CSC 2 Chapter 16: The Portfolio Management Process
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Canadian Securities Course 2 Chapter 16 Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is portfolio management?
Portfolio management is managing investments to meet specified objectives, involving the selection and oversight of a mix of assets to achieve desired risk and return profiles.
What are the 7 Steps of the Portfolio Management Process?
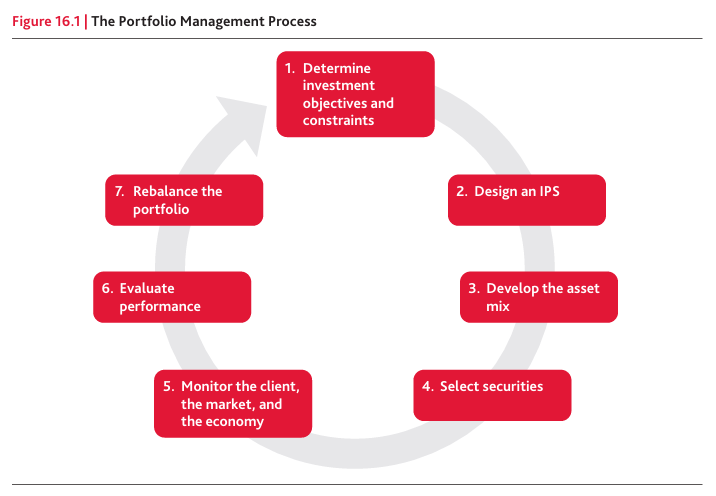
What is Step 1 in the 7 Steps of the Portfolio Management Process?
Define investment objectives and constraints
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is the 3 primary investment components that comprises an investor’s objectives?
Safety of Principal (perservation of capital)
Income
Growth of capital (capital gains
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is the goal of “Safety of principal”?
The goal of "Safety of principal" is to preserve the initial investment amount, minimizing the risk of loss.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is the goal of “Income”?
The goal of "Income" is to generate a steady stream of cash flow through dividends, interest, or other forms of income, providing regular returns to the investor.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is the goal of “Growth of capital”
The goal of "Growth of capital" is to increase the value of the investment over time, often through capital gains, enabling the investor to build wealth and outpace inflation.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What are the 2 secondary investment objectives?
Liquidity (or marketability)
Can sell the investment quickly for cash
Tax minimization
Choose investments with better tax treatment
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
Here is a chart about Securities and Their Investment Objectives
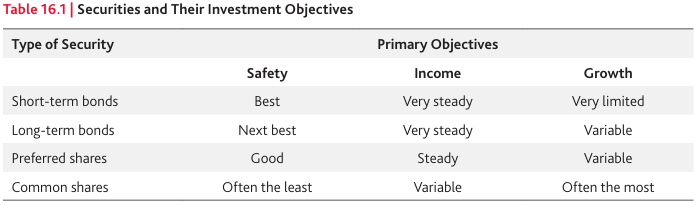
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is the 4 different risk categories?
Conserservative
Low risk; high capitalization; predictable earnings; high yield; high dividend payouts; lower price-to-earnings ratio; low price volatility
Growth
Medium risk; average capitalization, potential for above average growth in earnings; aggressive management; lower dividend payout; higher price-to-earnings ratio; potentially higher price volatility
Venture
High risk; low capitalization; limited earnings record; no dividends; price-to-earnings ratio of little significance, short operating history, highly volatile
Speculative
Maximum risk; shorter term; maximum price volatility, no earnings; no dividends; price-to-earnings ratio not significant
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What are the 5 investment constraints?
Time horizon
Liquidity requirements
Tax requirement
Legal and regulatory requirements
Unique circumstances
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is time horizon?
The time horizon refers to the duration until a client requires access to their invested funds, encompassing various life events such as retirement or major expenditures that may alter investment strategies.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is liquidity requirements?
Liquidity requirements refer to the need for easy access to cash or cash-equivalent investments, ensuring that funds can be quickly converted without significant loss in value to meet short-term obligations or unexpected expenses.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is tax requirements?
Tax requirements refer to the considerations related to taxable income and capital gains, which influence investment choices to optimize post-tax returns and ensure compliance with tax laws.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is legal and regulatory requirements?
Legal and regulatory requirements refer to the legal frameworks and regulations governing investment practices that must be adhered to, including compliance with securities laws, fiduciary responsibilities, and any industry-specific guidelines that impact investment decisions.
Step 1: Determine Investment Objectives and Constraints
What is unique circumstances?
Unique circumstances may include such preferences as the desire for ethically and socially responsible investing. Or religious restrictions
What is Step 2 in the 7 Steps of the Porfolio Management Process?
Design an investment policy statement
Step 2: Design an Investment Policy Statement
What is the main point of Step 2?
An Investment Policy Statement (IPS) is a formal statement between the client and the portfolio manager. It gives clear rules on how the client’s money will be invested.
It guides the manager’s decisions
It ensures the portfolio reflects the client’s goals and risk tolerance
Step 2: Design an Investment Policy Statement
What are the Key components of an IPS
Invest Objectives & Constraints
Goals (e.g., growth, income, preservation)
Risk tolerance, time horizion, liquidity needs, legal/tax concerns
Asset Allocation
How much to invest in cash, fixed income, equities, etc
Rules & Guidelines
Operating procedures (how the portfolio is run)
Acceptable/Prohibited Investments
What is allowed or not (e.g., no derivatives or crypto)
Performance Appraisal Method
How results will be measured and reviewed
Review Schedule
When the portfolio will be checked and rebalanced
What is Step 3 in the 7 Steps of the Porfolio Management Process?
Develop the asset mix
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
How is the asset mix determined?
Client goals
Risk tolerance
Market conditions
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What are the 3 main asset classes?
Cash
Fixed-Income Securities
Equity Securities
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What securities are included in the Cash Asset class?
Money market funds
GICs
Short-term bonds (under 1 year)
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is the purpose of having Cash in your asset mix?
Cash is needed to pay for expenses and to capitalize on investment opprtunities, but is primarily used as a source of liquid fund in case of emergencies
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What securities are included in the Fixed-Income Securities asset class?
Bonds due in more than 1 year
Strip bonds
Mortgage-backed securities
fixed-income exchange-traded funds
bond mutual funds
Preferred shares (technically a preferred share isn’t categoried in fixed-income, but it acts similar to it, Legally they are a equity security)
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is the purpose of having Fixed-income Security in your asset mix?
Primarily to produce income, but also to provide some safety of principal
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What securities are included in the Equity Securities asset class?
Common shares
Equity exchange-traded funds
Equity mutual funds
Convertiable bonds
Convertible preferred shares
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is the purpose of having Equity Securities in you asset mix?
To generate capital gains, either through trading or long-term growth in value
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What are some Other Asset Classes?
Collectibles, such as art or coins
Commodities, such as gold (which is considered a good hedge against inflation)
Derivatives
Hedge funds
Precious metals
Real estate
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
Here is a chart with the General Investment Strategies
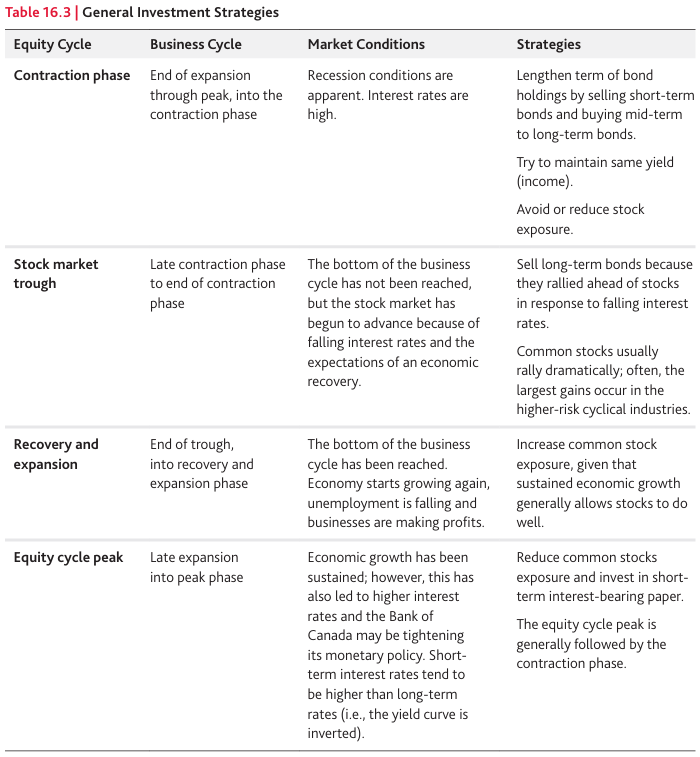
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is the SINGLE most important step in structuring a portfolio?
Asset Allocation
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is Strategic Asset Allocation?
Long-term mix that the manager will adhere to through monitoring and, when necessary, reblancing
It guides the portfolio over time. Even when markets shift, this mix is your long-term goal
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is Ongoing Asset Allocation?
Reblance in a disciplined manner: you should act before the mix gets too far out of balance, while remaing conscious of transation costs
You would typically specify that an asset class much move more than a certain percentage - perhaps 5% - before rebalancing
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is Dynamic Asset Allocation?
This is a portoflio mangement technique that adjusts the asset mix to systematically rebalance the portfolio back to its long-term target or strategic asset mix by responding to changing market conditions and risk factors.
Step 3: Develop the Asset Mix
What is Tactical Asset Allocation?
Involves adjusting the asset mix based on short-term market forecasts or economic indicators. It allows for engaging in tactical shifts to take advantage of perceived market opportunities.
What is Step 4 in the 7 Steps of the Porfolio Management Process?
Select the Securities
Step 4: Select the Securities
What is the purpose of Step 4?
The purpose of Step 4 is to identify and choose specific securities that align with the asset mix determined in Step 3, ensuring that these selections fit within the overall investment strategy and risk tolerance of the portfolio.
What is Step 5 in the 7 Steps of the Portfolio Management Process?
Monitor the Client, the Market, the Economy
Step 5: Monitor the Client, the Market, the Economy
What is the purpose of monitoring the client?
The purpose of monitoring the client is to ensure that investment strategies remain aligned with the client's changing financial goals, risk tolerance, and personal circumstances, enabling timely adjustments to the portfolio as needed.
Life changes
Update the client profile as needed
Step 5: Monitor the Client, the Market, the Economy
What is the purpose of monitoring the market?
The purpose of monitoring the market is to track market trends, economic indicators, and overall financial conditions that may impact the portfolio's performance, allowing for informed adjustments to investment strategies.
Keep up with economic and market trends
Adjust the portfolio if market conditions shift
Step 5: Monitor the Client, the Market, the Economy
What is the purpose of monitoring the economy?
The purpose of monitoring the economy is to assess macroeconomic factors and indicators that influence investment performance, enabling portfolio adjustments based on economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth.
Looks at forecasts (inflation, interest rates, GDP)
Use a range of estimates since predictions are not always exact
What is Step 6 in the 7 Steps of Portfolio Management Process?
Evaluate Portfolio Performance
Step 6: Evaluate Portfolio Performance
How would you evaluate a portfolio’s performance?
This involves analyzing the returns of the portfolio against benchmarks and objectives, assessing risk-adjusted performance, and ensuring alignment with the client’s financial goals.
Industry benchmarks (e.g., T-Bill + 4%)
Focus on long-term results over multiple periods to truly measure performance
What is Step 7 in the 7 Steps of Portfolio Management Process?
Rebalance the Portfolio
Step 7: Rebalance the Portfolio
What is the main point of Step 7?
The main point is that rebalancing keeps your portfolio aligned with its original strategic asset allocation by periodically selling assets that have grown above their target weights and buying those that have fallen below, using the same dynamic (and, where allowed, tactical) asset-allocation techniques you set up earlier.
Who created the grestest flashcards ever
Cyrus