Kidney Transplantation (Pathophysiology)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
ID the most common solid organ transplant?
Liver
Heart
Kidney
Pancreas
Lung
Kidney
Which donor kidneys generally last longer, living or deceased?
living
What are the top 3 (in order) leading causes of ESRD, which can lead to kidney transplantation?
DM
HTN
glomerulonephritis
The physiologic consequence of transplantation ______ quality of life and survival when compared with _______
improved, dialysis
What improves immediately after transplantation?
GFR
What improves days after transplantation?
SCr, BUN
What improves weeks after transplantation?
anemia, calcium/phosphate imbalance (CKD), altered lipid profiles
Why does SCr and BUN not improve immediately after transplants even though they are used to measure kidney function?
SCr and BUN are waste products that the kidney is tasked with filtering out. They are not only affected by the extent of kidney function, which leads to the lag in SCr and BUN after any change to the kidneys.
Correctly order the sequence of events of kidney transplant rejection:
initiation of immune effector mechanisms
recognition of histocompatibility (MHC) differences between donor and recipient
graft destruction
recruitment of activated lymphocytes
2, 4, 1, 3
The first step of graft rejection: recognition of _________ (___) differences between donor and recipient
histocompatibility (MHC)
The second step of graft rejection: recruitment of activated __________
lymphocytes
The third step of graft rejection: initiation of ______________________
immune effector mechanisms
The fourth step of graft rejection: _____ destruction
graft
In the activation of T cells, what is the preliminary step (step 0)?
MHC II molecule complexes recognizes by T cell recognition complex (TCR)
In the activation of T cells, what is the first step?
A costimulatory signal initiates signal transduction
In the activation of T cells, what is the second step?
Activation of calcineurin and dephosphorylation of NFAT
In the activation of T cells, what is the third step?
NFAT facilitates IL-2 gene transcription
In the activation of T cells, what is the fourth step?
IL-2 activates IL-2 receptor
In the activation of T cells, what is the fifth step?
IL-2 receptor signaling pathway
In the activation of T cells, what is the sixth step?
T cell proliferation and production of cytokines specific to T cell
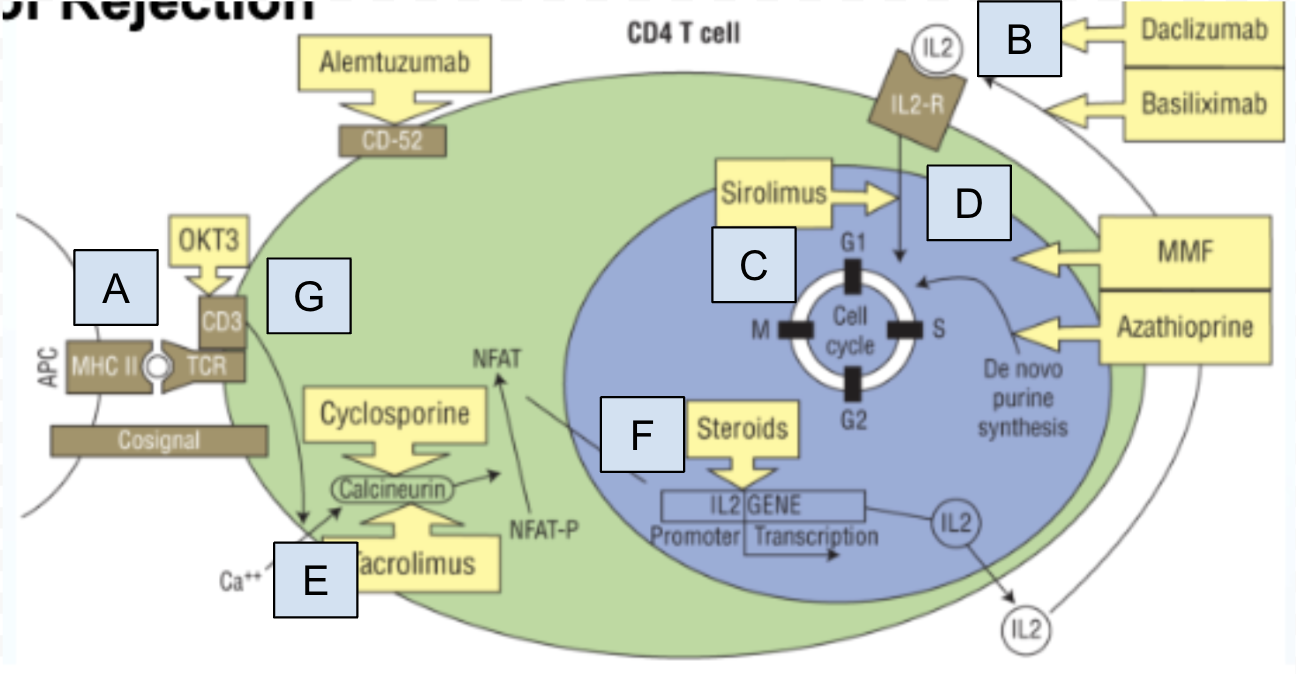
Which step of T cell activation is Box A
step 0: MHC II molecule complexes recognizes by T cell recognition complex (TCR)
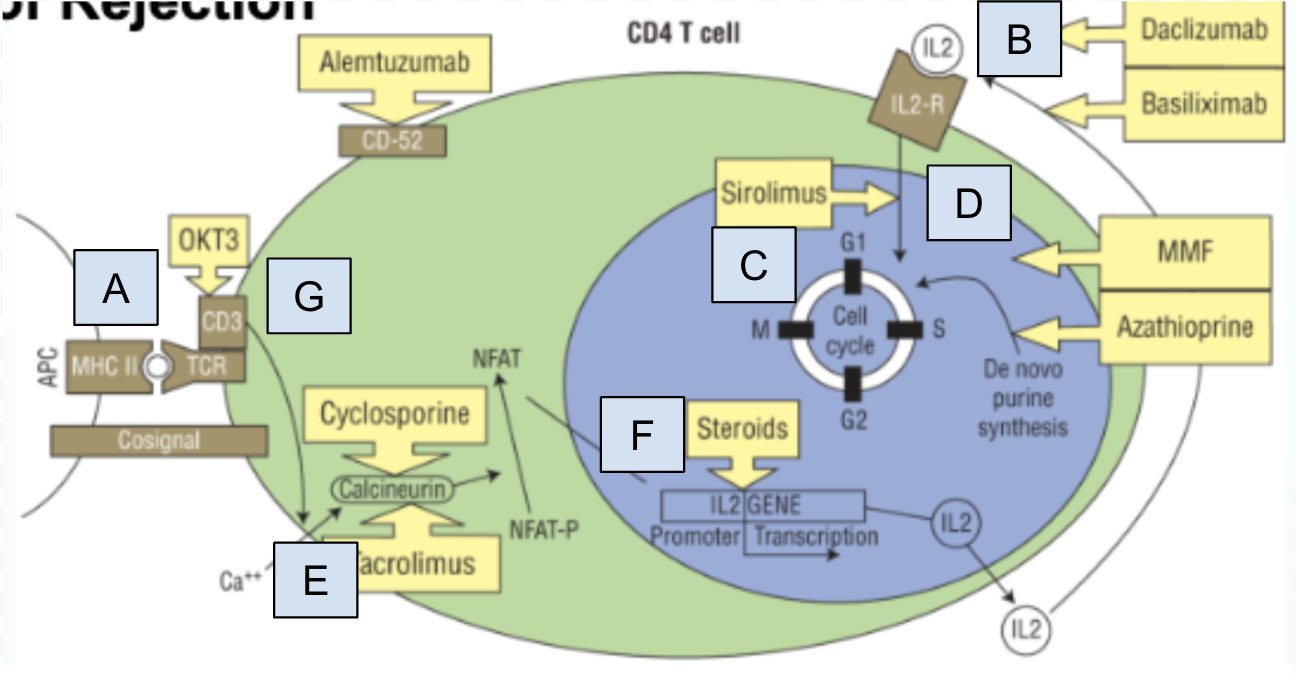
Which step of T cell activation is Box B
step 4: IL-2 activates IL-2 receptor
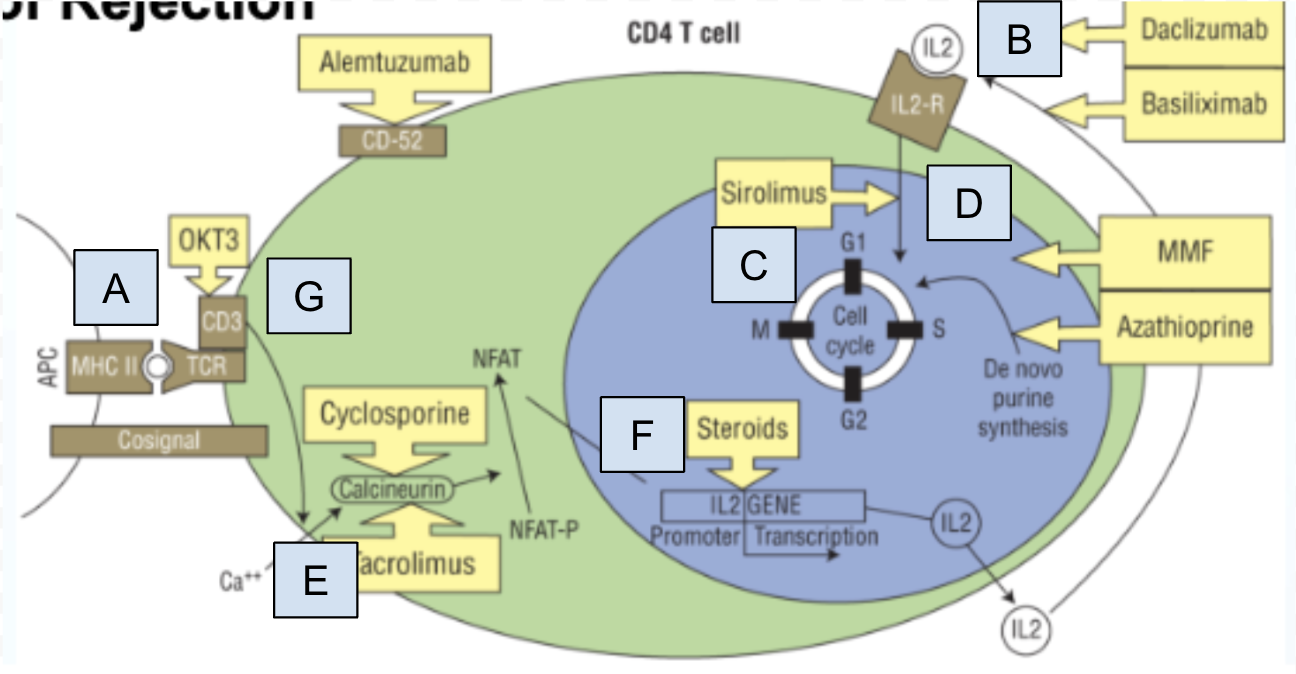
Which step of T cell activation is Box C
step 6: T cell proliferation and production of cytokines specific to T cell
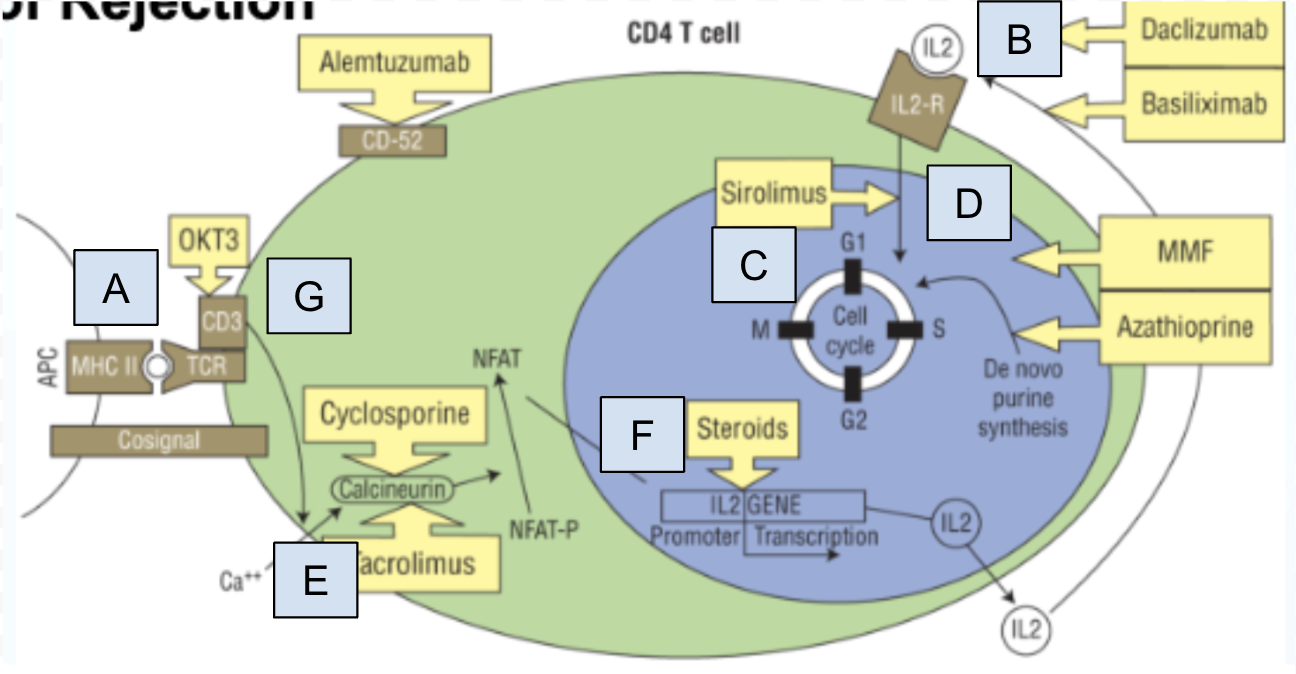
Which step of T cell activation is Box D
step 5: IL-2 receptor signaling pathway
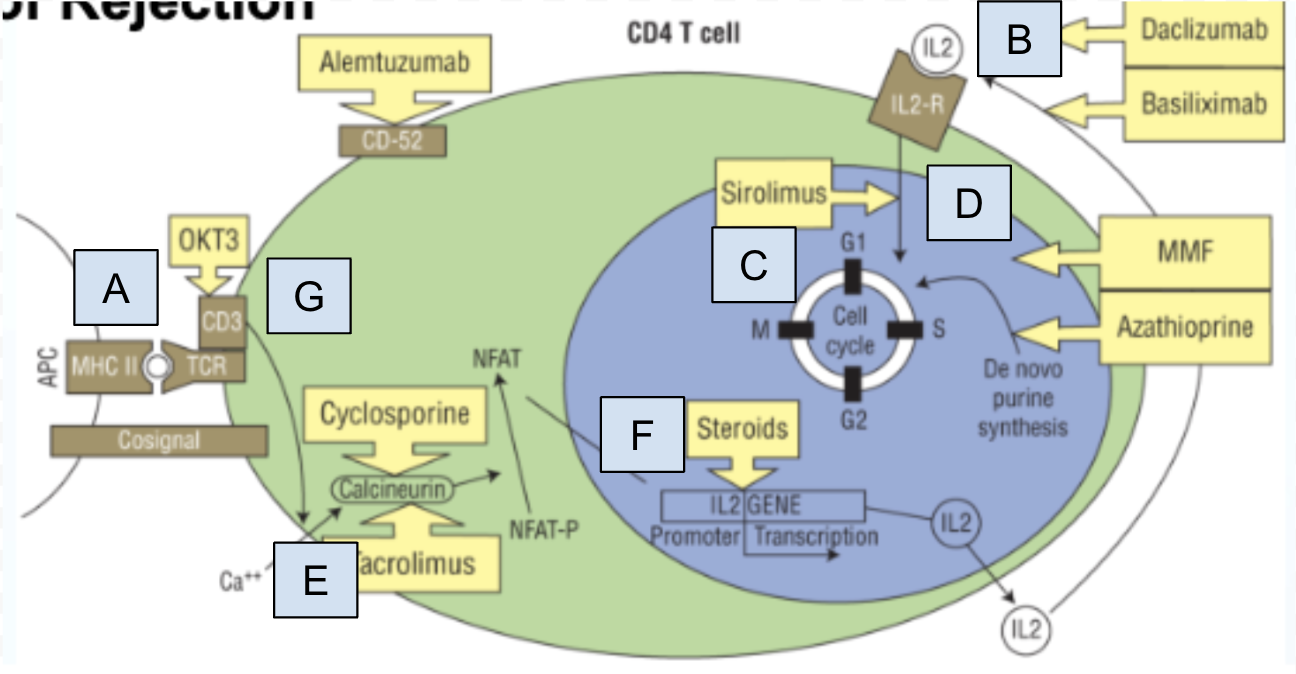
Which step of T cell activation is Box E
step 2: Activation of calcineurin and dephosphorylation of NFAT
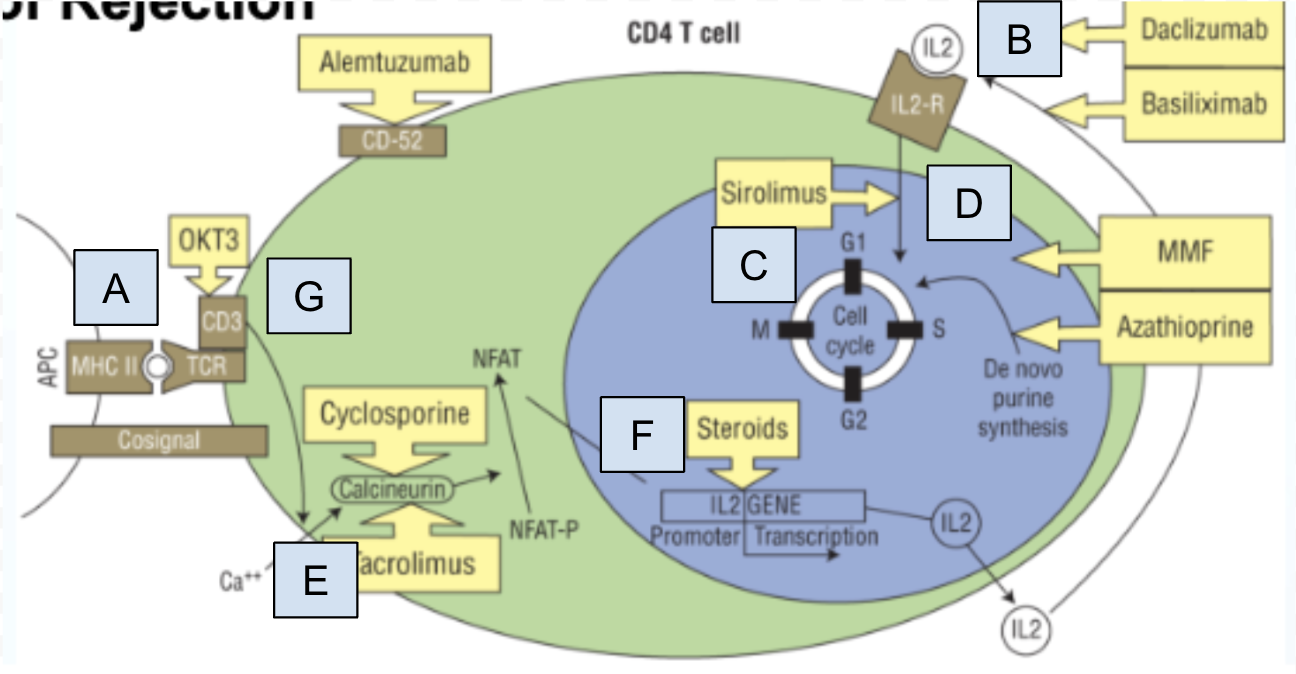
Which step of T cell activation is Box F
step 3: NFAT facilitates IL-2 gene transcription
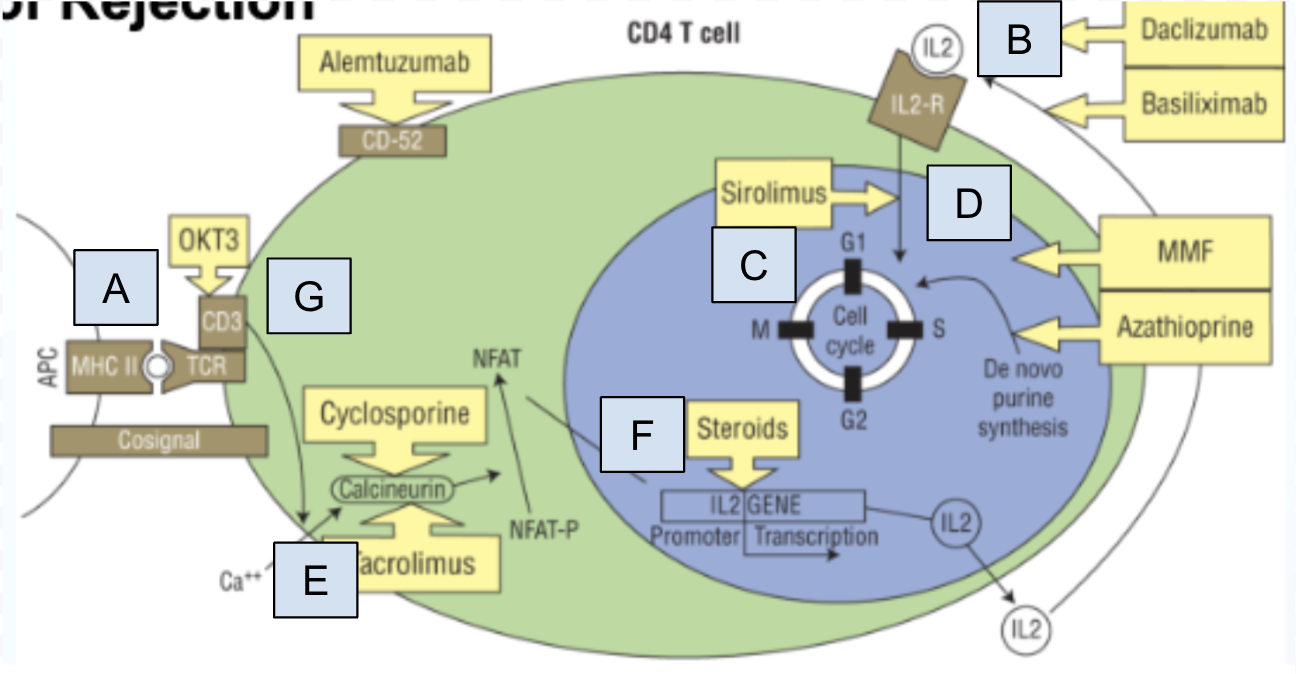
Which step of T cell activation is Box G
step 1: A costimulatory signal initiates signal transduction
What is hyperacute rejection?
can take minutes, donor-specific antibodies are present in the recipient
What is acute cellular rejection (ACR)?
can take few months, alloreactive T cells that appear in the circulation and infiltrate the allograft through the vascular endothelium
What is antibody-mediated rejection (AMR)?
can take months to years, vascular or humoral rejection characterized by the presence of antibodies directed against HLA antigens on teh donor vascular endothelium
What is chronic rejection?
can take months to years, cell and/or antibody mediated rejection; irreversible by immunosuppressants (major cause of graft loss)
What is the number one cause of ESRD?
DM
What kind of rejection irreversible by immunosuppressants?
Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR)
Acute cellular rejection (ACR)
Hyperacute rejection
chronic reaction
chronic rejection
How long after transplantation does GFR improve?
minutes
How long after transplantation does SCr improve?
days
How long after transplantation does BUN improve?
days
How long after transplantation does anemia improve?
weeks
How long after transplantation does Ca/Phos imbalance (CKD) improve?
weeks
How long after transplantation does altered lipid profiles improve?
weeks