Benign Proximal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
•**B**ENIGN
•**P**AROXYSMAL
•**P**OSITIONAL
•**V**ERTIGO
•**P**AROXYSMAL
•**P**OSITIONAL
•**V**ERTIGO
==What does BPPV stand for?==
* B
* doesn’t cause further illness, not life-threatening
* P
* sudden and intense episodes
* P
* symptoms are triggered by changes in body position
* V
* false sense of you or your environment moving
* B
* doesn’t cause further illness, not life-threatening
* P
* sudden and intense episodes
* P
* symptoms are triggered by changes in body position
* V
* false sense of you or your environment moving
2
New cards
peripheral vs central
________ vestibular disorder (inner ear) vs. ________ vestibular disorder (brainstem…)
3
New cards
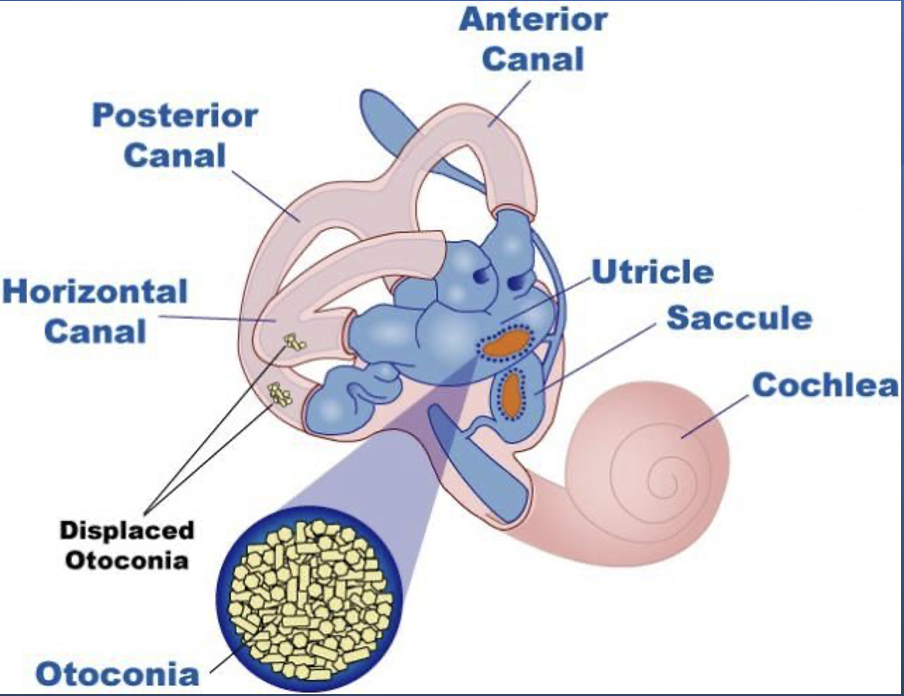
endolymph
free-floating particles in the ________ of the semicircular canals (SSC)
4
New cards
20 to 25
__% to __% of all vertigo is due to BPPV, most frequent cause of vertigo
5
New cards
otolith
==Results from damage to the. delicate sensory units of the:==
* Inner ear
* SSC
* ______ organs
* Inner ear
* SSC
* ______ organs
6
New cards
11 to 64
____ to ____ per 100,000
7
New cards
2\.4%
Lifetime prevalence =
8
New cards
54
Mean age at onset ____ years
\[11 to 84 is the documented range\]
* 50-70 is most common
\[11 to 84 is the documented range\]
* 50-70 is most common
9
New cards
64%
_____ women
10
New cards
bilateral
Most likely to be ________
\[95%\]
\[95%\]
11
New cards
15 to 50
__% to __% due to ear trauma or infection.
12
New cards
Episodic dizziness
Which is more common with BPPV:
* Persistent dizziness
* Episodic dizziness
* Persistent dizziness
* Episodic dizziness
13
New cards
rotational
Symptoms are often elicited by _______ movement of head rather than final position of head.
14
New cards
bone density
Pt’s with recurrent BPPV tend to have lower____ _____ scores
\[no evidence that treatment of osteoporosis impacts recurrent BPPV\]
\[no evidence that treatment of osteoporosis impacts recurrent BPPV\]
15
New cards
Symptoms
* dizziness
* vertigo
* lightheadedness
* imbalance/disequilibrium
* nausea
* postural instability
* vertigo
* lightheadedness
* imbalance/disequilibrium
* nausea
* postural instability
16
New cards
Dizziness
Vertigo
Lightheadedness
Imbalance/disequilibrium
Postural instability
Nausea
Vertigo
Lightheadedness
Imbalance/disequilibrium
Postural instability
Nausea
==BPPV Symptoms:==
DeVine LIP Ninjas
(DVLIPN)
DeVine LIP Ninjas
(DVLIPN)
17
New cards
Pt complaints
The illusion that you or your environment is moving or spinning.
Occurs with:
* rolls into a lateral position in bed
* gazing upward
* bending forward
* fast neck turn
\[Most common symptom\]
Occurs with:
* rolls into a lateral position in bed
* gazing upward
* bending forward
* fast neck turn
\[Most common symptom\]
18
New cards
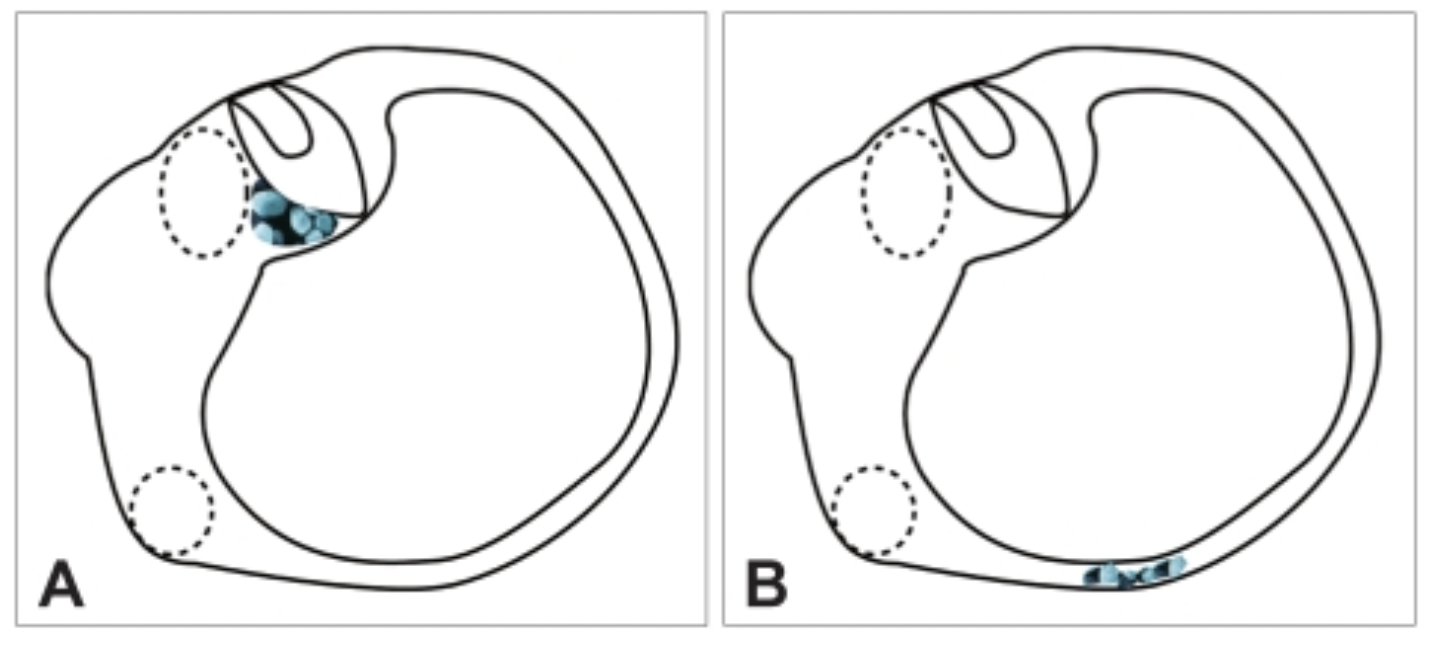
Canalithiasis
==B==
* Displacement of otoconia causing them to be free-floating in a semicircular canal
* ==Otoconia migrating into SSC==
* **Most common form of BPPV**
* Nystagmus:
* Later onset (10-40 seconds)
* A shorter duration of nystagmus will be seen
* Displacement of otoconia causing them to be free-floating in a semicircular canal
* ==Otoconia migrating into SSC==
* **Most common form of BPPV**
* Nystagmus:
* Later onset (10-40 seconds)
* A shorter duration of nystagmus will be seen
19
New cards
posterior
90
90
Canalithiasis most commonly occurs in the _____ canal __(______%)
* sends false signals to brain with head movement
* sends false signals to brain with head movement
20
New cards
Canalithiasis
Later onset nystagmus with a short duration occurs with ______
21
New cards
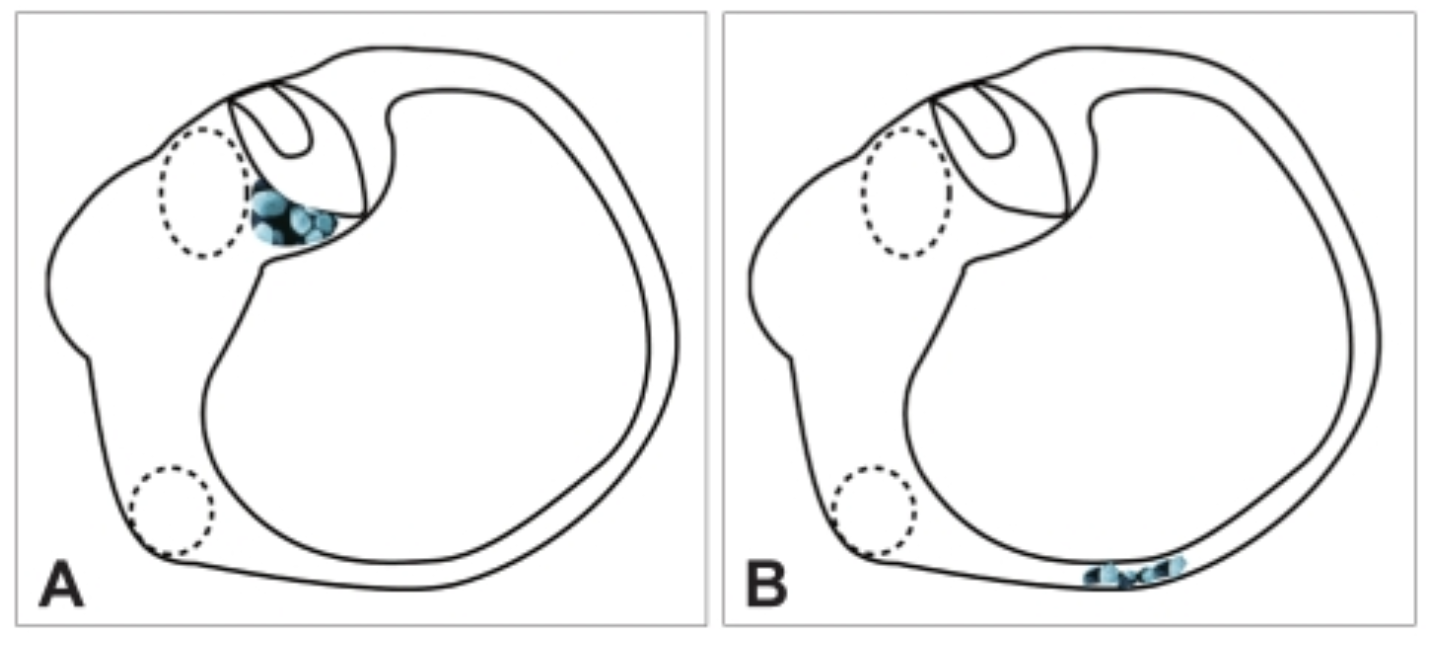
Cupulothiasis
==A==
* **Rare** form of BPPV
* Displacement of otoconia causing them to attach to the **cupula in a semicircular canal**
* Nystagmus:
* Immediate onset and longer duration of nystagmus will be seen
* **Rare** form of BPPV
* Displacement of otoconia causing them to attach to the **cupula in a semicircular canal**
* Nystagmus:
* Immediate onset and longer duration of nystagmus will be seen
22
New cards
Cupulothiasis
Nystagmus with immediate onset and long duration is associated with ______
23
New cards
Posterior Canal—90%
* Canalithiasis and cupulothiasis are causative factors
* Down side ear is affected during Dix-Hallpike
* ^^Geotropic (beating toward the earth)^^ rotary nystagmus
* Down side ear is affected during Dix-Hallpike
* ^^Geotropic (beating toward the earth)^^ rotary nystagmus
24
New cards
Anterior Canal—4%
* Up facing ear is provoked during Dix-Hallpike
* ^^Ageotropic (beating away from earth)^^
* ^^Ageotropic (beating away from earth)^^
25
New cards
Horizontal Canal -- 6%
* Best provoked by having patient lay flat in __**supine position and then move head quickly to the ear-down position**__
* (right and left)
* Horizontal geotropic nystagmus is observed while the patient is vertiginous (suffering from vertigo)
* (right and left)
* Horizontal geotropic nystagmus is observed while the patient is vertiginous (suffering from vertigo)
26
New cards
Head trauma
Labyrinthitis
Iatrogenic
Labyrinthitis
Iatrogenic
==Common causes of BPPV:==
* **______ ______** (most common cause of BPPV in people under 50)
* Degeneration of vestibular system (more common as people age)
* Viral
* **________**
* Prolonged Bed Rest
* **________:** following surgery or ototoxic medications
* **______ ______** (most common cause of BPPV in people under 50)
* Degeneration of vestibular system (more common as people age)
* Viral
* **________**
* Prolonged Bed Rest
* **________:** following surgery or ototoxic medications
27
New cards
Diagnostics
Vestibular case history
Videonystagmography (VNG)
Dix-Hallpike
Videonystagmography (VNG)
Dix-Hallpike
28
New cards
Videonystagmography (VNG
A battery of eye-movement tests given to people with dizziness, vertigo and/or balance disorders
* Identify or rule out other vestibular dysfunction or neurological problems
* Measures **nystagmus** (involuntary side-to-side eye movement) which helps distinguish type of BPPV
* Identify or rule out other vestibular dysfunction or neurological problems
* Measures **nystagmus** (involuntary side-to-side eye movement) which helps distinguish type of BPPV
29
New cards
Dix-Hallpike
* Standard clinical test for BPPV
* Helps reveal which canal is involved
* Differentiate canalithiasis or cupulolithiasis
* Steps for Pt:
* Turn head 45 degrees toward presumed affected side
* Clinician rapidly brings pt from upright to supine position with head hanging off table
* Particles will drift into posterior canal—nystagmus occurs within 10 seconds and fatigues within 30 seconds
* Pt is returned to upright position
\
* Helps reveal which canal is involved
* Differentiate canalithiasis or cupulolithiasis
* Steps for Pt:
* Turn head 45 degrees toward presumed affected side
* Clinician rapidly brings pt from upright to supine position with head hanging off table
* Particles will drift into posterior canal—nystagmus occurs within 10 seconds and fatigues within 30 seconds
* Pt is returned to upright position
\
30
New cards
Positive
______ Dix-Hallpike with the presence/recording of a burst of nystagmus.
31
New cards
VNG
* Can help with detecting presence and timing of nystagmus
* Caloric test is abnormal in 32 to 47% (Valente, p652)
* Caloric test is abnormal in 32 to 47% (Valente, p652)
32
New cards
Infrared nystagmography
Torsional eye movement can be detected directly
33
New cards
Posturography
Often abnormal but follow no predictable or diagnostic pattern
34
New cards
Audiogram
* often normal
* cochlea not affected
* cochlea not affected
35
New cards
Canalolithiasis of the posterior canal
(pc-BPPV)
(pc-BPPV)
* Recurrent attacks1 of positional vertigo or positional dizziness __**provoked by lying down or turning over in the supine position.**__
* Duration under ***
* Duration under ***
36
New cards
Canalolithiasis of the horizontal canal (hc-BPPV)
* Recurrent attacks of positional vertigo or positional dizziness __**provoked by lying down or turning over in the supine position.**__
* Duration ***
* Duration ***
37
New cards
2\.3. Cupulolithiasis of the horizontal canal (hc-BPPV-cu)
* Recurrent attacks of positional vertigo or positional dizziness provoked by lying down or turning over in the supine position.
* Positional nystagmus elicited after a brief latency or no latency by the supine roll test,
* Beating __horizontally toward the uppermost ear with the head turned to either side__ (apogeotropic (*ageotropic*) direction changing nystagmus)
* Lasting ***>*** **1 min**
* Positional nystagmus elicited after a brief latency or no latency by the supine roll test,
* Beating __horizontally toward the uppermost ear with the head turned to either side__ (apogeotropic (*ageotropic*) direction changing nystagmus)
* Lasting ***>*** **1 min**
38
New cards
Probable benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, spontaneously resolved
* Recurrent attacks of positional vertigo or positional dizziness provoked by lying down or turning over in the supine position.
* Duration of attacks ***
* Duration of attacks ***
39
New cards
Watchful waiting
* Benign so can resolve on its own
* Or over weeks or months
* Or over weeks or months
40
New cards
Vestibulo suppressant medication
* provides minimal relief to some patients
* does not stop vertigo
* does not stop vertigo
41
New cards
Canalith repositioning
* first choice in treatment
* cure rate of approximately 80%
* cure rate of approximately 80%
42
New cards
Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy (VRT)
* desensitizes balance system to movements that provoke symptoms
* exercises may increase symptoms at first but will diminish later
* exercises may increase symptoms at first but will diminish later
43
New cards
30 sec to 2 min
Each position in a manuerver is held for _________
Maneuvers:
* Epley maneuver
* Semont liberatory maneuver
* Brandt-Daroff exercises
Maneuvers:
* Epley maneuver
* Semont liberatory maneuver
* Brandt-Daroff exercises
44
New cards
Epley maneuver
* Relocate debris from SSC into the vestibule through a sequence of head movements.
* Patients with posterior, anterior, and horizontal canalithiasis
* Patients with posterior, anterior, and horizontal canalithiasis
45
New cards
Semont liberatory maneuver
* Patients with anterior and posterior cupulolithiasis
* Not common in U.S \~90% success rate after 4 sessions
* Not common in U.S \~90% success rate after 4 sessions
46
New cards
Brandt-Daroff exercises
* Patients with horizontal cupulolithiasis
* Use when side of BPPV is unclear
* 95% success rate
* Use when side of BPPV is unclear
* 95% success rate
47
New cards
Surgical Tx
Posterior canal plugging
Singular nerve section
Singular nerve section
48
New cards
Posterior canal plugging
* Only indicated for patients when both **office maneuvers and home exercises were ineffective**
* Block posterior canal without affecting functions of other canals or parts of the ear
* 3% risk of unilateral hearing loss 85-90% success rate
* Block posterior canal without affecting functions of other canals or parts of the ear
* 3% risk of unilateral hearing loss 85-90% success rate
49
New cards
Singular nerve section
Alternative to plugging
50
New cards
51
New cards
75
____% recovery rate in BPPV more than 6 months
52
New cards
97
____% recovered when sought treatment within one week
53
New cards
33
____% of patients will have a recurrence in the first year after treatment
54
New cards
50
____% will have recurrence within 5 years