TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Tissue
group of cells that work together to perform specific functions.
Four main types of tissues:
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
covers exposed surfaces; lines internal passageways and chambers; forms secretory glands; forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes absorbs, and filters!
Epithelial Tissue
fills internal spaces; provides structural support; stores energy; supports, protects, binds other tissues together.
Connective Tissue
contracts to produce/cause movement; includes skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Muscle Tissue
Conducts electrical Impulses; carries information; it’s for Internal Communication
Nervous Tissue
this contains the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Nervous Tissue
includes muscles attached to bones (skeletal), muscles of heart (cardiac), and muscles of walls of hollow organs (smooth).
Muscle Tissue
it’s the lining of digestive tract organs and other hollow organs. Also refers to the skin surface (epidermis).
Epithelial Tissue
includes the bones, tendons, fat and other soft padding tissue
Connective Tissue
It covers exposed surfaces, line internal passageways and chambers, and forms glands.
Epithelial Tissue
The functions of the Epithelial Tissue
Physical protection, Control permeability, provide sensation, and produce specialized secretions
Glandular Epithelia (exocrine and endocrine glands)
Specialized functions of Epithelial tissues
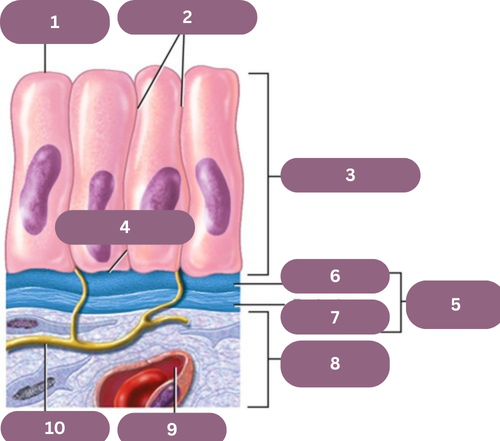
1.
Apical (free) Surface
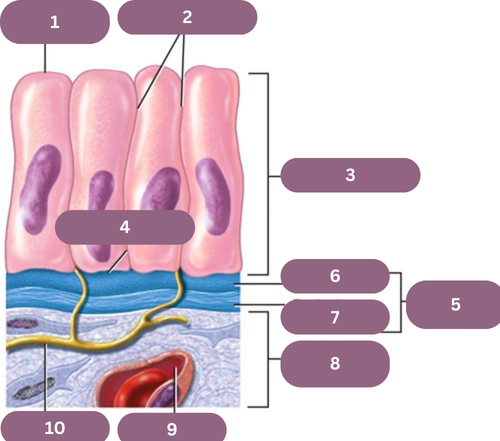
2.
Lateral Surfaces
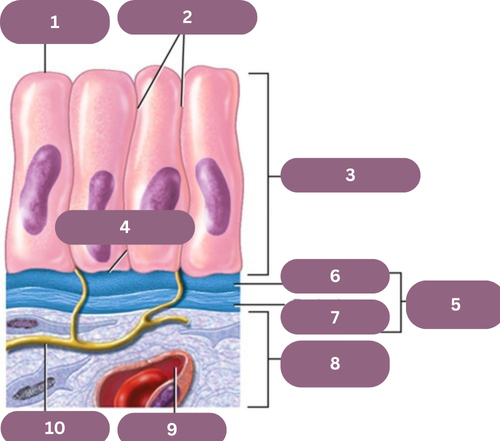
3.
Epithelium
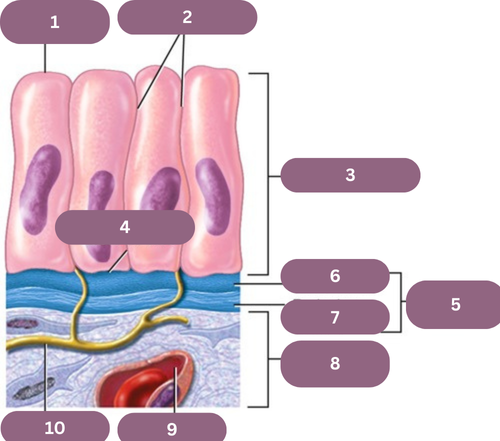
4.
Basal Surface
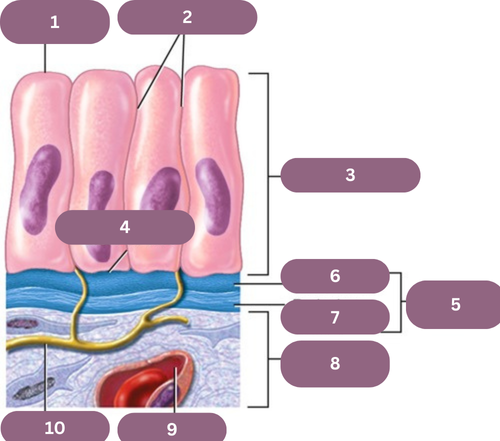
5.
Basement Membrane
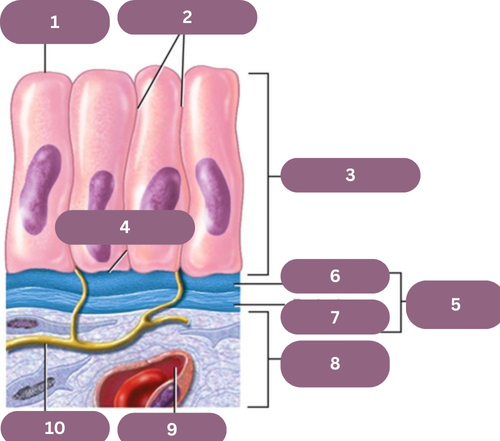
6.
Basal Jamina
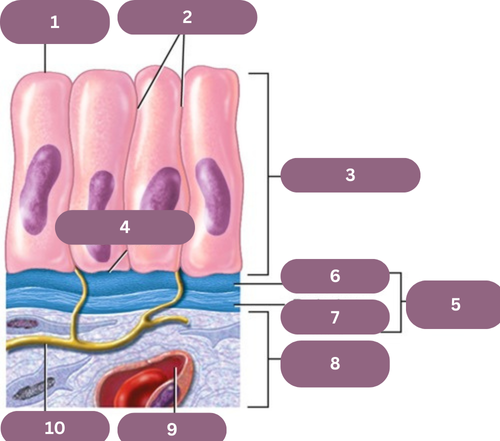
7.
Reticular Lamina
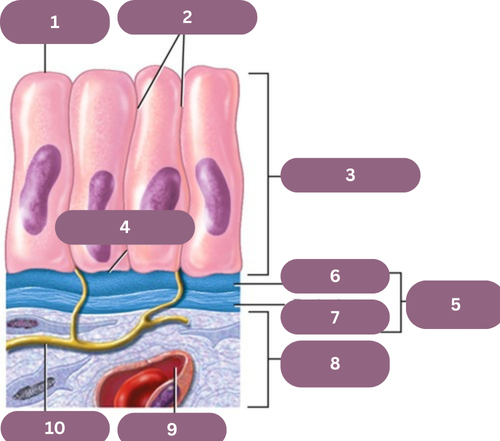
8.
Connective Tissue
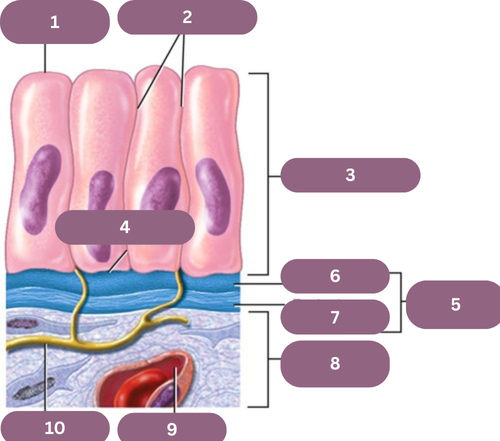
9.
Blood Vessel
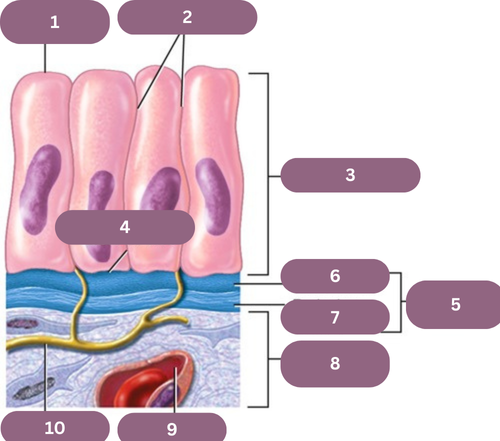
10.
Nerve
Exocrine Glands & Endocrine Glands
Types of Epithelial Glands