Ultrasound Theory waves+medical use
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What kind of waves are ultrasounds?
nonionizing
Mechanical waves (produce deformation of material thru contact forces)- results in perturbation (atoms shifted)
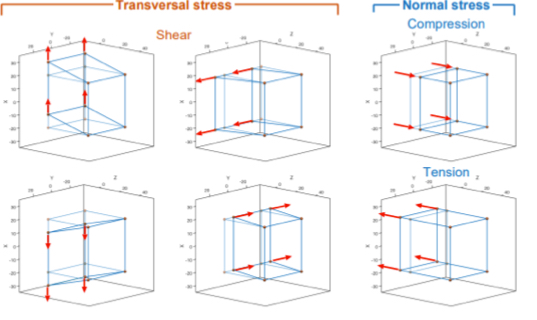
What is mechanical wave stress?
The force that acts per a unit of area, indicates how intense the force acting on each atom will be
Parallel application (normal)
Perpendicular (shear)
Shortens bonds- compressive
Lengthen bonds- tensile
What are the processes referred to when the stresses are small?
The deformation is proportional to the stress and so is considered an elastic process— if stress is large, it can results in deformation or fracture.
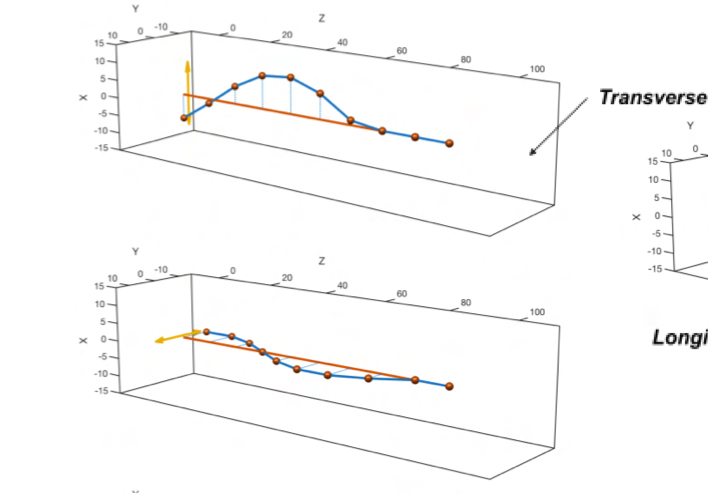
Explain transverse wave as a type of mechanical wave
Perturbations in X or Y axis result in oscillations in perpendicular direction (Z)- hence transverse waves are shear waves
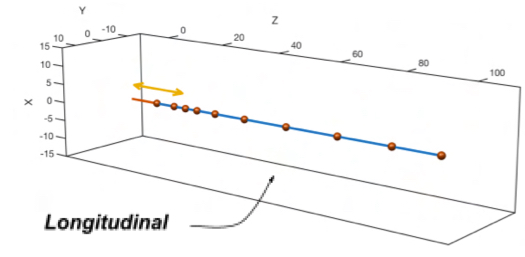
Explain longitudinal wave as a type of mechanical wave
Result due to pertrubation on Z axis, oscillation occurs same direction in which wave advances, hence they are waves of compression and tension (normal)
What are the sounds frequency categories?
infrasound: less than 20 Hz
Sound: between 20Hz and 20KHz
Ultrasounds: greater than 20 KHz
How are US waves used for medical purposes?
Diagnosis: Waves reflected by interior of body are registered and observed (piezoelectric crystal in device transmits its vibration to the mediums around it when subjected to voltage- it is called a transducer and acts as a source and reciever for waves)- echo reflected back is interpreted and creates image
Treatment:
lithotripsy-generate pressure waves and sear waves in kidney stones to break them into smaller parts
high-intenisty ultrasound (HIFU)- possible to destroy certain brain cells responsible for tremblinng in Parkinson’s disease.
Explain the echo grayscale for ultrasound
White/bright lines=big echo (echogenic), max intensity—inhomogenous materials like bones, calcium, metal(high attenuation+absorption)
Gray= solid tissues (intermediate attenuation)
Dark/black lines=no or almost no echo (an-echoic or non-echogenic)—fluids and air filled cavities (low attenuation+absorption)
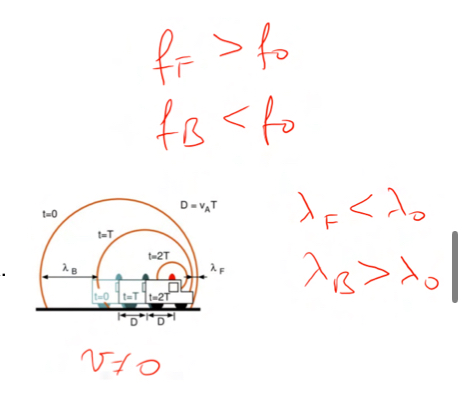
What is teh ultrasound doppler effect?
When ambulance is still and it generates a siren sound the sound propagates equally all aorund it, but when ambulance begins to move the sound becomes clustered in the front of the ambulance and expands near the back, hence the pitch chnages at the different locations— this can also be applied to red blood cells reflecting US waves moving thru the bloodstream, the velocity of these RBCs can be calculated by using the frequency of the reflected wave.. hence the equation in the image below can be used:

What is ultrasound doppler displacement?
Using the logic from the doppler effect with RBC, the angle at which the US waves hit and are therefore reflected back can be viewed in time to get a doppler shift that is eiether negative of positive, telling whether they are moving aaway(negative) or towrads(positive) the transducer
What is the thermal index (TI)
Energy being absorbed by tissue- increasing temperature
TI reflects the power absorbed in a specific tissue ccompraed to the power needed to increase 1Cº of that specific tissue- the ratio has t be smaller than one in order for the temperature increase to be safe
What is the Mechanical index (MI)?
If the US oscillates too lowly it can produce something that will locally increase the pressure (bubbles) dangerous in the body- causing a spontaneous change from liquid to vapor wheen pressure falls below Pvapour (this is called cavitation)))- the mechanical index is defined by the equation in the image. It is proportional to peak negative prssure p= and hence local pressure— MI has to be lower than 1.9
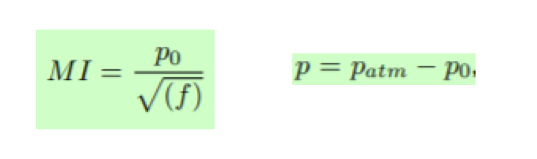
What equipment is required for US
Transducer/probe containing piezoelectric quartz crystal
Curvilinear: used to check abdomen, low frequencies, more pentrance, less resolution
Linear: used to see superficial structures like skin, high frequency, lower penetrance, higher resolution
Patient contact required
Connecter/cable to US machine
Images seen on monitor in real time
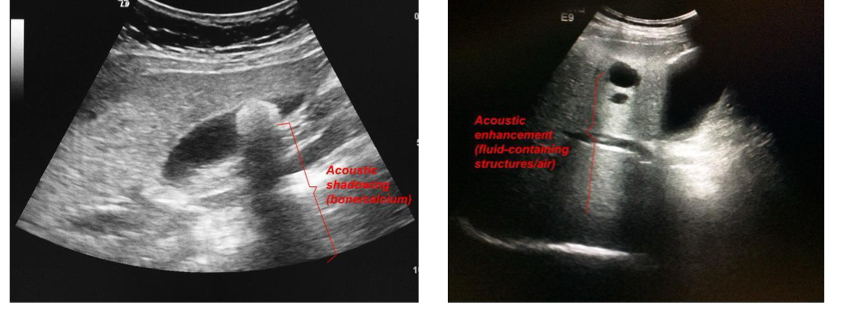
What is posterior acoustic shadowing and what is posterior acoustic enhancement?
Shadowing occurs when there is a region that doenst le US go thruCalci in kidney and gallbladder cause posterior acoustic shadowing, hepatic cyst (cystic structure typically fillled with liquid) shows posterior acoustic enhancement.
Doppler effecr usage in imaging explain
Can be used to determine blood movement and when color is added to blood moving towards or away from transducer, the imaging can be helpful:

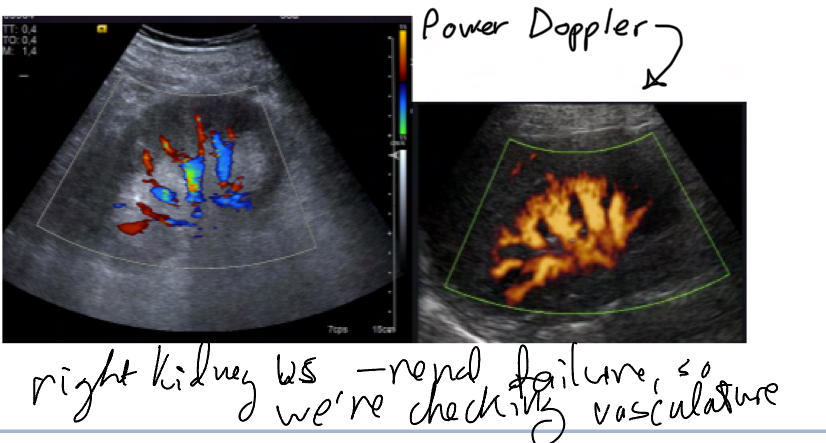
What is power doppler?
Checks vasculature, only to see movement, not direction
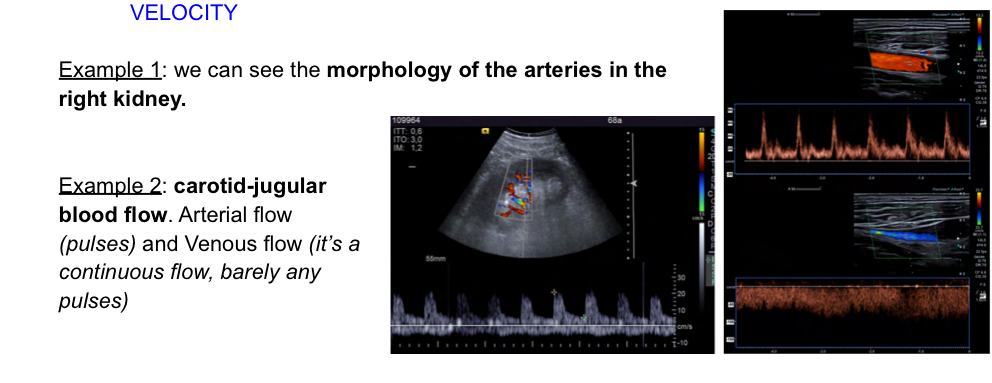
What is a pulsed doppler
Allows to quntify velocity and determine flow direction.. towards tranducer (posittive velocity) away (negative).
What are the advantages and limitations of US?
Adavantges:
no ionizing radiation
Protable, fast
In real time
Gives guidance for invasive procedures
Many perspective+angles
Cheap
Limitations:
operator needs experience
Csnnot penetrate bone or air filled structures
Limited in patients with obesity (low penetration)
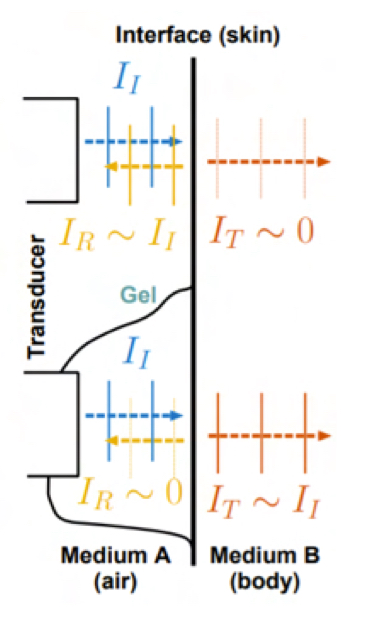
Why is gel used in US?
Since the wave is generated in air (which has low impedence), most of the wave that reaches the body (which has high impedance) is reflected at the skin and only shows skin int he imaging, therefore gell (with high impetence) allows for th wave to be generated in high impentence and so be absorrbed through the skin and be reflected only by organs within the body with different impetences.