Carbohydrates Metabolism/Glucose Unit 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the general description of carbohydrates?
Compounds containing Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen(O)
Classification of carbohydrates are based on?
Size of the base carbon chain
Location of the carboxyl function group
Number of sugar unit
Stereochemistry (Arrangment)
C6H2O6
sugar!
Aldose
Terminal carboyl group called aldehyde
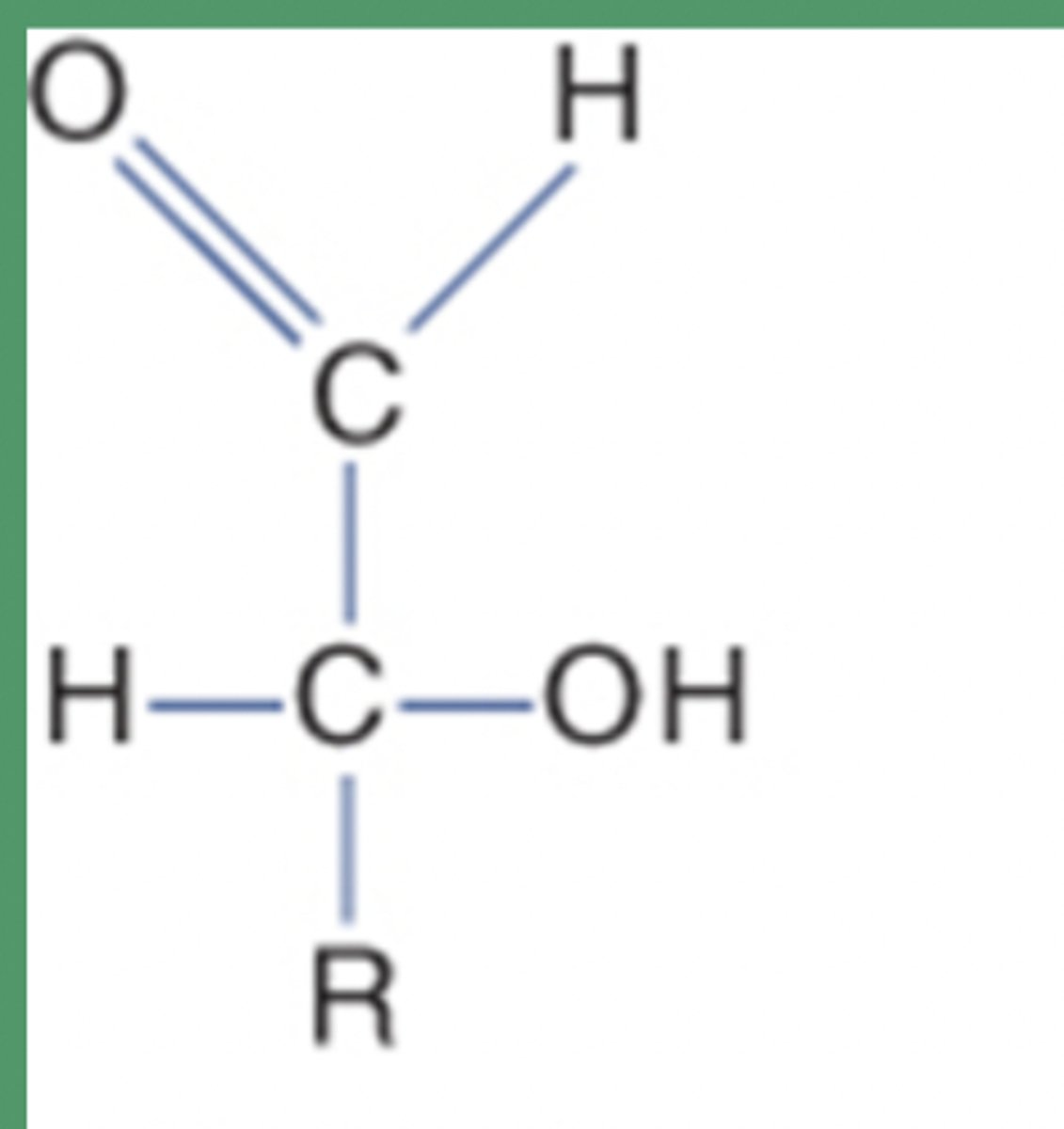
Ketose
Has carbonyl group in the middle linked with 2 other carbon atoms
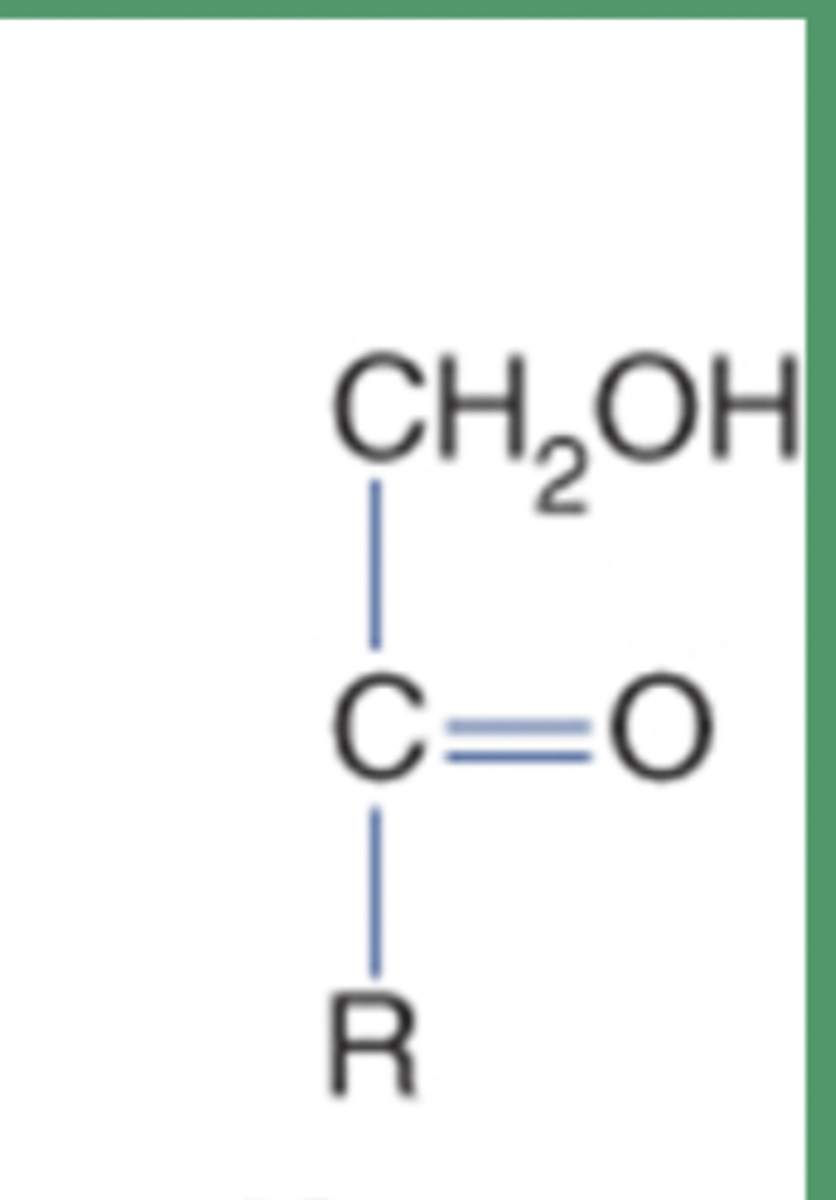
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bond.
Oligosaccharides
three to ten monosaccharides
polysaccharides
ten or more
Linkage for sugar?
glycosidic bond
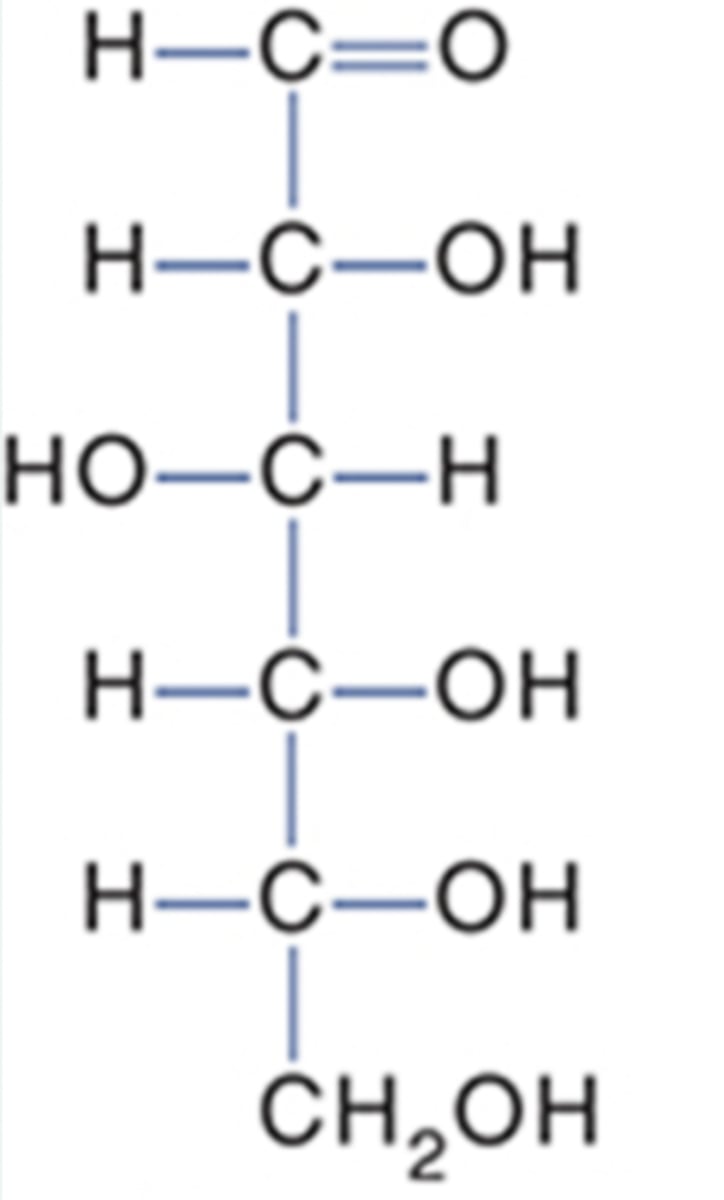
D-glucose structure
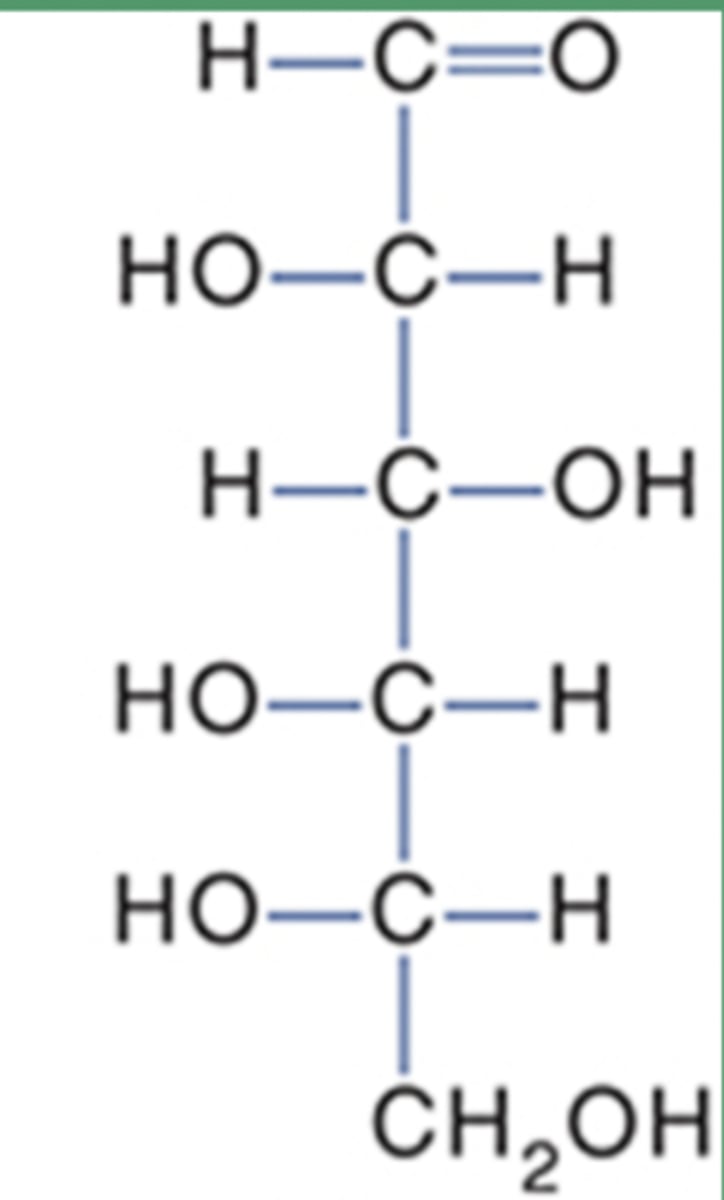
L-glucose structure
Salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase
responsible for digesting starch and glycogen into dextrin and disaccharides
Maltase (intestinal enzyme)
(sucrase and lactase)- Gut enzyme then hydrolysesthem to single monosaccharide components
How many glucose transporters are there? (GLUT)
14
What glucose transporters are the most important?
1-5
GLUT 1
Erthrocytes
GLUT 2
Liver, pancreatic beta, cells, intestine
GLUT 3
brain
GLUT 4
Fatty tissue, skeletal muscle, heart
GLUT 5
Jejunum, kidney
What does insulin do for glucose transporters?
Opens glucose transporters
Which GLUTs are not insulin dependent?
1,2,3,5
What is glucose in the liver?
glycogen
Glycolysis
Metabolism of glucose molecue to pyruvate or lactate for production of energy
Gluconeogenesis
Formation of glucose-6-phosphate from noncarbohydrate sources
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose to use as energy
Glycogenesis
Conversion of glucose to glycogen for storage.
Lipogenesis
Conversion of carbohydrates to fatty acids
Lipolysis
Decomposition of fats
How many ATP are "invested"?
2 ATP
What is the "gross" ATP in glycolysis?
4 ATP
What is the net ATP in glycolysis?
2 ATP