Bio112 Lab Quiz 1
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Ocular Lens
Eyepiece of a microscope; 10x magnification (meaning you will 10x the objective lens)
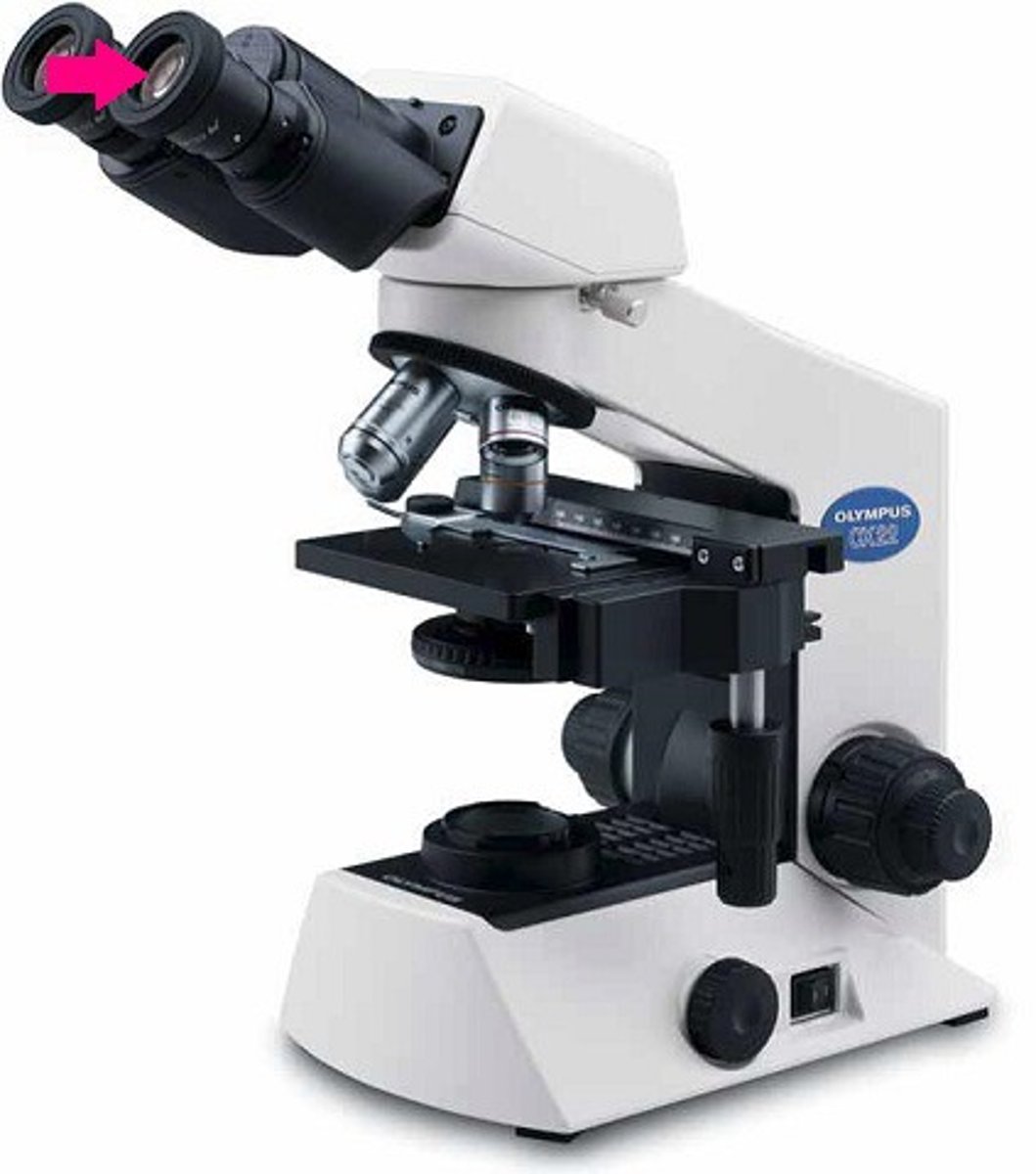

Arm
Used to support the microscope when carried

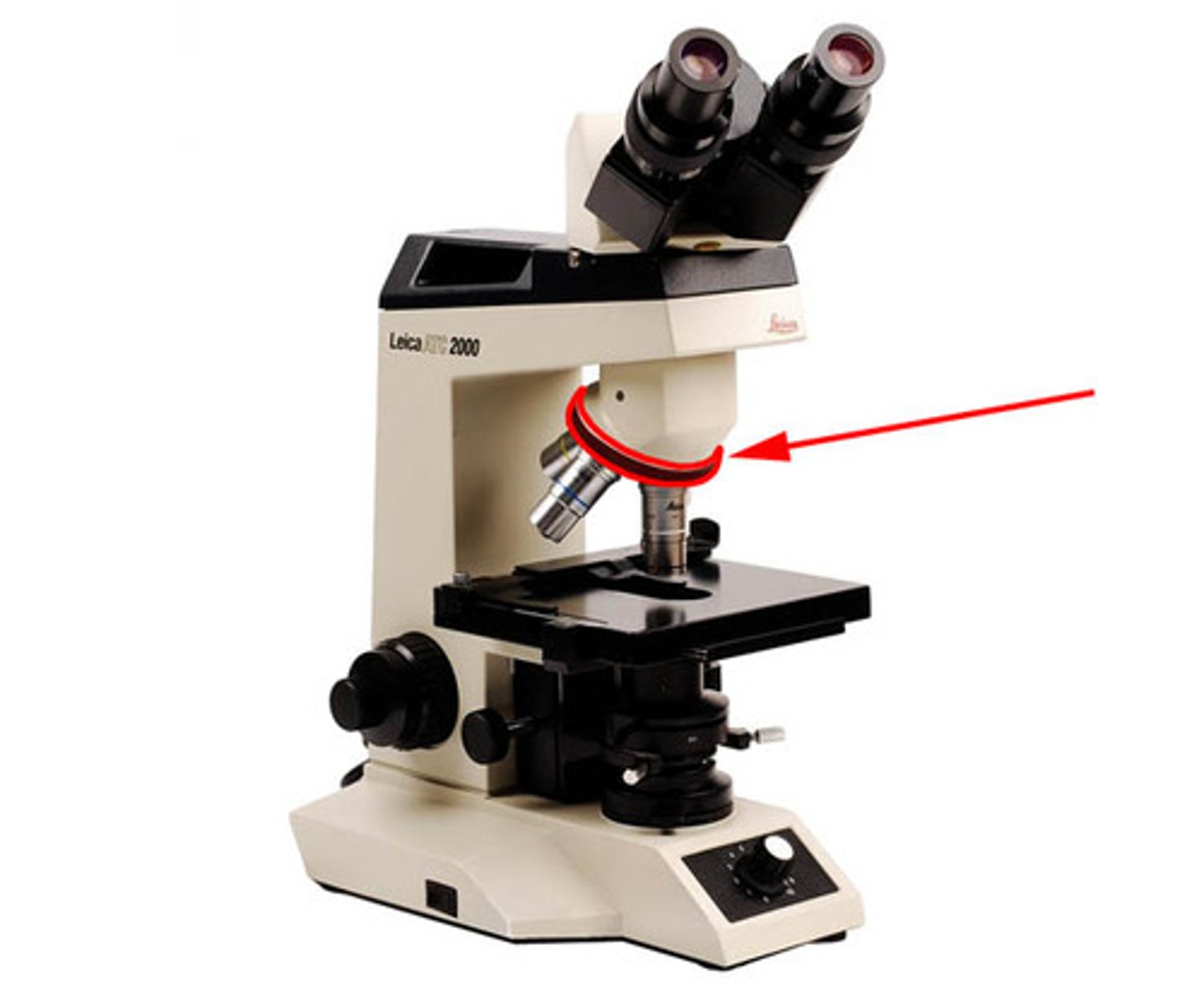
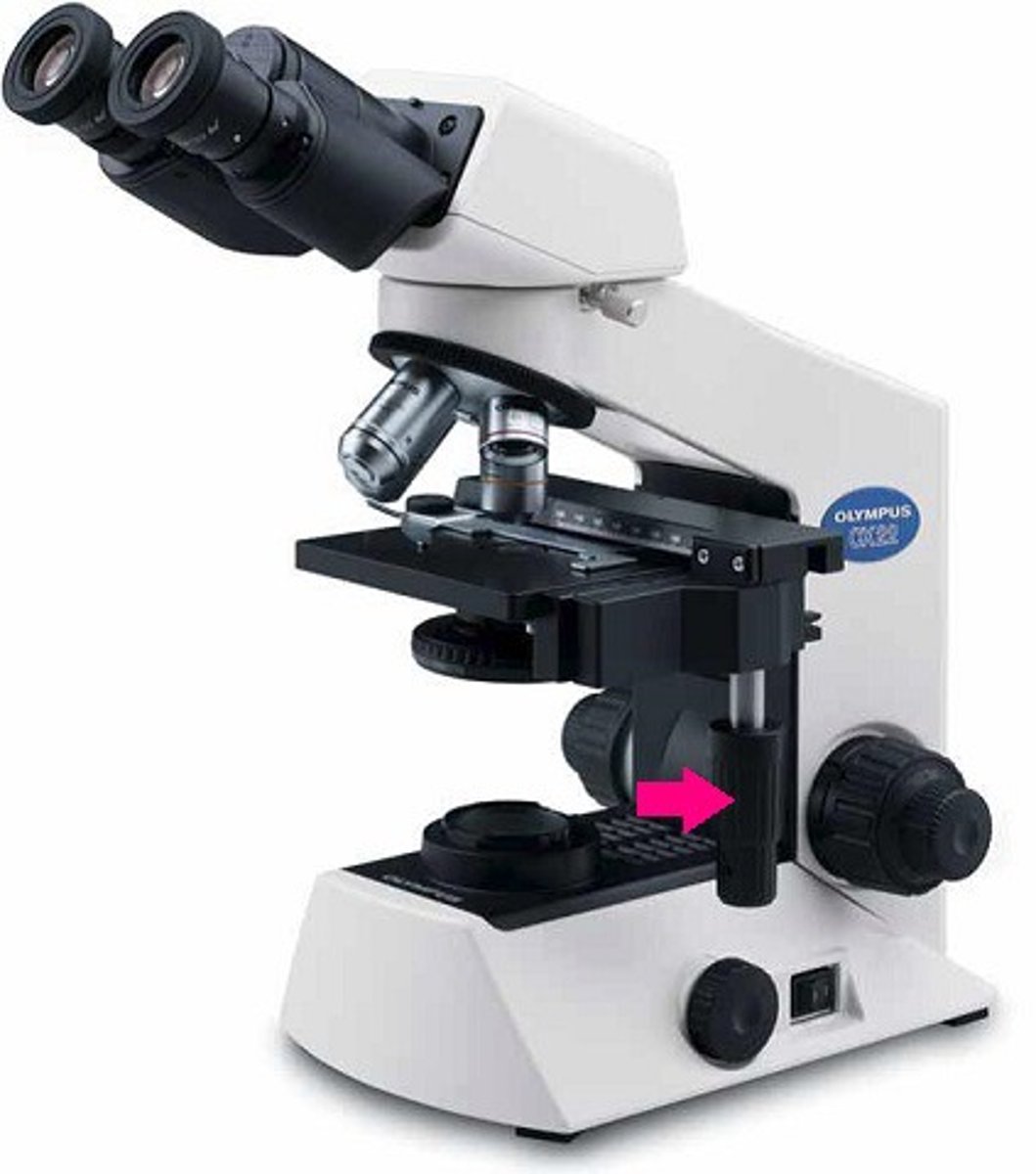
rotating (revolving) nosepiece
contains objective lenses, allowing for changing of lenses for variable magnification of slide image
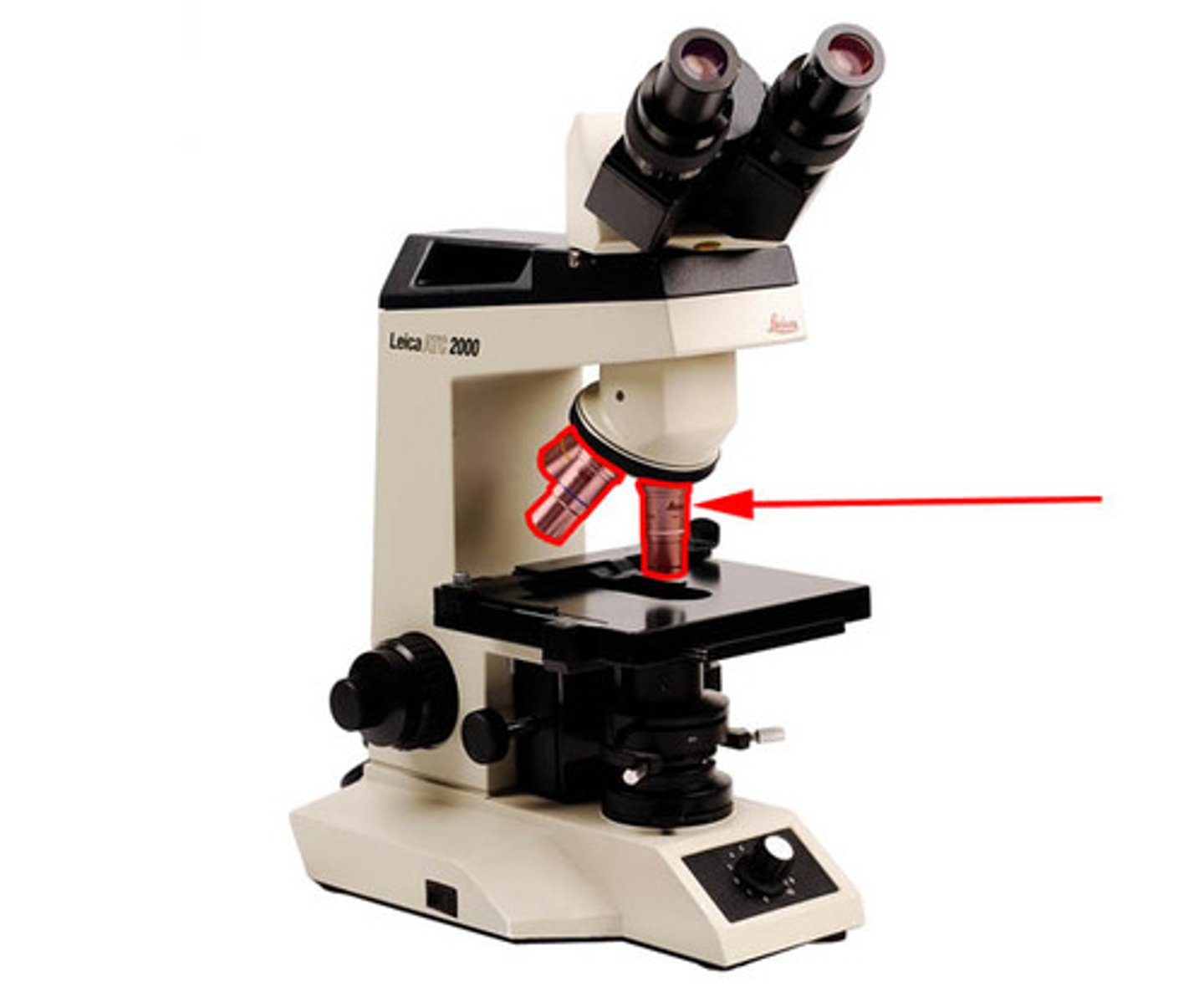
objective lenses
Primary lenses that magnify the specimen, 4x (red stripe/short) 10x (yellow stripe) 40x (blue stripe) 100X (longest lens)
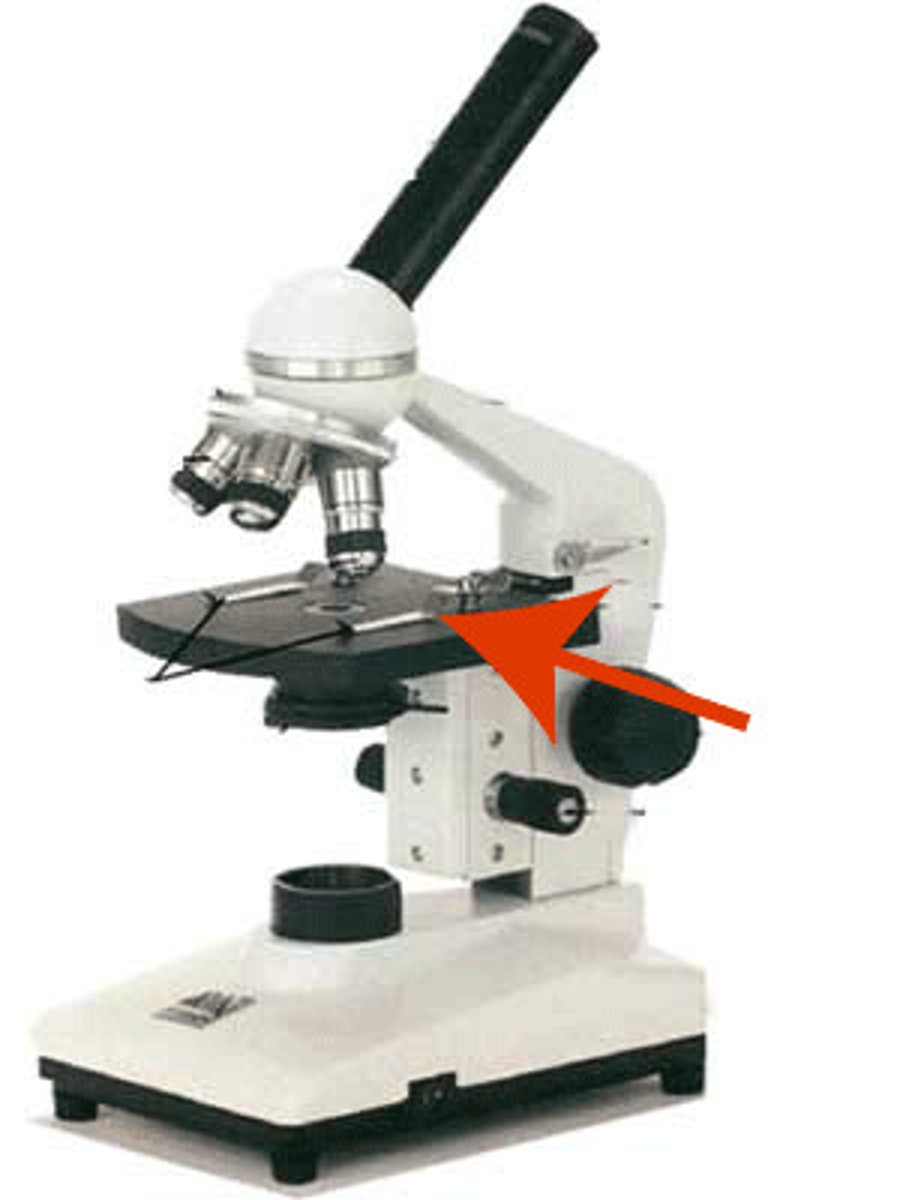
stage
Supports the slide being viewed, is moved up and down in order to focus

stage clips
Holds the slide in place
mechanical stage control
adjust in order to move the slide around the(front,back,left,right) stage to see the different sections of the slide.

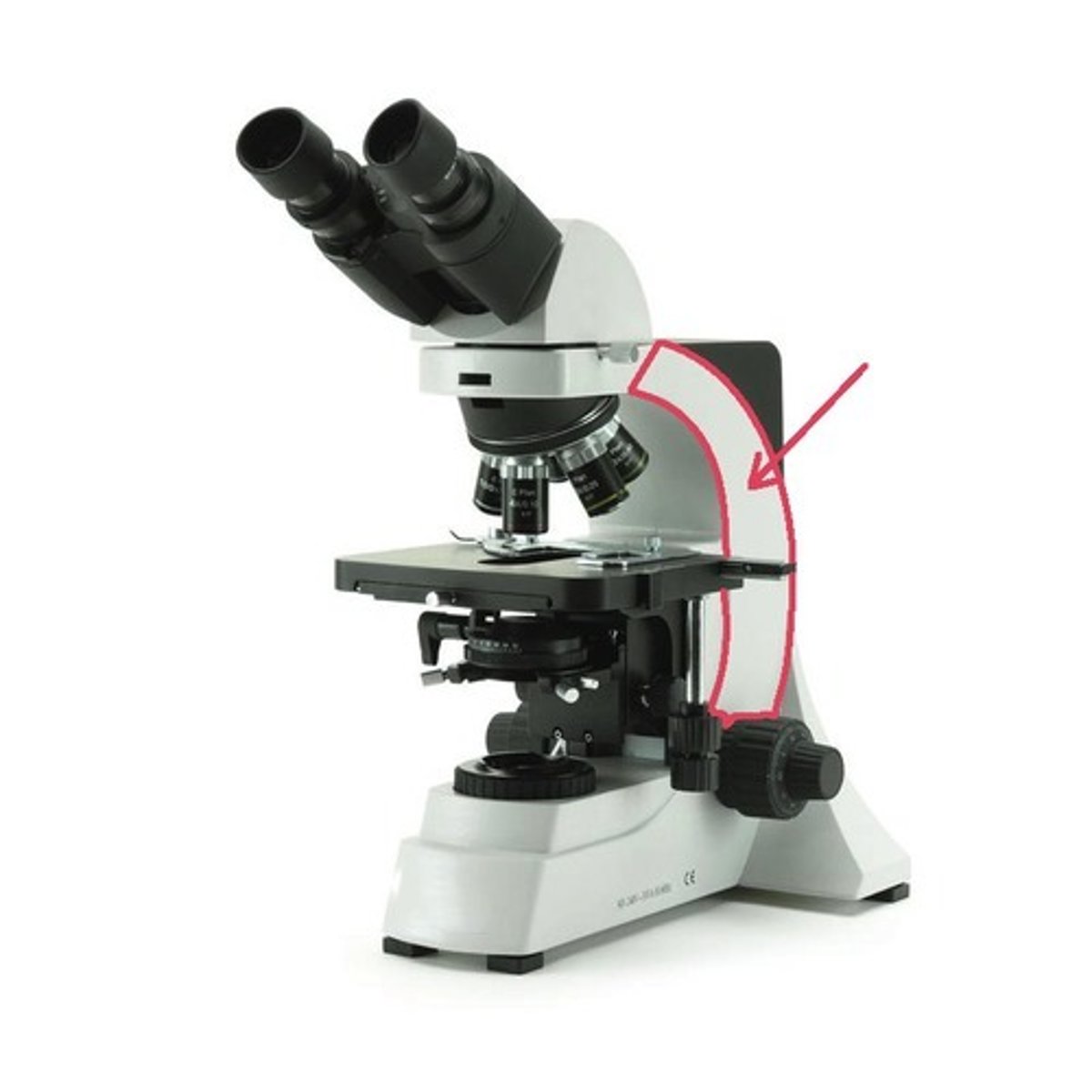
fine focus adjustment knob
this part moves the stage slightly to help you sharpen or "fine" tune your view of the specimen

coarse focus adjustment knob
this part moves the stage up and down to help you get the specimen into view
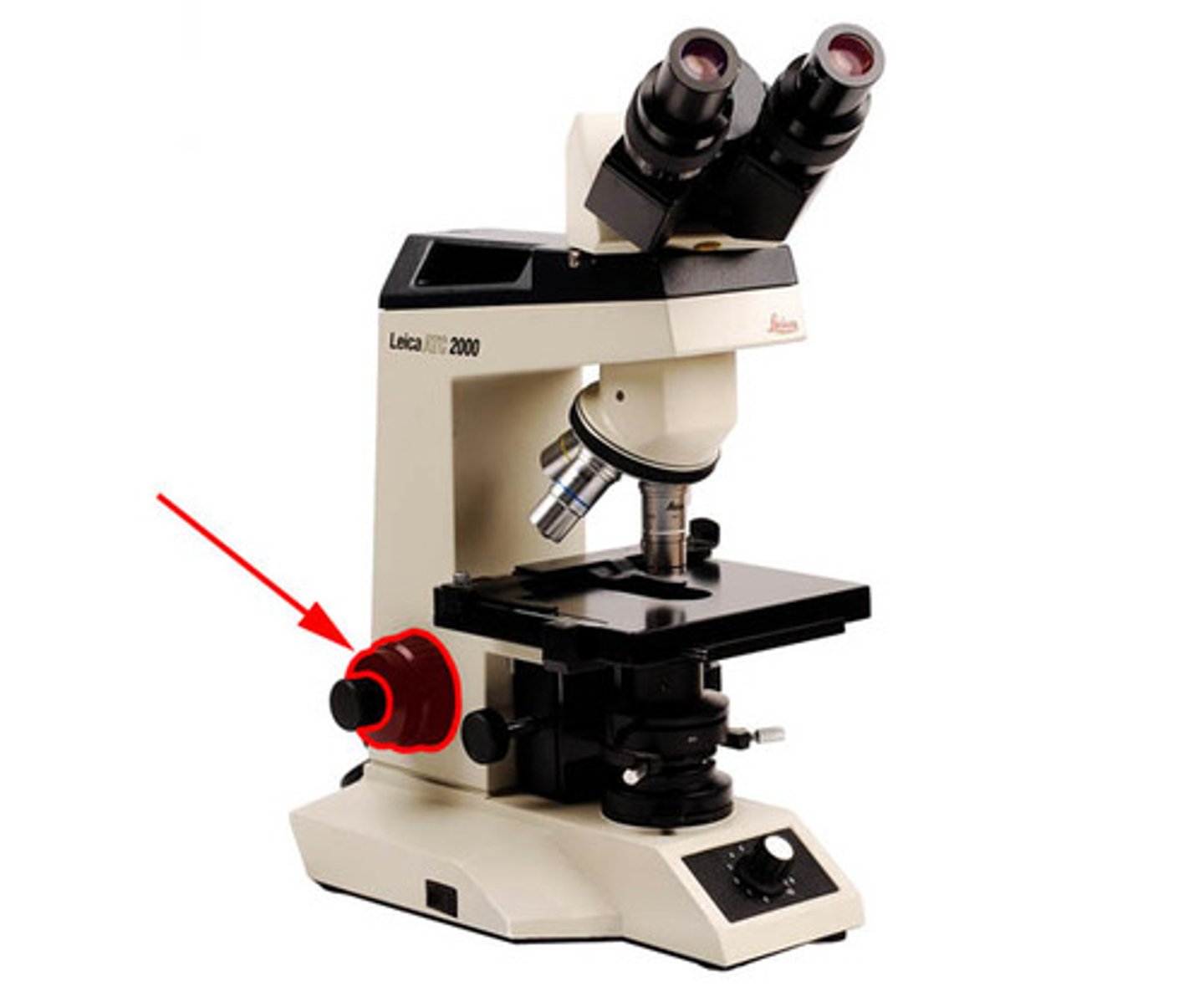
Light Control
controls intensity of light
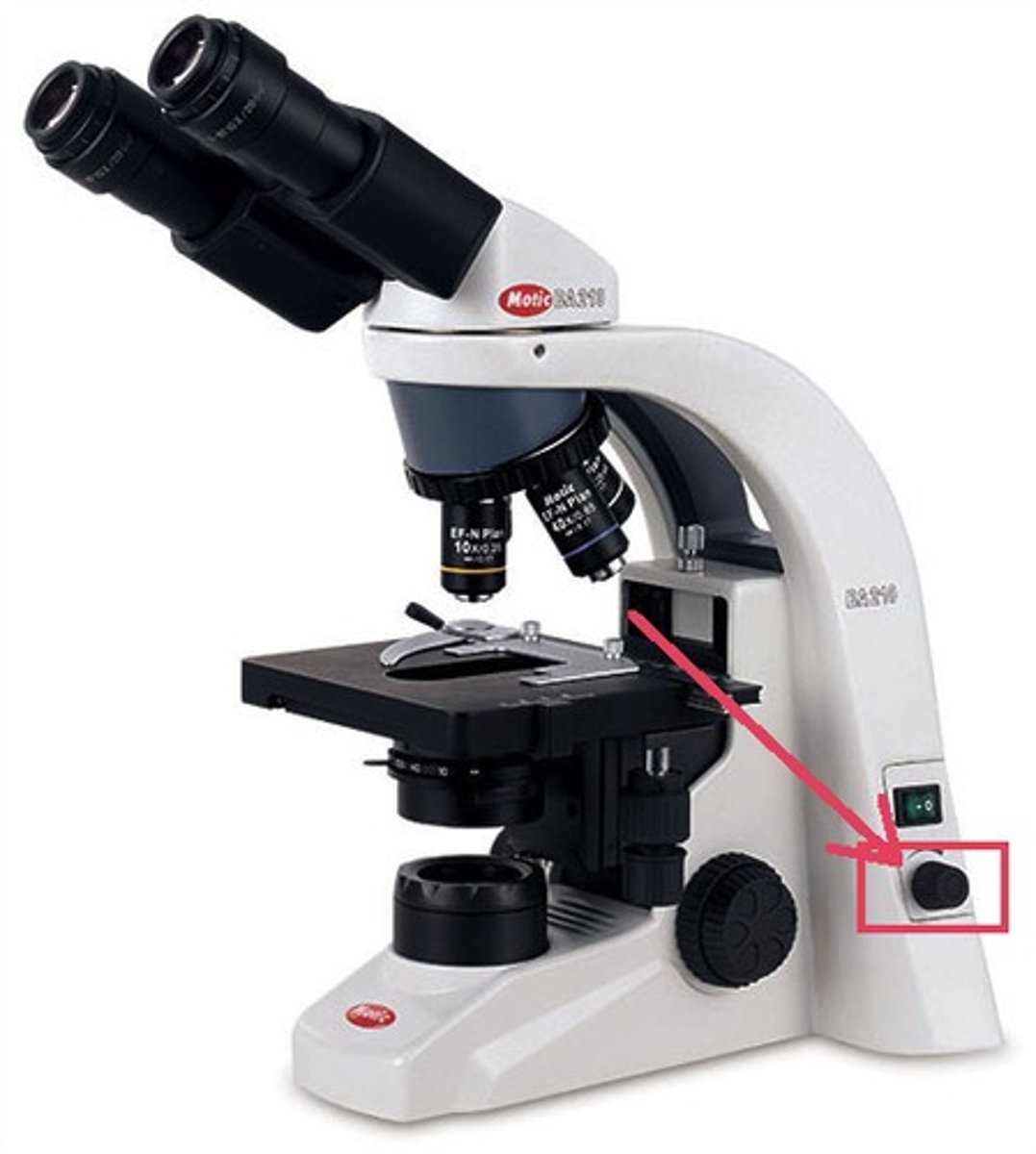
Condenser
focuses light through the specimen
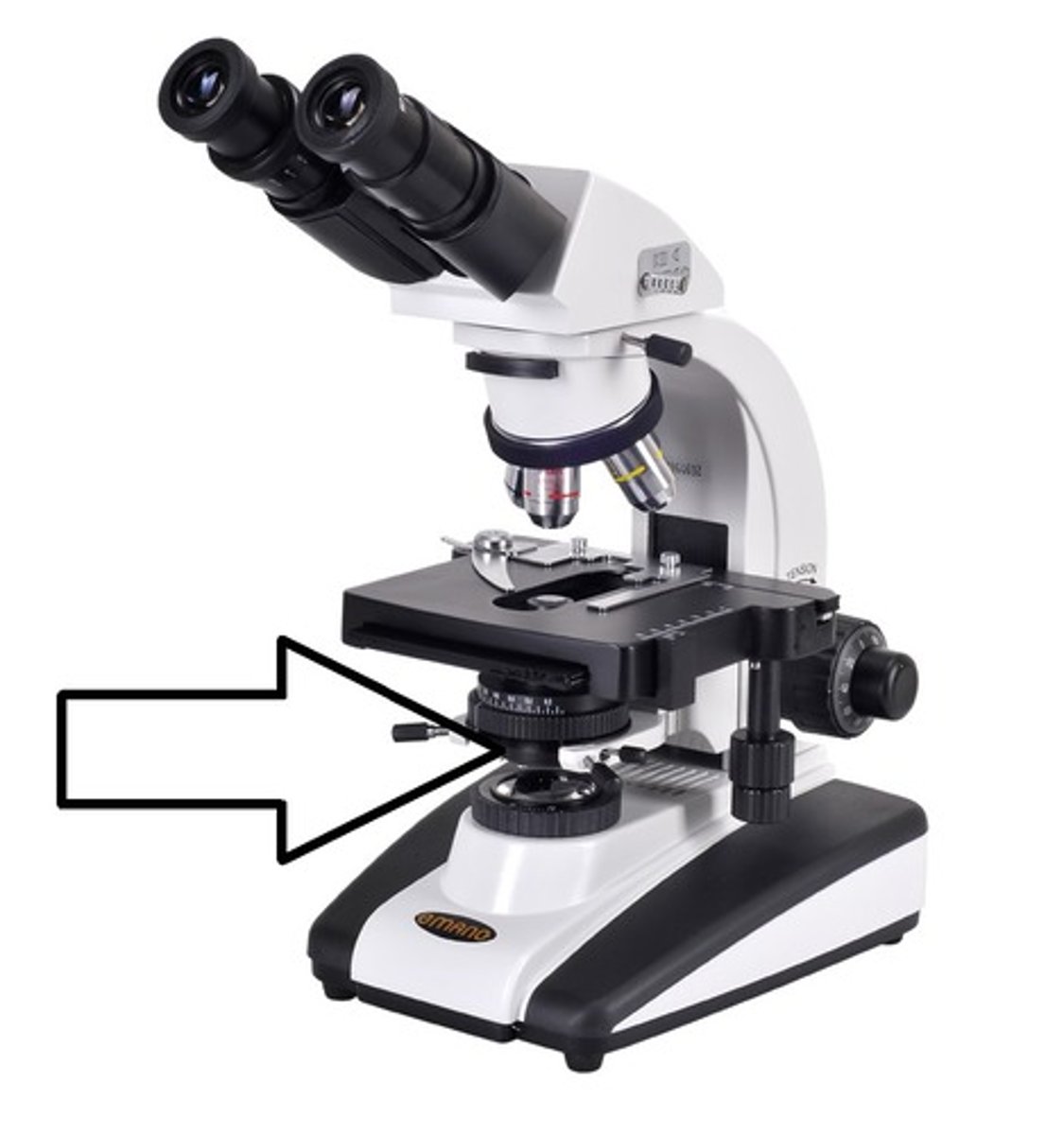

Iris Diaphragm Lever
regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser
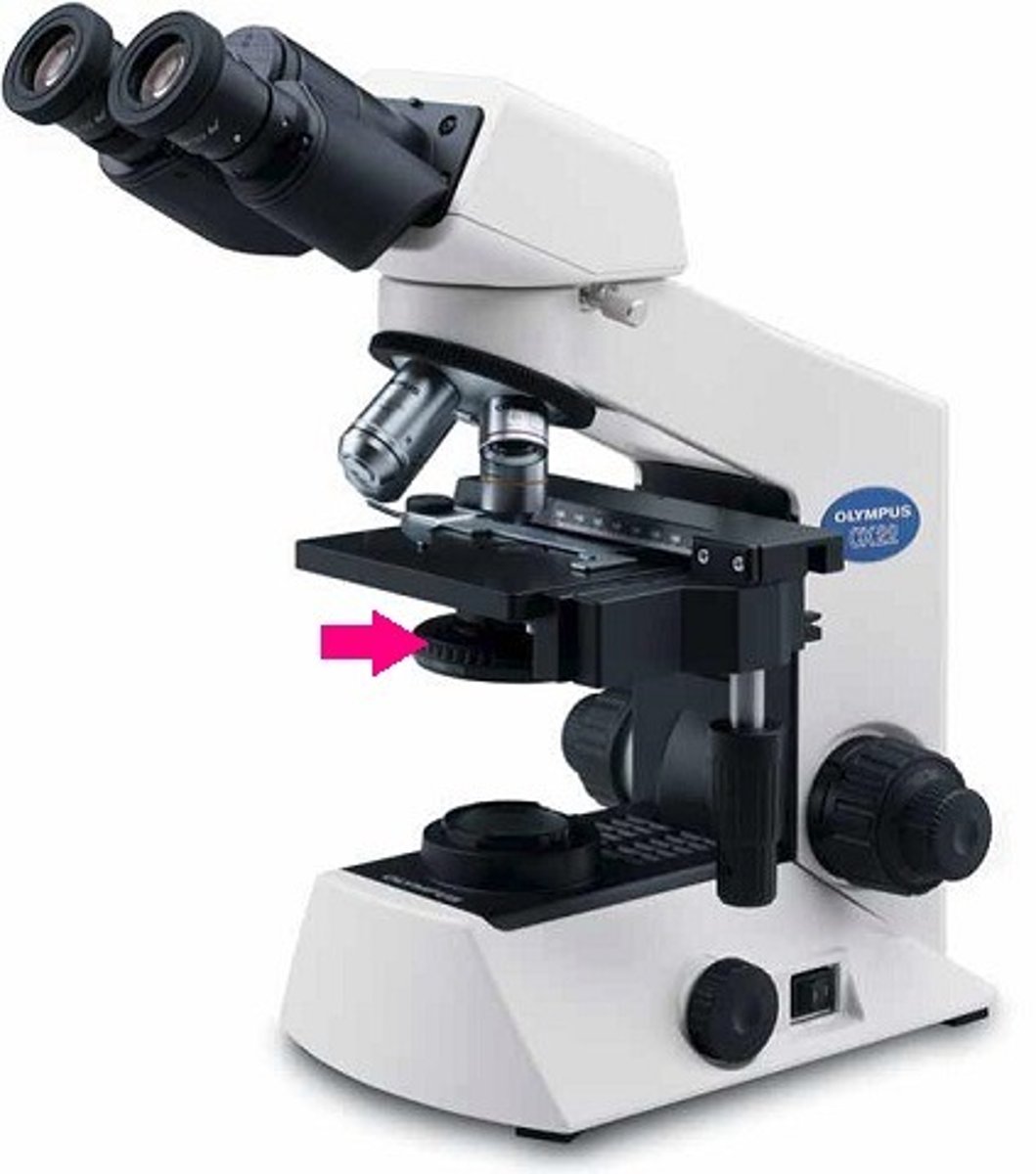

Proper microscope storage
1. turn off light 2. lower stage 3. remove slide 4. put to lowest objective 5. wrap cord on back of scope, 6. cover with bag 7. store
Carry a microscope
two hands, one on base one on arm
Unviewable Slide
not focused, light off, specimen is not in field of view
Ventral Cavity
front of body, contains thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
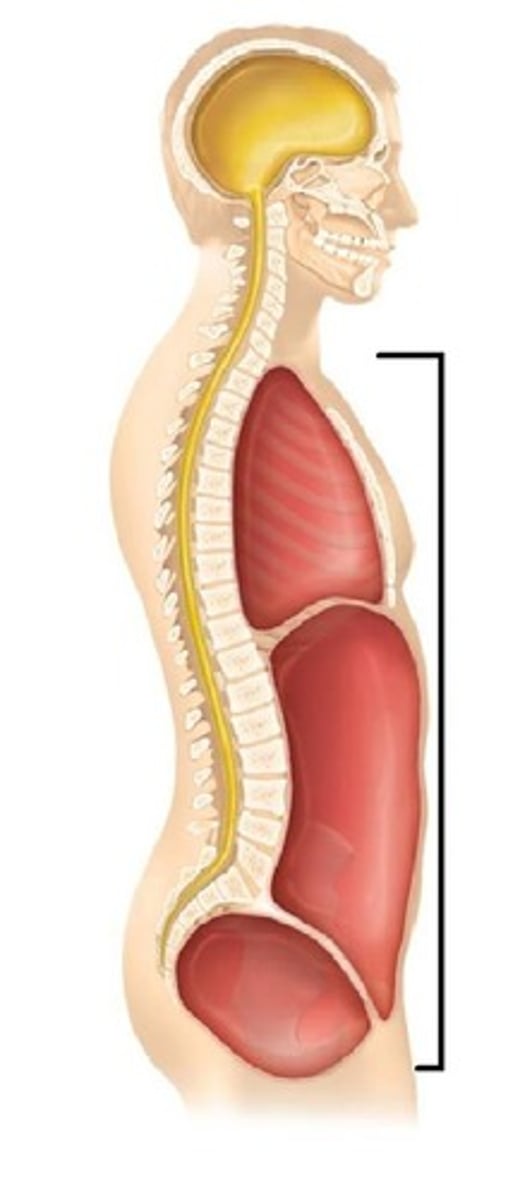
Dorsal Cavity
includes cranial and vertebral cavities
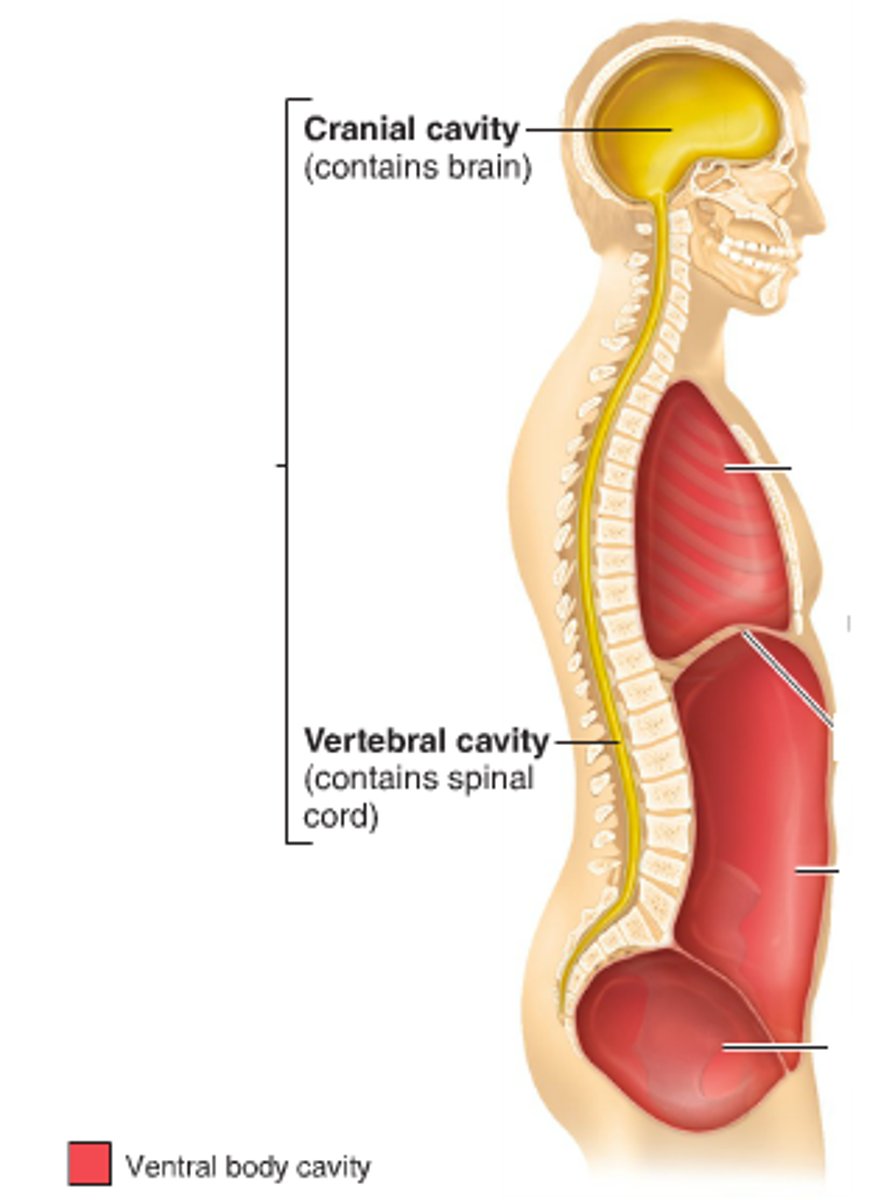
thoracic cavity
upper ventral cavity, contains heart and lungs
Abdominal Cavity
middle portion of ventral cavity contains stomach, intestines, spleen, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidney
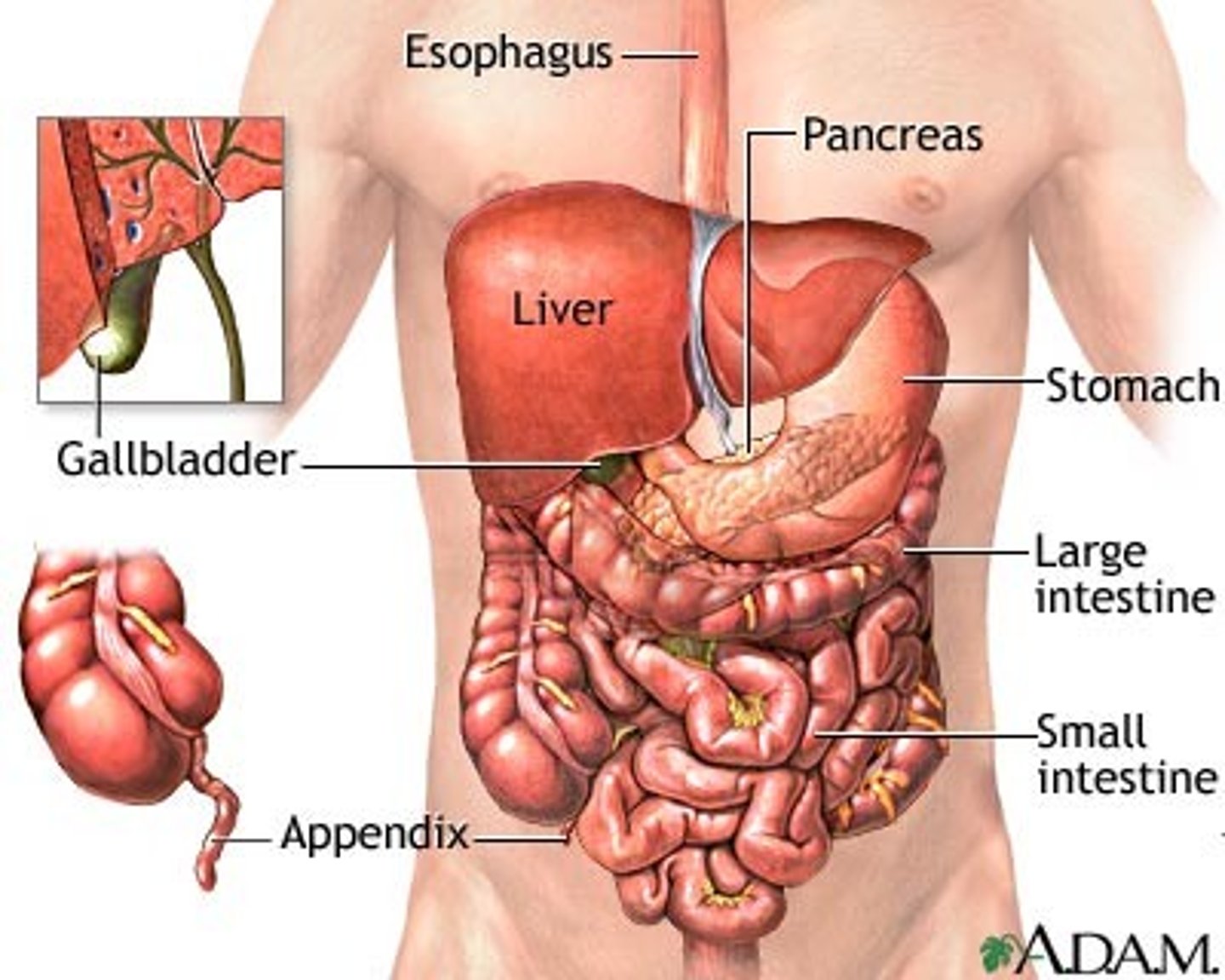
pelvic cavity
Lower ventral cavity, contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
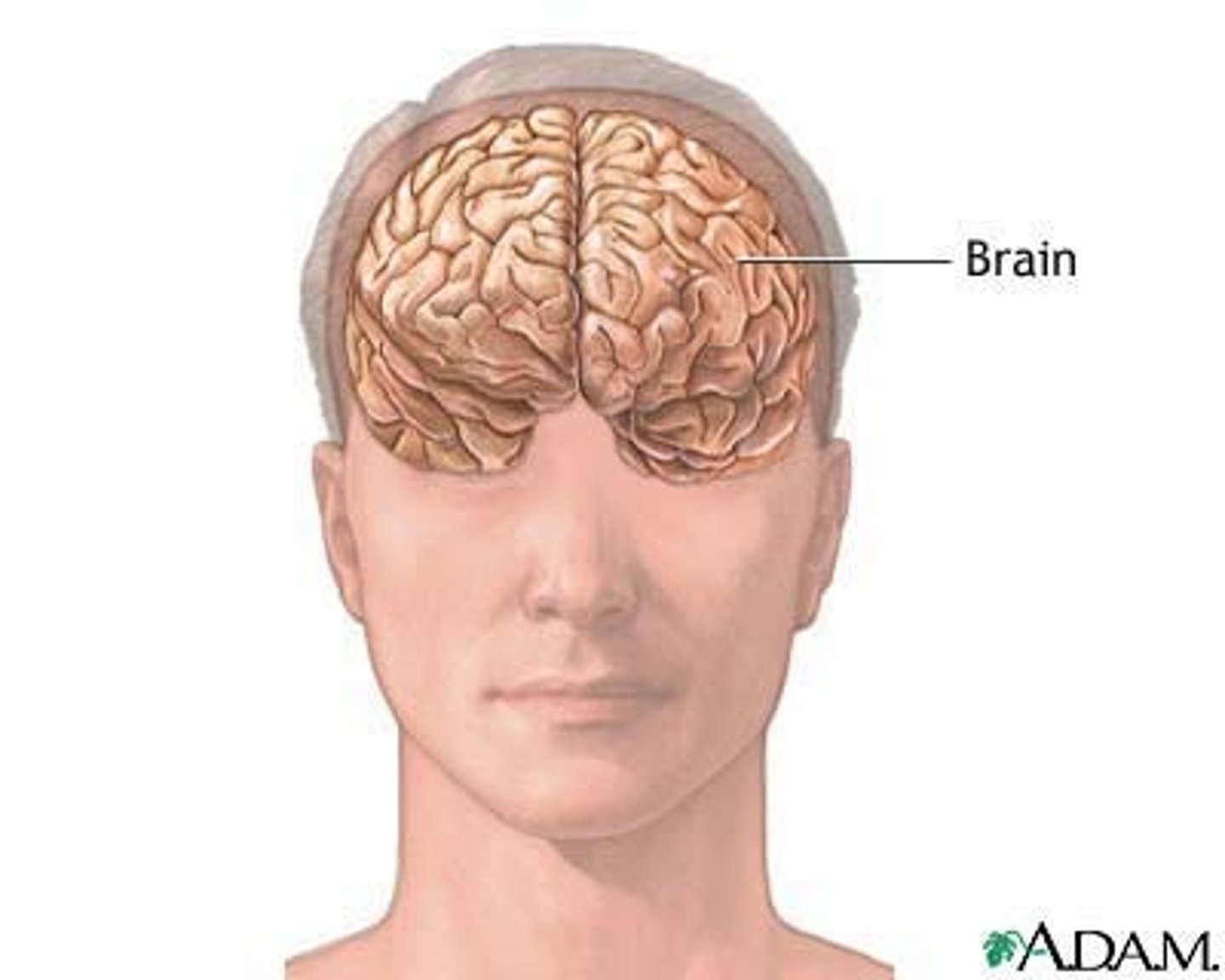
cranial cavity
upper dorsal contains the brain
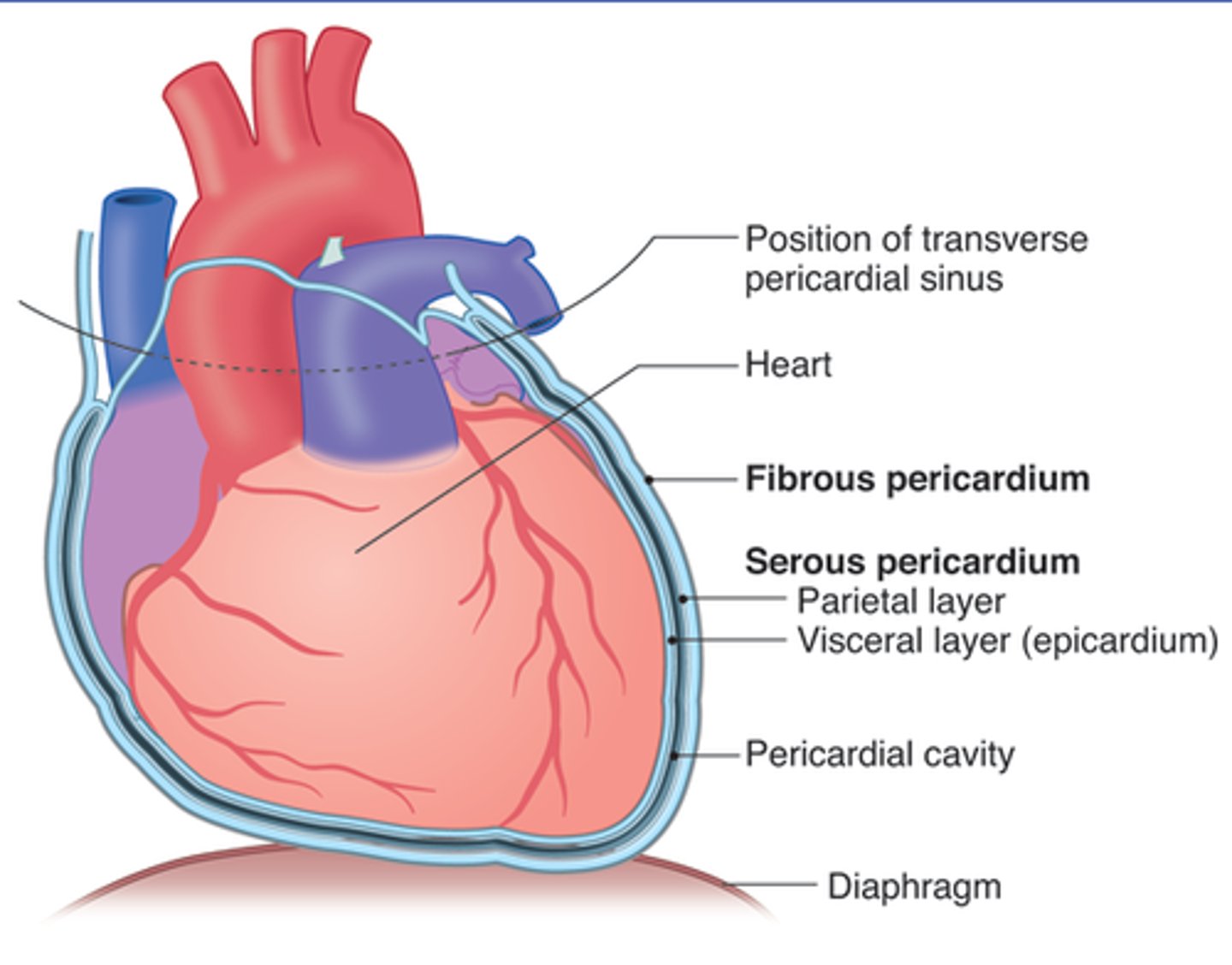
parietal pericardium
membrane surrounding heart cavity
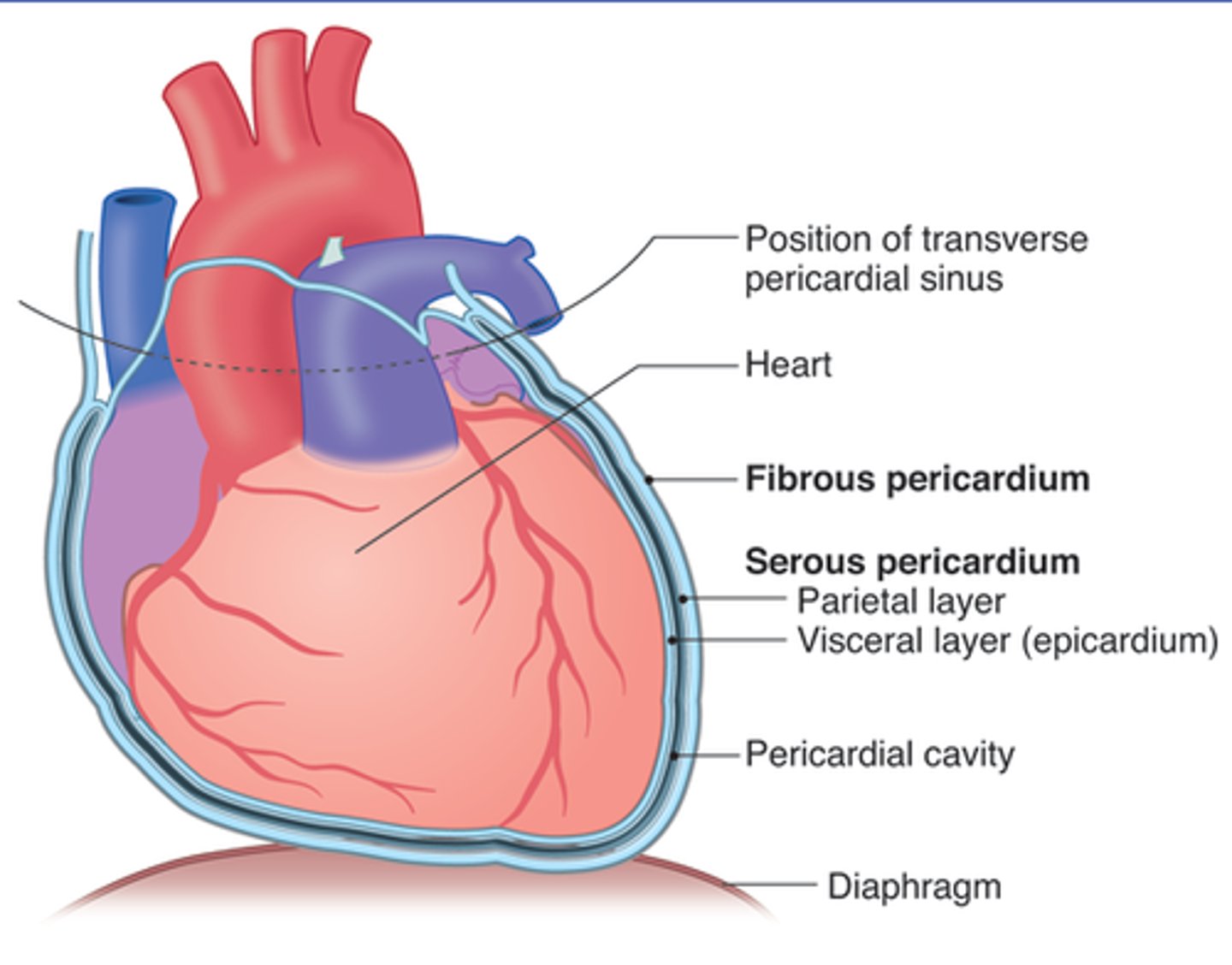
visceral pericardium
covers the surface of the heart
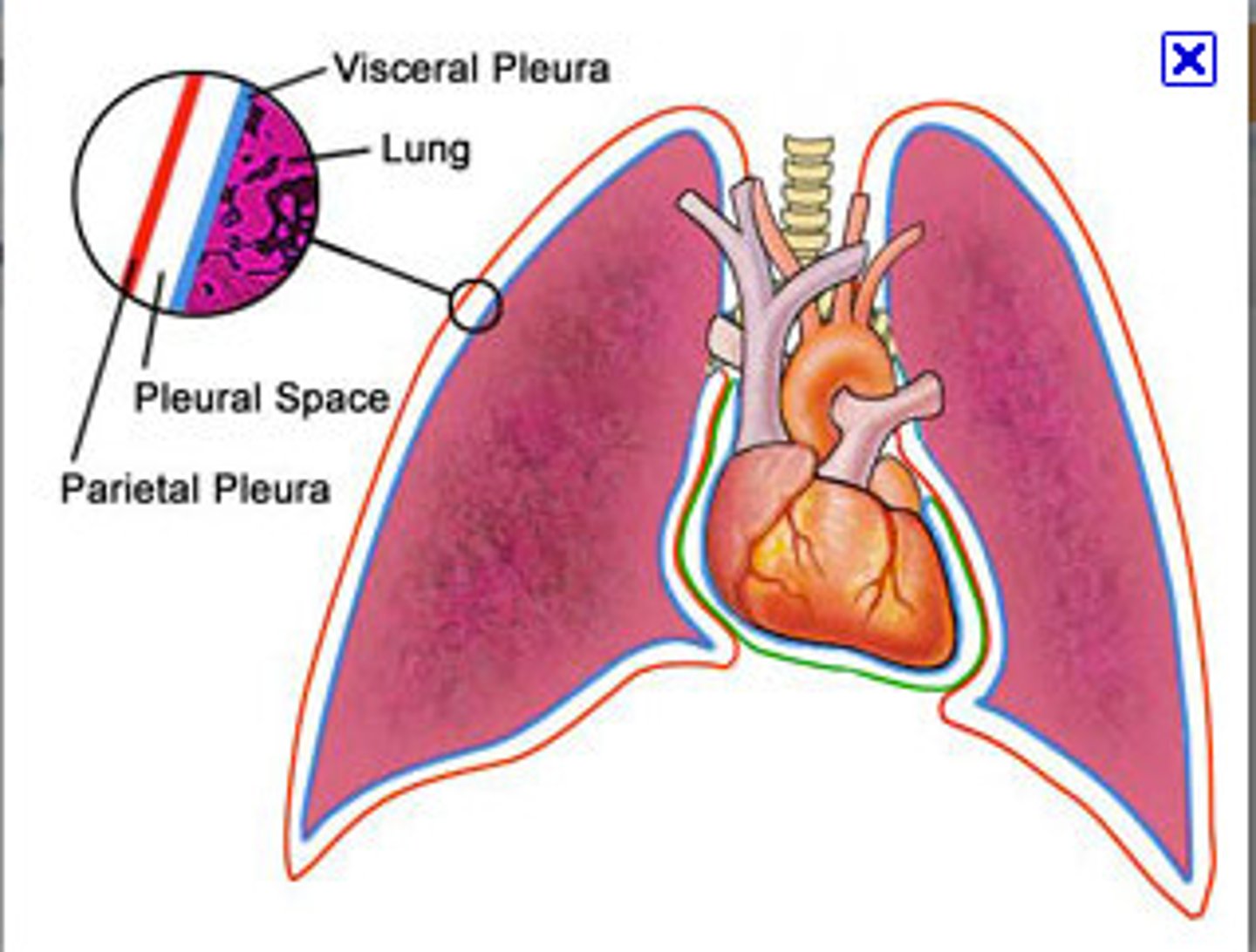
parietal pleura
lines lung cavity
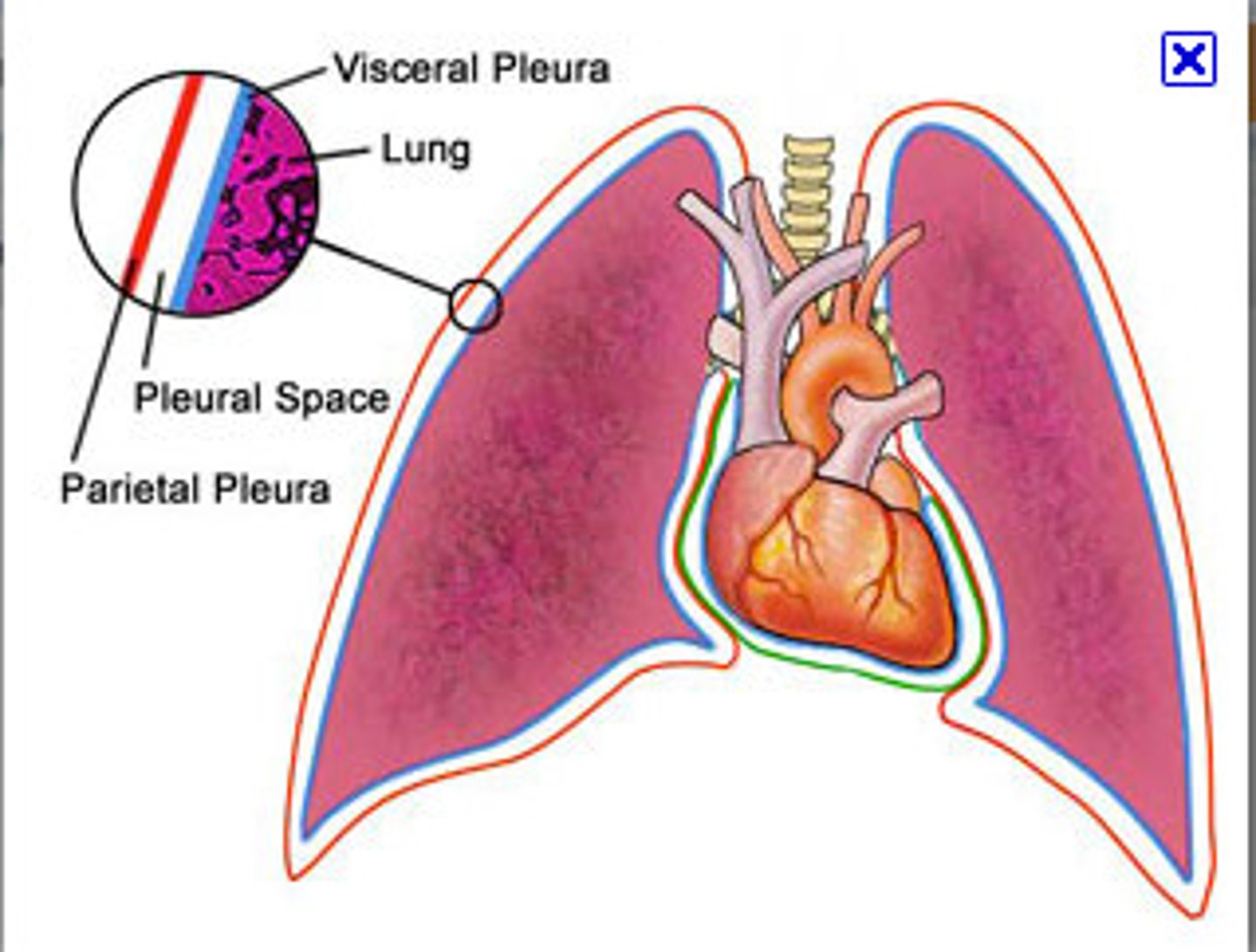
visceral pleura
covers the lungs
parietal peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity
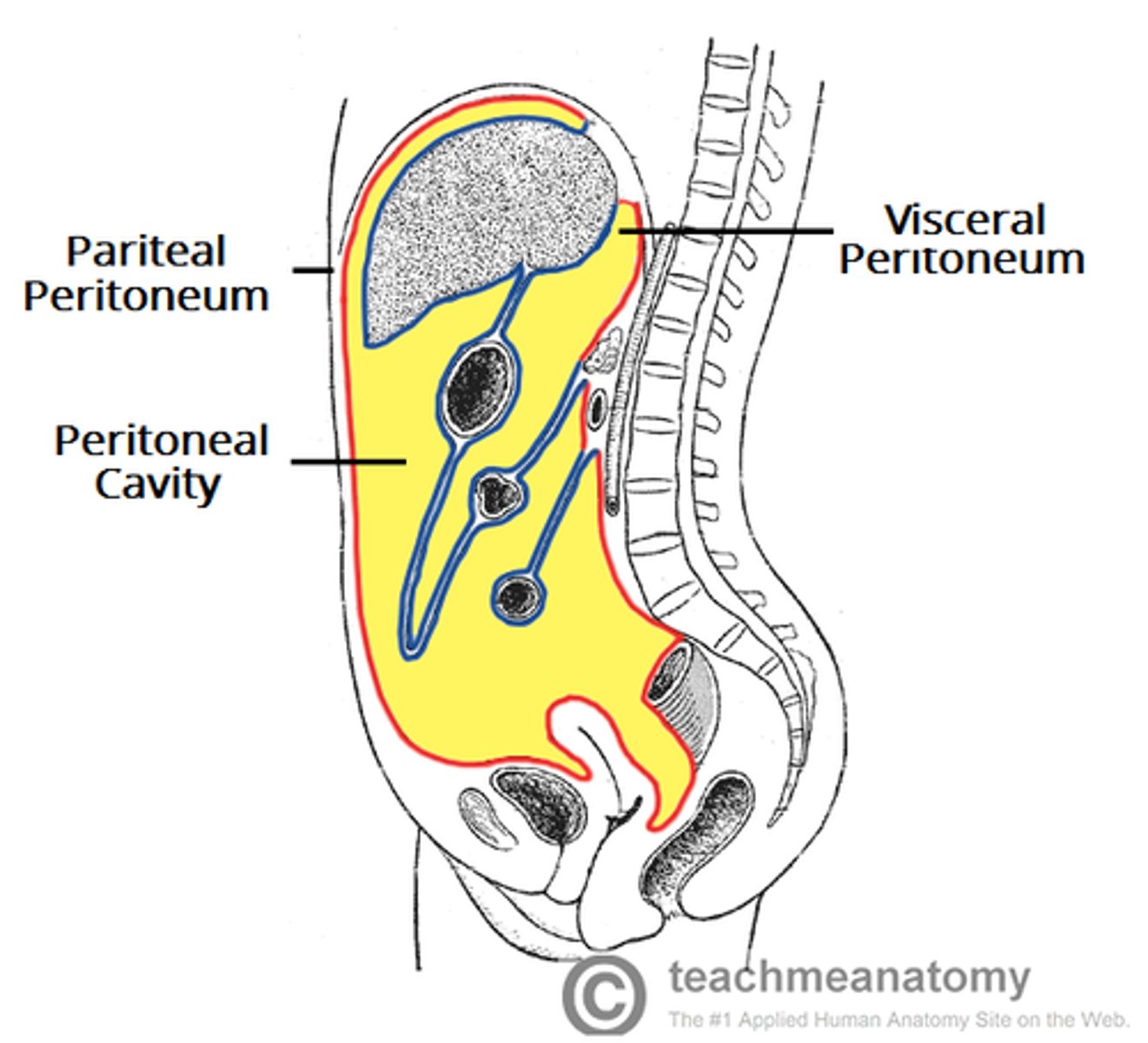
visceral peritoneum
covers the surface of the abdominal organs
Heart
located in thoracic cavity
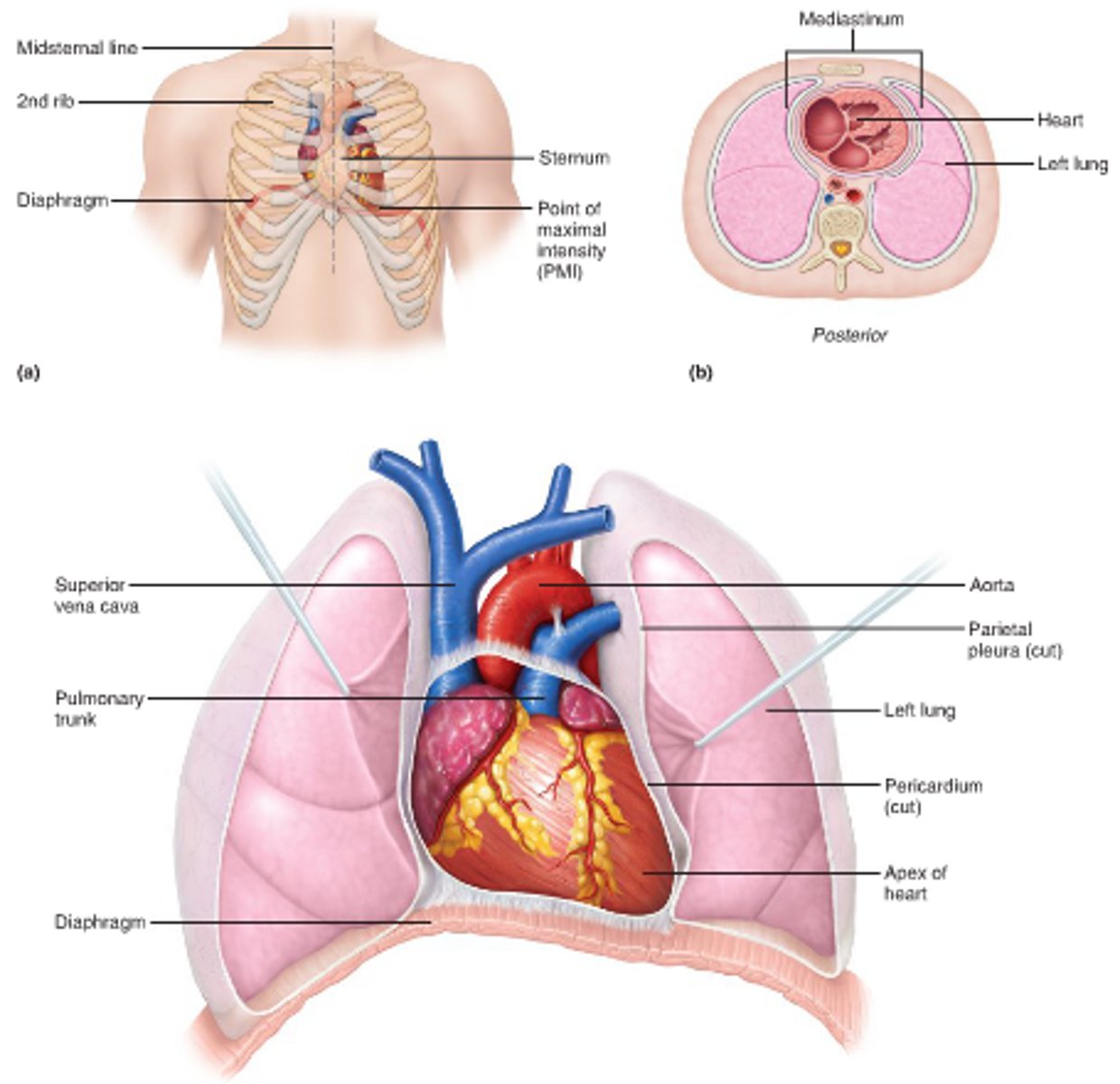
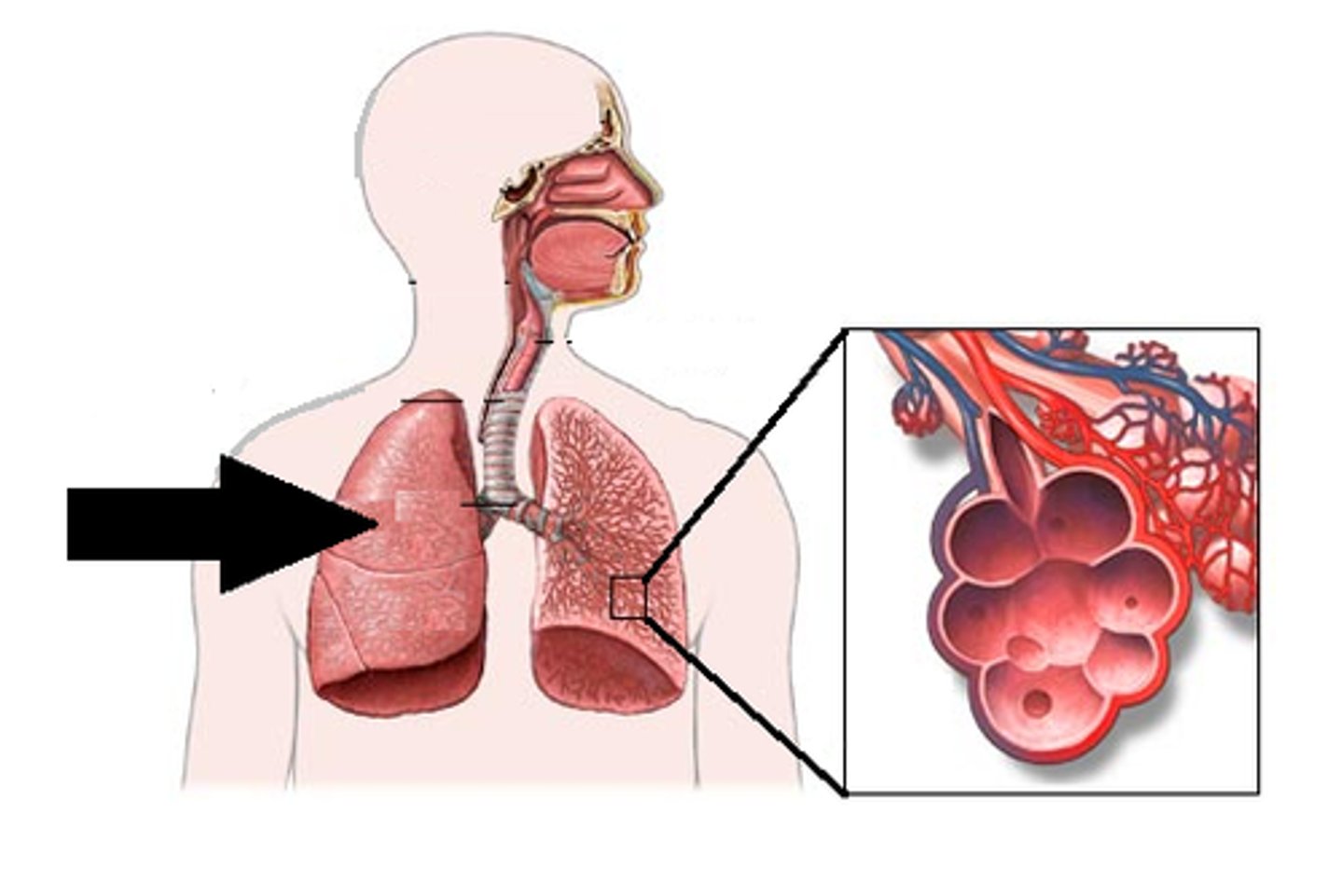
Lungs
located in thoracic cavity
Brain
located in cranial cavity
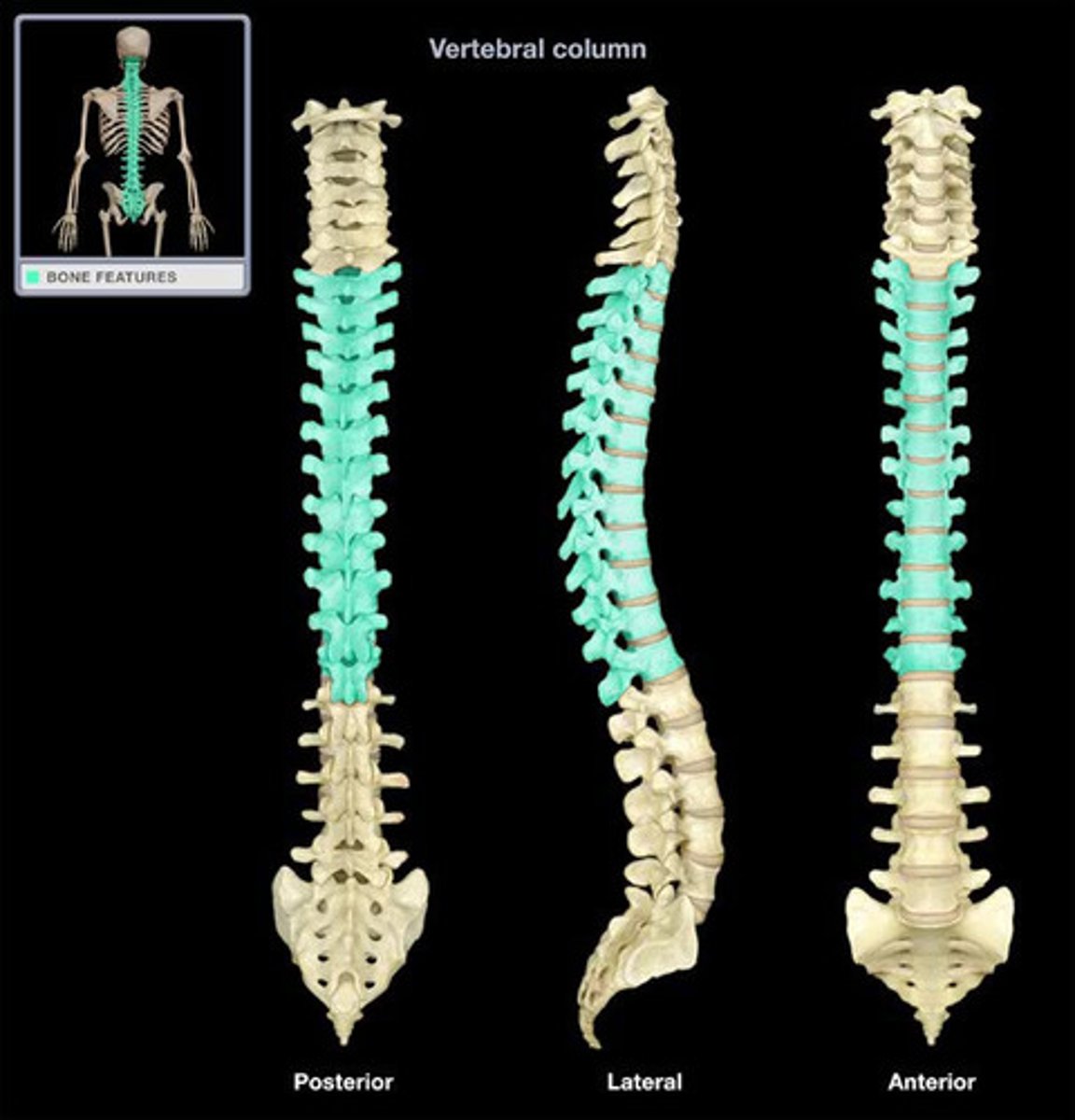
Spinal Cord, Vertebrae
located in vertebral cavity
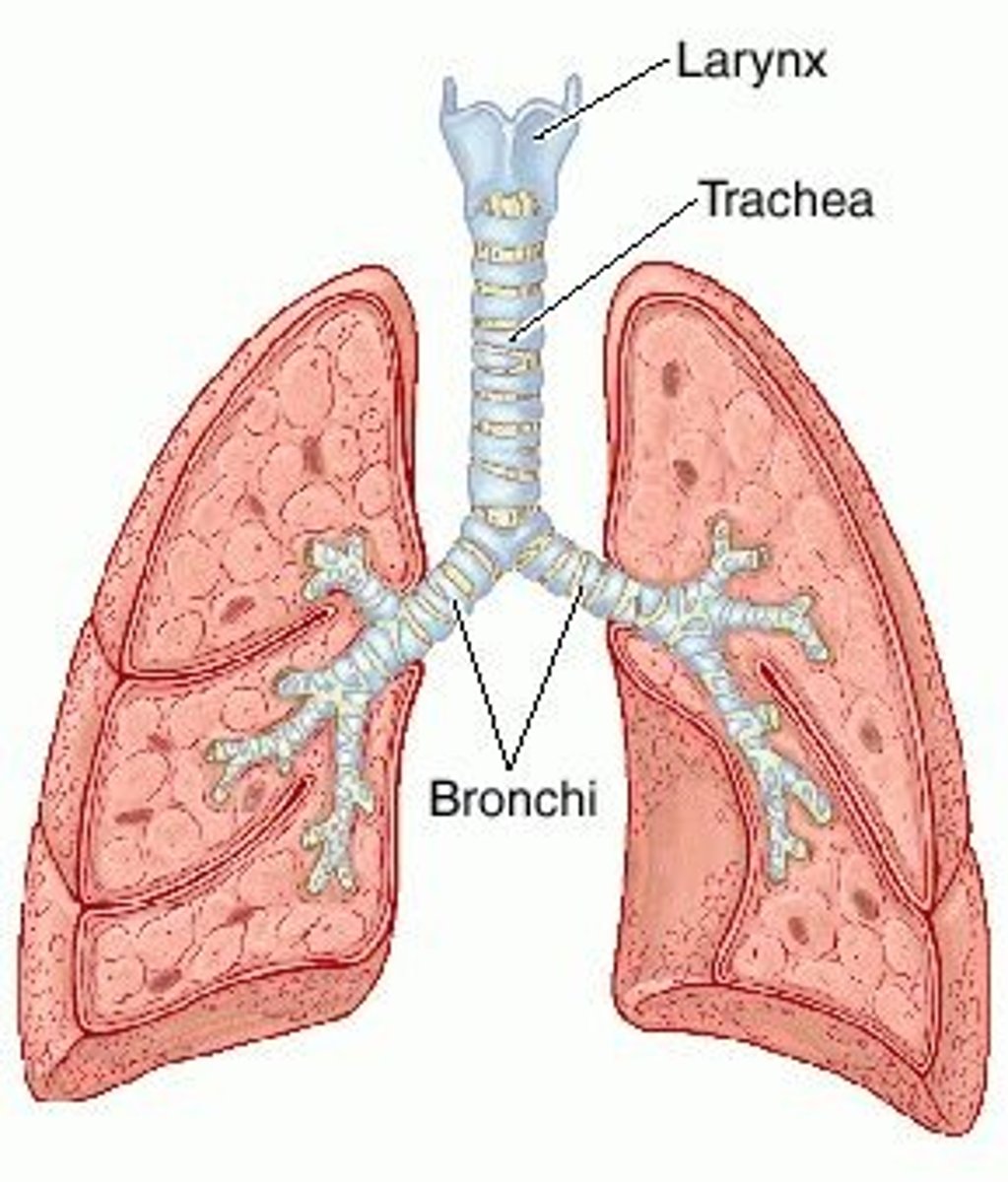
Trachea
Located in thoracic cavity
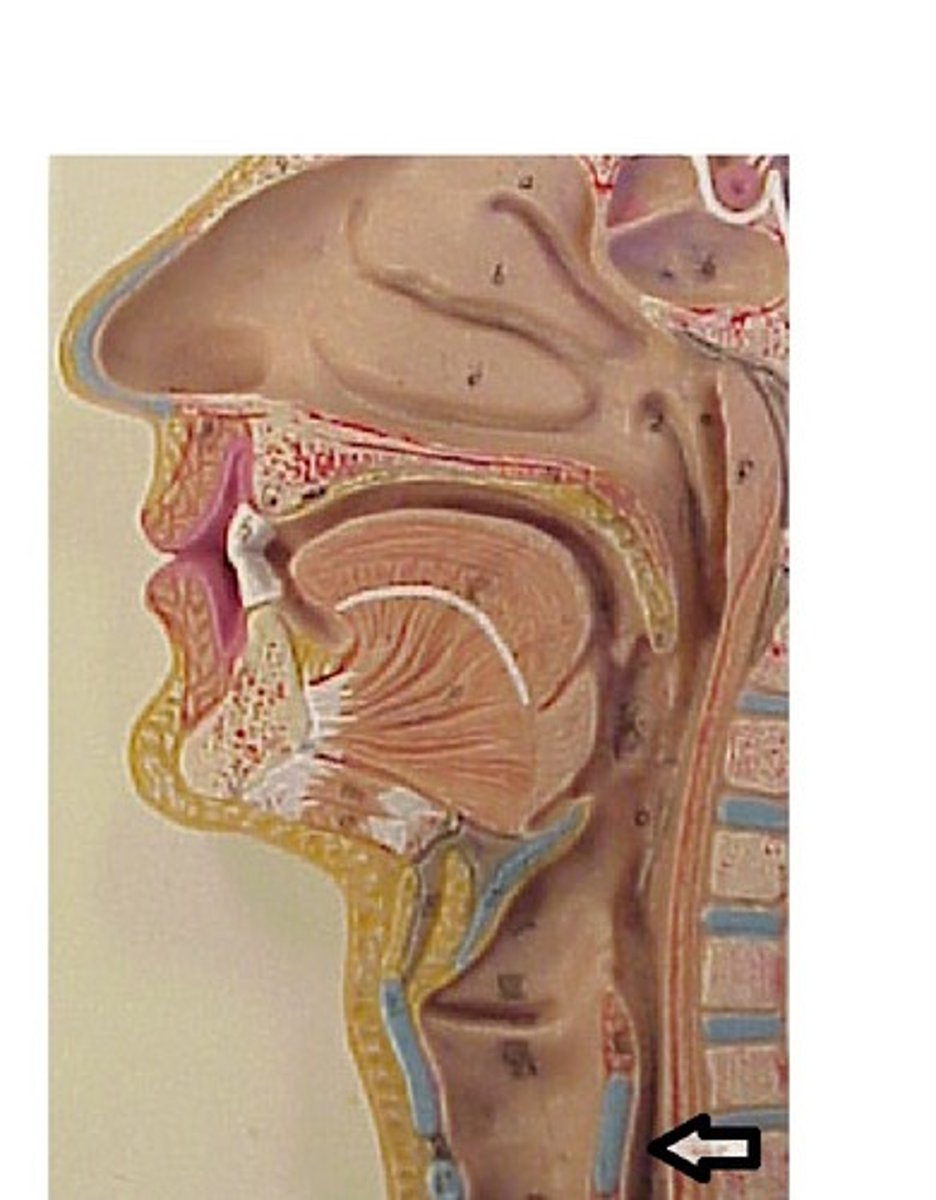
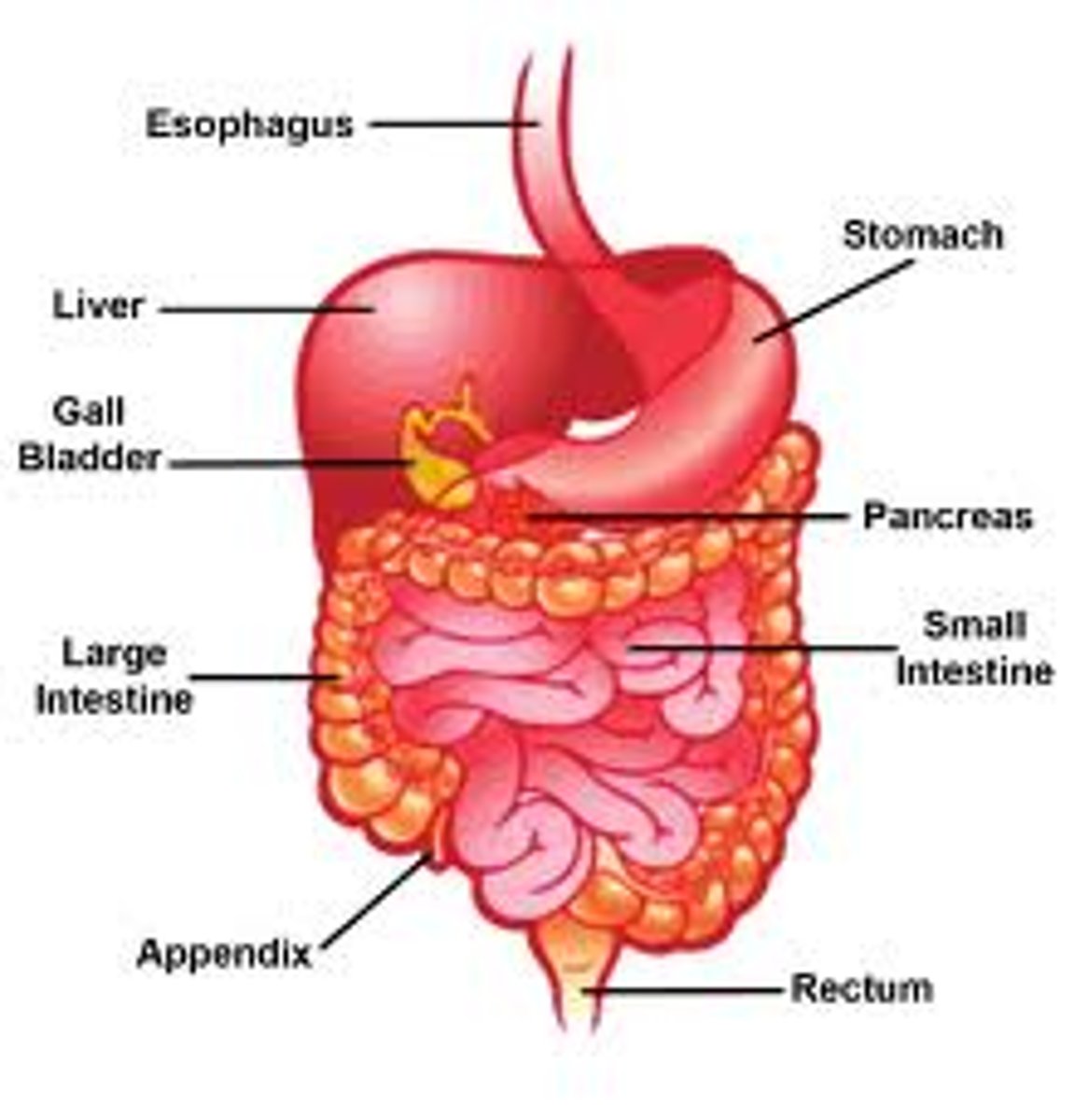
Esophagus
Located in thoracic cavity
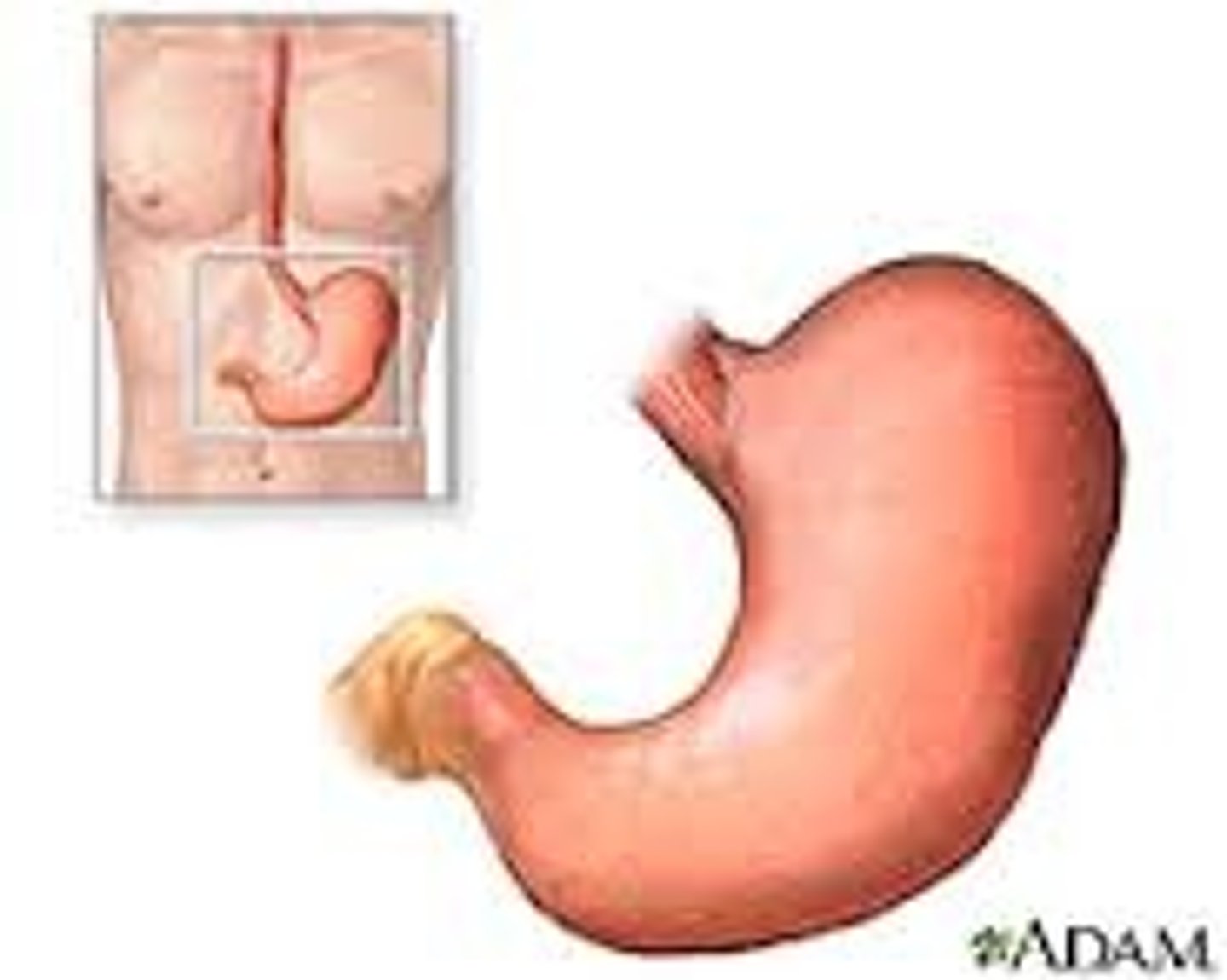
Stomach
abdominal cavity
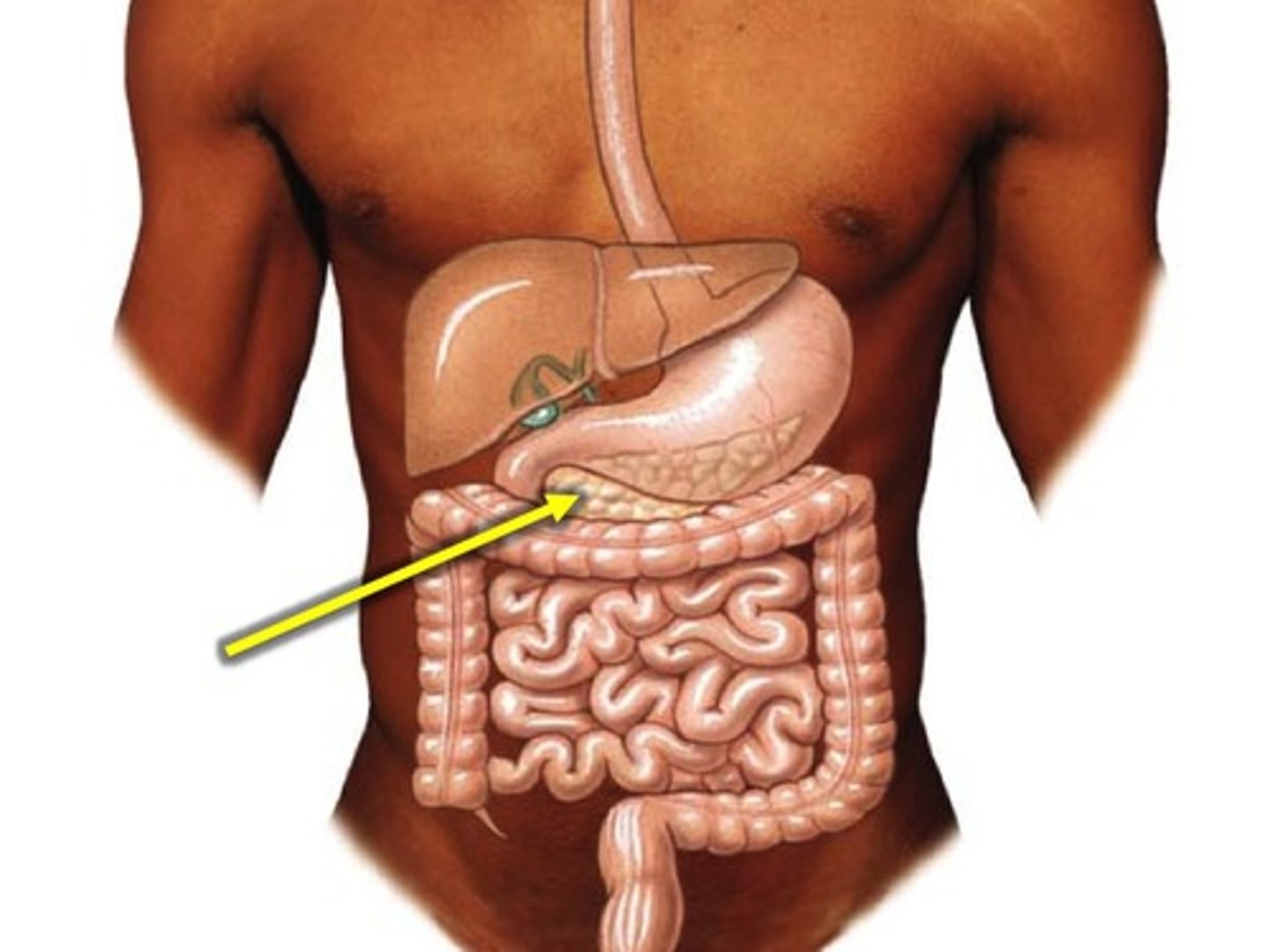
Pancreas
abdominal cavity
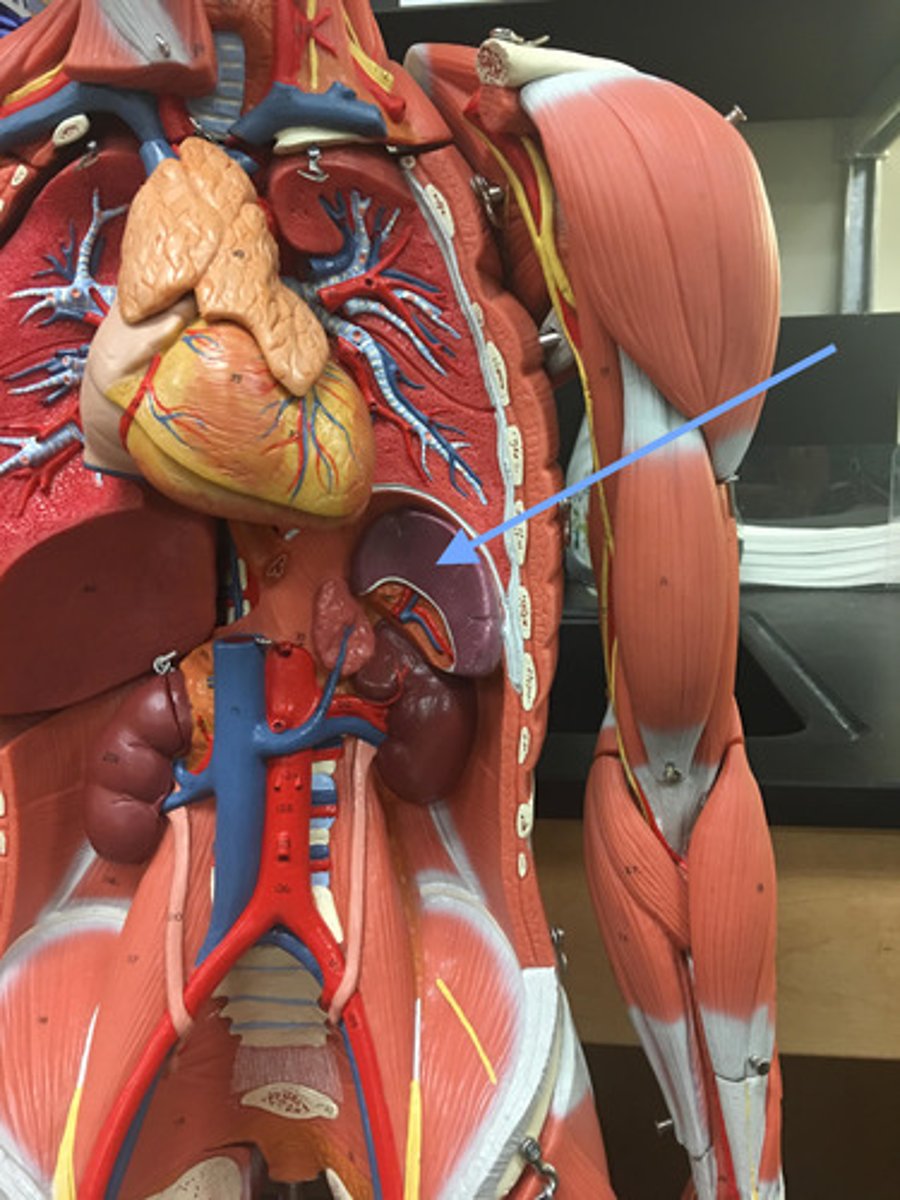
Spleen
Abdominal cavity
Liver
Abdominal Cavity
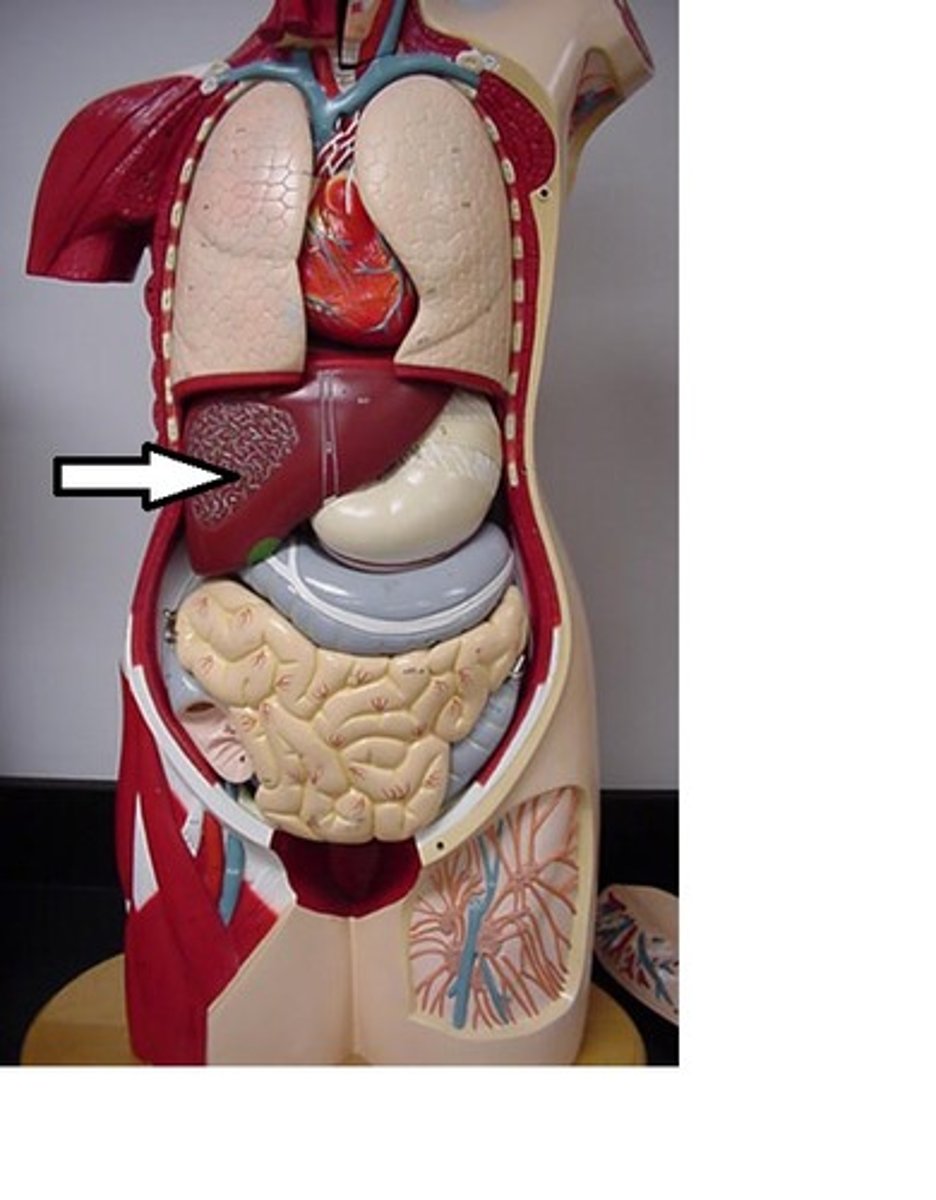
Kidneys
Abdominal Cavity
large and small intestine
abdominal cavity
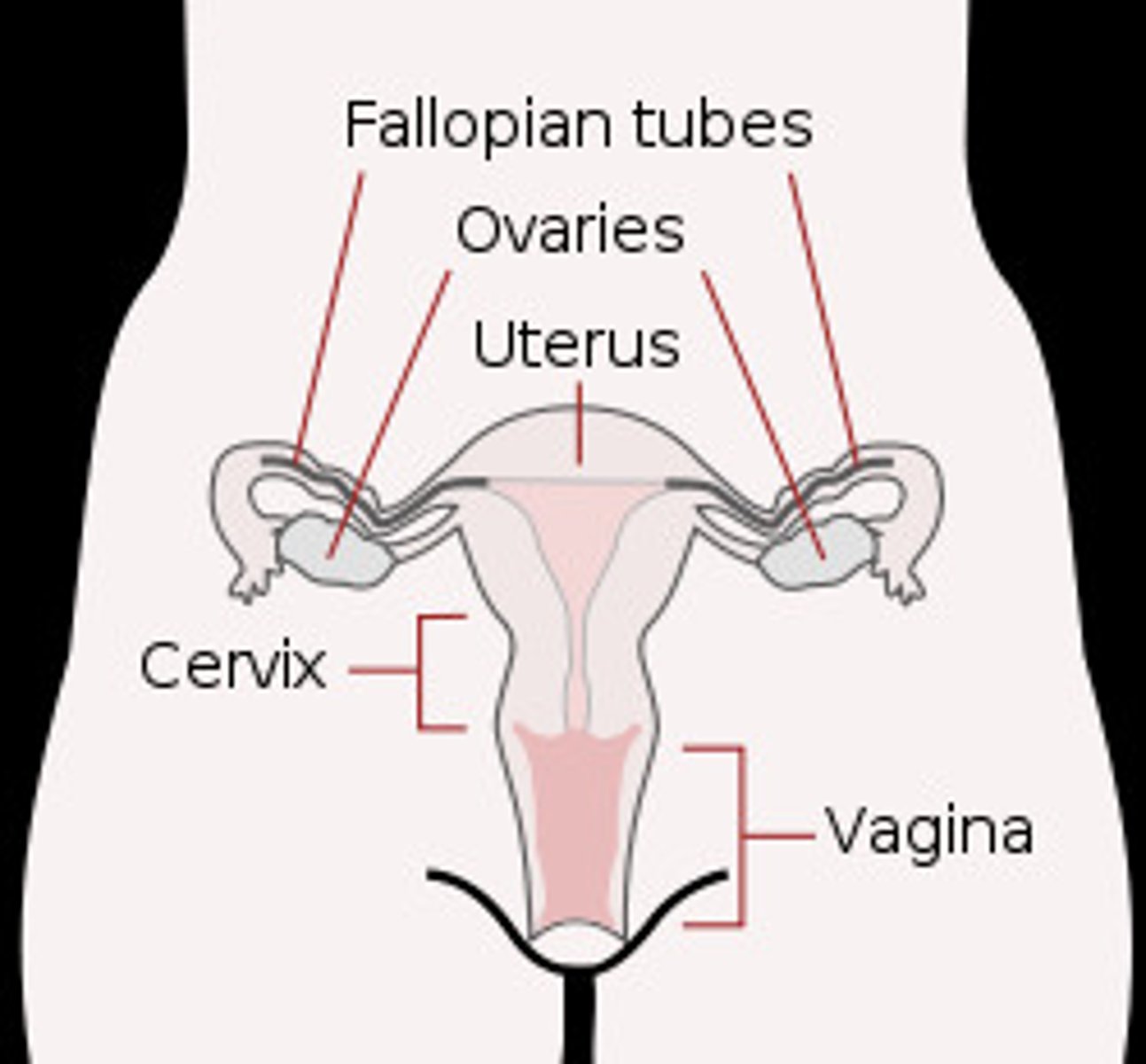
Ovaries
pelvic cavity
Testes
pelvic cavity
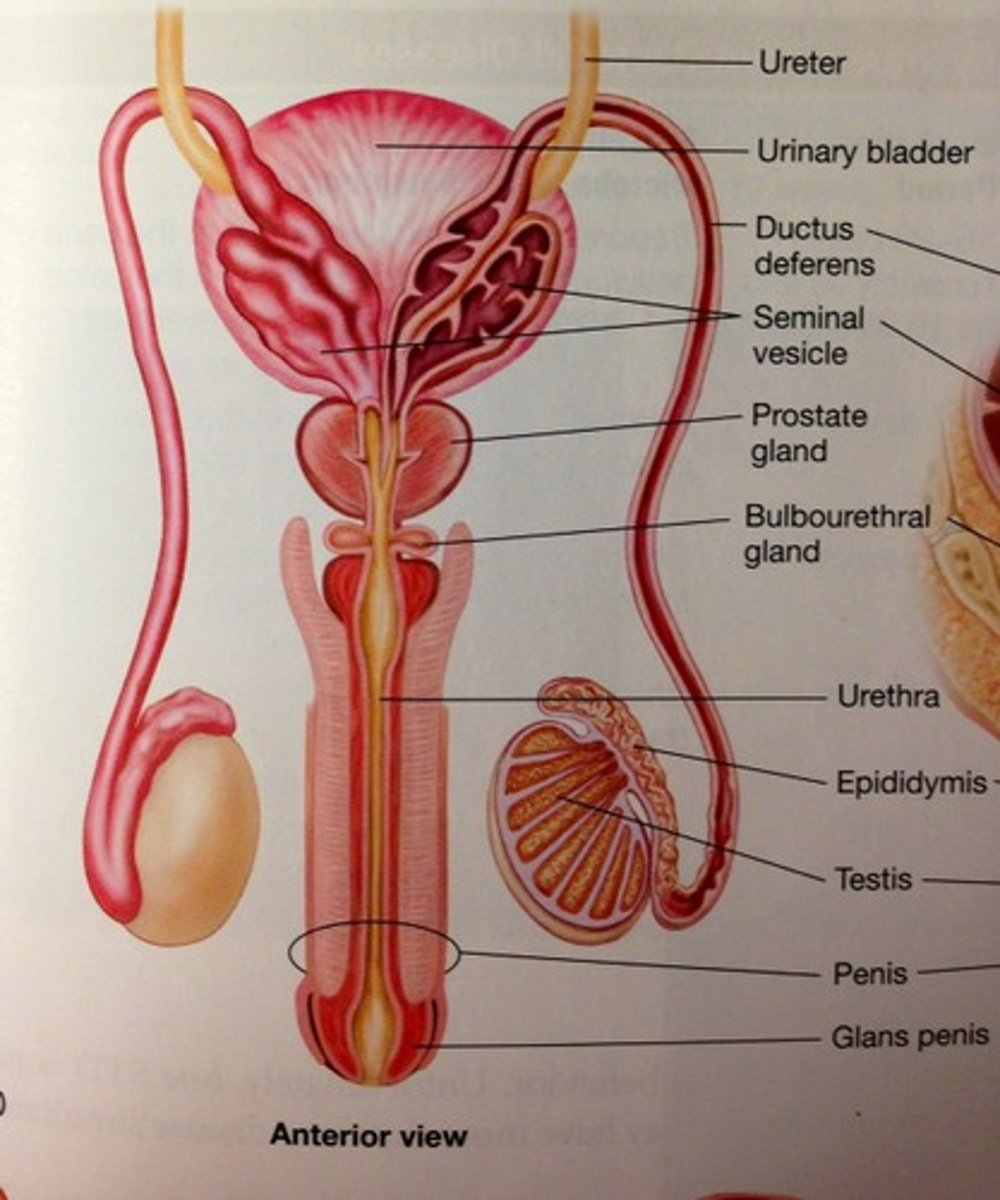
urinary bladder
pelvic cavity

Frontal (coronal) Plane
vertical plane dividing the body or structure into anterior and posterior portions front/back ventral/dorsal
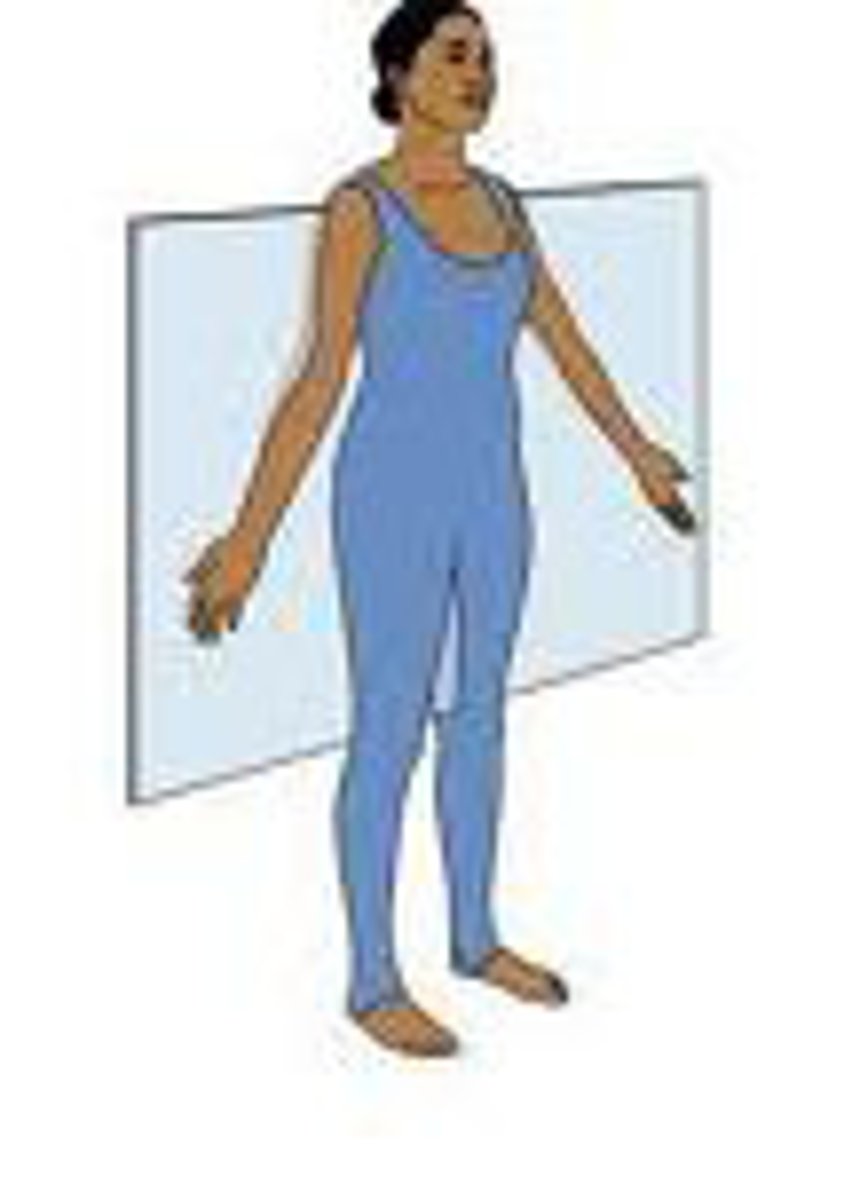

sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
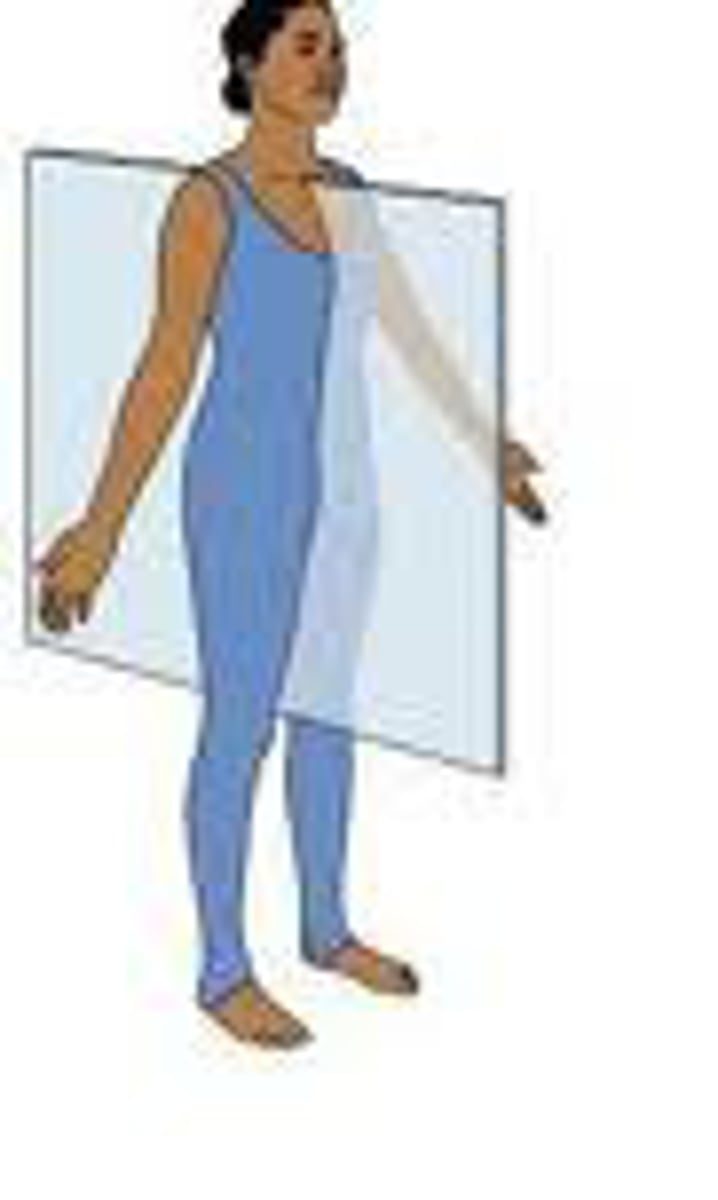
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions Superior/inferior

Directional Terms
Superior and Inferior; Anterior (ventral) and Posterior (dorsal); Medial and lateral; Proximal and distal; Superficial and deep
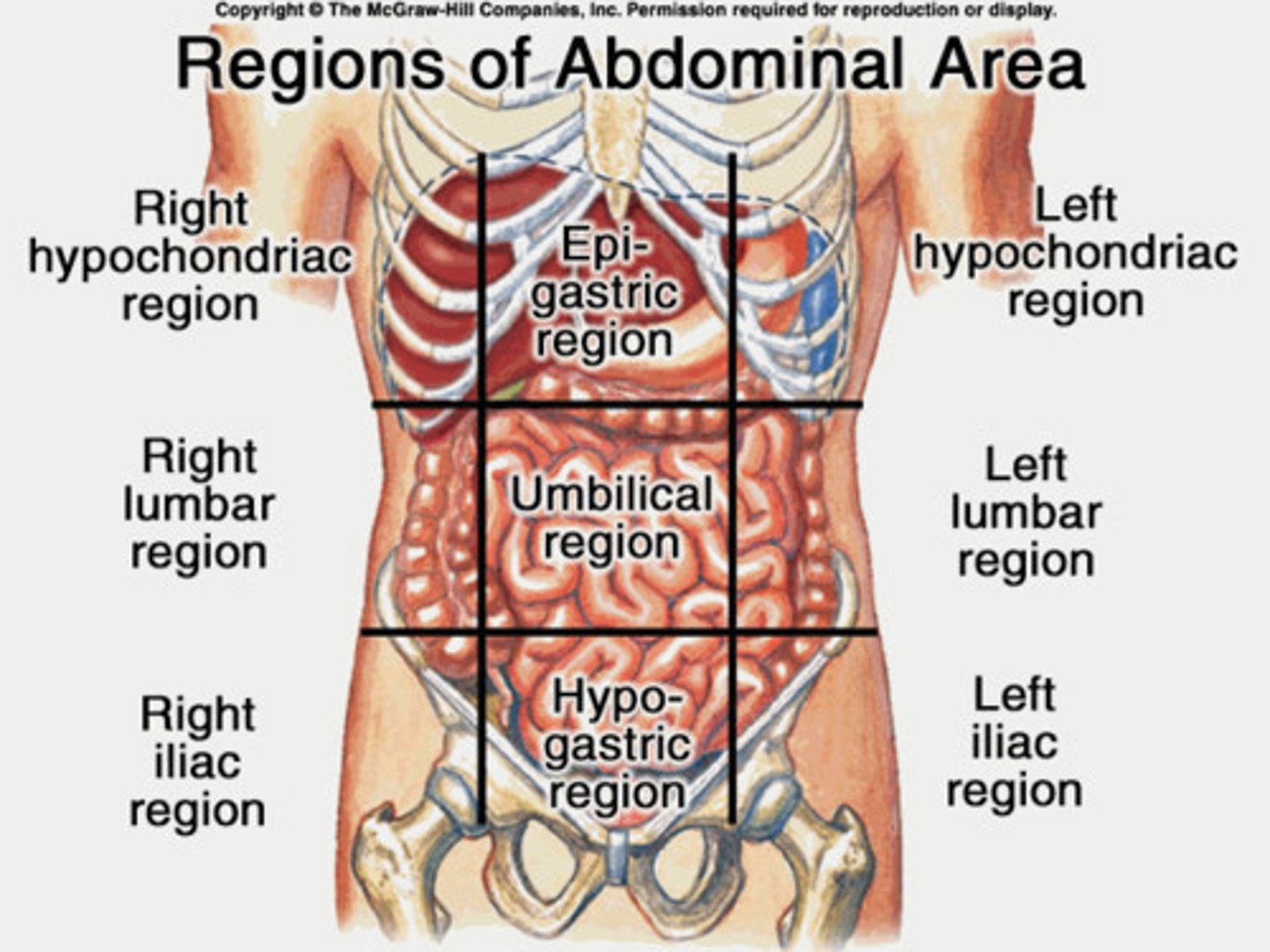
Abdominal Regions
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac
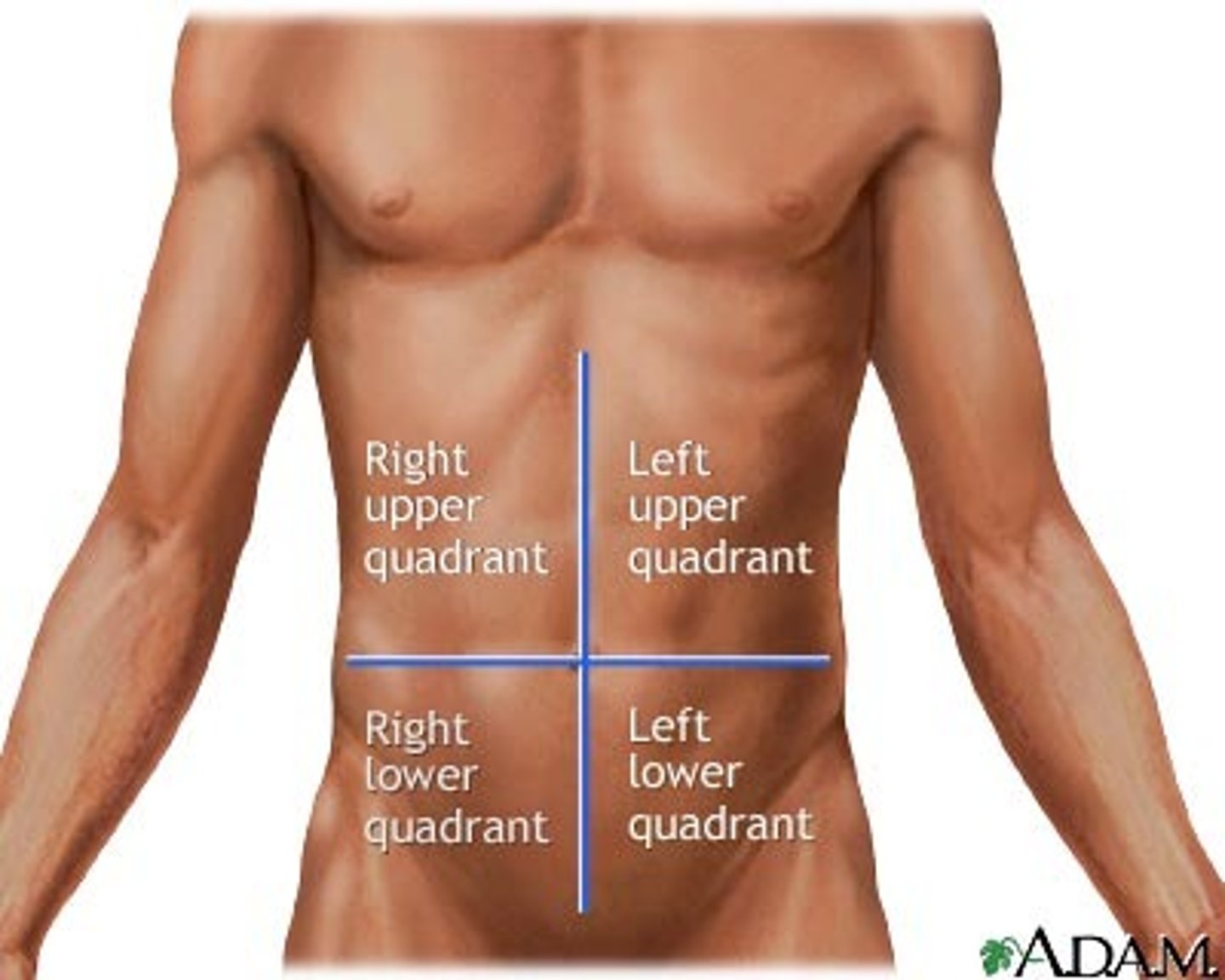
abdominal quadrants
right upper quadrant, left upper quadrant, right lower quadrant, left lower quadrant
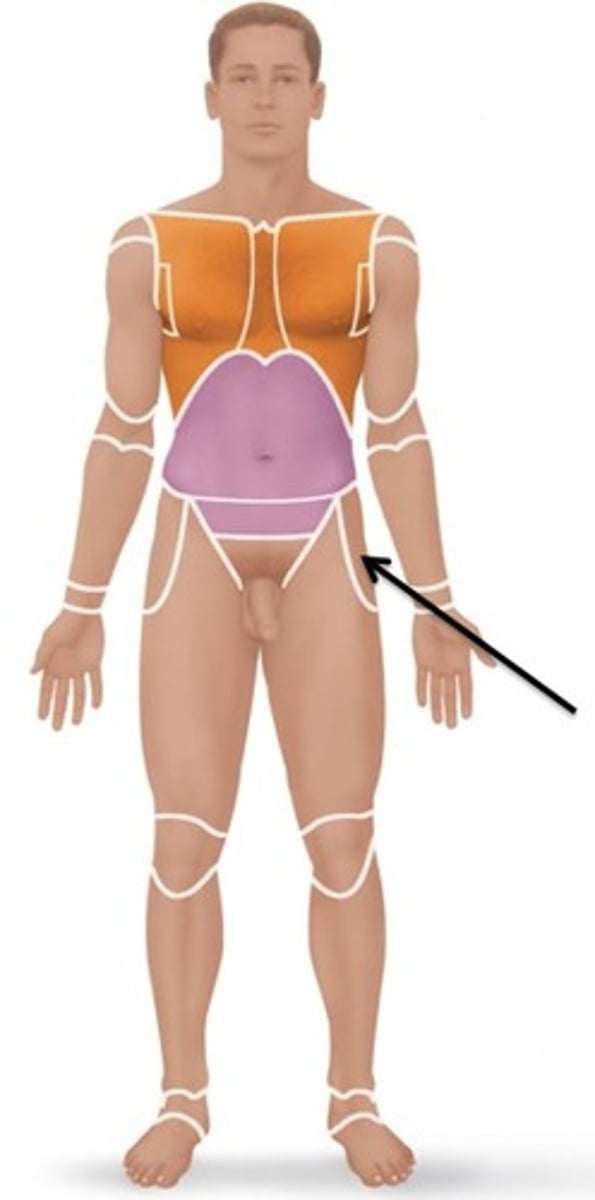
Abdominal
region between thoracic and pelvic
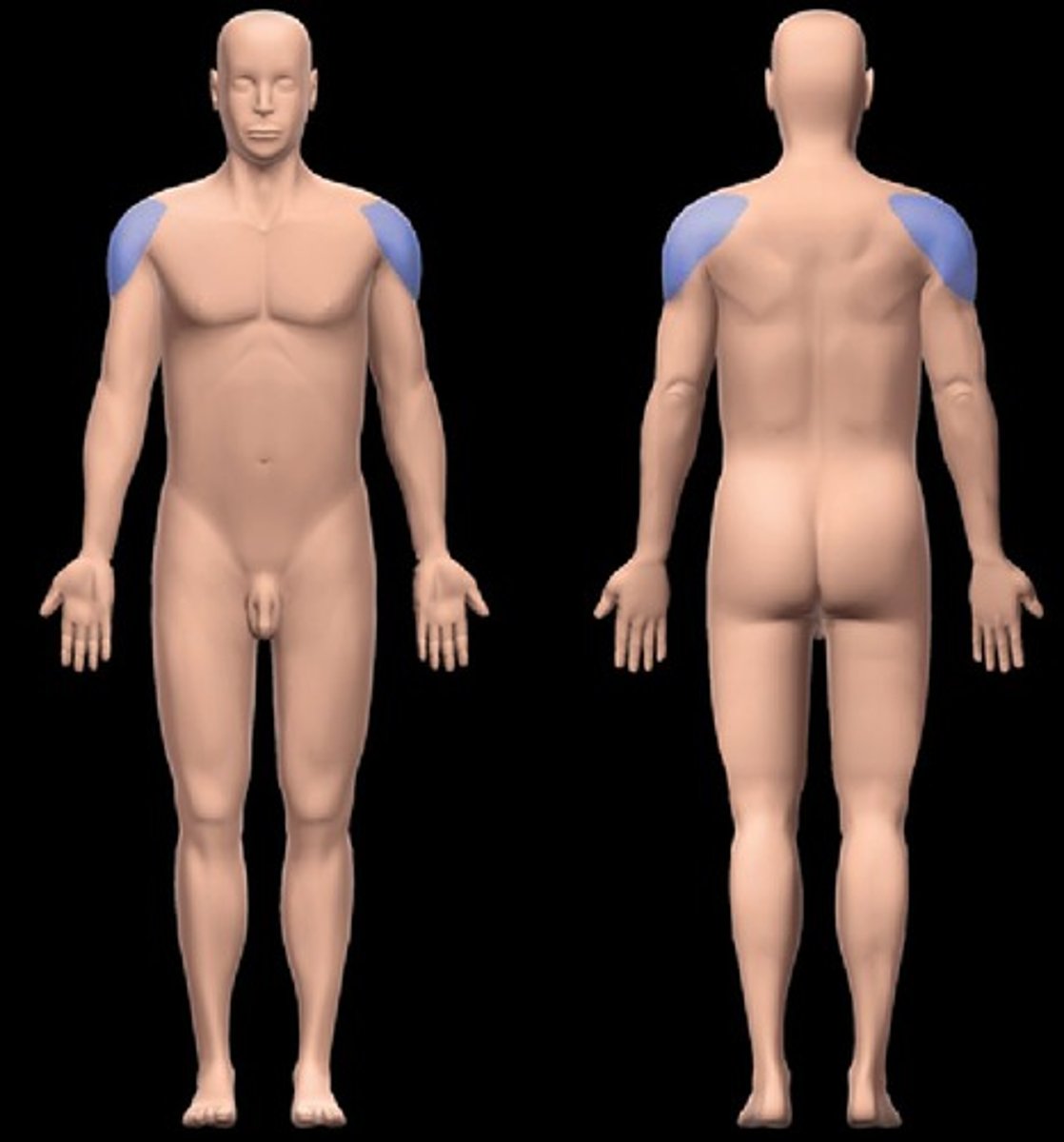
Acromial
point of shoulder
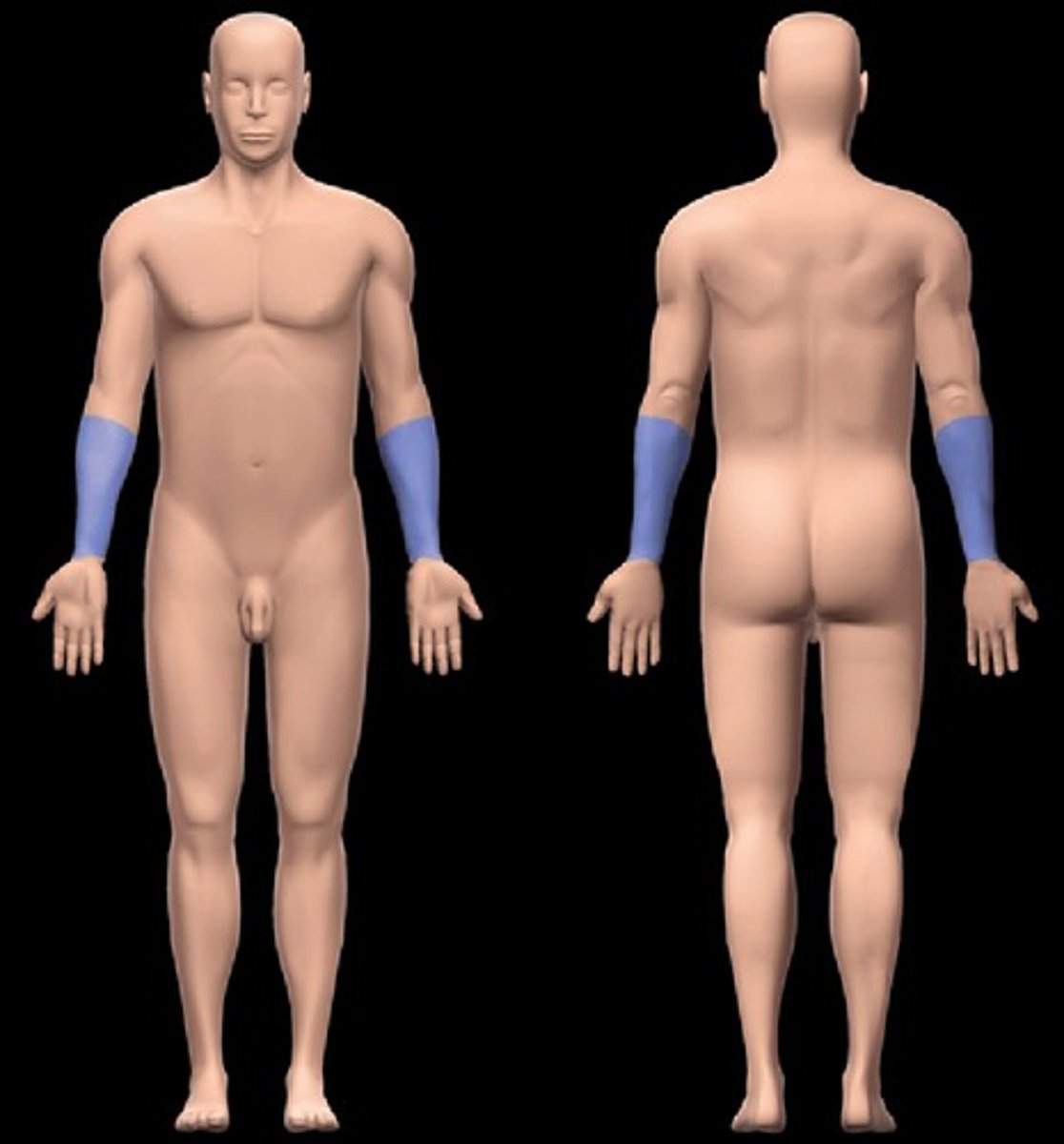
Antebrachial
forearm
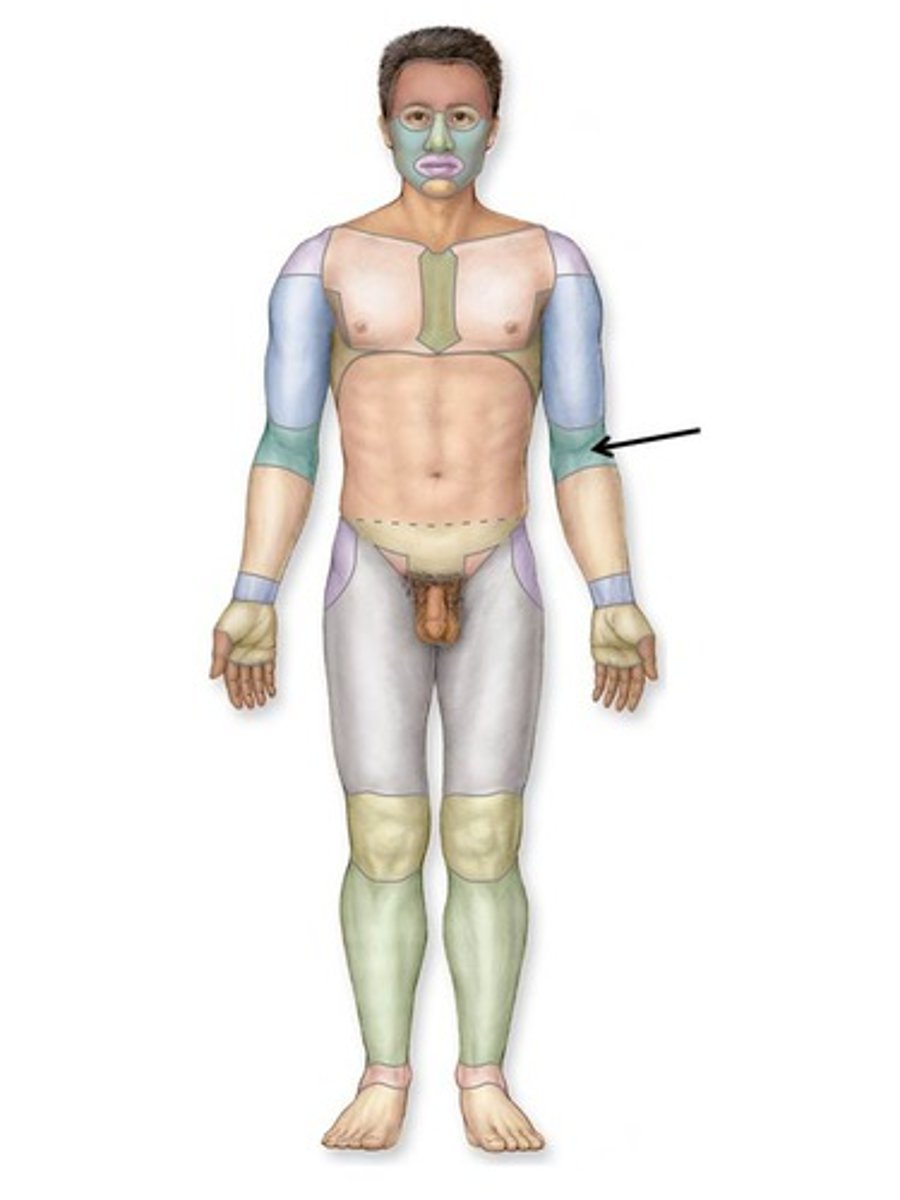
Antecubital
anterior surface of elbow
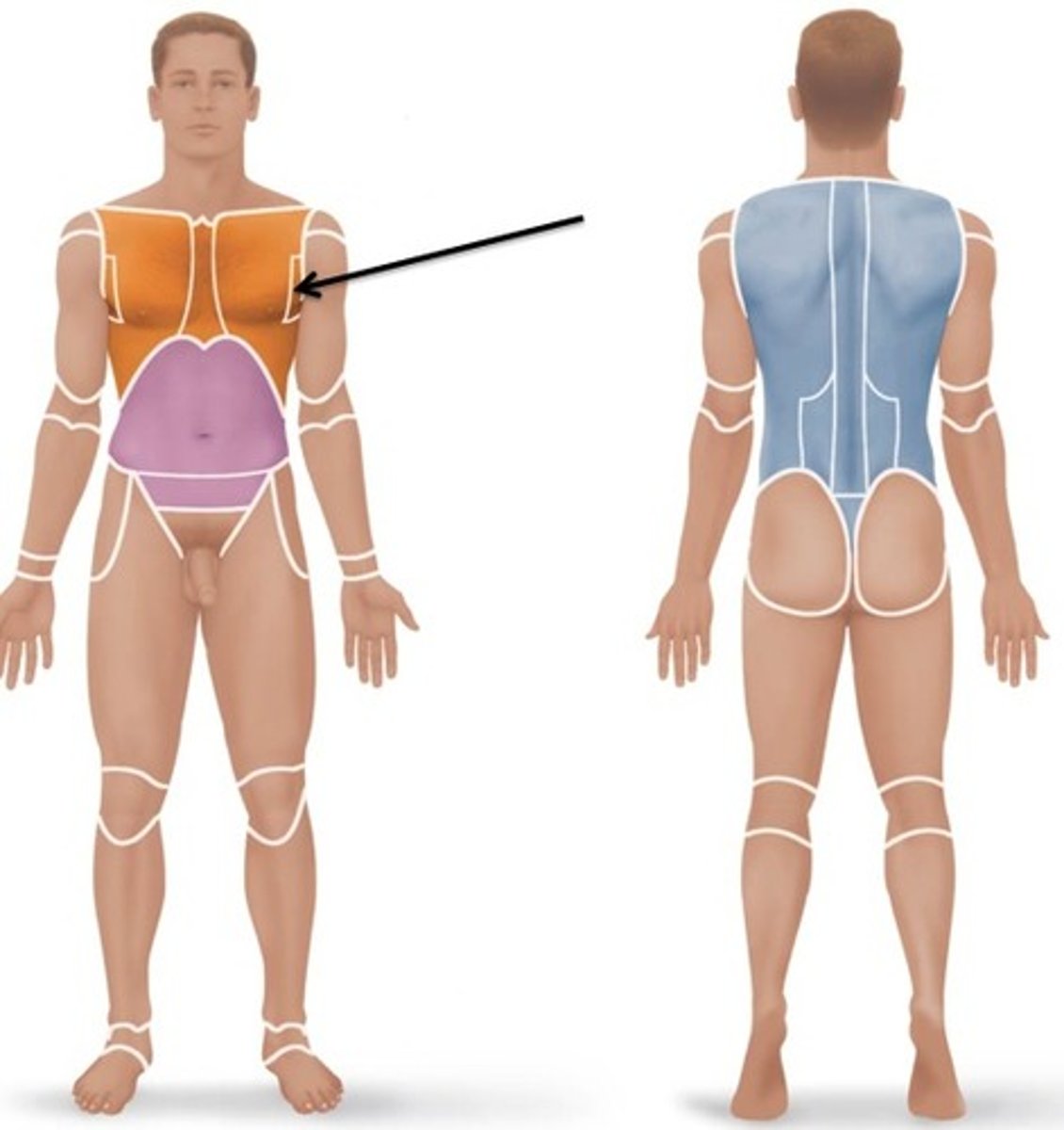
Axillary
armpit
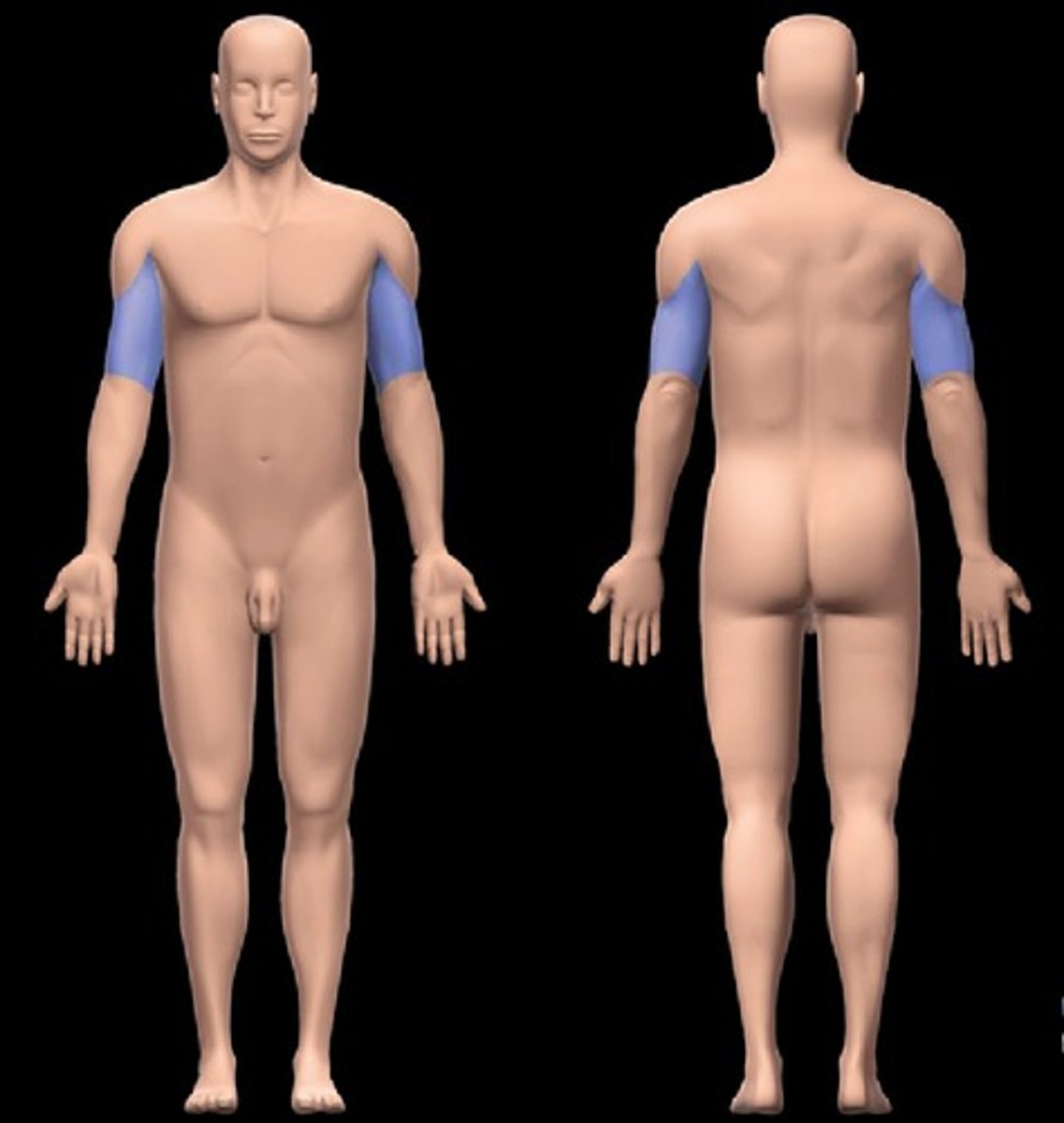
Brachial
upper arm
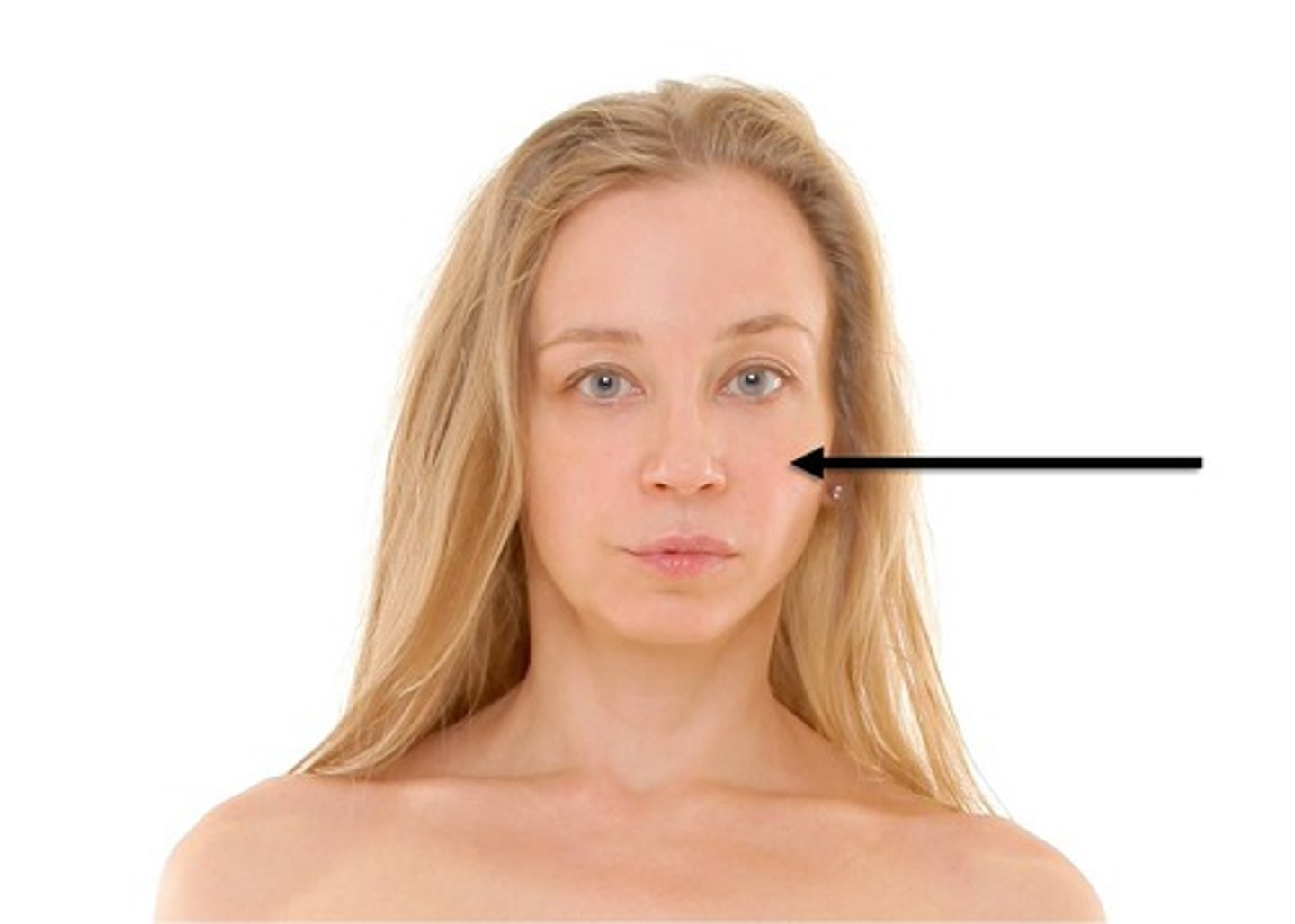
Buccal
Cheek
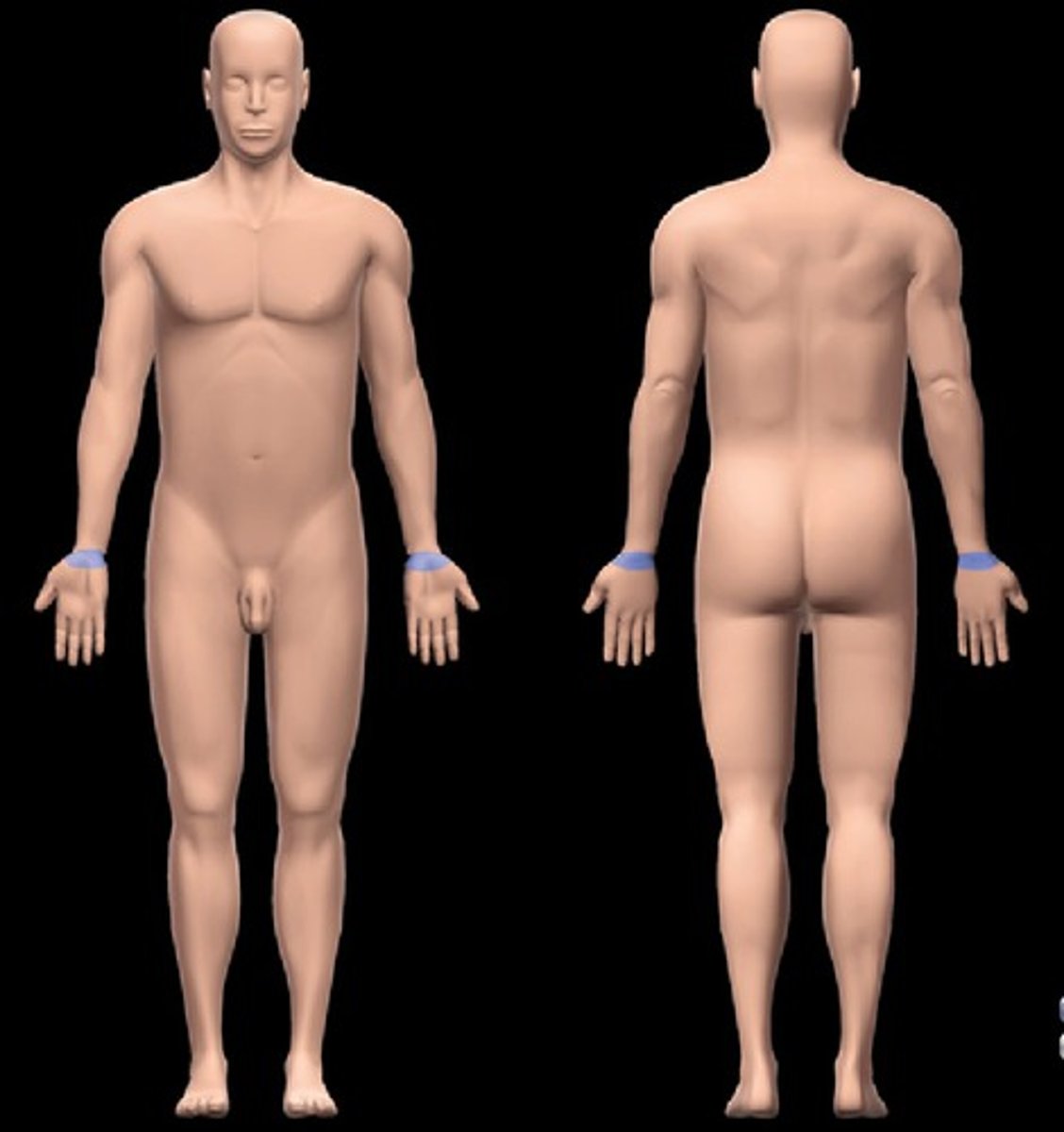
carpal
wrist
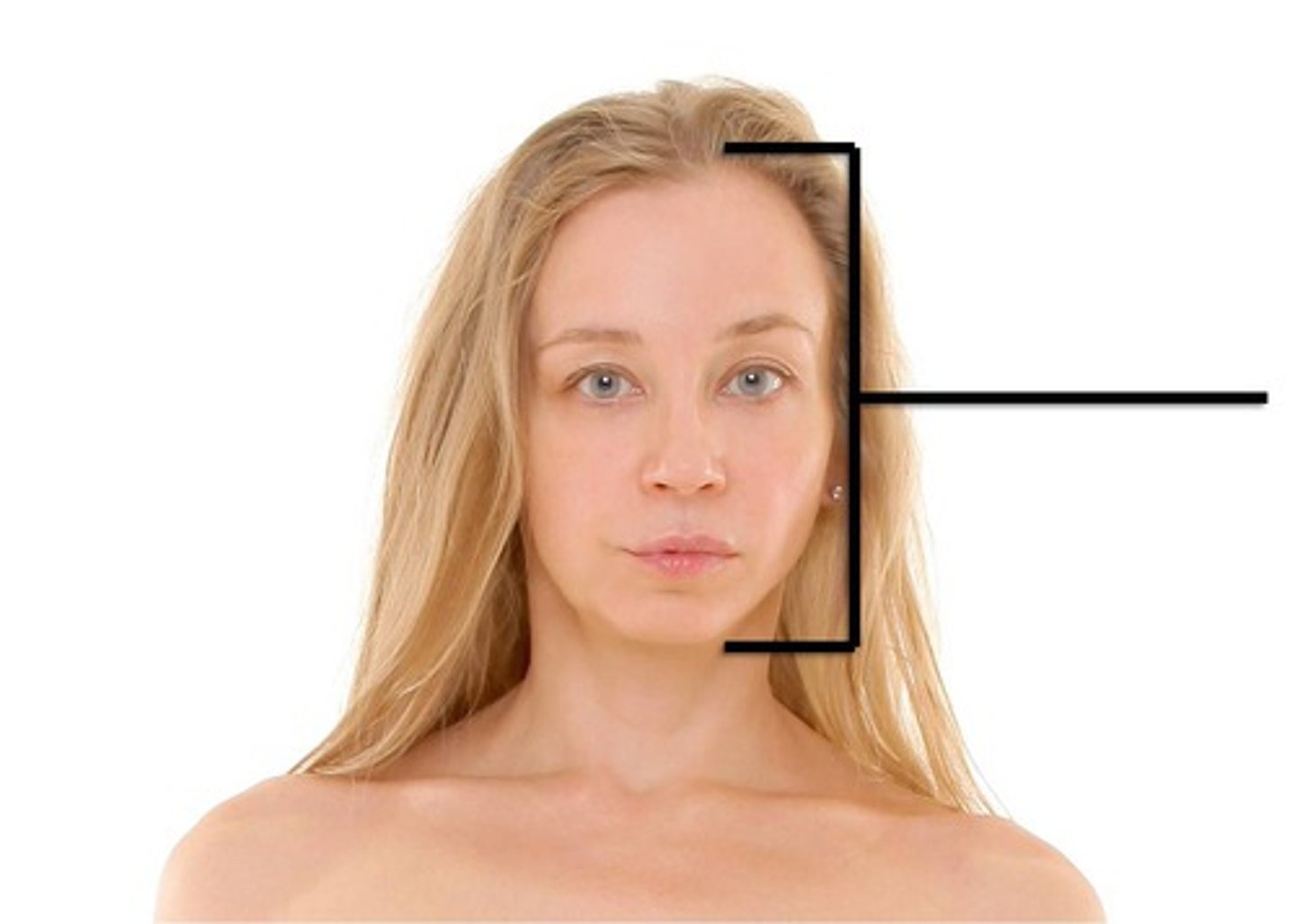
cephalic
head
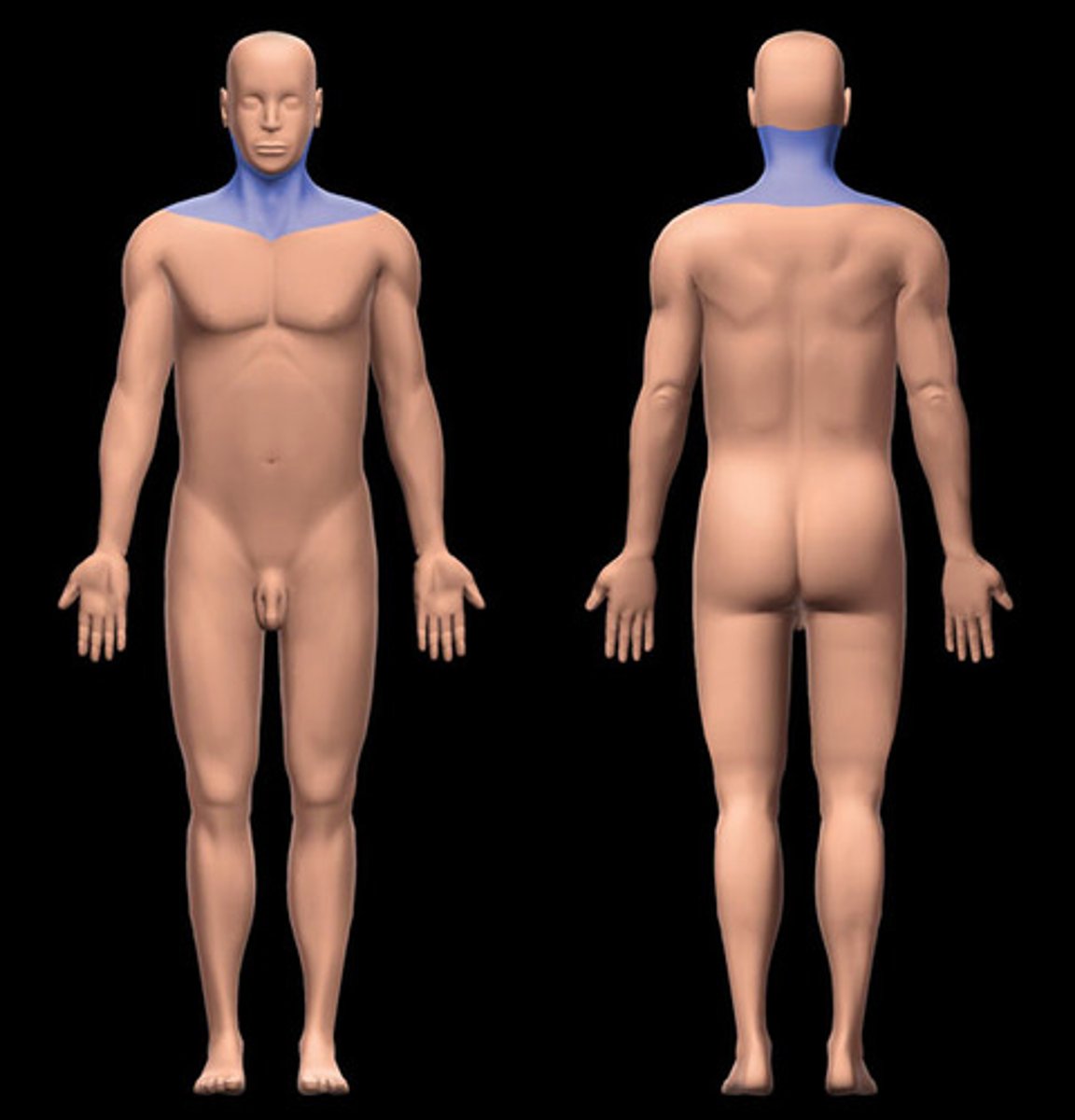
Cervical
neck
coxal
hip
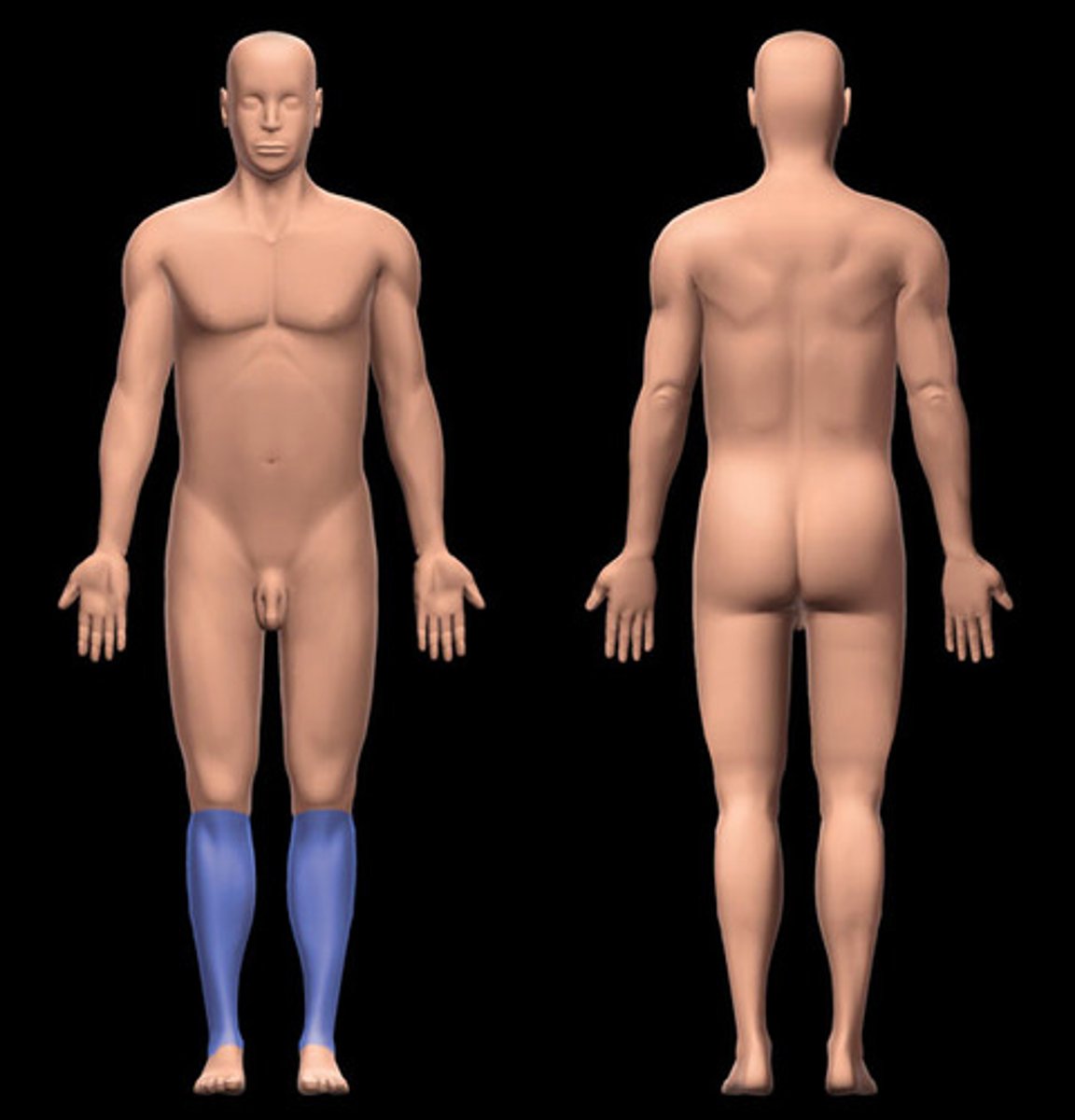
crural
leg
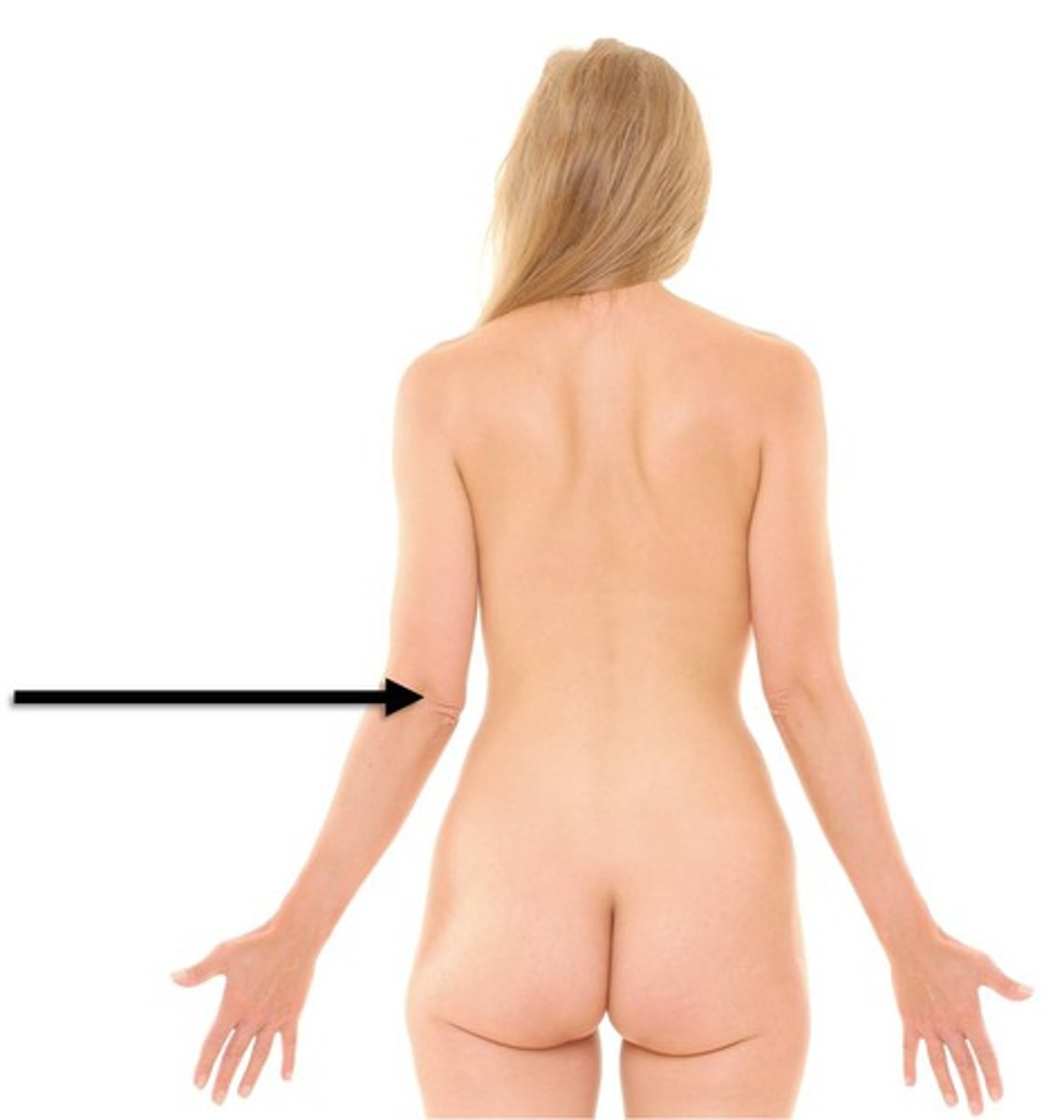
Cubital
elbow
digital
fingers, toes
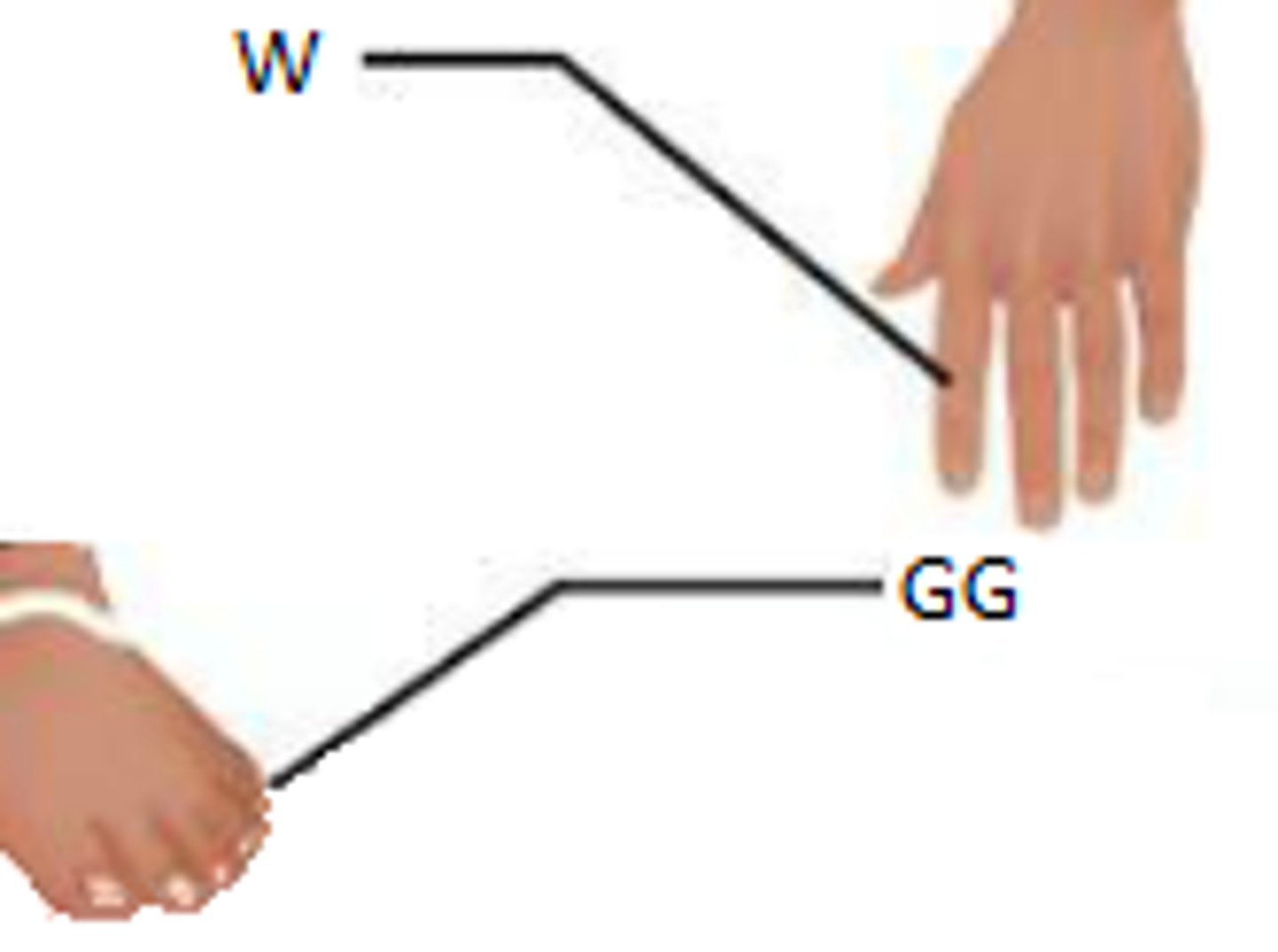
dorsal
back
femoral
thigh

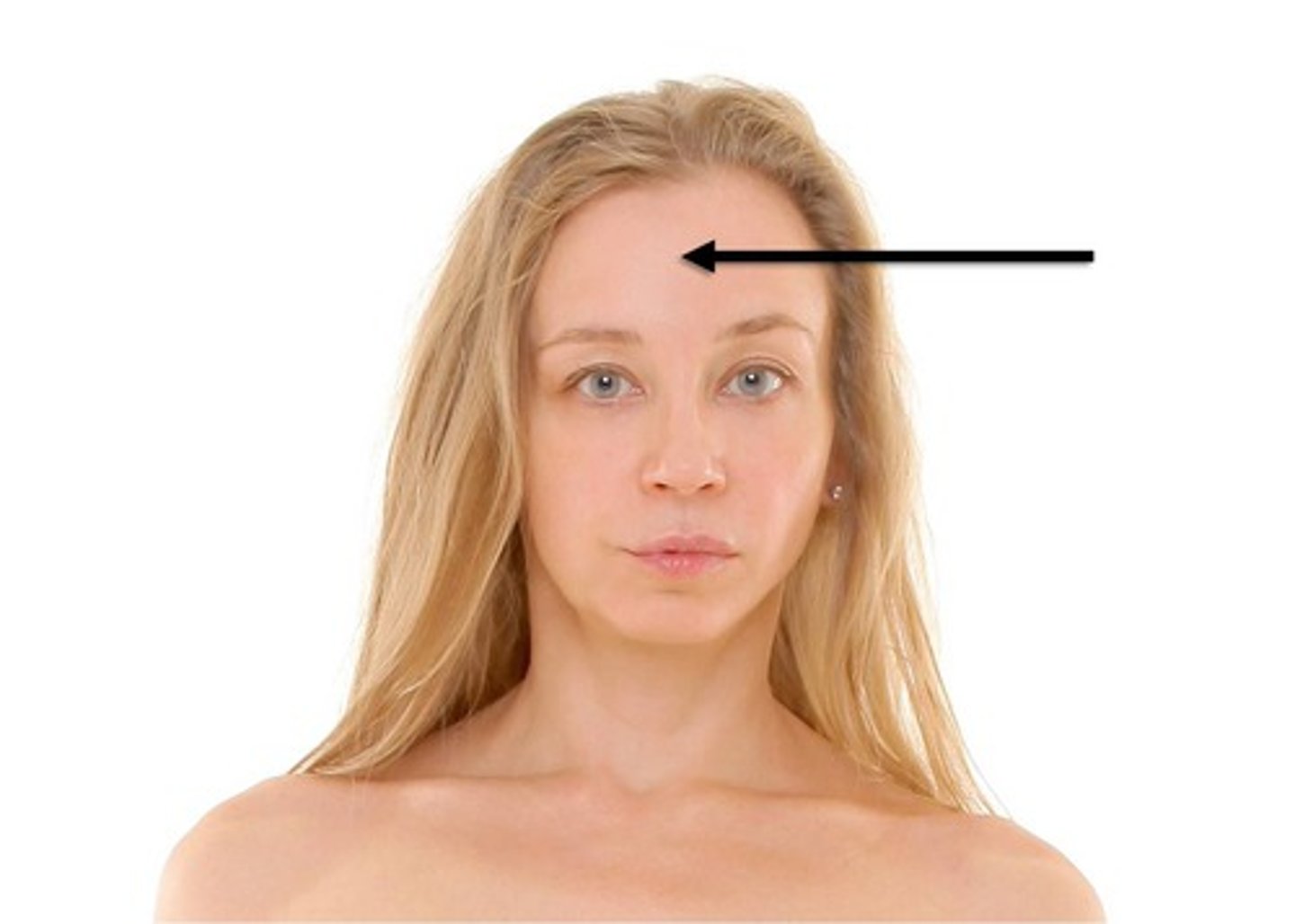
frontal
forehead
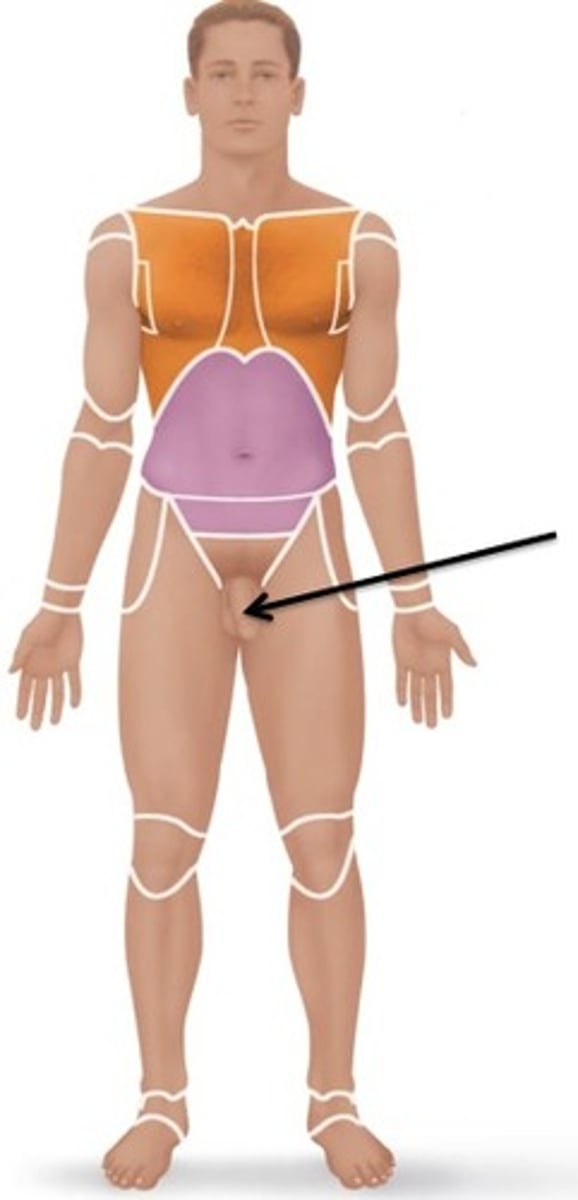
genital
external reproductive organs
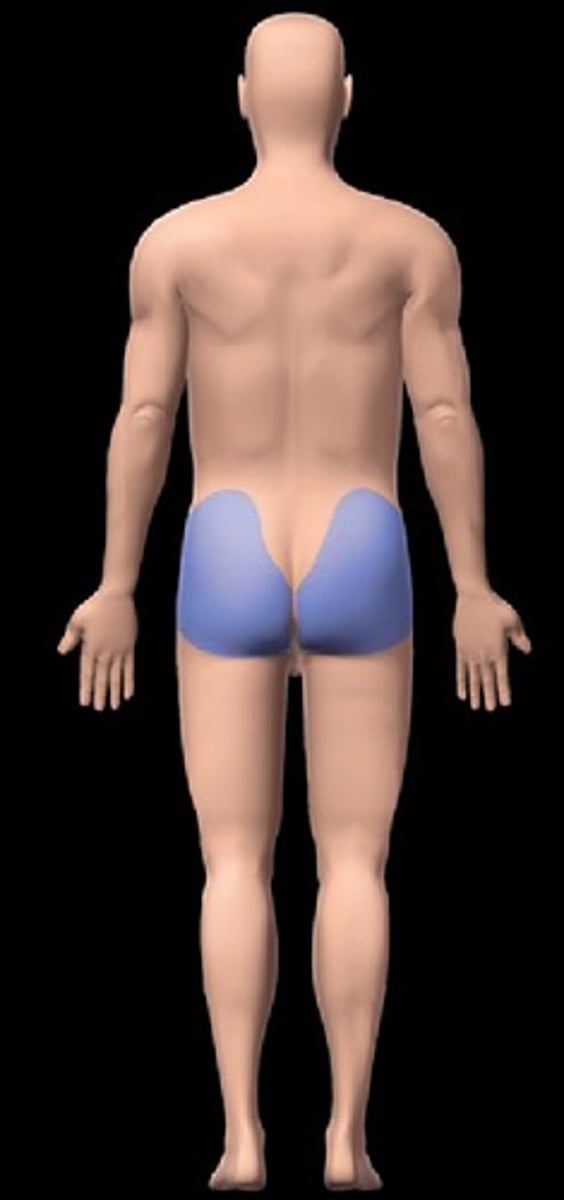
gluteal
buttock
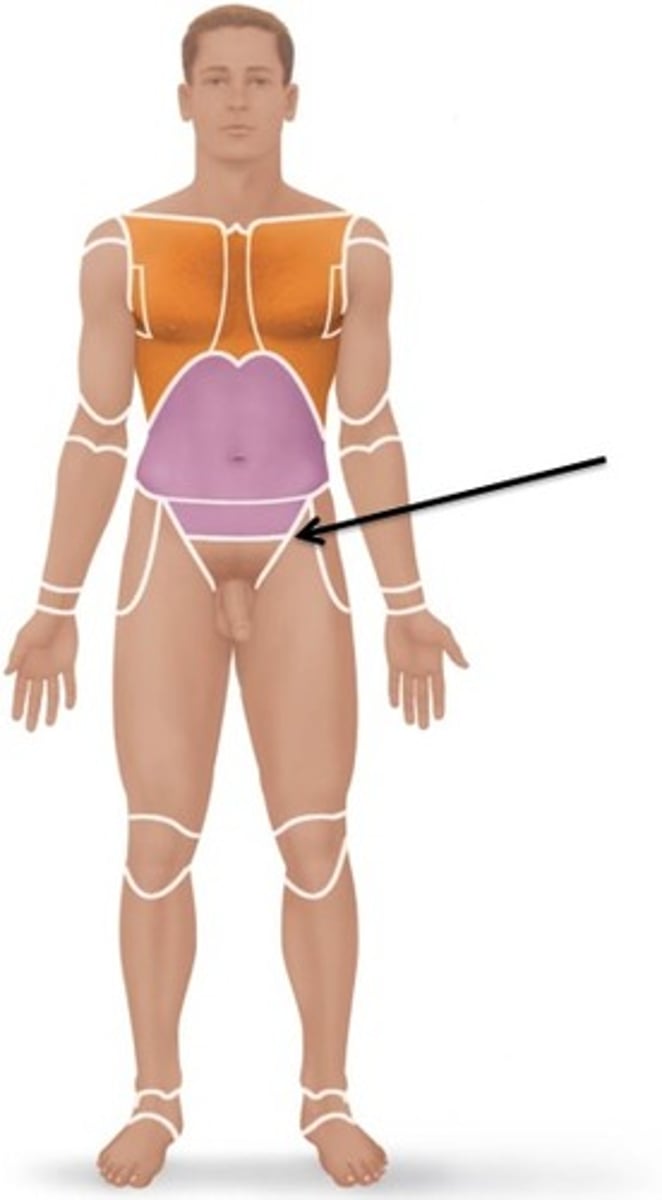
inguinal
groin
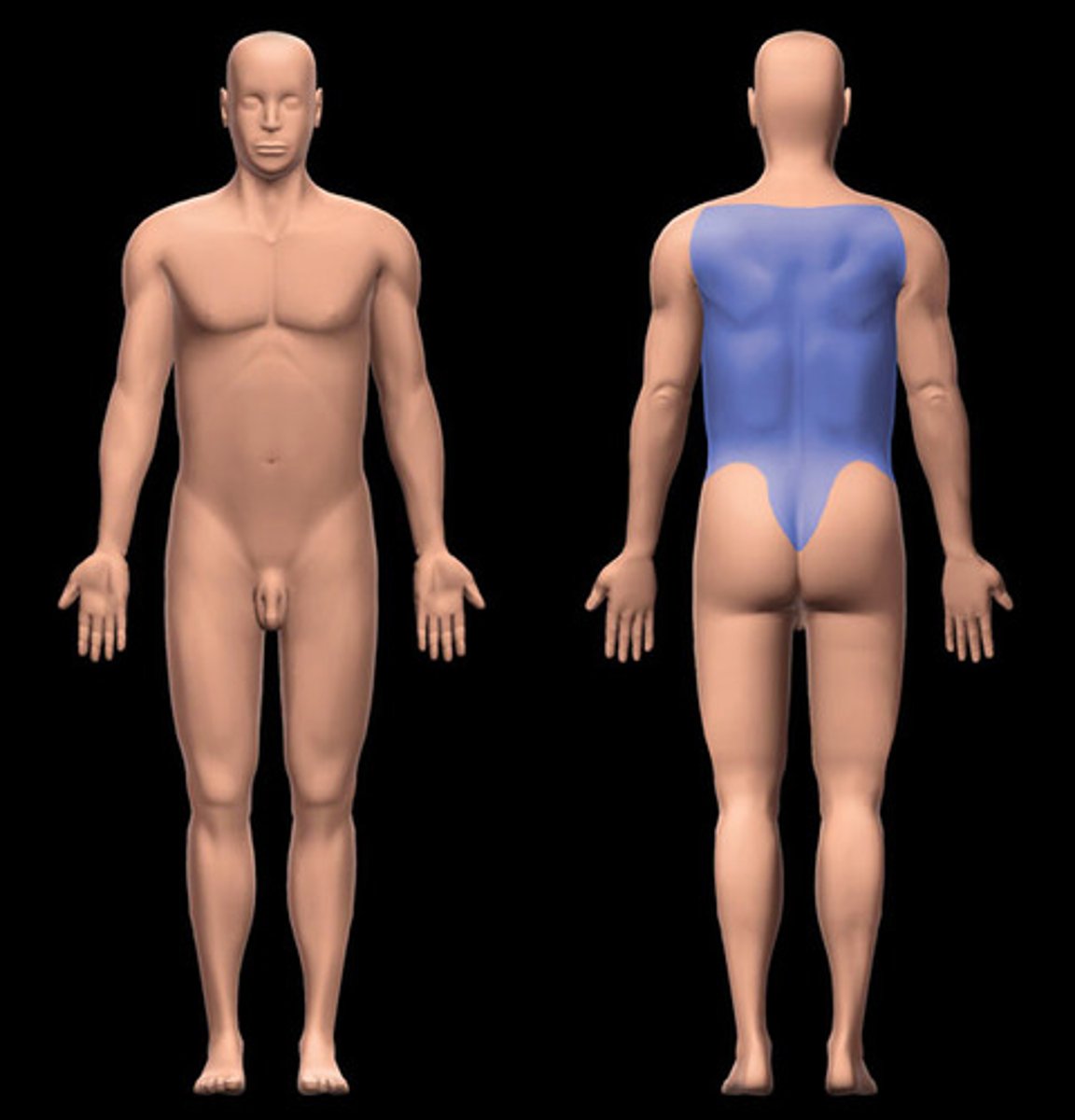
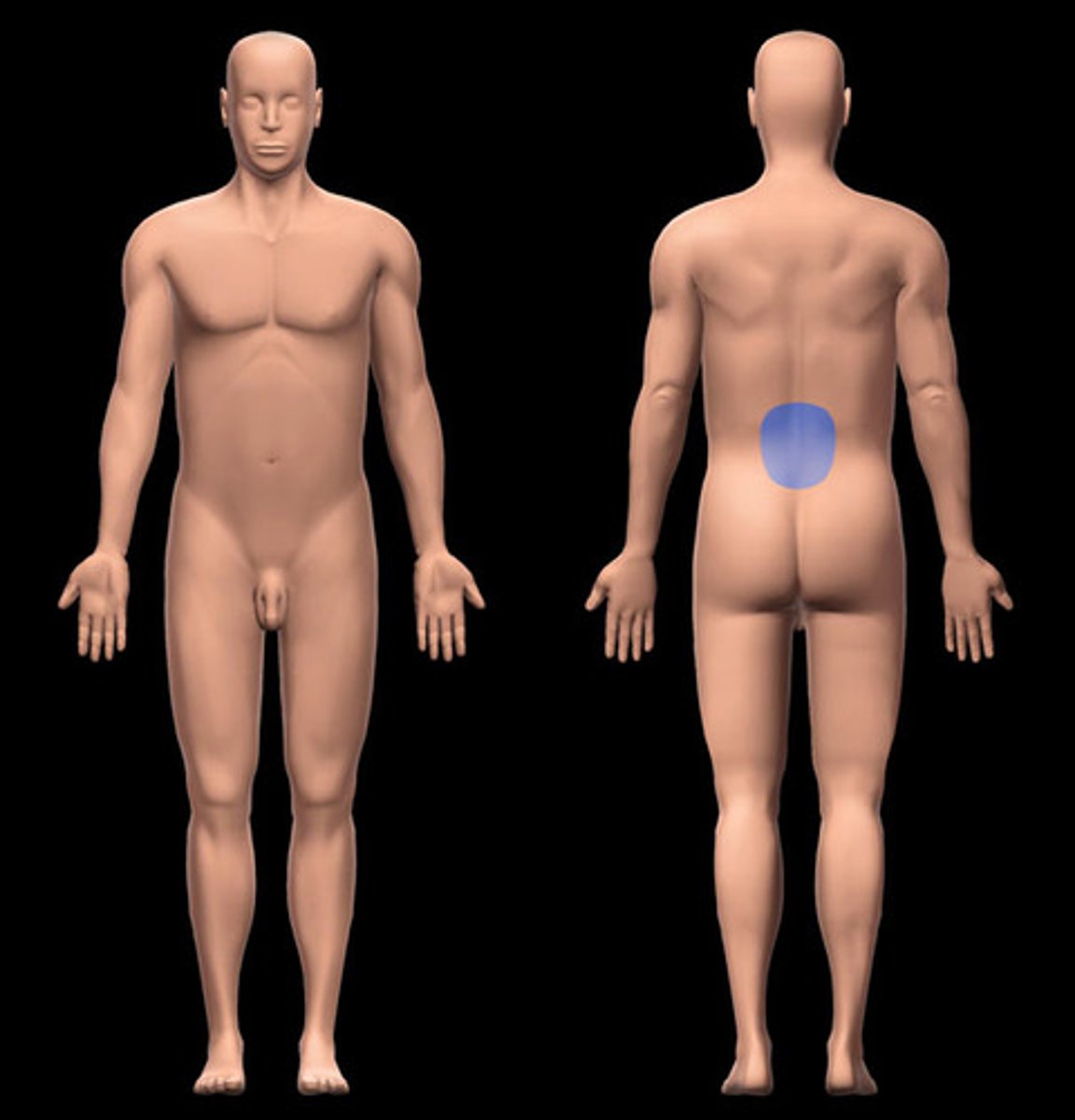
lumbar
lower back
mammary
breast

mental
chin

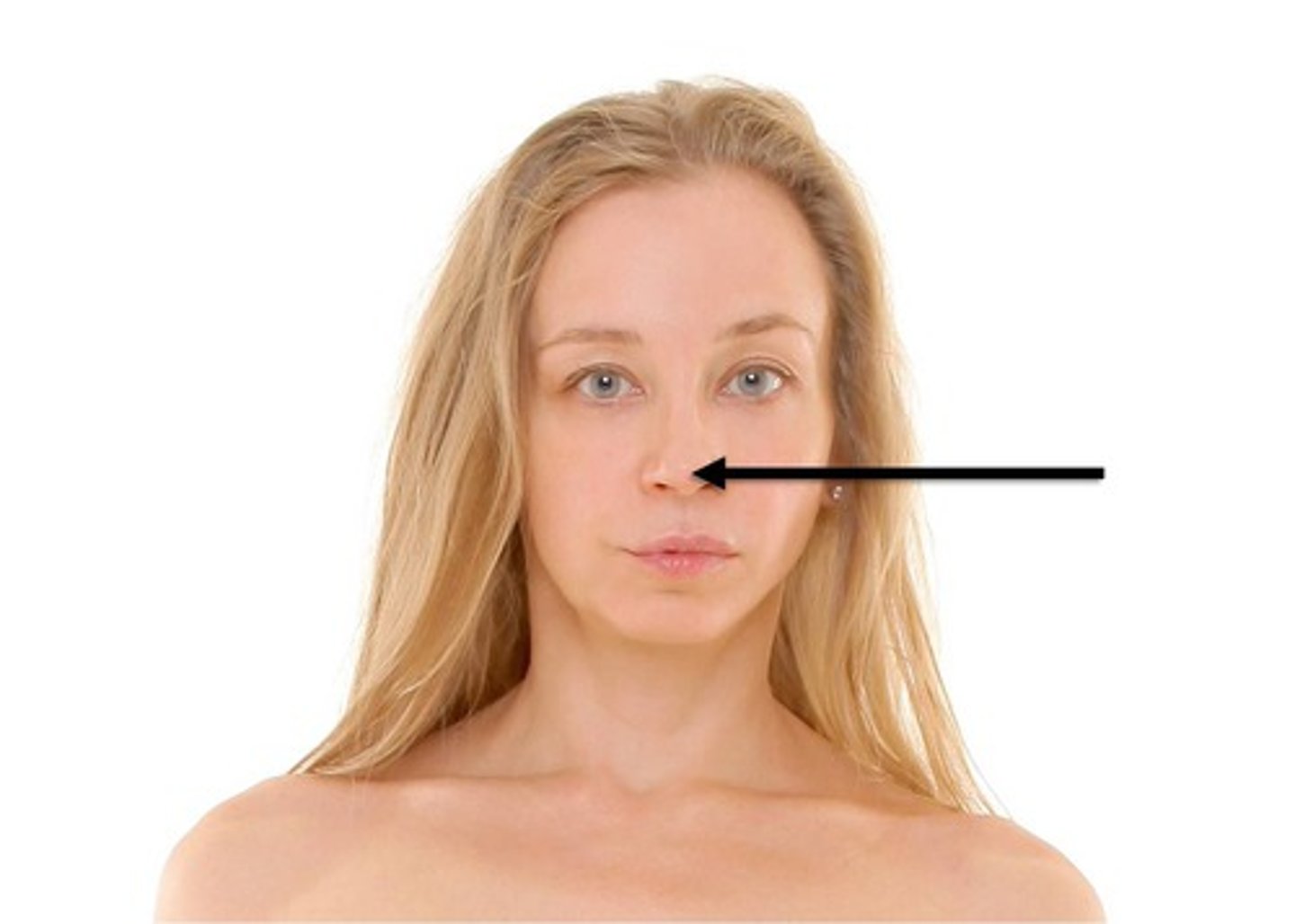
nasal
nose
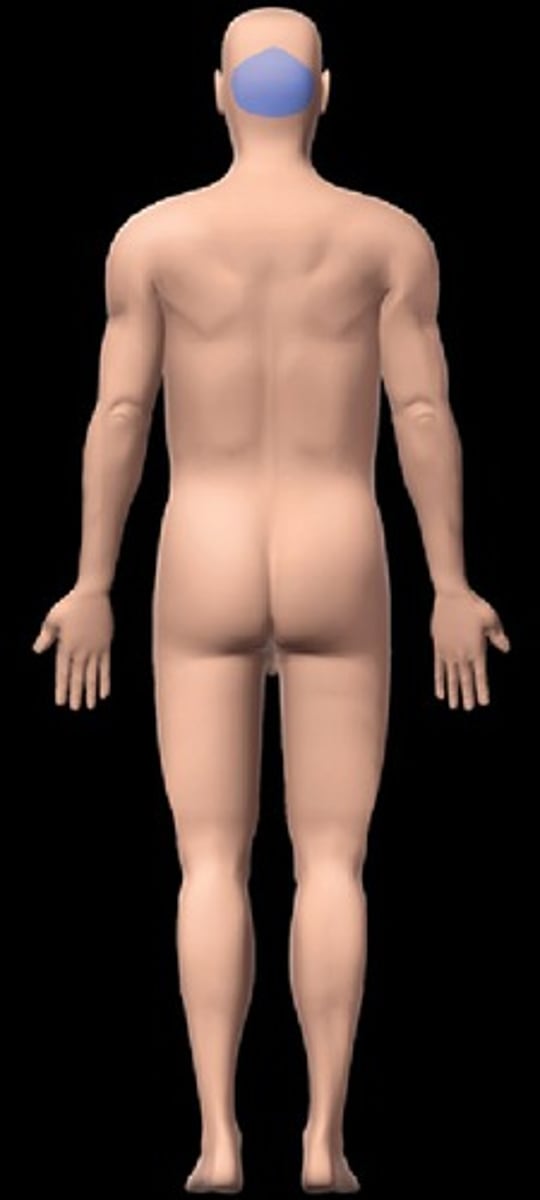
occipital
back of head
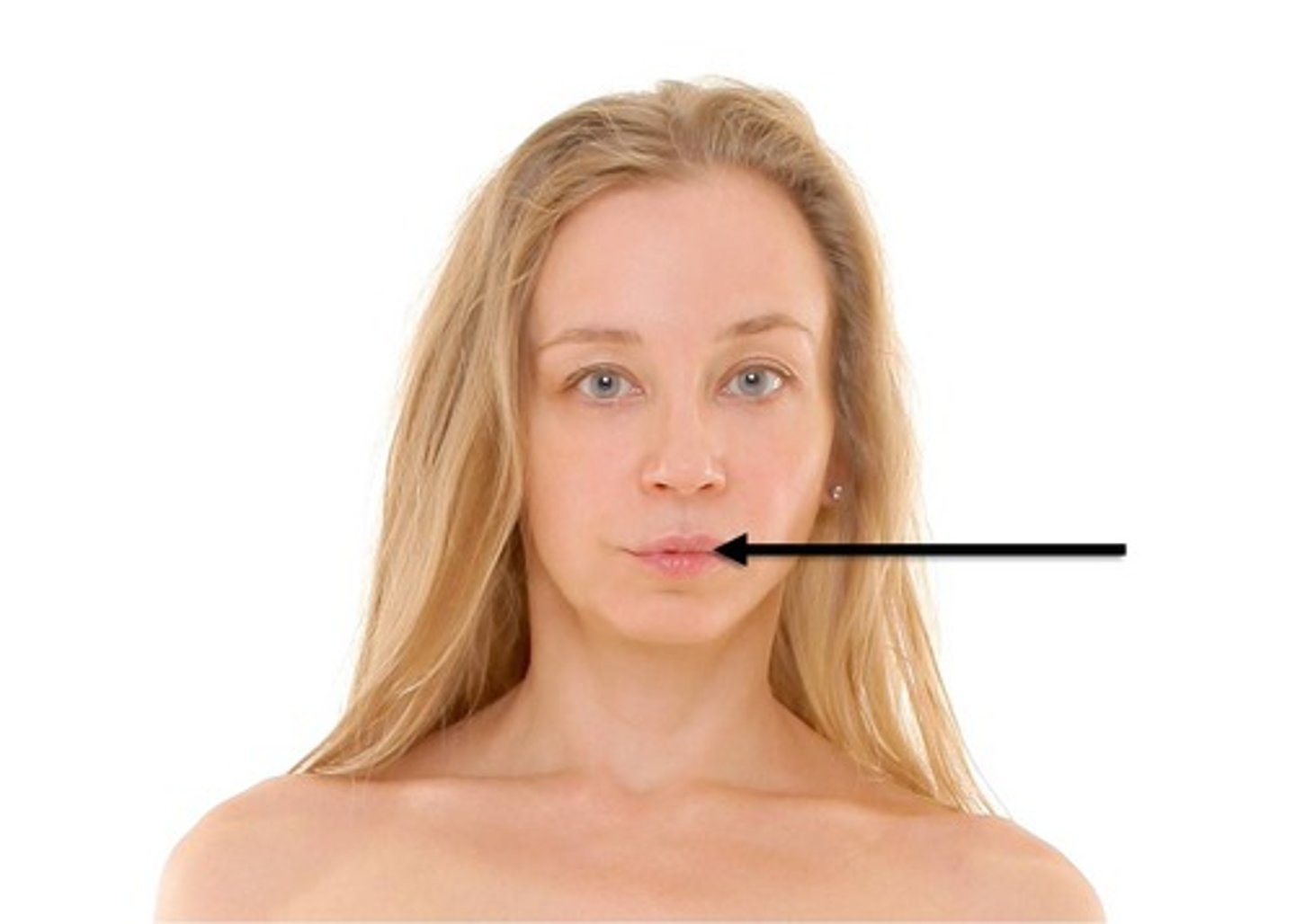
oral
mouth
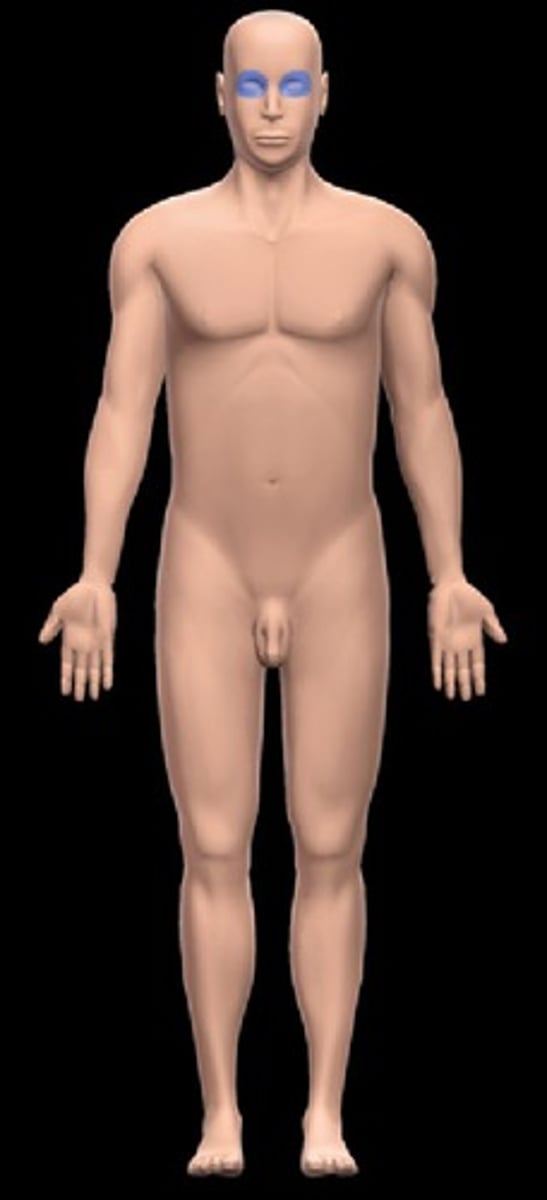
Orbital
eye
Otic
ear
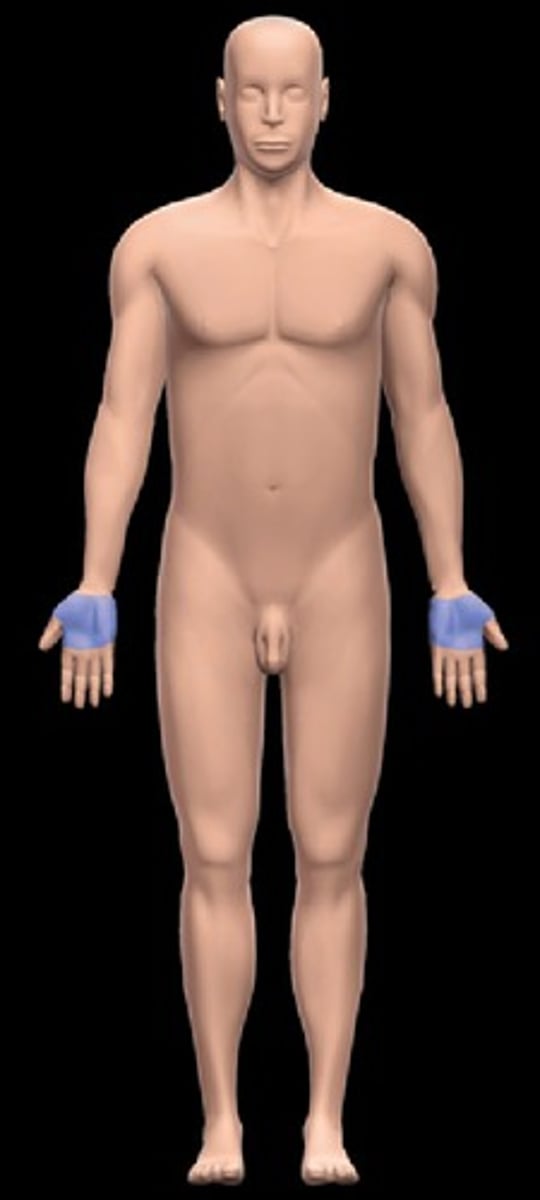
Palmar
palm or hand
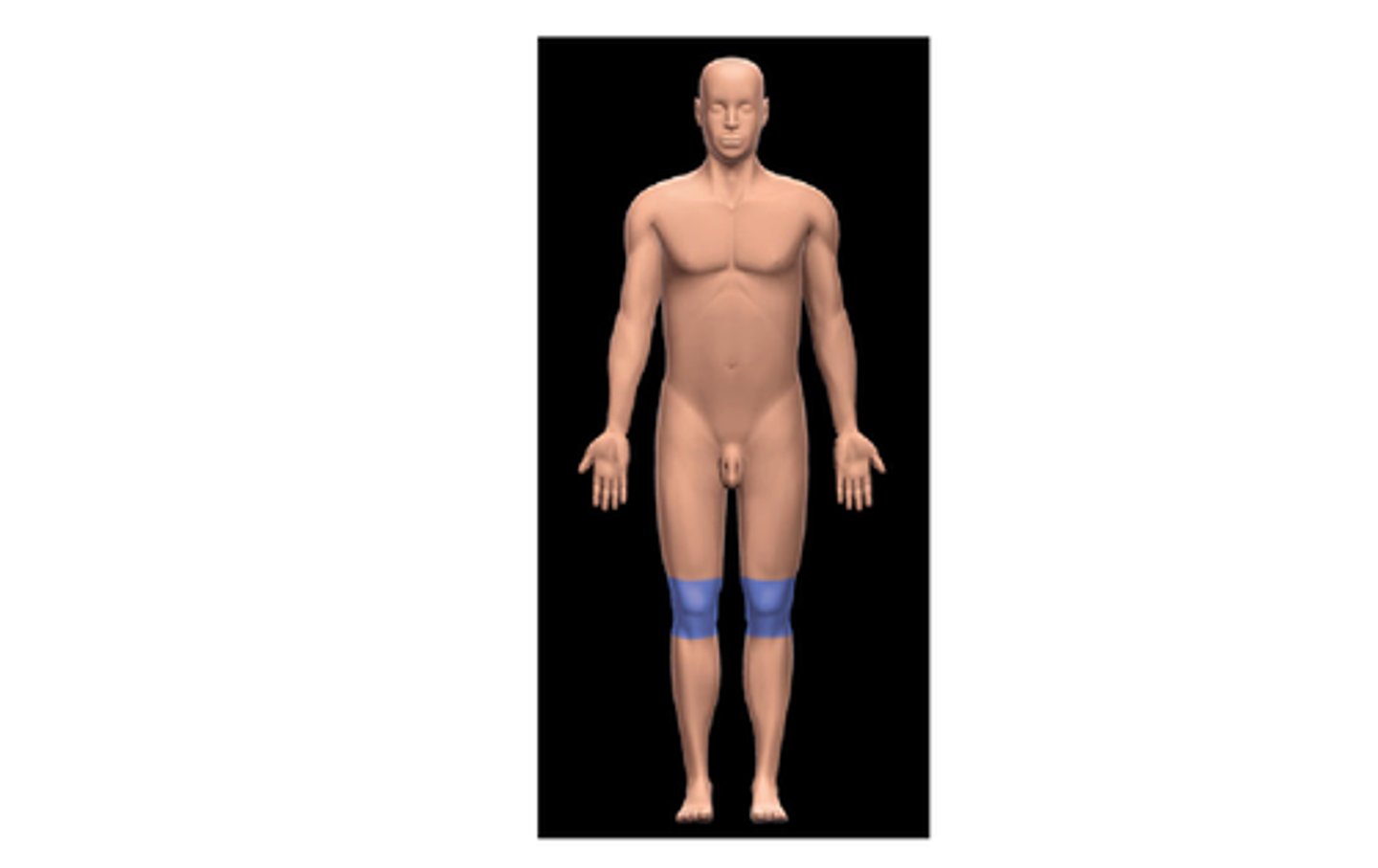
patellar
anterior knee
pectoral
chest

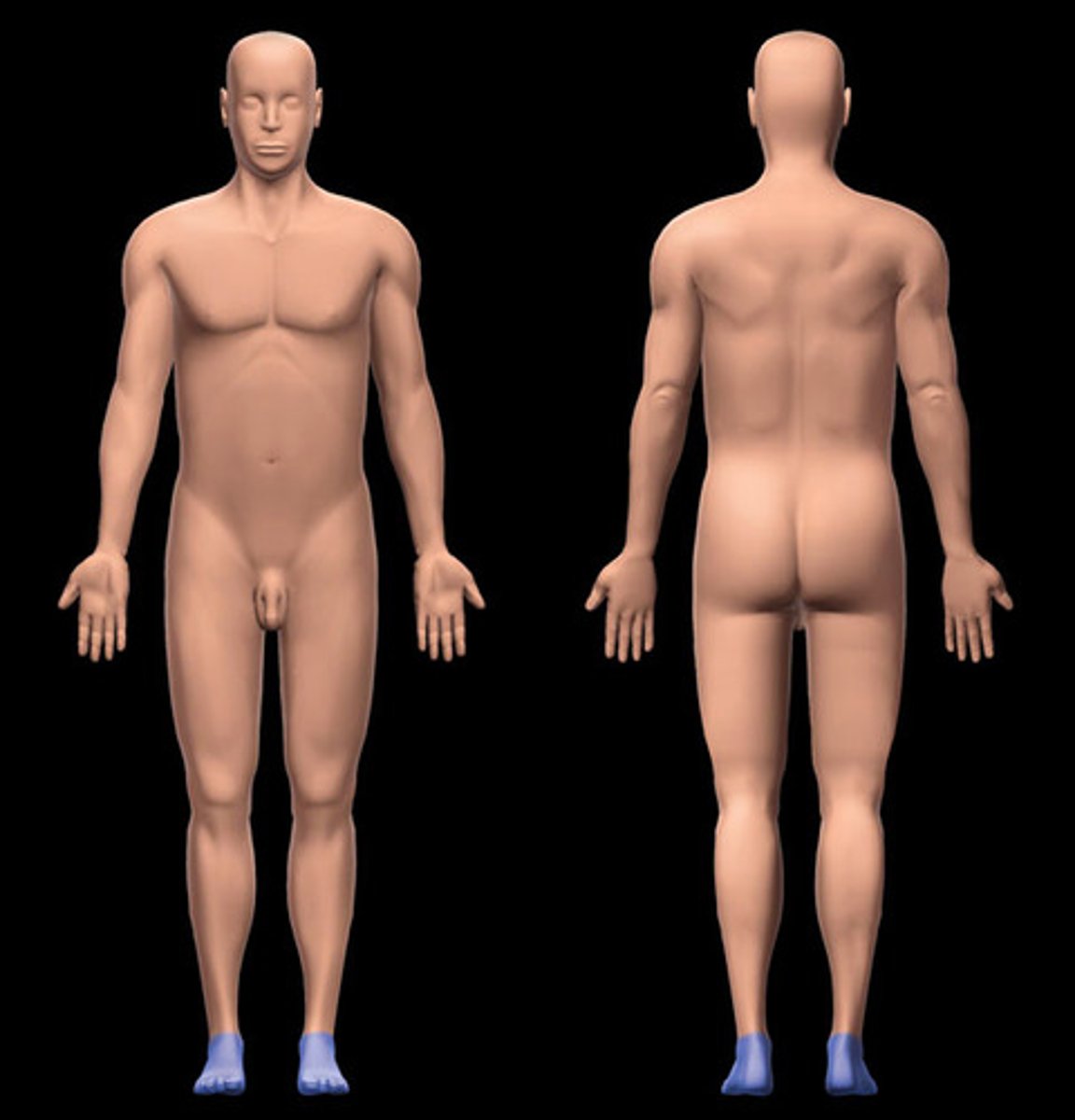
pedal
foot
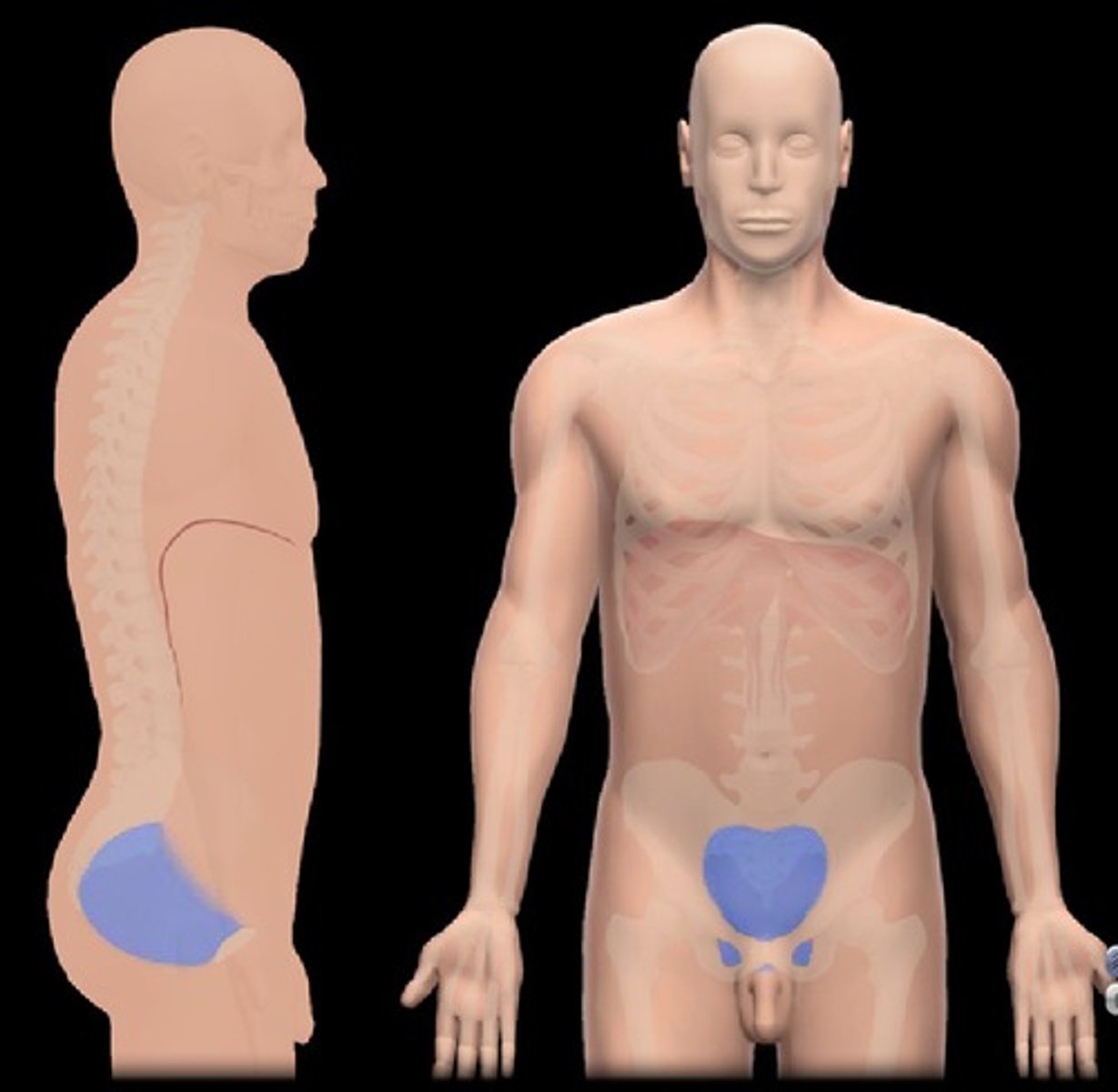
pelvic
pelvis
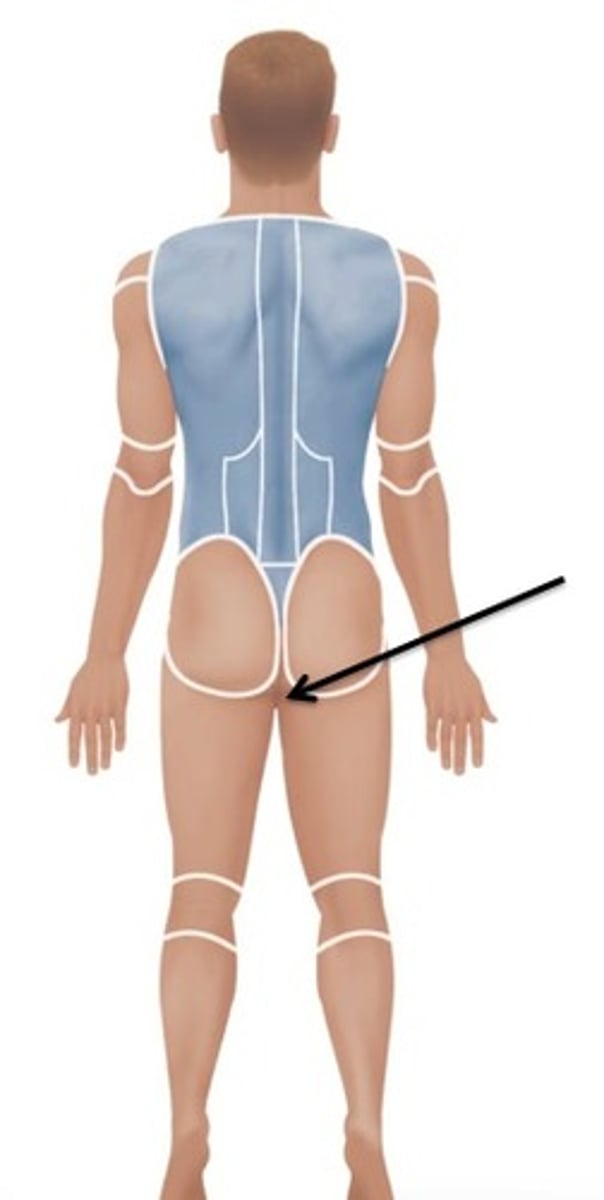
perineal
region between the anus and external genitalia
plantar
sole of foot
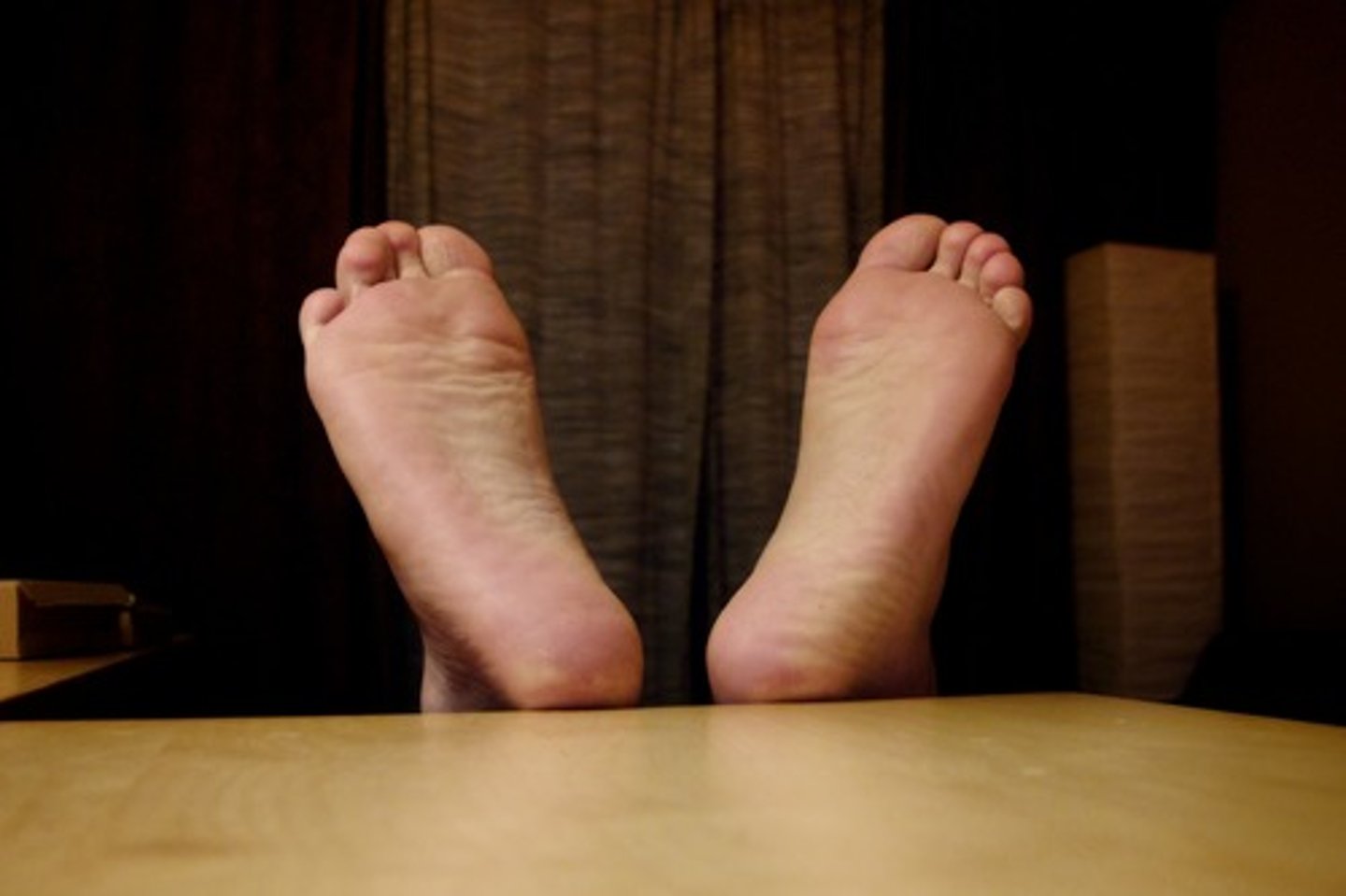

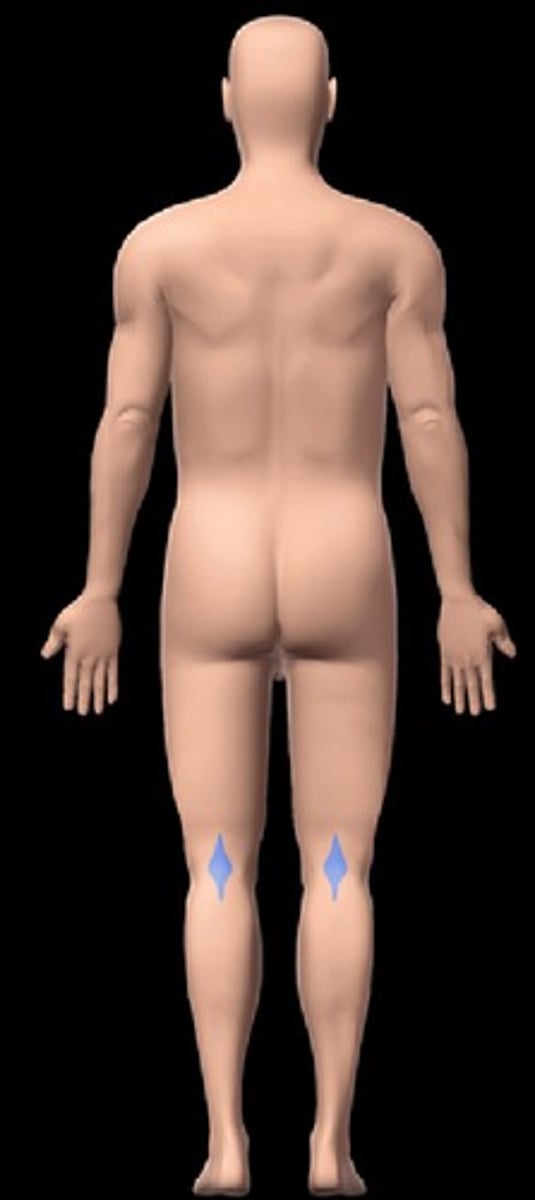
popliteal
posterior knee area
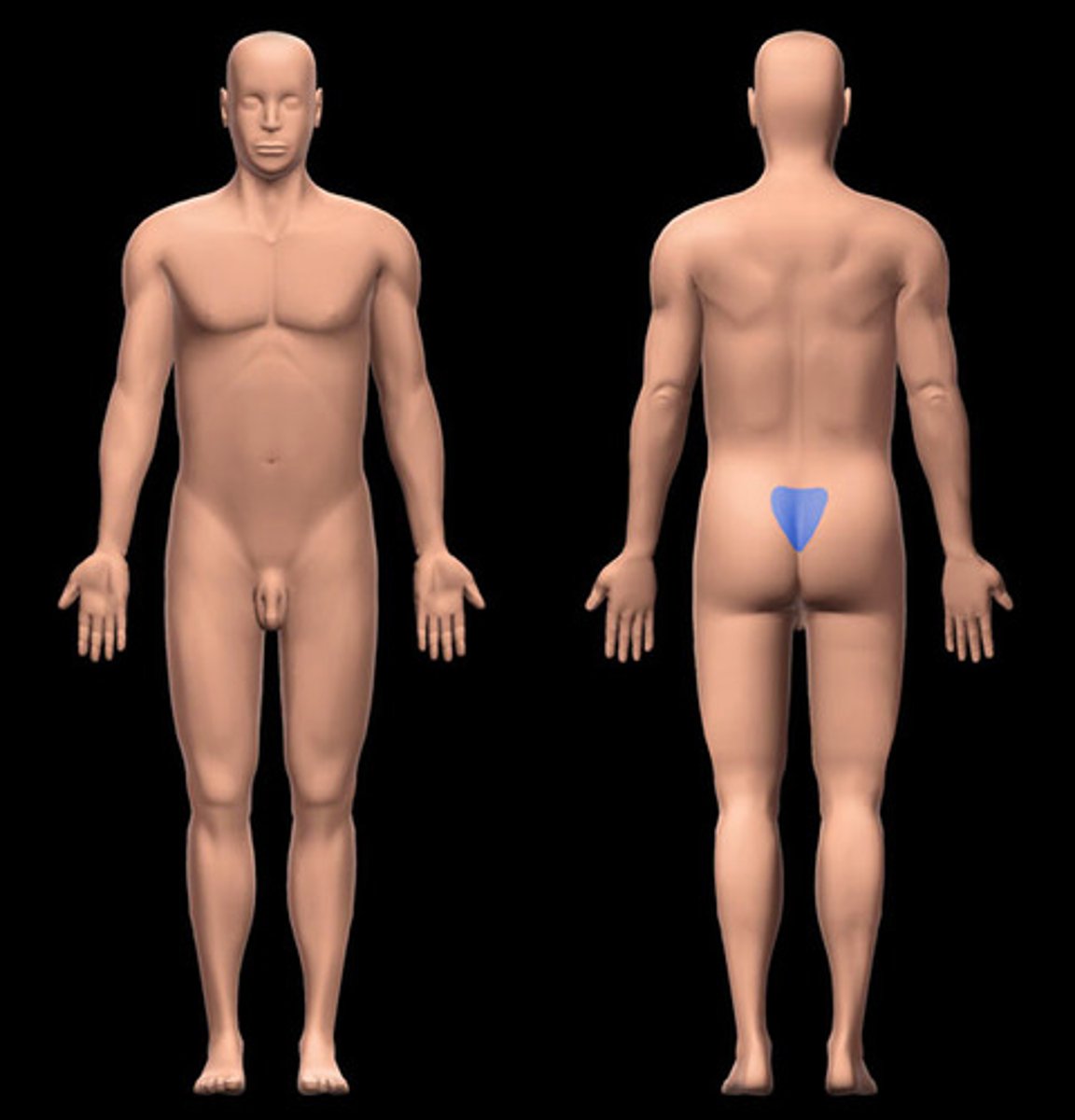
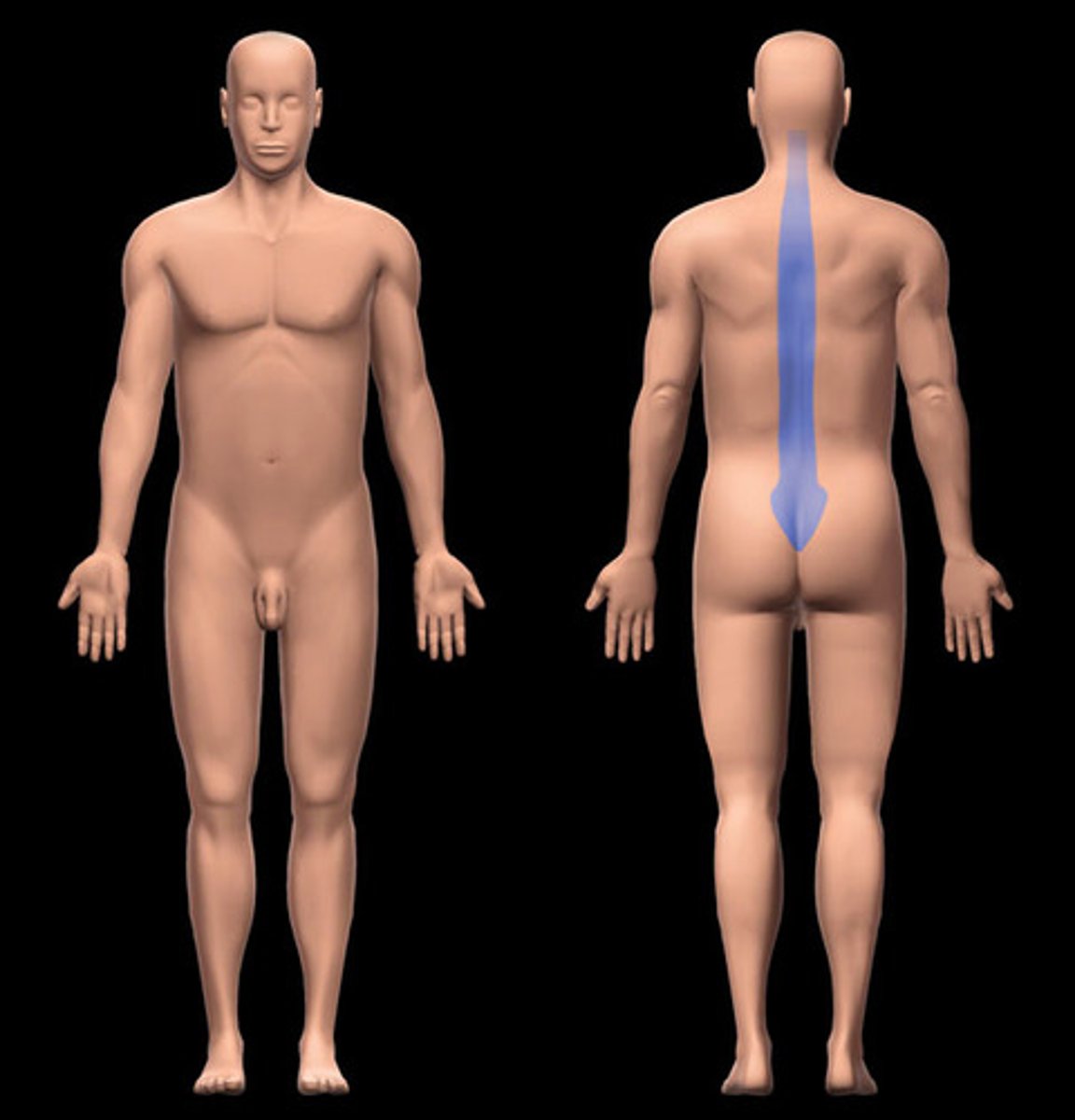
sacral
Posterior region between the hip bones
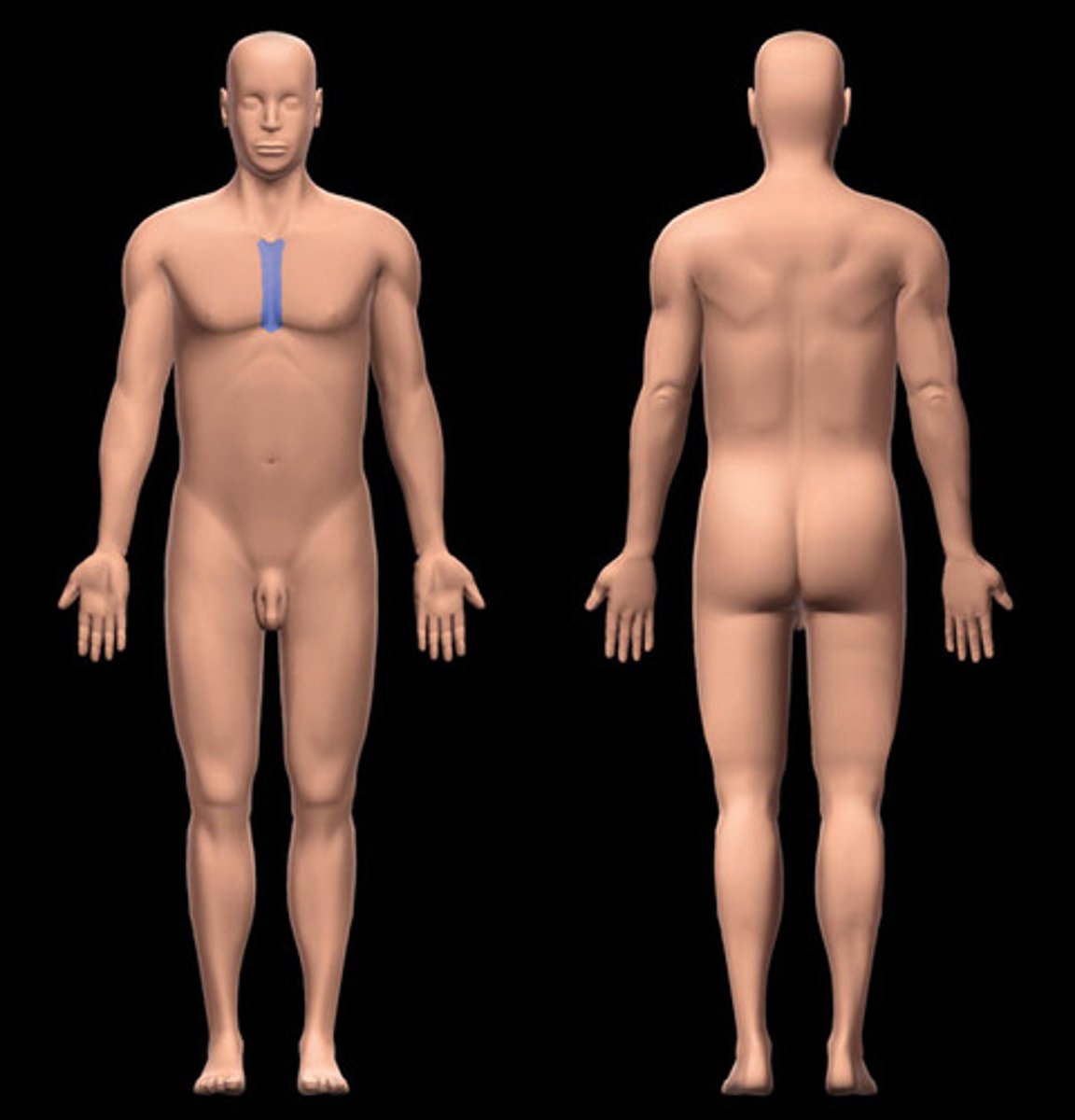
Sternal
sternum
tarsal
ankle
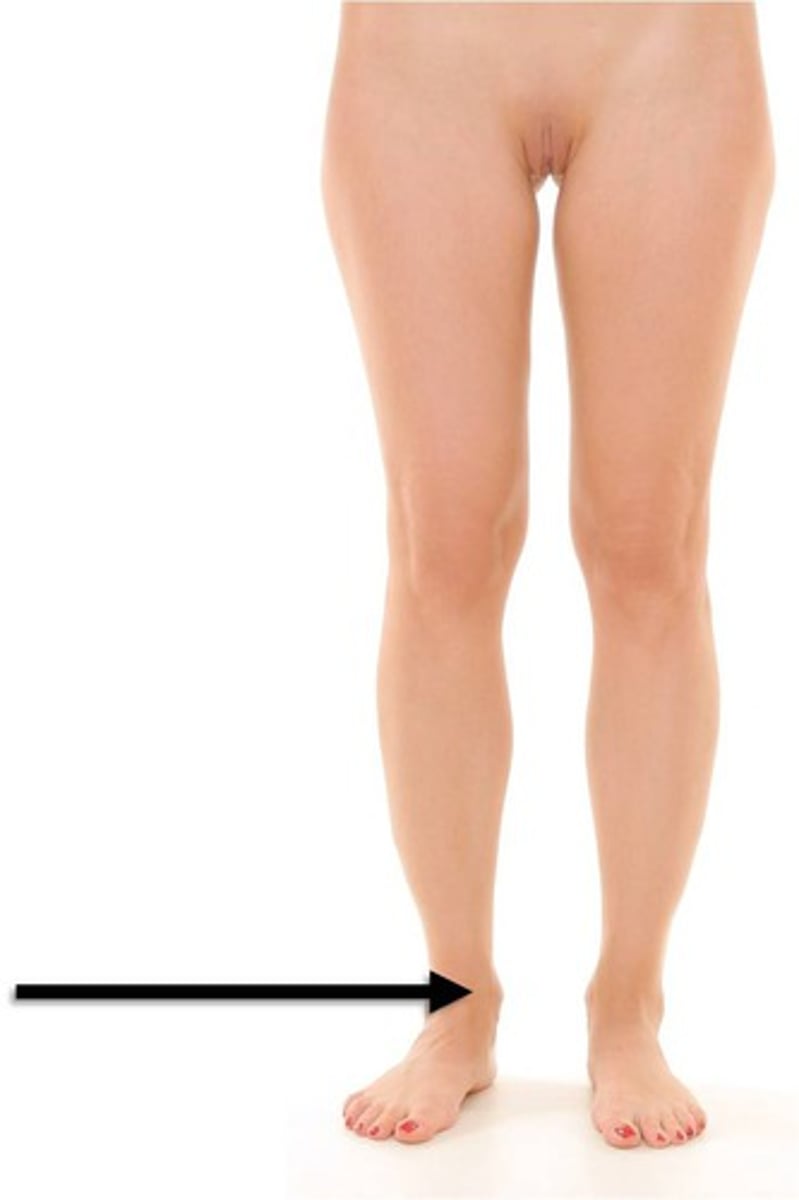

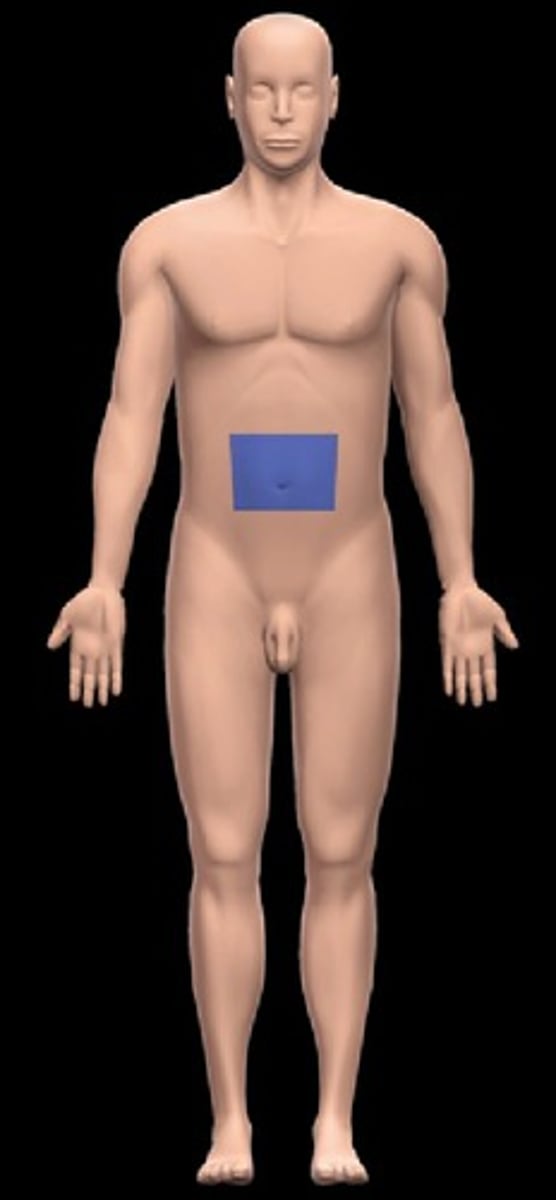
umbilical
navel
vertebral
spinal column
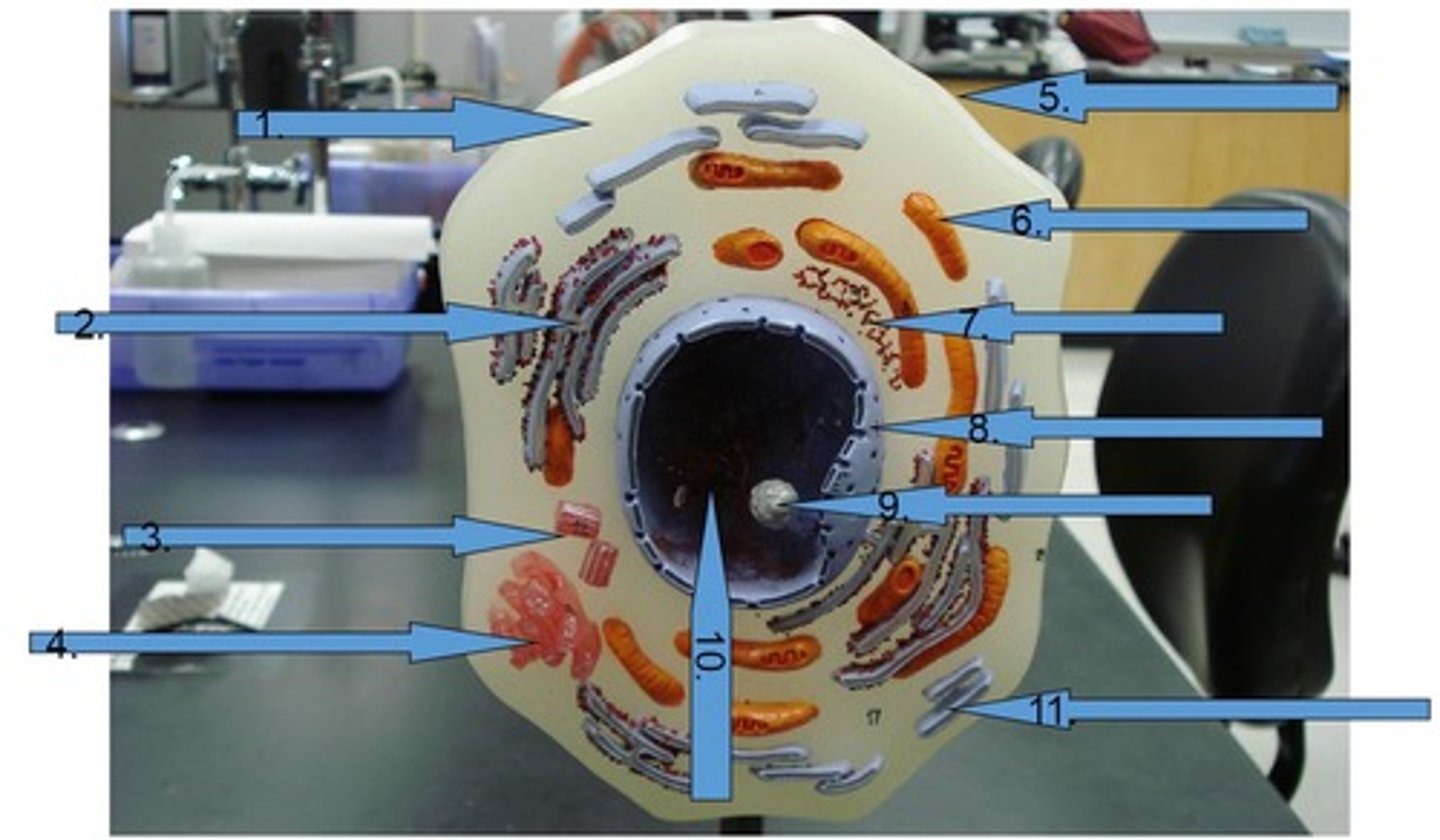
Cell
basic unit of life
Plasma (cell) membrane
encloses and protects cell & its contents #5
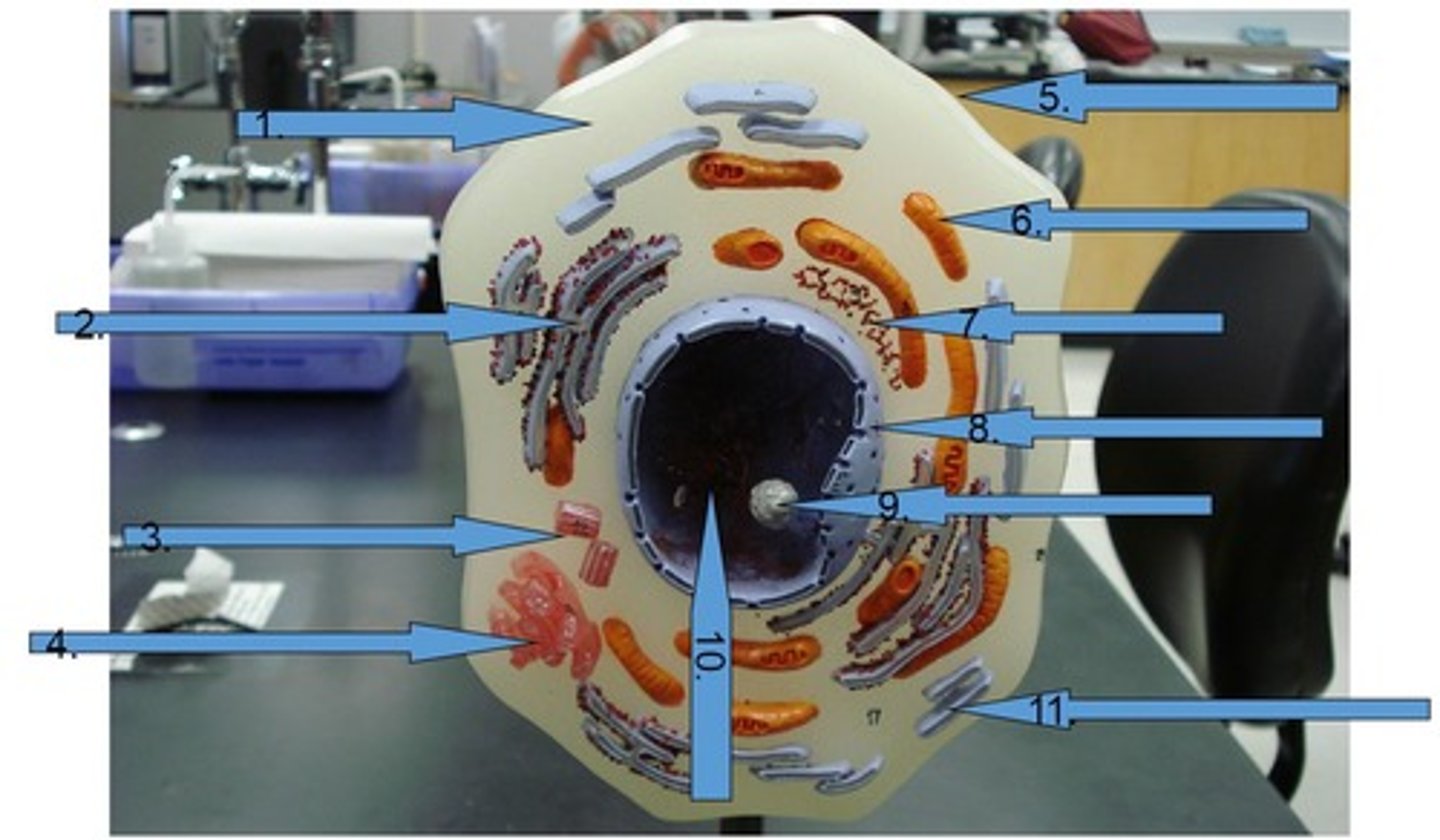
Cytoplasm
semifluid in cell that suspends organelles #1
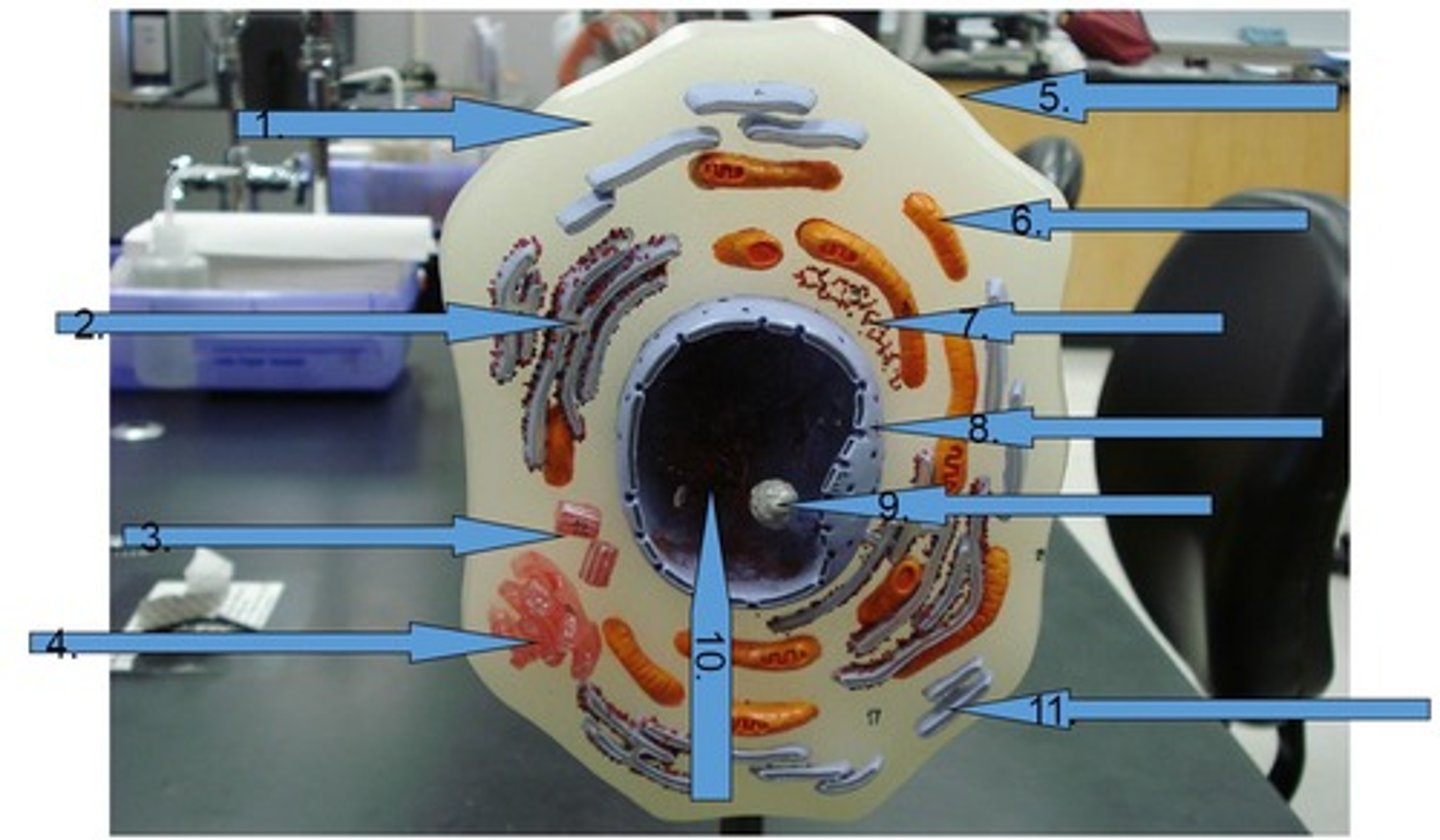
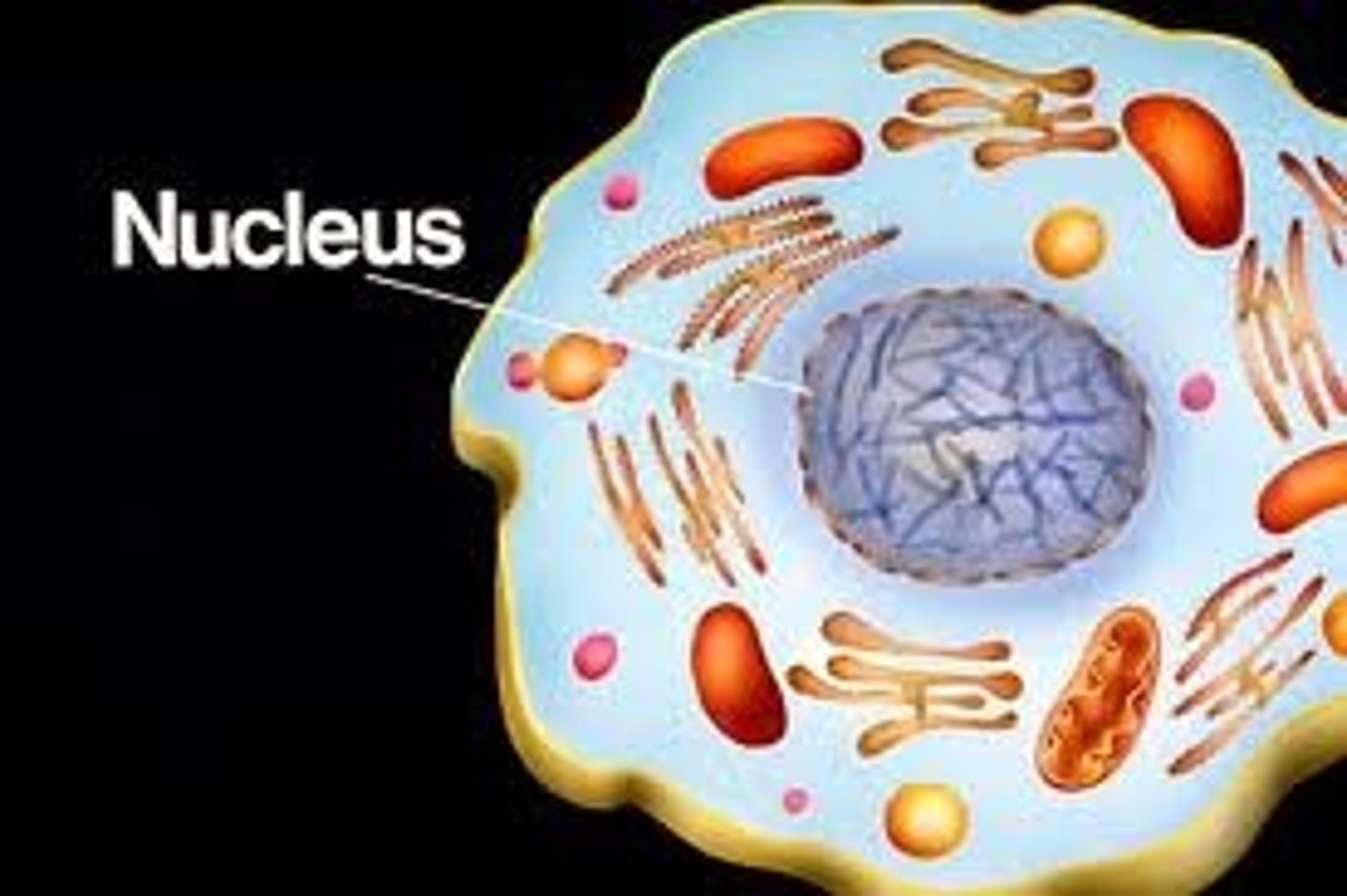
nucleus
houses all genetic material (DNA)
nucleolus
inside nucleus, makes ribosomes (RNA) #9
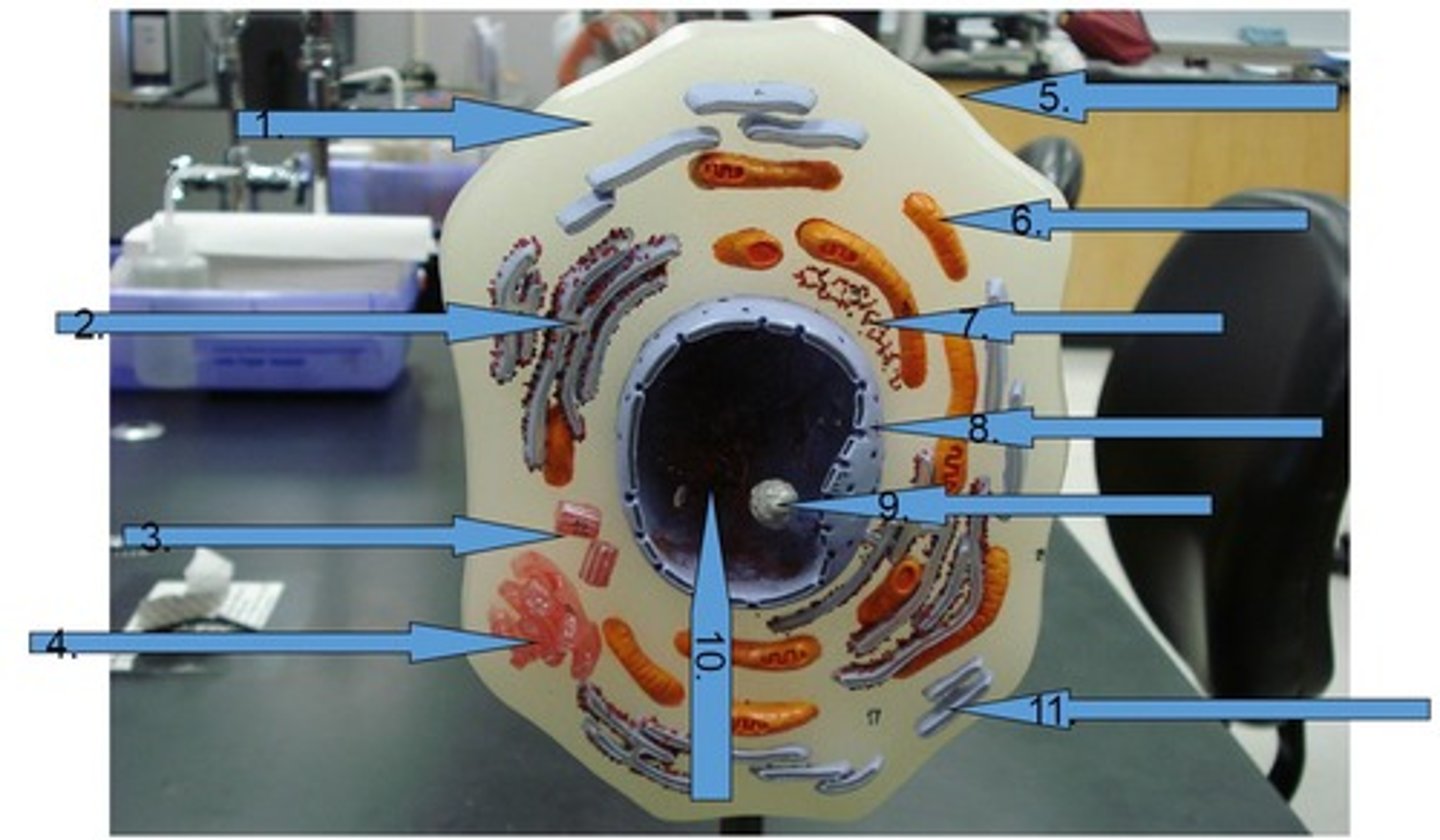
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane perforated with pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus. #8
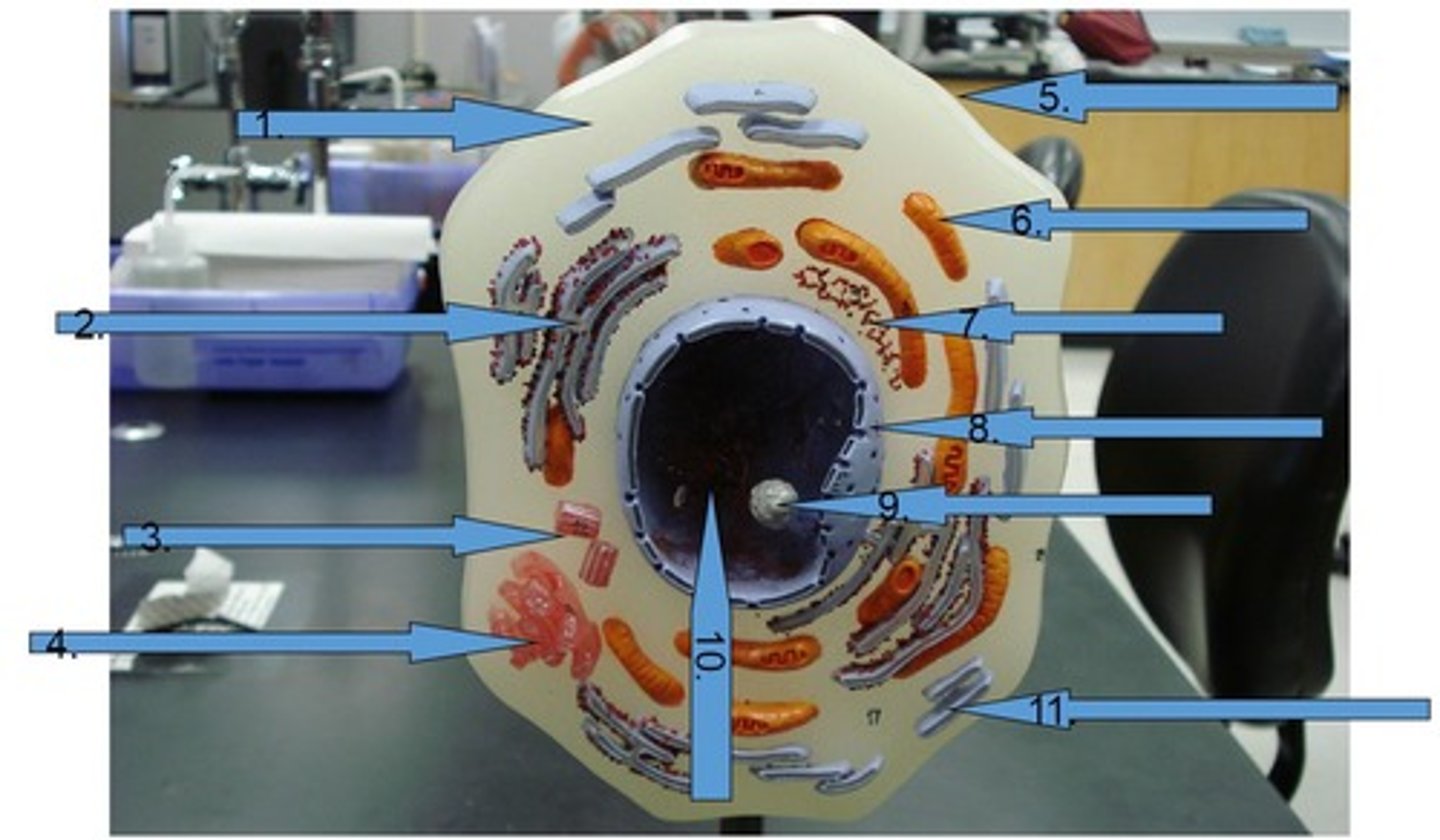
Chromatin
is loosely coiled DNA and its associated proteins located inside of nucleus #10
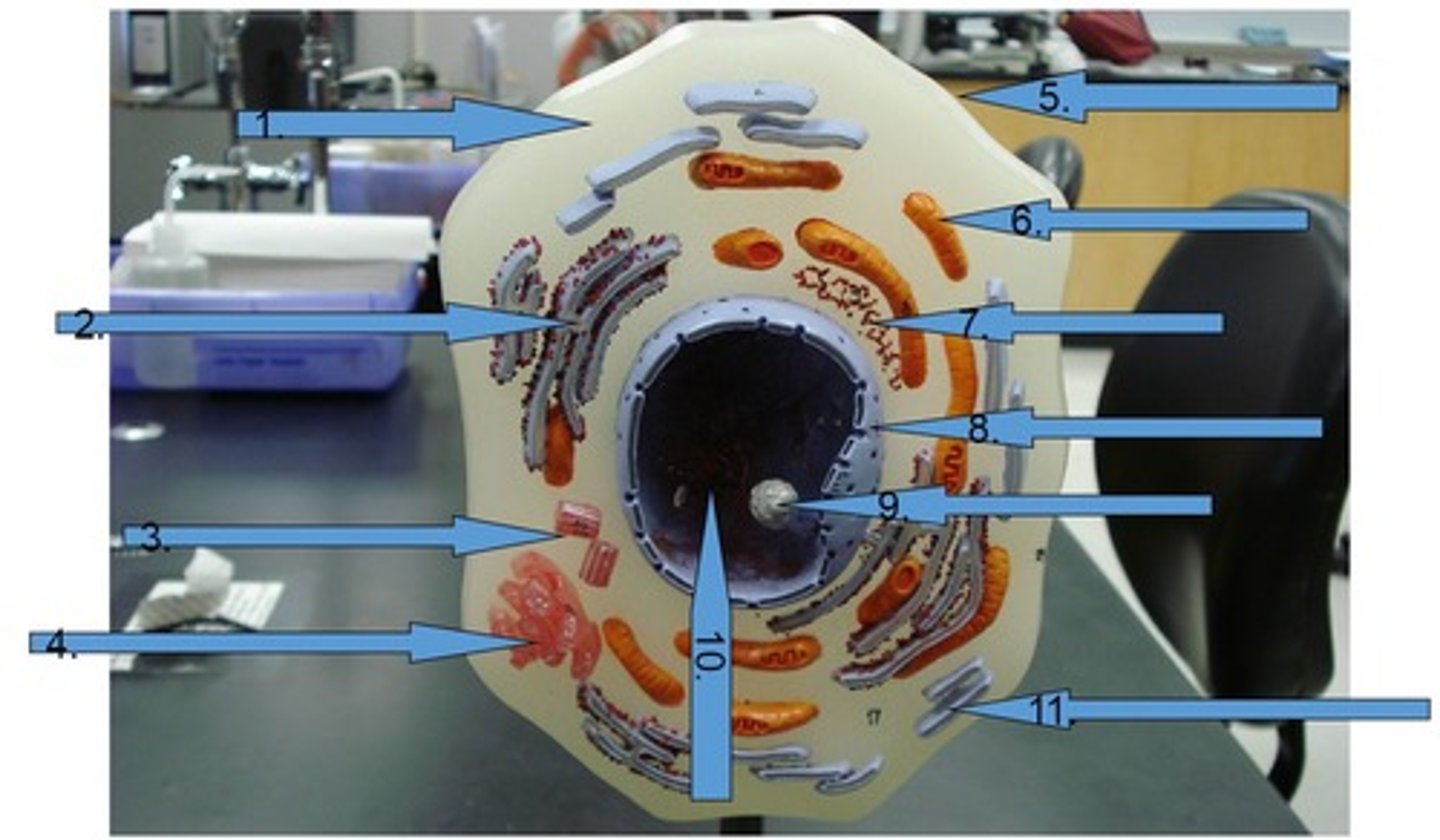
Centrioles
Cell organelle that makes spindle fibers for cell division #3
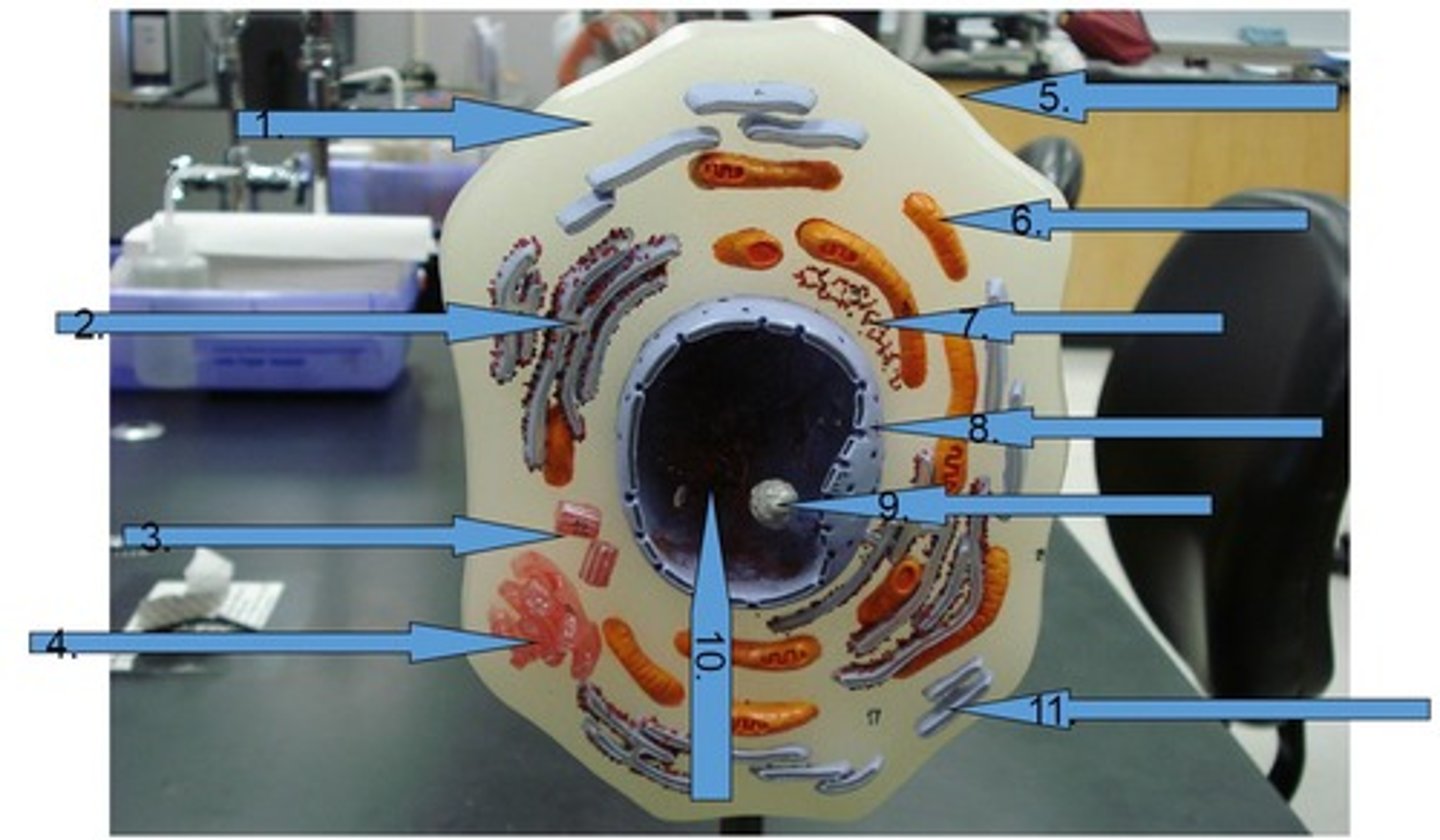
Golgi apparatus
a series of flattened membranous sacs that package secretions and waste, acts as UPS of cell #4
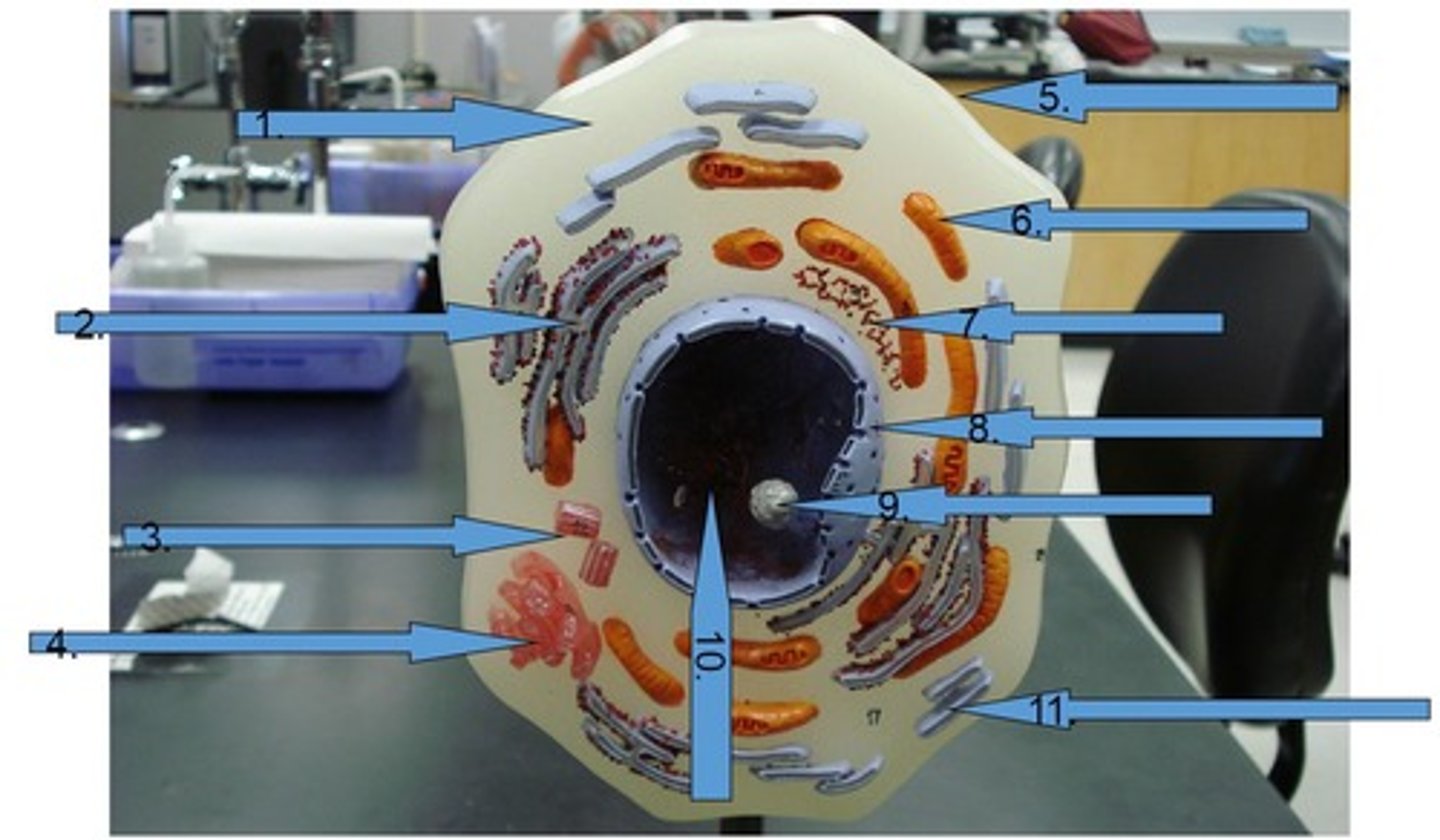
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER)
studded with ribosomes and is involved in protein processing and transport
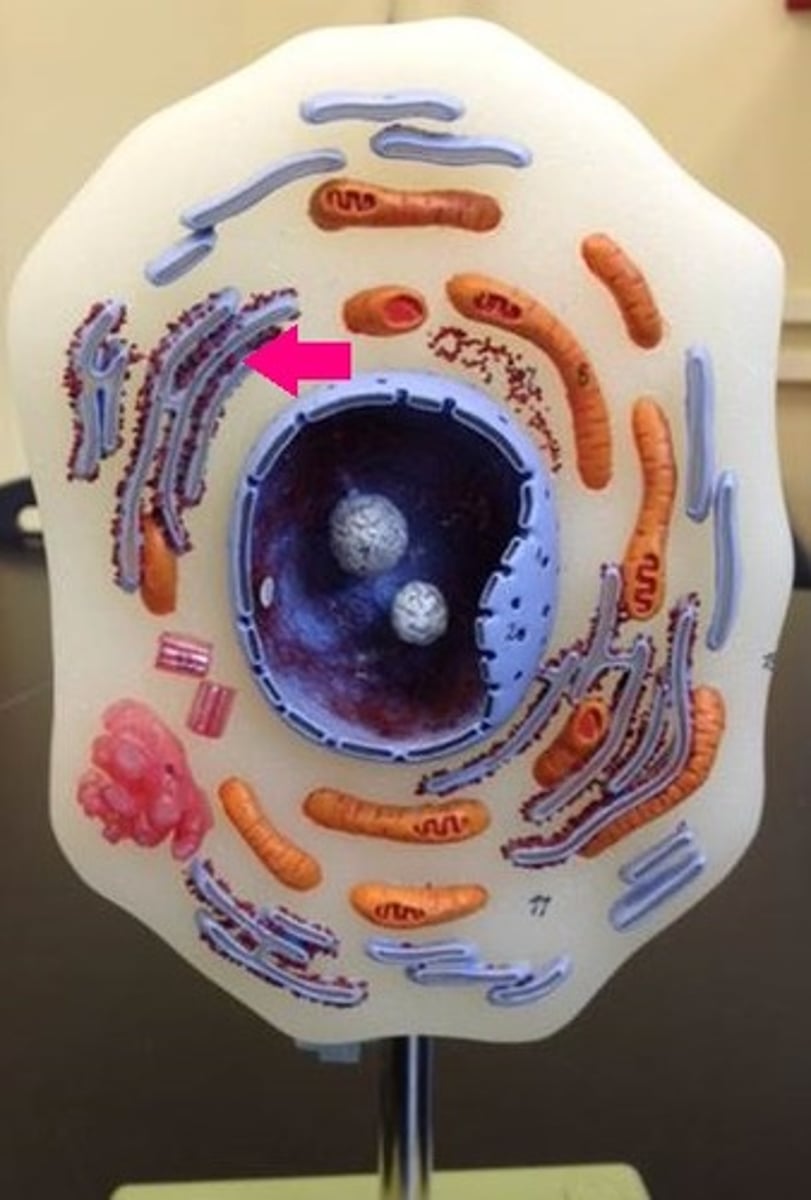
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER)
is involved with the processing of toxins and lipids, lacks ribosomes #11