AP Biology - Enzymes
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:21 AM on 9/16/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
enzyme
a protein catalyst that speeds up a chemical reaction
2
New cards
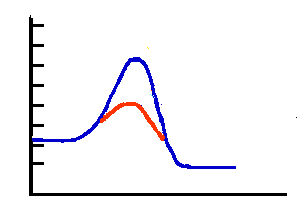
red
Which line (red or blue) represents an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
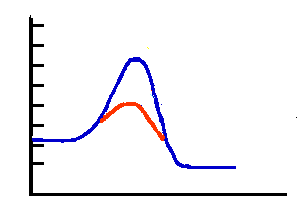
3
New cards
blue
Which line (red or blue) represents an uncatalyzed reaction?
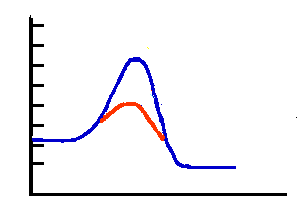
4
New cards
progress of reaction
What is the x-axis of this graph?
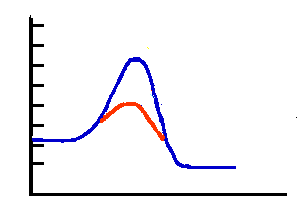
5
New cards
energy
What is the y-axis of this graph?
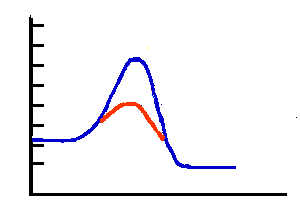
6
New cards
activation energy
What is the "hill" of this graph called?
7
New cards
decrease
Does an enzyme increase or decrease the activation energy of a reaction?
8
New cards
substrate
the reactant in an enzyme catalyzed reaction
9
New cards
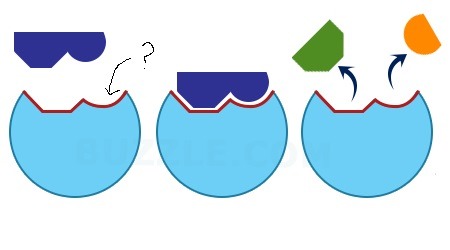
active site
the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds
10
New cards
active site
What is the arrow pointing at?
11
New cards
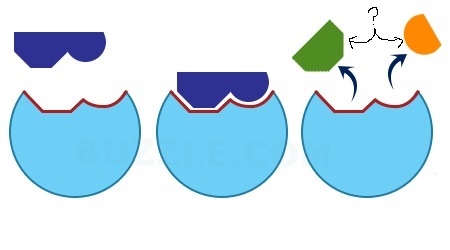
products
What is the arrow pointing at?
12
New cards
reaction rate
a measure of how fast an enzyme catalyzed reaction occurs
13
New cards
enzyme activity
another word for reaction rate
14
New cards
optimum conditions
the temperature and pH where enzyme activity is highest
15
New cards
denaturation
destruction of the active site of the enzyme by breaking the weak bonds of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures
16
New cards
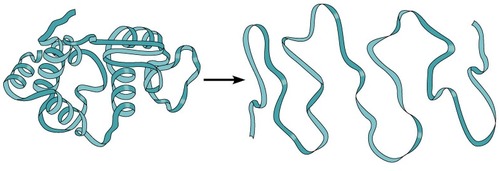
denaturation/loss of 3D Shape
What has happened to this protein?
17
New cards
high temperatures or changes in pH
What are two environmental factors that can denature a protein?
18
New cards
inhibitor
prevents the substrate from binding to the enzyme, decreasing enzyme activity
19
New cards
competitive inhibitor
binds to the enzyme at the active site and blocks the substrate from binding
20
New cards
competitive inhibitor
What kind of inhibitor is this?

21
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitor
binds to the enzyme somewhere other than the active site and changes the shape of the active site
22
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitor
What kind of inhibitor is this?

23
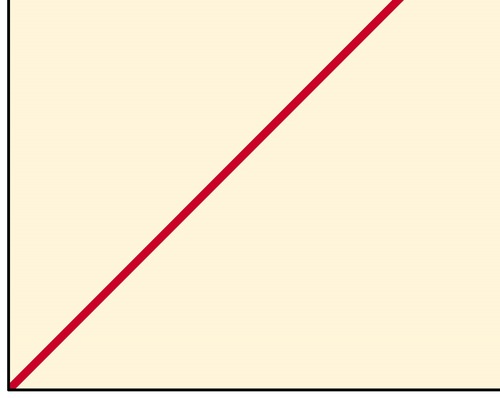
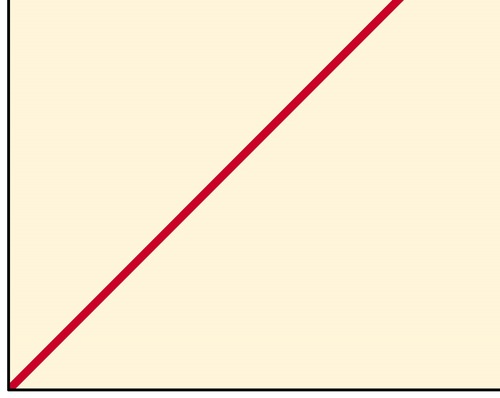
New cards
enzyme concentration
What is the x-axis on this graph?
24
New cards
enzyme activity
What is the y-axis on this graph?
25
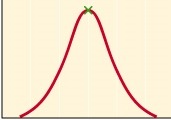
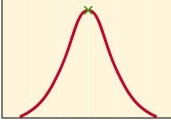
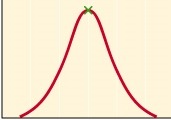
New cards
pH
What is the x-axis on this graph?
26
New cards
enzyme activity
What is the y-axis on this graph?
27
New cards
optimum pH
What does the green x represent?
28
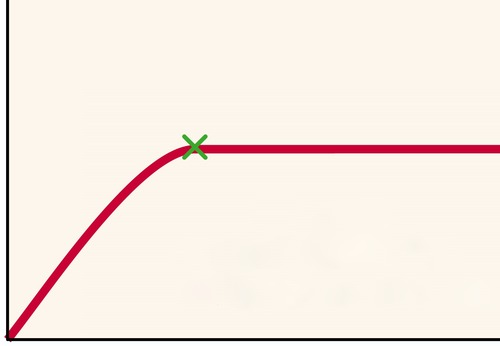
New cards
substrate concentration
What is the x-axis on this graph?
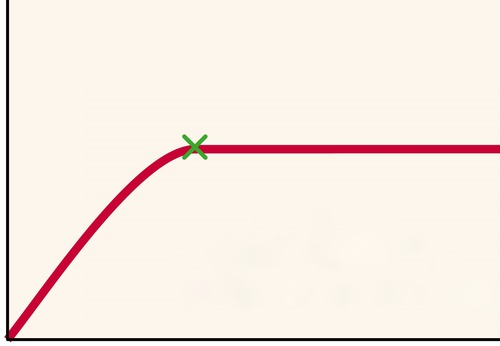
29
New cards
enzyme activity
What is the y-axis on this graph?
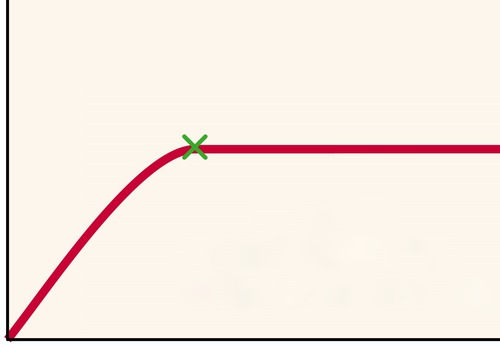
30
New cards
point of saturation
What does the green x represent?
31
New cards
temperature
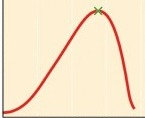
What is the x-axis on this graph?
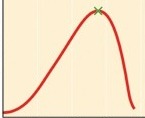
32
New cards
optimum temperature
What does the green x represent?
33
New cards
catabolic pathways
Series of reactions that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds.
34
New cards
anabolic pathways
Series of reactions that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones.
35
New cards
free energy
Measures the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell.
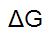
36
New cards
endergonic
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
37
New cards
exergonic
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy.
38
New cards
energy coupling/ATP couples...
The use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one.
39
New cards
catalyst
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
40
New cards
enzyme substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms:
41
New cards
coenzymes and cofactors
What are two types of activators?
42
New cards
Cofactor
inorganic compound example heme
43
New cards
Coenzyme
Non-protein Organic helpers, example thiamin and vitamin B1
44
New cards
competitive inhibitors
Reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites.
45
New cards
noncompetitive inhibitors
Impede enzymatic reactions by binding to another part of the enzyme (other than the active site) allosteric site and changes the structure of the active site
46
New cards
by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur
How do enzymes catalyze reactions?
47
New cards
Temperature, pH and Concentration of the Substrate
An enzyme's activity can be affected by what three factors?
48
New cards
Breakdown of H2O2
What reaction does catalase catalyze?
49
New cards
activation and inhibition
What kinds of regulation exist for enzymes?
50
New cards
turn on the enzyme
What does activation do?
51
New cards
turn off the enzyme
What does inhibition do?
52
New cards
competitive and allosteric
What are the two types of inhibition?
53
New cards
What is another name for allosteric inhibition?
noncompetitive inhibition
54
New cards
The reactants or the product amounts
How do you measure the rate of an enzymatic reaction?
55
New cards
lock and key
What is the interaction between the active site and the substrate like?
56
New cards
they speed up reactions and lower the activation energy necessary to catalyze them
What is the advantage for using an enzyme?
57
New cards
the allosteric site
Where does a noncompetitive inhibitor bind?
58
New cards
changes the shape of the active site, by bonding to the allosteric site
What does a noncompetitive inhibitor do?
59
New cards
phosphorylation
the released phosphate moves to another molecule to give energy
60
New cards
induced fit
enzymes will change the shape of their active site to allow the substrate to bind better
61
New cards
allosteric activator
substrate binds to ONE active site and stabilizes the shape of the enzyme so that the active sites remain OPEN
62
New cards
allosteric inhibitor
substrate binds to allosteric site and stabilizes the shape of the enzyme so that the active sites are CLOSED (inactive form)
63
New cards
cooperatively
substrate binds to one active site (on an enzyme with more than one active site) which stabilizes the active form
CONSIDERED ALLOSTERIC REGULATION SINCE BINDING AT ONE SITE CHANGES THE SHAPE OF OTHER SITES
CONSIDERED ALLOSTERIC REGULATION SINCE BINDING AT ONE SITE CHANGES THE SHAPE OF OTHER SITES
64
New cards
feedback inhibition
The end product of a metabolic pathway can act as an inhibitor to an early enzyme in the same pathway