Chemistry Quarter 3 Test Review
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Alcohol
ol
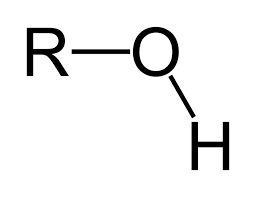
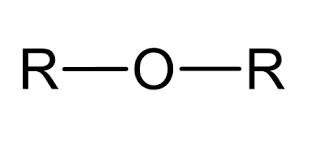
Ether
yl ether
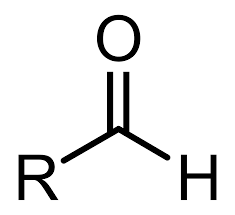
Aldehyde
al
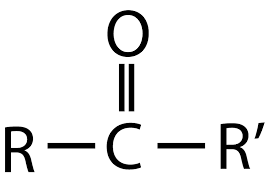
Ketone
one
Carboxylic Acids
oic acid
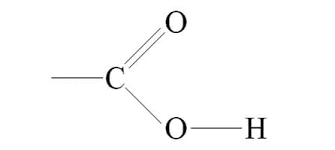
ester
ate
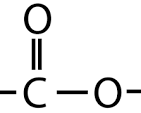
amine
yl amine

Hydrocarbon
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
All can be considered nonpolar → Only contains London Dispersion forces
Saturated hydrocarbon
C-C bonds are all single bonds (alkane)
Alkane
Type of bonding between carbon atoms that only are single bonds
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
C-C bonds contain multiple bonds (alkene, alkyne)
Alkene
Type of bonding between carbon atoms that are double bonds
Alkyne
Type of bonding between carbon atoms that are triple bonds
Structural isomer
Occurs when two molecules have the same atoms but different bonds
Organic Chemistry Prefix: 1
meth
Organic Chemistry Prefix: 2
eth
Organic Chemistry Prefix: 3
pro
Organic Chemistry Prefix: 4
bu
Prefix: 5
pent
Prefix: 6
hex
Prefix: 7
hept
Prefix: 8
oct
Prefix: 9
nona
Prefix: 10
deca
Methane
1 carbon
CH4
Ethane
2 carbons
C2H6
Propane
3 carbons
C3H8
Butane
4 carbons
C4H10
Pentane
5 carbons
C5H12
Hexane
6 carbons
C6H14
Heptane
7 carbons
C7H16
Octane
8 carbons
C8H18
Nonane
9 carbons
C9H20
Decane
10 carbons
C10H22
Methyl
-CH3
ethyl
-CH2CH3
propyl
-CH2CH2CH3
butyl
-CH2CH2CH2CH3
Cyclic alkanes
Carbon atoms that form rings containing only C-C single bonds
Basic Intermolecular Forces
Hydrogen Bonds
Dipole-Dipole
London Dispersion Bonds
Stronger IMFs mean
High Boiling Point
High Melting Point
Lower Vapor Pressure
Synthetic polymers
Plastics
Teflon
Polybinylchloride (PVC)
Nylon
Kevlar
Naturally occurring polymers
Proteins
Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA)
VSEPR
Electrons arrange themselves in a molecule so as to be as far apart as possible
Shared electrons pairs repel one another
Lone Pairs occupy a slightly larger orbital than shared electrons, so shared bonding orbitals are pushed together slightly by lone pairs
Nonpolar Covalent
Equal sharing of electrons between the two elements
≤ 0.3
Symmetric molecule
Polar covalent bond
Unequal sharing of electrons
0.4 < x < 1.7
Greater the electronegativity, the more polar the bond
Asymmetric molecule
Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces that hold identical molecules together
London Dispersion Forces
Weakest IMF
Dominant force of attraction between identical nonpolar molecules
Weakest due to forces being temporary
Additive property → the larger the molecule (mass), the greater the effect
Present in all covalent molecules
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Medium strength IMF
Attraction between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
Hydrogen Bonds
Strongest IMF
Attraction between polar molecules
Exists when hydrogen is bonded to FON
Ionic bonds
between metal and nonmetal
Covalent bonds
Between nonmetal and nonmetal
Metallic bonds
Between atoms of the same metal
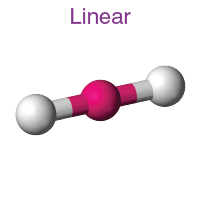
Linear
Hybridization: sp
Bond Angle: 180o
Example: HCI, CO2
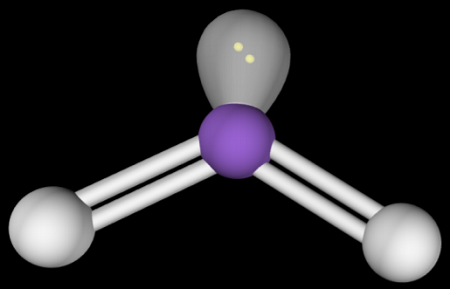
Bent (1 Lone Pair)
Hybridization: sp2
Bond Angle: <120o
Example: O3, SO2
Bent (2 Lone Pairs)
Hybridization: sp3
Bond Angle: 104.5o
Example: H2O, SBr2
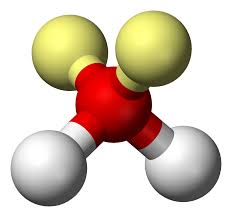
Trigonal Planar
Hybridization: sp2
Bond Angle: 120o
Example: SO3, BF3
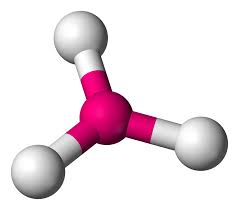
Tetrahedral
Hybridization: sp3
Bond Angle: 109.5o
Example: CH4, SIF4
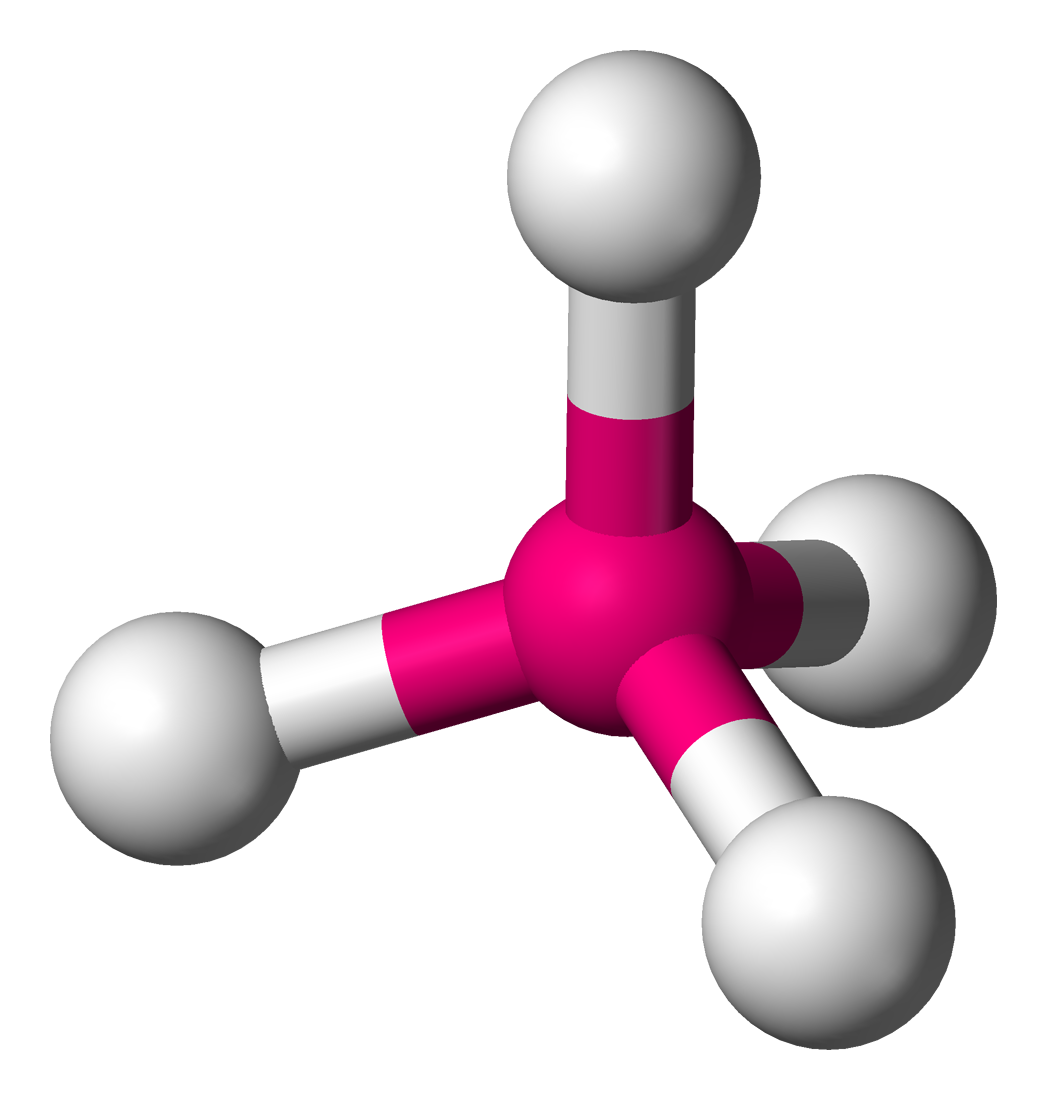
Trigonal Pyramidal
Hybridization: sp3
Bond Angle: 107o
Example: NH3, PCl3
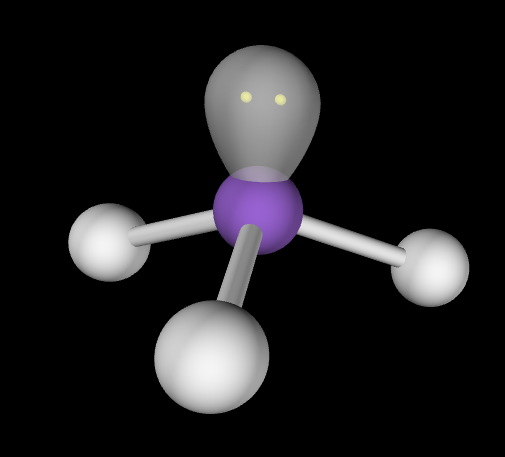
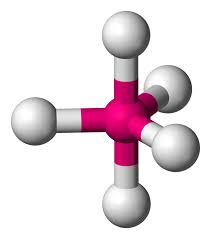
Trigonal bipyramidal
Hybridization: sp3d
Bond Angle: 120o & 90o
Example: PCl5
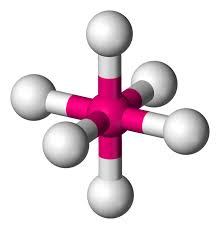
Octahedral
Hybridization: sp3d2
Bond Angle: 90o
Example: SF6
phosphate
PO43-
ammonium
NH4+
nitrate
NO3-
hydroxide
OH-
chlorate
ClO3-
acetate
C2H3O2-
carbonate
CO32-
sulfate
SO42-
Silver
Ag1+
Zinc
Zn2+
Cadmium
Cd2+
organic molecules
contain C and H
Single Bonds
Longest, weakest
Triple Bonds
Shortest, strongest
Cation
Metal
Lose electrons
Positively charged
Anion
Nonmetal
Gain electron
Negatively charged