chem exam 1
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
Chemistry
the study of the properties and behavior of matter
solutions
homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances
solvent
present in greatest abundance
solutes
all other substances in a solution
aqueous solution
when water is the solvent
solvation
how all substances dissolve, surrounding of the solute by solvent
dissociation
Ionic compounds dissolve by water surrounding the separated ions
Molecular compounds dissolve in water
disperse in water, most remain intact, some form ions in water
electrolytes
a substance that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water
Ex: NaCl (s) forms Na+ (aq) and Cl- (aq)
CH3CO2H (aq) forms CH3CO- (aq) and H+ (aq)
strong electrolytes
dissociates completely when dissolved in water; equation has a single arrow, the solution is a strong conductor of electricity
HCl (aq)-> H+(aq)+ Cl-(aq)
weak electrolytes
only dissociate partially when dissolved in water; equation indicates chemical equilibrium, a reaction goes both forward and backwards; double arrow
nonelectrolyte
may dissolve in water but does not dissociate into ions, the solution does not conduct electricity
Ex: C6H12O6 (s) forms C6H12O6 (aq)
C12H22O11 (s) forms C12H22O11 (aq)
precipitation reaction
occur when two solutions containing soluble salts are mixed and an insoluble salt is produced; the solid is called a precipitate.
precipitate
the solid in a reaction
acids
substances that ionize in aqueous solutions to form H+, hydrogen ions; Strong acids completely dissociate in water, weak acids only partially
bases
substances that react with, or accept, H+ ions; increase concentration of OH-, hydroxide ions, when dissolved in water; do not have to contain OH- to be a base
strong bases
dissociate to metal cations and hydroxide anions in water
weak bases
only partially react to produce hydroxide anions
neutralization reaction
between an acid and a base;
ionic compound production
when the base is a metal hydroxide: water and salt
ionic compound written
if a weak electrolyte is involved it is not separated into ions
ionic compound carbonate or bicarbonate w/ acid reaction
the products are salt, carbon dioxide, and water
ionic compound sulfides
predicted results
oxidation and reduction
loss of electron; gain of electron
one cannot occur without the other, reactions are called redox reactions
concentration
the amount dissolved
molarity
one way to measure the concentration of the solution
titration
an analytical technique in which one can calculate the concentration of a solute in a solution
titrant
solution containing a known concentration of one reactant
analyte
solution containing reactants of unknown amount of concentration
standard solution
solution of known concentration; used to determine the unknown concentration of another solution
equivalence point
when the reaction is complete; based on the seen end point
indicators
added to cause a change in color near the equivalence point of titration
end point
the volume of titrant actually measured
thermodynamics
study of energy and its transformations
thermochemistry
study of chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat
Electrostatic potential energy
most important form of potential energy in changed particles
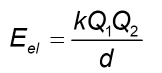
attraction between ions
opposites attract; bonds are formed- energy is released (Eel<0) bonds are broken- energy is consumed (Eel>0)
system
the portion of the universe we single out to study (represented by a chemical reaction)
open, closed, and isolated systems
can exchange heat and mass with its surroundings; only heat can be exchanged; heat and mass cannot be exchanged
positive and negative ΔE
system gains energy from the surroundings; system loses energy to the surroundings
internal energy of a system
the sum of all kinetic and potential energies of all components of the system; Generally don’t know it just how it changes
state functions
depends on present state of system not path to get to that state; ex- internal energy
enthalpy
represented as H; extensive; reverse reaction= opposite sign; the change depends on the states of reactants and products
calorimetry
the measurement of heat flow; we dk the enthalpy of the reactants and products so we use this to measure ΔH
heat capacity
the amount of energy(E) required to raise the temperature(T) of a substance by 1K (1*C)
specific heat
E needed to heat 1 gram of a substance by 1*C
molar heat capacity
E needed to heat 1 mole of a substance by 1*C
The enthalpy is associated with
breaking one mole of a particular bond in gaseous substance
bond enthalpy is always positive bc
Energy is required to break chemical bonds
The greater the bond enthalpy
the stronger the bond
Electromagnetic radiation
moves as waves through space at the speed of light
Wavelength λ
distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves
frequency
the number of waves passing a given point per unit of time
Three observed properties associated with how atoms interact with electromagnetic radiation that cannot be explained by waves
Blackbody radiation- the emission of light from hot objects, Photoelectric effect- emission of electrons from metal surfaces on which light is shown, and Emission spectra- emission of light from electronically excited gas atoms
quanta
packets that energy comes in
As an electron changes energy states
energy is emitted or absorbed by the electron as a photon
nf>ni vs nf<n
a photon is absorbed, emitted
Quantum mechanics
mathematical treatment in which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated
uncertainty principle
the more precisely you know the momentum the less you know the position
n
principal quantum number; describes energy level; as it increases the orbital and electrons energy increase
l
Defines the shape(type) of orbital; range 0 to n-1
m
describes 3D orientation of the orbital; range -l to l; spinning up +½ down -½
orbital
a region of probability where an electron can be found
s orbital
L is 0; Sphere shape; # of peaks = n; L or # of nodes (zero probability of finding an electron) = n-1
p orbital
L =1 ; infinity sign shaped
d orbital
L = 2; An x or infinity + donuts
f orbital
L=3; Complicated shapes
Pauli exclusion principle
No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers, No two electrons in the same atom can have the exact same energy
electron configuration
the way electrons are distributed in an atom
ground state
most stable organization and lowest possible energy
Hund’s rule
For a set of orbitals in the same sublevel there must be one electron in each orbital before pairing and the electrons have the same spin
Valence electrons
Elements in the same group of the periodic table with the same number of electrons in the outermost shell
core electrons (noble gases)
filled inner shell electrons
types of chemical bonds
Ionic (electrostatic attraction between ions), Covalent (sharing of electrons), Metallic (free electrons hold metal atoms together)
ionic bonding
between metals and nonmetals, very exothermic, 1 element readily gives up an electron (low ionization energy), Another element readily gains an electron (high electron affinity)