Cell Biology Lecture Notes - Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts from a cell biology lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Microscopy
Tool used to study cells
Robert Hooke
Observed cell walls in 1665
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
Crafted glass lenses able to visualize living cells
Light microscopy (LM)
Visible light passes through the specimen and then through glass lenses to magnify the specimen.
Magnification
Ratio of an object’s image size to its real size
Resolution
Measure of clarity of image; minimum distance 2 points can still be distinguished as separate
Contrast
Difference in brightness between light and dark areas of an image
Electron microscopy
Focuses a beam of electrons through the specimen or onto its surface
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Useful for the study of the topography of a specimen using a beam that scans the surface coated in a thin film of gold.
Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Used to study the internal structure of cells by aiming an electron beam through a very thin section of the specimen stained with heavy metals.
Cytology
Study of cell structure
Biochemistry
Study of functions/chemical processes (metabolism) of cells.
Cell fractionation
Takes cells apart and separates major organelles and other subcellular organelles from one another.
Centrifuge
Spins test tubes holding mixtures of disrupted cells at a series of increasing speeds.
Prokaryotes
Bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotes
Protists, fungi, animals and plants
Cytosol
Semi-fluid, jelly-like substance where subcellular components are suspended
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotes where DNA is concentrated and that isn’t membrane bound
Plasma membrane
Separates external environment from internal environment
Nucleus
Contains most of the genes of eukaryotes
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding nucleus
Nuclear lamina
Protein filaments that maintain nuclear shape
Nuclear pores
Allow proteins and RNA to move in and out of the nucleus
Chromatin
30% DNA, 60% histone proteins, 10% RNA
Nucleoli
rRNA produced here/Sites of ribosome assembly
Ribosomes
Protein factories
Endomembrane system
Membranes within the eukaryotic cell
Vesicle
Sacs made of membrane used for transport
Endomembrane system function.
Metabolism, transportation of proteins, proteins synthesis, movement of lipids and detox of poisons
Endoplasmic reticulum
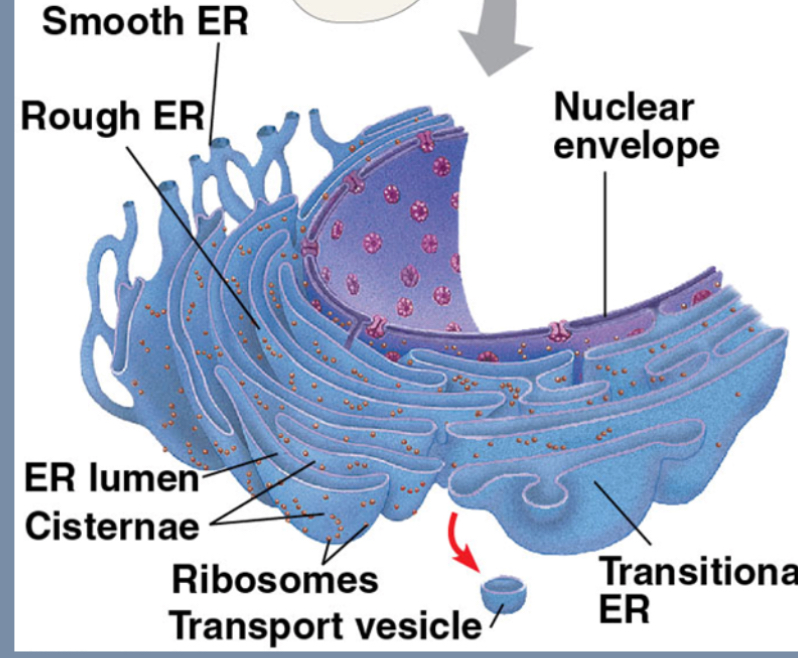
Endoplasmic reticulum
Extensive system of tubes enclosing fluid-filled cavities (cisternae)
Smooth ER functions
Lipid synthesis (oils, steroids and phospholipids), carbohydrate metabolism, and detox
Rough ER functions
Receives proteins produced by ribosomes/Makes membranes allowing cell to grow or form transport vesicles (makes phospholipids)
Glycoproteins
Secretary proteinsin the ER lumen with carbohydrates bound
Golgi apparatus
Stack of thin membranous sacs and small vesicles
Golgi apparatus role
Traffic director of cellular proteins
•Modify, concentrate, and package proteins and lipids made in RER
•Transport vesicles from RER fuse to cis face of Golgi and shipped on trans face
Lysosomes and vesicles
Vesicles fuses with lysosomes and digestion occurs
Lysosomes
Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes
Phagocytosis
Engulf small food particles and bring into cell as vacuoles
Digestion products
Simple sugars, amino acids and other monomers
Autophagy
Degrade worn-out organelles
Vacuoles
Large vesicles derived from ER and Golgi
Food vacuole
Formed by phagocytosis
Contractile vacuoles
In unicellular eukaryotes, pump excess water out of the cell to maintain suitable ion and molecule concentration
Central vacuole
In plant cells, develops by joining of several smaller vacuoles
Mitochondria
Cellular respiration/ATP production site
Chloroplasts
In plants and algae, photosynthesis site
Endosymbiont theory
early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed an oxygen-using non-photosynthetic prokaryotic cell
Mitochondria membranes
Outer is smooth; Inner is folded to form cristae where ATP synthesis occurs
Thylakoids
Flattened interconnected sacs creating membrane system in chloroplast
Granum
Fluid in thylakoids
Stroma
Fluid outside thylakoids that has chloroplast DNA and enzymes
Peroxisomes
Specialized metabolic compartment containing enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms from molecules and transfer them to oxygen to produce H2O2
Glyoxysomes
Found in fat-storing tissues of plant seeds and are used for energy until plant can produce own energy via photosynthesis
Cytoskeleton
Network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
Cell motility
Changes in cell location and movements of cell parts
Microtubules
Hollow rods constructed from tubulin
Centrosome
Region near nucleus where microtubules grow out from
Centrioles
Pair found within the centrosome composed of nine sets of triplet microtubules arranged in ring
Cilia and flagella
Microtubule–containing extensions that project from some cells
Dyneins
Large motor proteins attached along each outer microtubule doublet allow bending
Microfilaments/actin filaments
Thin solid rods built from molecules of globular protein, actin
Plasma membrane
Creates the cortex, a more gel-like substance than liquid-like substance of cytoplasm
Intermediate filaments
Specialized for bearing tension
Cell walls of plants
Extracellular structure of plant cells
Primary cell wall
Young plant secretes thin, flexible cell wall
Middle lamella
Between primary walls of adjacent cells is filled with sticky polysaccharide
Extracellular matrix of animal cells
Glycoproteins and carbohydrate-containing molecules secreted by cells
Plasmodesmata
Channels that connect cells and perforate cell walls
Tight junction
Integral proteins fuse to adjacent cell’s proteins
Desmosome
Anchoring junctions that reduces chances of tissue tearing
Gap junctions
Communicating junction, that directs communication between cells
Cell size
Is limited by cells ability to transport things
Large organisms
Don’t have large cells they juss have more cells
-they have two outer membranes( prokaryotes enguklfed has 2 outer membrames)
-have ribosomes, as well as circular dna
-they are autonomous, can grow or reproduce on their own with in the cell
Endosymbiont theory proof
place where ATP synthesis takes place
cristae