Physiological Psychology: Key Concepts and Disorders
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Hemispheric Lateralization
Lateralization is the localization of a function in one hemisphere or the other; for example, Broca's area on the left is for language while the right corresponds to singing.
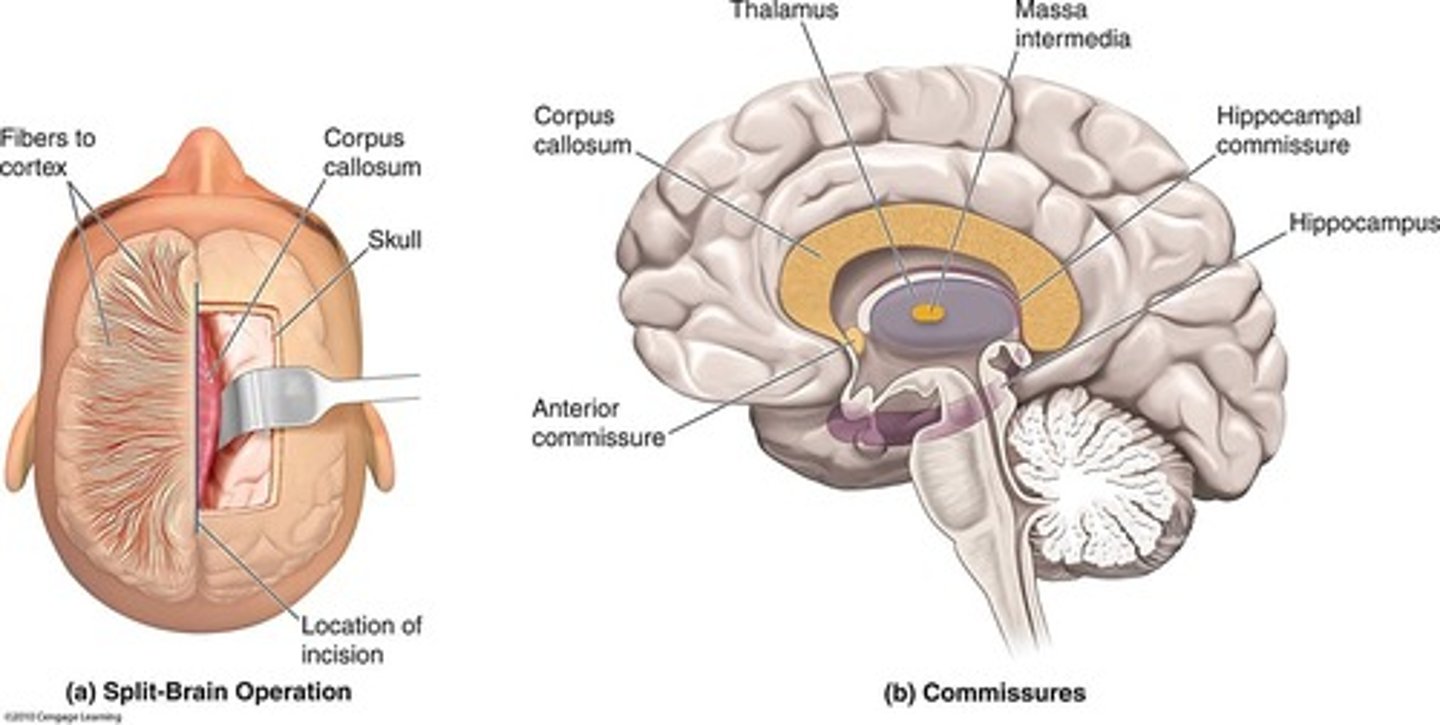
Split-Brain operation
Corpus callosotomy, where pathways connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres are severed to treat epilepsy, resulting in no change in personality, intelligence, or speech.
How is the Split-Brain Operation performed?
the cortex is retracted to access the corpus callosum, which is then severed; Joseph Bogen's classic procedure involved severing all four commissures.
Lateralization in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Research shows reduced lateralization in individuals with autism spectrum disorder compared to typical individuals.
Language
Defined as a system of communicating thoughts and feelings using arbitrary signals, such as sounds, gestures, or written signals, found in all human cultures.
Origins of language
No human culture exists without language; possible existence of an independent 'language module' in the brain and genes related to aspects of language (FOXP2) show important mutations about 100,000 years ago.
Patient Tan
Paul Broca's patient (real name Leborgne) experienced significant damage in Broca's area, indicating the importance of localization of language functions.
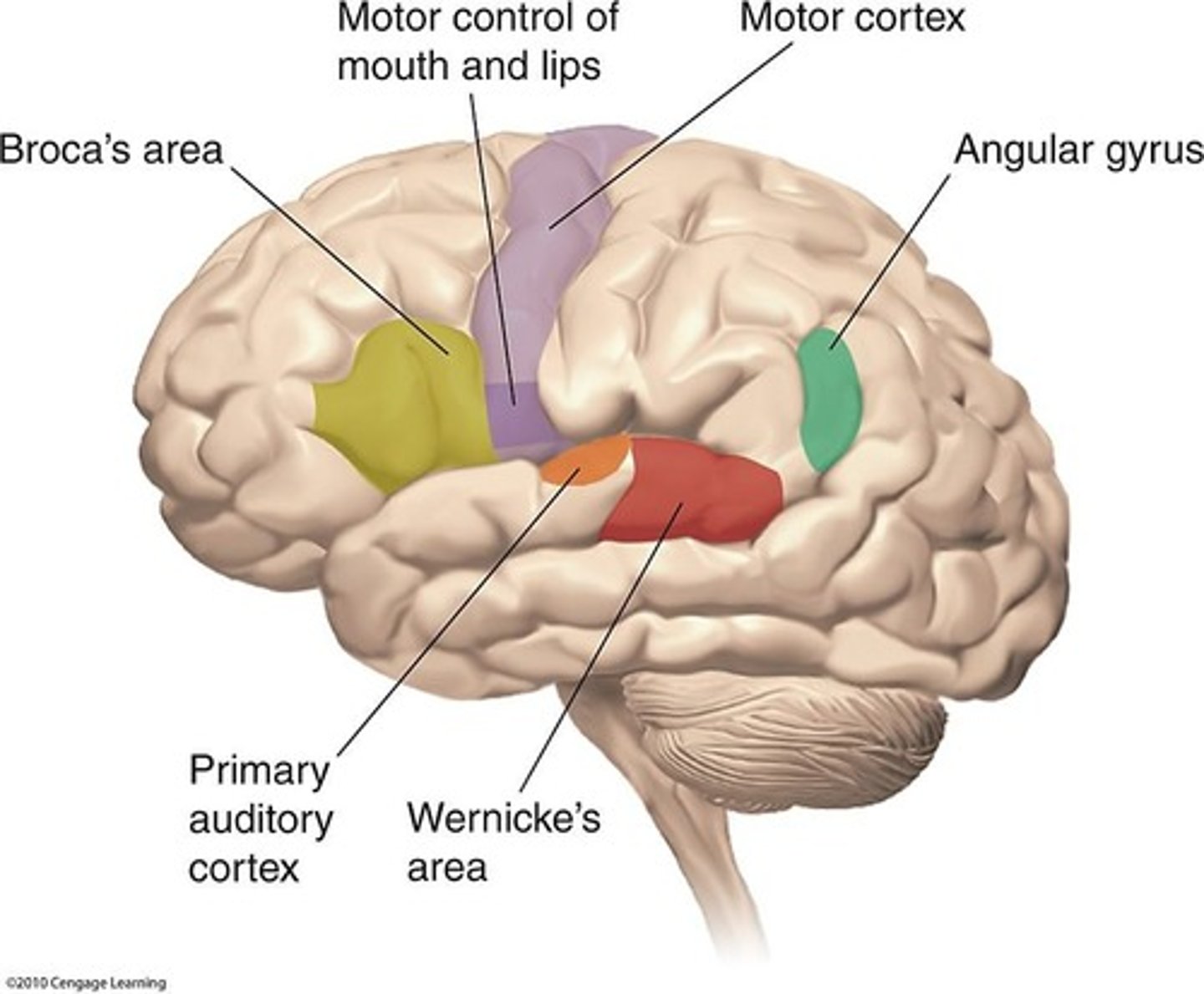
Broca's and Wernicke's Aphasias
Broca's aphasia is characterized by a lack of ability to speak clearly with slight deficits in comprehension, while Wernicke's aphasia features rapid and fluent speech that is meaningless with poor comprehension.
Conduction aphasia
Difficulty repeating speech. Damage to the arcuate fasciculus and the adjacent cortex. Speech remains fluent and comprehension is fairly good.
Difficulty repeating speech
Damage to the arcuate fasciculus and the adjacent cortex
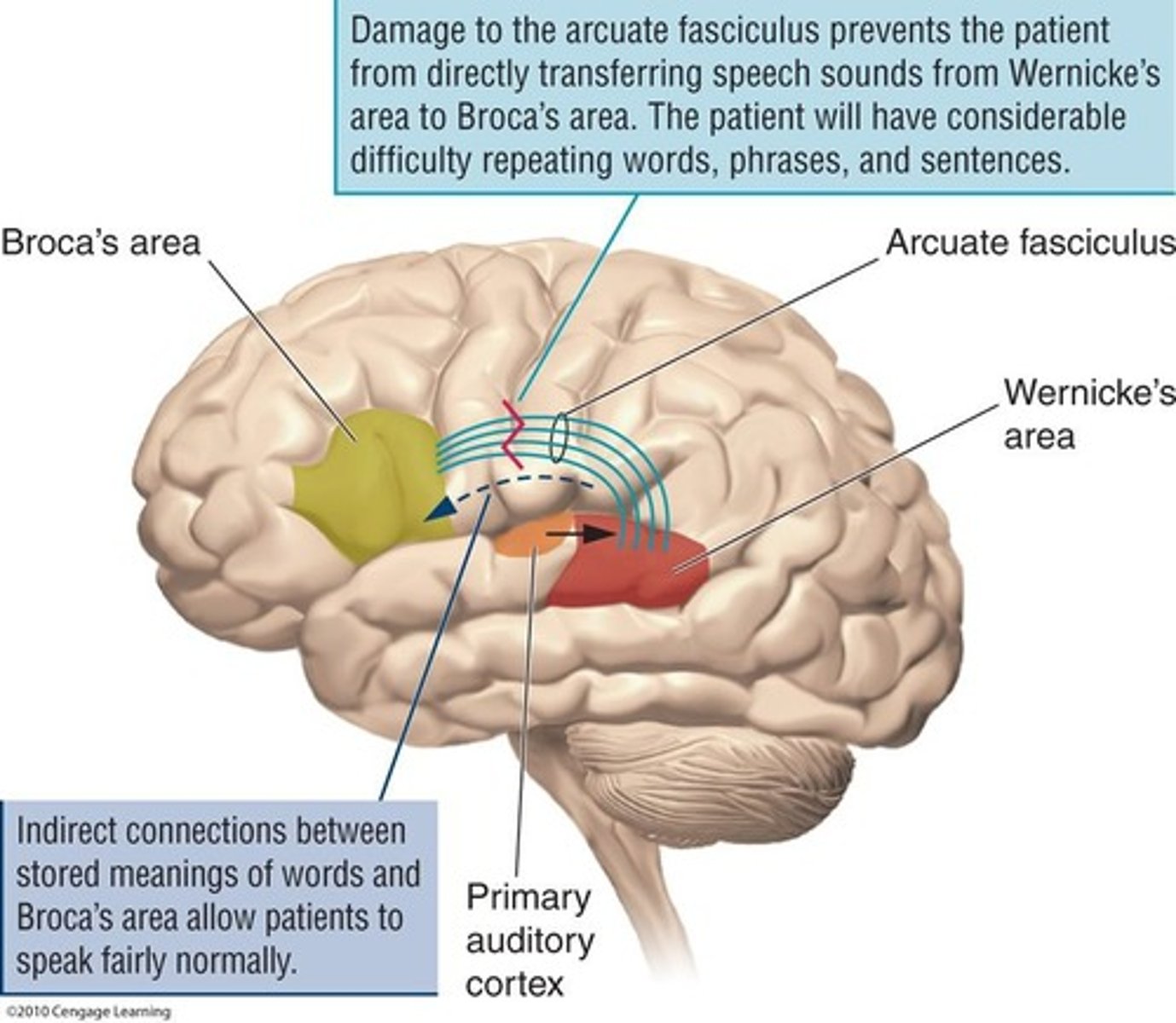
Global aphasia
Loss of all language functions
Transcortical aphasias
Types of aphasia characterized by the ability to repeat speech despite other language impairments
Transcortical motor aphasia
Speech is not fluent, but words can be repeated; affects higher cognitive aspects of speech production
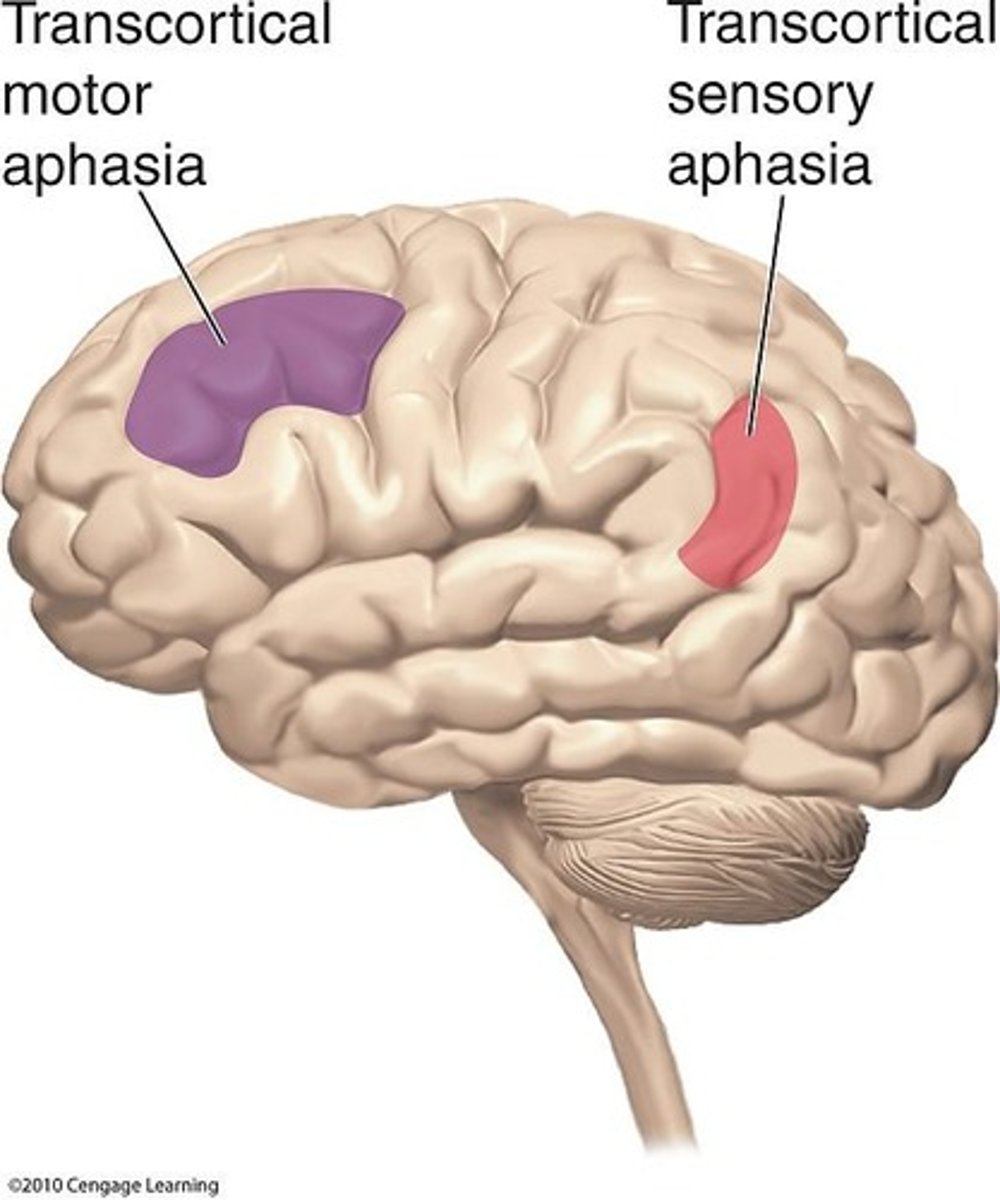
Transcortical sensory aphasia
Fluent speech with impaired cognition and deficits in word meanings
Alexia
Normal speech and comprehension but unable to read or recognize letters
Agraphia
Inability to write
Dyslexia
Most common learning disability characterized by difficulty learning to read, with a genetic component and related to asymmetry
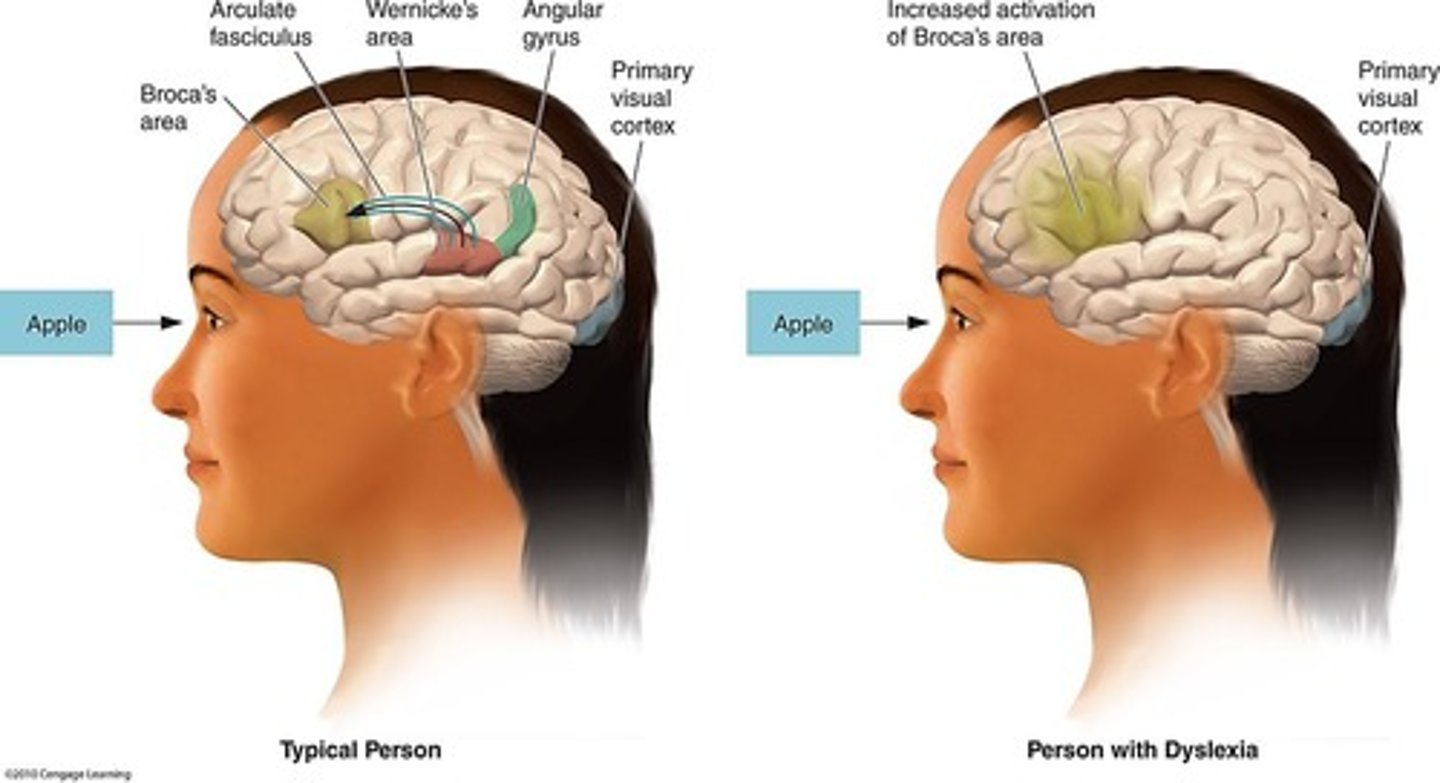
Phonological awareness
Overactivation of rostral language areas and lack of activation of posterior language areas
Stuttering
Producing repetitions or prolonging of sounds, primarily genetic in origin, more common in males
Network states of intelligence
Describes the brain in terms of modular organization, with contributions from most areas of the brain
Crystallized Intelligence
Use of knowledge that is easy to reach
Fluid Intelligence
Ability to manage novel situations such as problem-solving, identifying patterns, and reaction time, which is difficult to reach
Neuropsychologists
Licensed doctoral level clinical psychologists (PhD or PsyD) who complete specialized training and often work in collaboration with neurologists or neurosurgeons
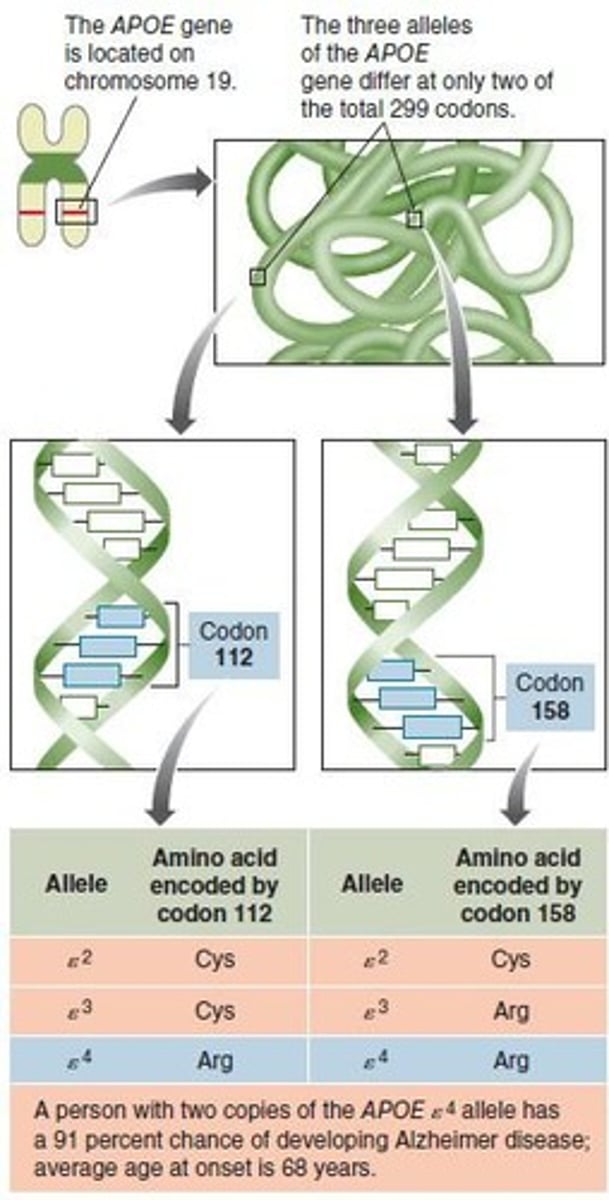
Genetic cause of Alzheimer's Disease
Risk increases with age; the e4 variant of the APOE gene increases risk significantly
Diagnostic methods for Alzheimer's Disease
Include autopsy, biomarkers in CSF and blood, PET and MRI scanning
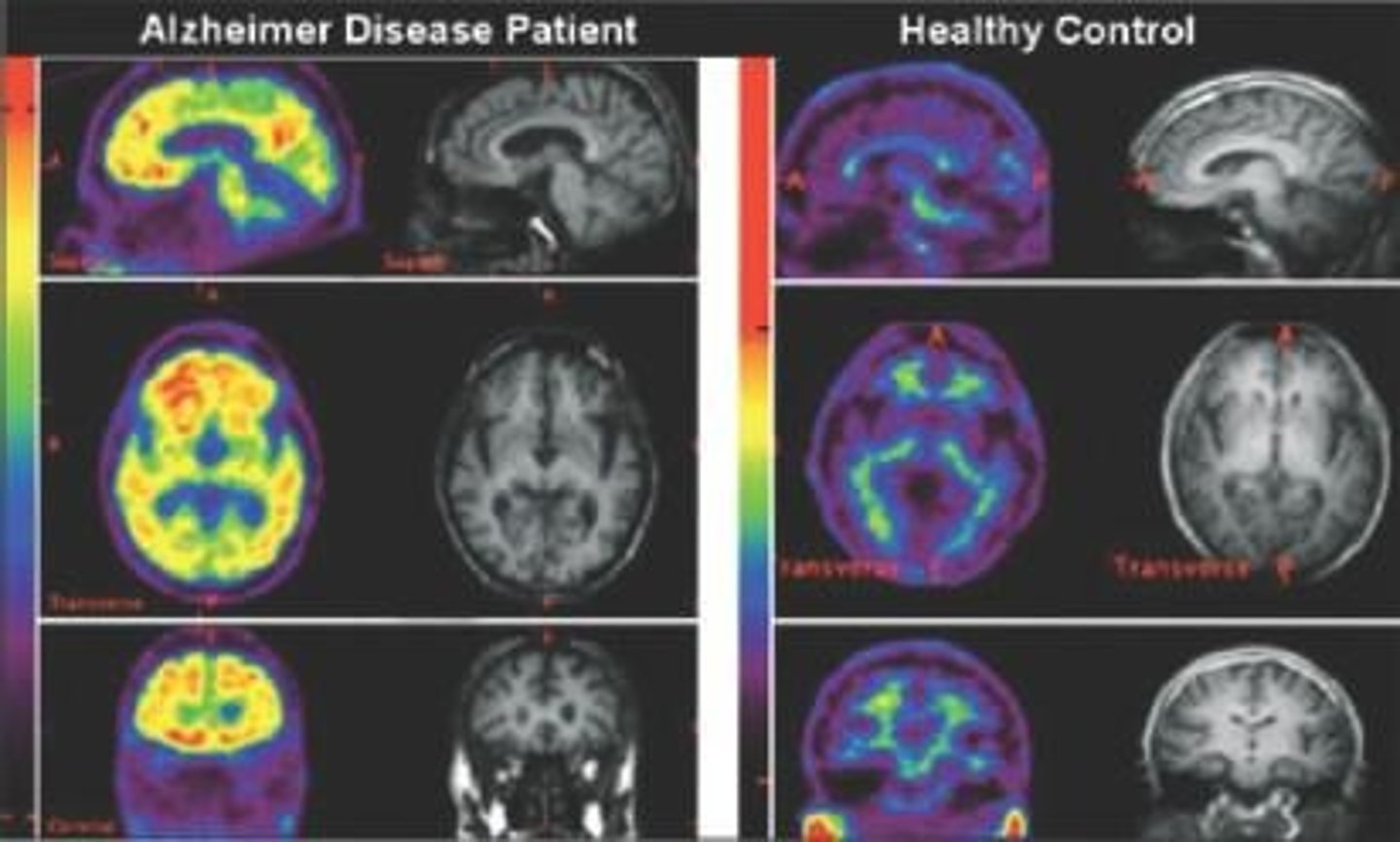
Amyloid plaques identification
Identified in the brain using a PET scan that shows much more amyloid in patients with Alzheimer's disease compared to healthy individuals
Vascular disease (Stroke)
Occurs when the brain's blood supply is interrupted
Transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
Mimic stroke symptoms and predict stroke
Types of Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Include physical damage to the brain from open head injuries and closed head injuries (concussions)
Open head injuries
Involve penetration of the skull and have worst consequences when affecting ventricles, both hemispheres, and multiple lobes of the brain
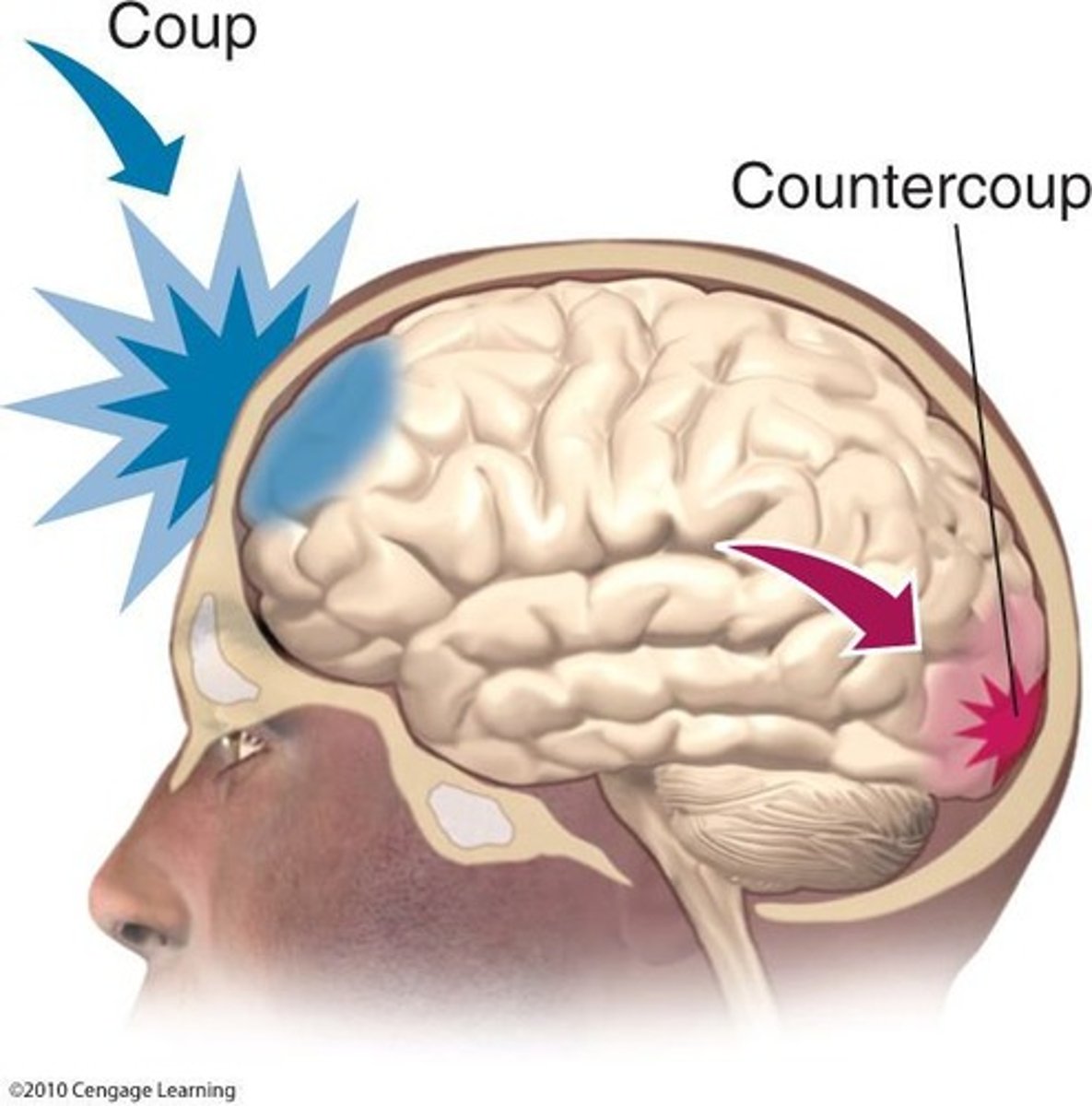
Closed head injuries
Result from a blow to the head, including coup and countercoup injuries
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
A condition more likely to develop in athletes, exemplified by the case of former NFL player Phillip Adams

Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
A condition that can produce a range of problems including dementia and impulsivity, often seen in sports with increased likelihood of head injuries.
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSEs)
Disorders resulting from abnormal proteins called prions.
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
Also known as mad-cow disease, a type of TSE.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
A rare prion disease that can be genetic or caused by infection from unclean surgical equipment.
Kuru
A prion disease similar to CJD that results from cannibalism.
Fatal Familial Insomnia
A genetic prion disease that leads to severe insomnia and ultimately death.
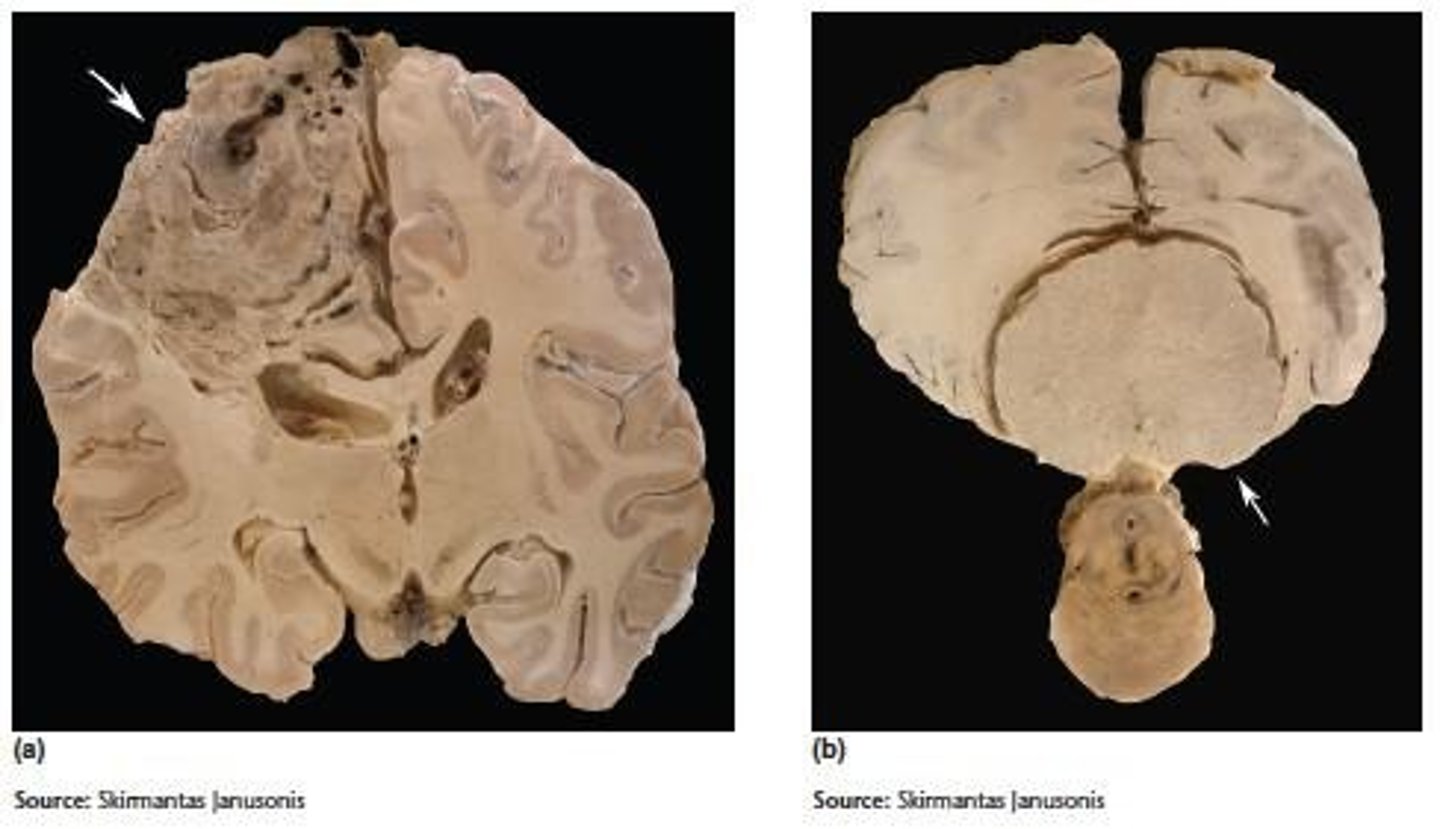
Brain Tumors
Independent growths of new tissue in the brain that lack purpose.
Primary Tumors
Rare tumors of the brain with unknown causes, but radiation is a risk factor.
Secondary Tumors
Tumors that arise from glial cells, meninges, and ependymal cells, and are the most common type of tumor until age 19.
Malignant Tumors
Tumors that can spread to other parts of the body.
Benign Tumors
Tumors that do not spread and are unlikely to return after removal.
Metastasis
The process by which tumors spread to the brain from other locations in the body.
Glioma
A tumor arising in glial cells.
Meningioma
A tumor that arises in the meninges that envelop the brain.
Treatment for Brain Tumors
Includes surgical removal, whole brain radiation, stereotaxic radiosurgery, ultrasound therapy, chemotherapy, thalidomide, and experimental delivery of stem cells with anticancer genes.
Neurocysticercosis
A condition caused by pork tapeworm eggs that can produce partial seizures.
Encephalitis
Inflammation of the brain after a viral infection, with herpes simplex being the most dangerous.
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges, which can be bacterial, viral (most common and least dangerous), or fungal (rare).
Epilepsy
A condition characterized by repeated, unprovoked seizures due to uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain.
Partial Seizures
Seizures that can be simple (no change in consciousness) or complex (altered consciousness).
Aura
A premonition of an impending seizure.
Generalized Seizures
Seizures that symmetrically affect both sides of the brain and include tonic-clonic and absence seizures.
Treatment for Epilepsy
Includes antiepileptic drugs (usually GABA agonists), surgery, and a ketogenic diet in children.
Multiple Sclerosis
An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks oligodendrocytes, leading to demyelination of axons.
Possible Causes of Multiple Sclerosis
Includes modest heritability, exposure to viruses (e.g., Epstein-Barr), and lack of vitamin D due to lack of sunlight.
left hemisphere
language and logical thought
right hemisphere
spatial processing
corpus callosotomy
split brain operation
Four commissures connect the two cerebral hemispheres
the corpus callosum, the anterior commissure, the massa intermedia, and the hippocampal commissure
dorsal pathway
connects the superior temporal gyrus, which contains both the primary auditory cortex and Wernicke’s area, to Broca’s area and the frontal operculum, a part of the frontal lobe.This pathway supports the conversion of sound to movements necessary for speech.
ventral pathway
connects the superior temporal sulcus to the inferior temporal gyrus and the middle temporal gyrus and supports the conversion of sound to meaning.
High activity here in stuttering
basal ganglia
How are Amyloid plaques identified in the brain in a living person?
PET scan
Broca’s aphasia
Lack of ability to speak clearly Slight deficits in comprehension Can still understand other people’s speech
Wernicke’s aphasia
Speech is rapid and fluent but meaningless. Poor comprehension. Can’t understand other people’s speech
Aphasia
A total or partial loss of the ability to either produce or comprehend spoken language.
Treatments for Stuttering
Reducing rates and which speech is produced and stress associated with the disordere
A stroke occurs when brain blood supply is interrupted by
Cerebral hemorrhage (balloon-like artery) or sudden blockage of a blood vessel
ischemia
low oxygen levels
infarct
area of dead tissue
Trombosis
blockage that does not move
Embolism
blockage that does move
Causes of sudden blockage of blood vessels
ischemia, infarct, transient ischemic attacks, thrombosis, embolism
coup
point of impactc
countercoup
point of second impactthat occurs on the opposite side of the brain from the original impact.
treatment for multiple sclerosis
medications slow progression, quit smoking and exercise
Types of Generalized Seizures
Tonic-clonic and absence
Tonic-Clonic
grand mal, violent complusions
Absence
petit mal, mild seizure with brief unconsciousness
earliest form of human language
click language