psyc 100-Chapter 3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Neuroscience
studies the connection between the brain and behavior
Types of Neurons: Sensory Neuron
bring information from the world into the body and to the brain
Types of Neurons: Interneurons
internal neurons that pass communication between sensory and motor neurons
Types of Neurons: Motor Neuron
carry messages away from central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to muscles and glands
What are Neurons composed of?
Soma, Dendrites, Axon, Terminal buttons
Soma (cell body)
Contains DNA
dendrites
extensions from soma that receive info
axon
extends from cell body, carries electrical potential
terminal buttons
emits a chemical message that reaches adjacent neurons
Glial cells
supportive and protective for neurons (outnumber neurons in the brain)
Myelin cells
type of glial cell that wraps around the neuron axon to increase speed of action potential (common on longer neurons)
Myelination
The formation of a myelin around nerve fibers that increases the speed and efficiency of neural communication.
Continues until about age 12.
Children learn and react more slowly and differently than adults.
Action potential
Occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts in response to incoming signal from adjacent neuron
Triggered when a signal causes the membrane potential to reach about -55 mV.
Ion channels open, allowing sodium (Na⁺) to enter, making the inside positive.
Resting potential is restored as other channels open and sodium is pumped back out.
Resting Membrane Potential
The axon’s membrane carries an electrical charge at rest.
The inside of the axon is more negative than the outside (≈ -70 mV)
Synapse
junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent nerve cell
Neurotransmitter
Molecules are released from the axon terminal into the synapse when the action potential arrives at the axon terminal region
Agonists
Drugs that mimic or enhance neurotransmitters
Amphetamine - stimulates release of dopamine
Nicotine - acts like acetylcholine (involved in thought, learning, and memory)
Antagonist
Drugs that block the action of neurotransmitters
Anti-psychotic meds block dopamine receptors
Botox – blocks the release of acetylcholine
Resting Membrane & Action Potential: Resting Potential
The neuron’s stable electrical state (≈ -70 mV).
Resting Membrane & Action Potential: Threshold Potential
The point at which an action potential begins (≈ -55 mV).
Resting Membrane & Action Potential: Depolarization
Rapid influx of positive charge, reaching about +30 mV.
Resting Membrane & Action Potential: Repolarization
The neuron returns toward resting potential
Resting Membrane & Action Potential: Hyperpolarization
A brief overshoot where the charge becomes more negative than resting level.
Synaptic Transmission
1. Action potential reaches end of axon
2. vesicles transport NTs to membrane and release them into the synapse
3. NT interact with the postsynaptic receptors
4. May cause action potential in the post synaptic neuron
5. NT deactivation starts (e.g. reuptake)
Excitatory Drugs
Increase neural activity by stimulating neurotransmitter release or mimicking their effects.
Examples: Caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines.
Effect: Heightened alertness, energy, and mood; can lead to overstimulation.
Inhibitory Drugs
Decrease neural activity by blocking neurotransmitter release or enhancing inhibitory signals.
Examples: Alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates.
Effect: Relaxation, drowsiness, slower reactions.
Mixed (Excitatory & Inhibitory) Drugs
Affect multiple neurotransmitter systems, producing both stimulating and calming effects.
Examples: Cannabis (THC), MDMA (ecstasy), opioids.
Effect: Can cause both euphoria and sedation depending on dose, setting, and individual response.
How do we study the human brain?
Brain Damage
Case Studies
Brain lesion studies (animals typically)
Disadvantage: no/limited control in studies
E.g., Phineas Gage
Activating the Brain
Chemical injection or electrode placement in brain (animals)
E.g., seizure reduction surgery in humans
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
Brain Recordings
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Various imaging techniques (PET, MRI)
Allows us to study human brain in real time
How do we view/ record the brain?
Structural brain imaging methods:
CT scan (Tumors, Stroke) , MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Functional brain imaging methods:
EEG, PET Scan, fMRI
Altering brain activity:
TMS (Transcranial magnetic stimulation)
Hindbrain: Reticular formation
Controls arousal and sleep
Hindbrains: Pons
Controls unconscious movement and some reflexes like sneezing
Hindbrain: Medulla
Controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure
Hindbrain: Cerebellum
“little brain” - Controls balance, coordination
Midbrain: Substatia nigra
Controls helps control movements
Midbrain: Superior collicus
Controls sensory relay center, coordinates responses, processes visual information
Midbrain: Inferior collicus
auditory sound relay center & coordinates responses to sound
Forebrain: Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex Lobes: The two hemispheres of the brain are divided into four lobes, each with distinct functions:
Frontal: Decision-making, problem-solving, movement, speech, and personality. Fully develops around age 25.
Parietal: Processes touch and spatial awareness.
Temporal: Handles hearing, language, and memory.
Occipital: Controls vision and visual recognition.
Forebrain: Thalamus
relay center for sensory information from body to the cortices
Forebrain: hypothalamus
regulates motivation and the pituitary gland
Forebrain: Pituary gland
regulates and monitors hormones
Forebrain: Amygdala
emotional processing and reactivity
Forebrain: Hippocampus
memory
Brain stem
Controls breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and consciousness
Midbrain: Upper part of the brain stem, involved in auditory and visual
processingPons: Middle part of the brain stem, controlling sleep and arousal
Medulla oblongata: Lower part of the brain stem, controlling breathing, heart rate, blood pressure
Primary Motor Cortex
In the frontal lobe; controls voluntary movement.
Moves the Opposite side of body
Somatosensory Cortex
In the parietal lobe; processes touch and body sensations.
Feels for the Opposite side of body
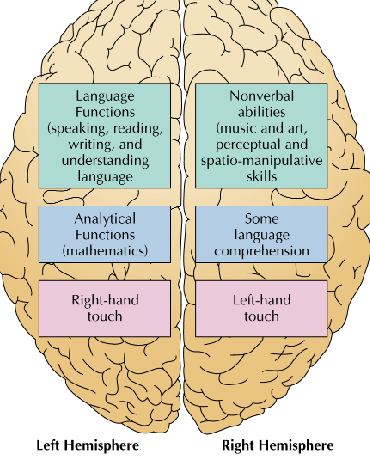
What divides the brain into two hemispheres?
Corpus Callosum
Left Hemisphere
Specializes in language, logic, math, and analytical thinking
Right Hemisphere
Handles spatial awareness, creativity, music, and emotion
Which side of the body does each brain hemisphere control?
Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body
The left hemisphere controls the right side
The right hemisphere controls the left side
Broca’s Area
In the frontal lobe; controls speech production. Damage → trouble speaking.
Lower front of brain
Wernicke’s Area
In the temporal lobe; controls language comprehension. Damage → trouble understanding speech.
Upper back of brain
Lateralization
the right side of brain controls left side of body and vice versa
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Processes information and sends commands.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All nerves outside the CNS
connects body to brain.
Peripheral Nervous System Divisions: Somatic
Controls voluntary movements and sensory input.
Peripheral Nervous System Divisions: Autonomic
Controls involuntary functions (organs, glands).
Subdivision’s
Sympathetic: Activates “fight or flight” response.
Parasympathetic: Promotes “rest and digest” functions.
The Endocrine System
A network of glands that produce and release hormones into the bloodstream.
Slower than the nervous system (effects last days or weeks).
The hypothalamus regulates hormone release.
Hormones influence metabolism, growth, sexual behavior, and stress response.
Natural Selection
the theory that certain traits get selected over generations in improve “fitness” of a species
Genes
Segments of chromosomes that contain instructions for influencing and creating
hereditary characteristics
Genotype: actual genetic message
Phenotype: traits observable characteristic
Epigenetics
The study of how environmental factors affect gene expression without changing DNA itself.
Examples:
● Lifestyle differences (diet, stress, smoking) affect identical twins gene expression differently.
● Chemicals in cigarette smoke cause epigenetic changes in lung cells.
● Babies conceived during the famine had epigenetic changes that made them more prone to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease later in life.