ADMN201: Introduction to Business Studies (Rev. 5)
1/203
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Athabasca University - 2025 - This is for chapter 1-7, specifically for the midterm for this course.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
204 Terms
Profit
What remains (if anything) after a business’s expenses are subtracted from it’s sales revenue.
Not For Profit Organization
An organization that provides goods and services to customers but does not seek to make a pro whiles doing so.
Economic System
the way in which a nation allocates it's resources among it’s citizens.
Factors of Production
The resources used in the production of goods and services, including land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Labour
The human effort, both physical and mental, used in the production of goods and services.
Capital
The financial resources and assets used to fund production and operations in a business, including machinery, buildings, and money.
Entrepreneurs
Individuals who organize, manage, and assume the risks of a business, often innovating and driving economic growth.
Natural Resources
The raw materials and environmental resources used in the production of goods and services, including land, water, and minerals.
Command Economy
An economic system in which the government controls all or most factors of production and makes all or most production decisions.
Market Economy
An economic system in which individuals control all or most factors of production and make all or most production decisions.
Market
An exchange process between buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.
Input Market
Firms buy the resources they need for the production of goods and services.
Output Market
Firms supply goods and services in response to demand on the part of consumers.
Capitalism
An economic system in which markets decide what, when, and for whom to produce.
Mixed Market Economy
An economic system with elements of both a command economy and a market economy, which in practice is typical of most nations’ economies.
Privatization
The transfer of activities from the government to the private sector.
Deregulation
A reduction in the number of laws affecting business activity.
Competition Act
Prohibits a variety of business practices that lessen competition.
Lobbyist
A person hired by a company or an industry to represent its interests with government officials.
Trade association
An organization dedicated to promoting the interests and assisting the members of a particular industry.
Demand
The willingness and ability of buyers to purchase a product or service.
Supply
The willingness and ability of producers to offer a good or service for sale.
Law of demand
The principle that buyers will purchase (demand) more of a product as the price drops.
Law of supply
The principle that producers will offer (supply) more of a product as the price rises.
Demand and supply schedule
Assessment of the relationships between different levels of demand and supply at different price levels.
Demand curve
A graph showing how many units of a product will be demanded (bought) at different prices.
Supply curve
Graph showing how many units of a product will be supplied (offered for sale) at different prices.
Market price (equilibrium price)
Profit-maximizing price at which the quantity of goods demanded and the quantity of goods supplied are equal.
Surplus
A situation in which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
Private enterprise
An economic system characterized by private property rights, freedom of choice, profits, and competition.
Private Property
Ownership of the resources used to create wealth is in the hands of individuals.
Freedom of Choice
You can sell your labour to any employer you choose. You can also choose which products to buy, and producers can usually choose whom to hire and what to produce.
Competition
Competition is evident when two or more businesses compete for the same resources or customers.
Perfect Competition
A market or industry characterized by a very large number of small firms producing an identical product so that none of the firms has any ability to influence price.
Monopolistic Competition
A market or industry characterized by a large number of firms supplying products that are similar but distinctive enough from one another to give firms some ability to influence price.
Oligopoly
A market or industry characterized by a small number of very large firms that have the power to influence the price of their product or resources.
Monopoly
A market or industry with only one producer that can therefore set the prices of its products and resources.
External Environment
Everything outside an organization’s boundaries that might affect it.
Economic Environment
Conditions of the economic system in which an organization operates.
Aggregate Output
The total quantity of goods and services produced by an economic system during a given period.
Business Cycle
Pattern of short-term ups and downs (expansions and contractions) in an economy.
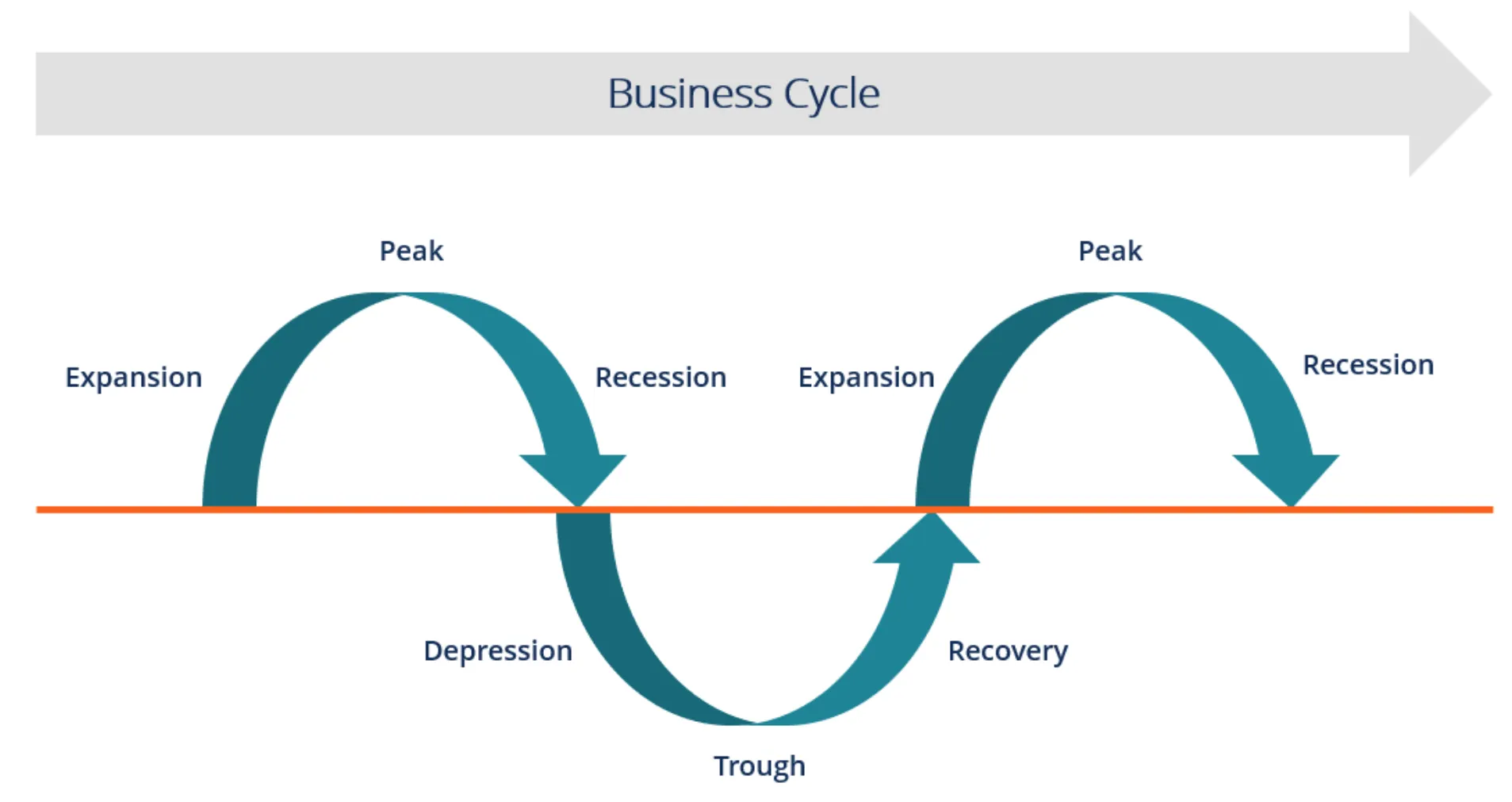
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The total value of all goods and services produced within a given period by a national economy through domestic factors of production.
Gross national product (GNP)
The total value of all goods and services produced by a national economy within a given period, regardless of where the factors of production are located.
GDP per capita
Gross domestic product per person.
Real GDP
GDP is calculated to account for changes in currency values and price changes.
Purchasing power parity
The principle that exchange rates are set so that the prices of similar products in different countries are about the same.
Productivity
A measure of economic growth that compares how much a system produces with the resources needed to produce it.
Balance of Trade
The total of a country’s exports (sales to other countries) minus its imports (purchases from other countries).
National Debt
The total amount of money that a country owes its creditors.
Budget Deficits
The result of the government spending more in one year than it takes in during that year.
Inflation
The occurrence of widespread price increases throughout an economic system.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
A measure of the prices of typical products purchased by consumers living in an urban area.
Deflation
A period of generally falling prices.
Unemployment
The level of joblessness among people actively seeking work in an economic system.
Fiscal policies
Policies whereby governments collect and spend revenues.
Monetary policies
Policies whereby the government controls the size of the nation’s money supply.
Research and development (R&D)
Those activities are necessary to provide new products, services, and processes.
Political–legal environment
Conditions reflecting the relationship between business and government, usually in the form of government regulation.
Sociocultural Environment
Conditions include the customs, values, attitudes, and demographic characteristics of the society in which an organization operates.
Michael Porter’s 5 Forces
Suppliers, buyers, substitutes, rivalry, and the threat of entrants.
Outsourcing
Strategy of paying suppliers and distributors to perform certain business processes or to provide needed materials or services.
Business process management
An approach by which firms move away from department-oriented organization and toward process-oriented team structures that cut across old departmental boundaries.
Acquisition
The purchase of a company by another, larger firm that absorbs the smaller company into its operations.
Merger
The union of two companies to form a single new business.
Poison Pill
A defence that management adopts to make a firm less attractive to an actual or potential hostile suitor in a takeover attempt.
Divestiture
Occurs when a company sells part of its existing business operations to another company.
Spinoff
Strategy of setting up one or more corporate units as new, independent corporations.
Strategic alliance
An enterprise in which two or more persons or companies temporarily join forces to undertake a project.
Business Ethics
Ethical or unethical behaviours by a manager or employee of a business.
Managerial Ethics
Standards of behaviour that guide individual managers in their work.
Conflict of interest
Occurs when an activity benefits the employee at the expense of the employer.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
The idea is that a business should balance its commitments to individuals and groups that are directly affected by the organization’s activities.
Fair-trade movement
A movement designed to help workers in developing countries receive fair payments for their work.
Organizational stakeholders
Groups, individuals, and organizations that are directly affected by the practices of an organization and that therefore have a stake in its performance.
Consumerism
A social movement that seeks to protect and expand the rights of consumers in their dealings with businesses.
Whistle-blower
An individual who calls attention to unethical, illegal, or socially irresponsible practices on the part of a business or other organization.
Insider trading
The use of confidential information to gain from the purchase or sale of stock.
Social audit
A systematic analysis of how a firm is using funds earmarked for social responsibility goals and how effective these expenditures have been.
Sustainable development
Activities that meet current needs but will not put future generations at a disadvantage when they try to meet their needs.
Small business
An independently owned and managed business that does not dominate its market.
New venture
A recently formed commercial organization that provides goods and/or services for sale.
Entrepreneurship
The process of identifying an opportunity in the marketplace and accessing the resources needed to capitalize on it.
Entrepreneur
A businessperson who accepts both the risks and the opportunities involved in creating and operating a new business venture.
In-trepreneurs
People who create something new within an existing large firm or organization.
Private sector
The part of the economy made up of companies and organizations not owned or controlled by the government.
Sales forecast
An estimate of how much of a product or service will be purchased by prospective customers over a specific period.
Franchise
An arrangement that gives a franchisee (the buyer) the right to sell the product of the franchiser (the seller).
Business plan
A document in which the entrepreneur summarizes their business strategy for the proposed new venture and how that strategy will be implemented.
Bootstrapping
Doing more with less.
Franchising agreement
Stipulates the duties and responsibilities of the franchisee and the franchiser.
Collateral
Assets that a borrower uses to secure a loan or other credit and that are subject to seizure by the lender if the loan isn’t repaid according to the specified repayment terms.
Sole proprietorship
Businesses are usually owned and operated by one person who is responsible for all of its debts.
Unlimited liability
A person who invests in a business is liable for all debts incurred by the business; personal possessions can be taken to pay debts.
Partnership
A business with two or more owners who share in the operation of the firm and in financial responsibility for the firm’s debts.
General Partner
A partner who is actively involved in managing the firm and has unlimited liability.
Limited Partner
A partner who generally does not participate actively in the business and whose liability is limited to the amount invested in the partnership.
Corporation
A business considered by law to be a legal entity separate from its owners with many of the legal rights and privileges of a person; a form of business organization in which the liability of the owners is limited to their investment in the firm.
Shareholders
Investors who buy shares of ownership in the form of stock.
Common stock
Shares whose owners usually have last claim on the corporation’s assets (after creditors and owners of preferred stock) but who have voting rights in the firm.
Board of directors
A group of individuals elected by a firm’s shareholders and charged with overseeing and taking legal responsibility for, the firm’s actions.