(41) MCAT Behavioral Science: Chapter 1 - Biology and Behavior Lecture (1/4)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Neuropsychology
The study of the relationship between brain function and behavior.
Phrenology and who made it?
The doctrine that specific brain areas correspond to specific psychological traits would expand. Franz Gall
Pierre Florence
First person to study the major function of the brain. The brain had specific parts for specific functions and when removed affects the function
William James and what did he created
Father of American psychology and created Functionalism
Functionalism
A psychological approach that focuses on how mental processes help individuals adapt to their environment.
Paul Brocca
Specific functional impairments could be linked with specific brain legions. (Founder of the Broca’s area)
Broca's area
A region in the left side of the brain that is associated with speech production.
Herman Van Helmoltz
First to measure the speed of nerve impulse.
Types of Nerve cells (3)
Sensory neurons
Motor neurons
Interneurons
Sensory Neurons
(afferent neurons) transmits sensory information from receptors to the spinal cord
motor neurons
efferent: transmits information from the brain & spinal cord to muscles and glands
interneurons
found between other neurons are the most numerous
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
Somatic: consist of sensory or motor neurons distributed through the skin and motor muslces
autonomic ( sympathetic and parasympathetic) manages involuntary muscles associated with internal muscles and glands and helps maintain body temp
Autonomic nervous system
A part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary functions such as heartbeat and digestion.
Sympathetic nervous system
A branch of the autonomic system that prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses.
accelerates heart rate and inhibit digestion
Parasympathetic nervous system
A branch of the autonomic system responsible for 'rest and digest' activities.
conserve energy
constricts pupil
decelerates heart rate and increases digestion
Hindbrain
The part of the brain responsible for basic life functions such as breathing and heart rate, and sleeping.
during fetal stage, it is the thombencephalon
contains cerebellum, medulla oblongata, and rencular formation
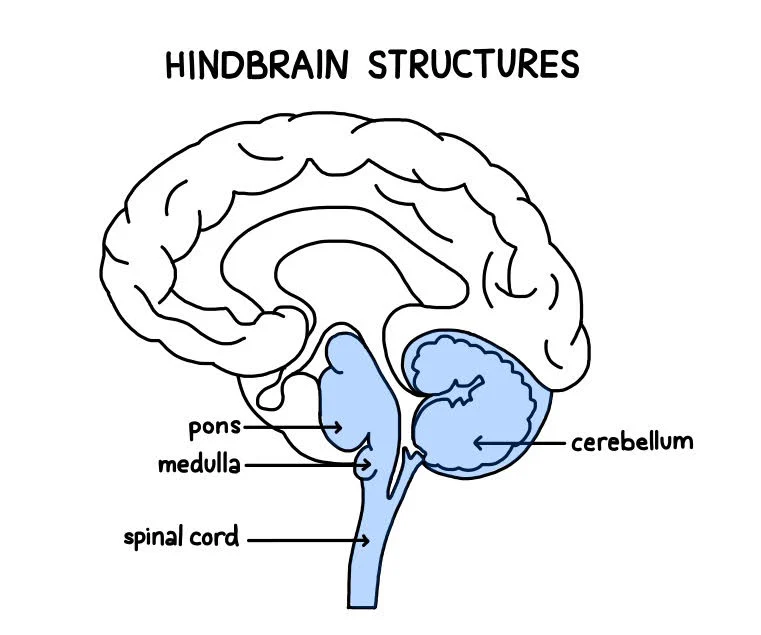
myelencephalon
medulla oblangata
metencephalon
pons and cerebellum
what happens if your cerebellum is damaged
you loose balance and your speech could be slurred
Midbrain
The part of the brain involved in controlling sensory and motor functions and involuntary reflexes.
in fetal stage it is the mesencephalon
Forebrain
part of the brain associated with complex functions such as emotion, memory, and higher cognitive functions.
Cerebral spinal fluid
A clear fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord.
Meninges
The three protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons
Neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons, primarily found in the brain and spinal cord.
Extirpation
A method that involves surgically removing brain areas to study their function.
Electrodes
Devices used to stimulate or record electrical activity in the brain.
Reflex arc
A neural pathway that controls an immediate response to a sensory stimulus.
Dura mater
The outermost layer of the meninges, providing a tough protective covering for the brain.
Thalamus
A brain structure that acts as a relay station for incoming sensory information.
All senses except for smell
Hypothalamus
A brain region that controls various bodily functions and regulates homeostasis.
also for emotional experiences, aggressive behavior and sexual behavior
Lateral hypothalamus
triggers eating and drinking
What happens if the lateral hypothalamus is destroyed
the person will lack hunger, the lateral hypothalamus helps the person to be hungry
Ventromedial Hypothalamus?
What happens when they are destroyed
what could it lead to
It tells someone when they are full
when they are destroyed it leads to not knowing when you are full
this could lead to obesity
Anterior Hypothalamus
sexual arousal
if damaged they become asexual
Posterior Pituitary
site of release for the hypothalamic hormon antidiuretic hormone ADH and oxytocin
Pineal Gland
what hormones does it release
a key player in several biological rhythms
melatonin
melatonin
hormone that regulates circadian rhythm
Basal ganglia
coordinate muscle movement as they receive information from the cortex. help make our movements smooth and posture steady
Limbic System
1) septal Nuclei; one of the primary pleasure centers of the brain
2) amygdala; role in defensive and aggressive behavior
3) Hipocampus: learning and memory process
What are the two types of amnesia
retrograde amnesia: unable to recall events in the past but they can usully form new memories.
anterograde amnesia: you remember past memories but you cant make any new memories
Frontal Lobe
comprised of two regions
prefrontal lobe
motor cortex
broccas areas: speech production
prefrontal lobe:
executive function supervises other brain region ( perception, emotion, long term planning). if damaged they can become impulsive or depressed
motor cortex
initiates voluntary motor movements by sending neural impulses down the spinal cord towards the muscle
Parietal Lobe
-destination for all incoming sensory information for touch, temperature, pain
-spacial awarnes and manipulation
Occipital Lobe
visual cortex
temporal lobe
auditory cortex - hearing
wrenicks area- language comprehension
contralateral comunication
one side of the brain communicated with the oposite side of the body
ex: the left brain controls the right side of the body
ipsilateral
one side of the brain interacts with the same side of the body
Dominant hemisphere
the left side of the brain
primary analytic
nondominant hemispher
right
associated with intuition and creativity and spatial processing
Neurotransmitters (7) Andino Eats Good Sour Grapes Every Day
Acetylcholine
Epinephrin
Gaba glycine
Serotonin
Glutamate
Endorphines
Dopamine
Acetylcholine
voluntary muscle control, attention, alertness, parasympathetic nervous system,
Epinephrine
Fight or flight response, wakefulness, alertness
Dopamine
smooth movement, postural stability
Serotonin
mood sleep eating and dreaming
Gaba and glycine
brain stablization
Glutamate
brain excitation
endorphins
natural pain killer
Endocrine system
is it faster than the nervous system
uses hormones
no the endocrine system is slower b/c the hormones travel through the blood stream
Pituatary Gland
secretes hormones
anterior
posteriar
adrenal glands
medula (epinephrine)
adrenal cortex ( cortisol, and sex hormones)
Gonads
Sexual Glands
increasing estrogen in females and testosterone in men
innate behavior vs learned behavior
Genetically programmed, it is seen in all individuals regardless of environment or experience.
learned behavior is not based on heredity but instead on experience and environment
Family studies
and whats the flaw with these studies
rely on the assumption that genetically related individuals are going to be more similar than unrelated individuals
the flaw is they cant pinpoint if a behavior is based on the environment or genetics because family tend to live together while having similar genetics
twin studies
studies genetic component on how strong it is on behavior between twins
adoptive studies
helps us to understand environmental influences on behavior, comparing biological relatives to adoptive child or with their adoptive parents