economics and the economy
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what economics analyses
what to produce
how to produce
for whom to produce for
how economists make choices
act rationally
willingness to pay
opportunity costs
incentives
rationality
use available information to make the best decisions which only occurs if benefits outweigh costs
willingness to pay
maximum amount of money you are willing to pay for something, which represents your benefit from it
opportunity cost
the value of the best alternative you must sacrifice, includes monetary and non monetary costs
market
a set of arrangements by which buyers and sellers are in contact to exchange goods and services
demand
the quantities of a good buyers wish to purchase at each conceivable price
measures relationship between price and quantity for buyers
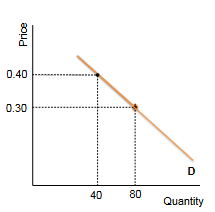
demand curve
as price increases, quantity demanded decreases
downward curve
supply
the quantities of a good sellers wish to sell at each conceivable price
measures relationship between price and quantity for sellers
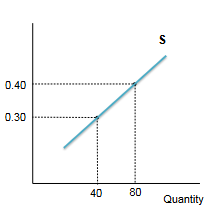
supply curve
as price increases, quantity supplied increases (as less demand due to high price equals more supply)
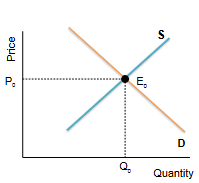
market equilibrium
quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
the equilibrium price is P0 and quantity is Q0
equilibrium price
price at which quantity supplied equals quantity demanded
movements along the supply curve
results from changes in the price of the good
supply shifts
caused by changes in technology,
input costs
government regulations
business expectations