrical connection from atria to ventricles
AV bundle splits into right and left branches
Purkinje Fibers: completes the pathway
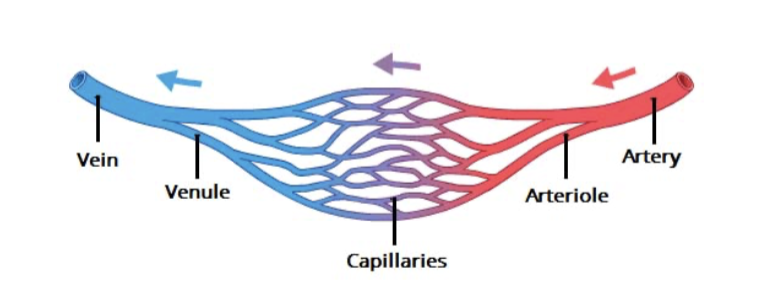
Circulation
Artery → Arteriole → Capillary → Venule → Vein
Tunica Intima
Made up of endothelium
Minimizes friction
Tunica media
Smooth muscle’
Vasoconstriction: decreases in diameter
Vasodilation: increased in diameter
Tunica Externa
Loosely woven collage fibers
Contains vasa vasorum
Venous Blood Flow
Openh venous valve
Contracted skeletal muscle
Closed venous valve
Vein
Direction of blood flow
Anastomosis
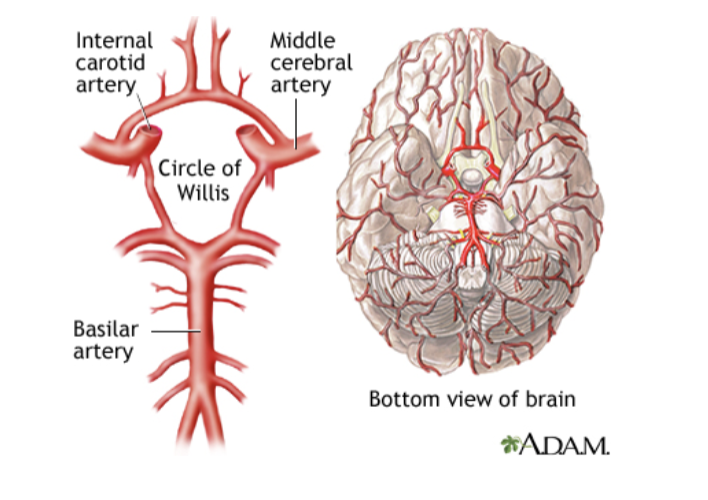
ACA
Supplies the medial and superior parts of frontal love and anterior parietal love
MCA
Blood to lateral (side)area of the frontal , temporal, and parietal lobes
PCA
Blood to occipital love, inferior temporal love, deep structures like thalamus and posterior limb of internal capsule.