D3.1 Reproduction
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
D3.1.1 Sexual vs asexual reproductino
Asexual: 1 parent, no meiosis, identical, no genetic variations; good genes passed on
Sexual: 2 parents, meiosis, differences, gen variation; evolve in env: offspring>parent
D3.1.2 Meiosis in sexual reproduction
Fusion of gametes: form new indiv.: brings allele tg in new combi: fertilization: n→2n
Meiosis: 1dip→4 hap. Break up parenal combis→new combi. 2n → n
Meiosis: 2n → n, Fertilization: n→2n
D3.1.3 Female vs male gametes
Male: travel to fem, small (fast), less food, many produced
Fem: non-motile, large(food reserves), more food(for embryo), very few
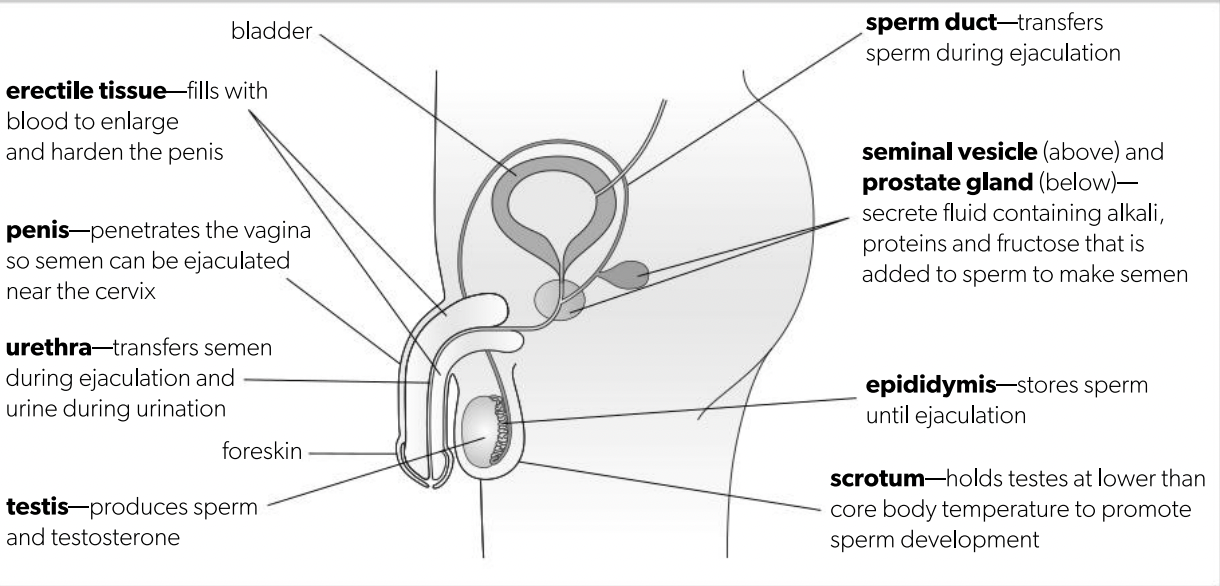
D3.1.4 Structure reproductive syst
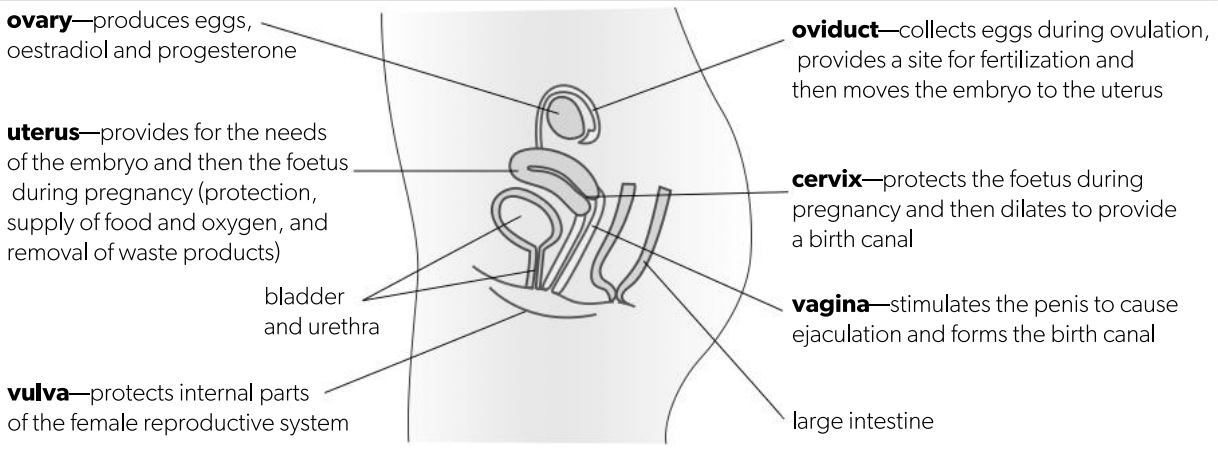
D3.1.5 Menstrual cycle (physical)
28 days. Happen in ovaries+uterus.
Ovarian cycle: follicles develop in ovary: release its egg on day 14 (ovul), after evol, wall of follicle enlarge → corpus luteum. If not fertilized: breaks down at end cycle
Uterine cycle: endometrium(inner layer ut) thickens:more blood, prep for implant embryo No embryo; thickening break and passes out of body: menstruation/period: day 1
D3.1.5 Menstrual cycle (hormonal)
4: Negative + positive feedback.
FSH + LH bind to receptors in membr of follicle cells
Oestradiol + Progesterone affect gene expression: development uterus+tits n stuff
Day 1-7 all semi low (menstruation, follicle starts developing)
Day 7-14: oestradiol rises (endometrium thickening, follicle matures)
Day 14: FSH,LH,oestradial tip (ovulation)
Day 14-21: FSH,LH low again, Oestrad lowens, then minmax at 21. Prog high→21
Day 21-28: Prog+oestr lower again (endometrium still remains thick, corpus luteum)
Day 6-14: follicular phase
Day 15-19: ovulation
Day 20-28: luteal phase
Day 1-5: menstruation
D3.1.5 Hormones functions
Protein hormones: pituitary gland:
FSH: follicle stim horm: constant high day 1-10 (stimul foll devel). Stim oestr secretion
LH: lut horm: rizes→peak day 14→ maturation of oocyte/ovul→burst fol wall: + corp lut
Steroid hormones; wall of follicle/corpus lut:
Oestradiol: rise to peak in 7-14. Stim repair+thick of endomet: Increase in FSH→boost oestradiol prod (+feed), high levels: oest inhibit FSH: (- feed) - IN FOLLICLE
Progesterone: rise after ov→peak then fall if no emb: promote thick/maint of endomet: inhibits FSH/LH secretion - feedback
D3.1.6 Fusion of sperm + egg cell: fertilization
Fertilization: fusion of sperm + egg to form zygote.
Sperm: receptor in plasm/mem that detect chemical released by egg: guide where swim
Egg: cloud layer:follicle cells + layer of glycoproteins (zona pellucida)
Sperm pushes between cells: digest route through glycprot to reach egg cell. Sperm tip has proteins that bind to egg cell plasmmem. First sperm binds and egg+sp fuse.
That moment = fertilization: immediately after: glycoprotein harders: prevent more sperm
Sperm components: tail + mitochondria broken down.
Sperm + egg nuclei remain seperate until zygotes first mitosis: both membranes break down: use same set of spindle fibres → 2 identical nuclei produced: 23+23→46 chrom
D3.1.15 Polyspermy prevention
>1 sperm + 1 egg. Structures make it infrequent: zona pellucula surround/protect egg: when sperm touches it. Sperm releases enzymes (from acrosome), digest small part of zona pellucila; sperm penetrates and reaches egg → fuse → egg releases cortical granule contents (cortical reaction): harden zona pellucila: difficult to penetrate, also alter binding glycoproteins…(sperm cant bind anymore)
D3.1.7 In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Natural fertilization: in vivo (inside body), can also happen in dishes: in vitro: IVF
Used to overcome fertility issues,
1. paused cycle 2. add FSH: follicles dev 3. matured 4. collected 5. fertilization 6. embryo transferred
D3.1.17 Pregnancy testing
hCG = protein indicator of presence of embryo, any stage…
Preg test test whether hCG is present; test has 3 types of antibodies on it:
1. Urine on strip → capillary action takes it along:
2. Meet antibody A+bluedye: hCG molecul bind do antiA; move along strip
3. Immobile antiB: bind to antiA that have hCG: blue bind
4. other antiA (no hCG) move along strip and reach anti(lgG): control: working test
2 lines: preg, 1 line: no preg
D3.1.14 Gamete production
Gametogenesis: spermatogenesis=testes and oogenesis=ovaries.Mitos,grow,meios,diff
Spermatogenesis: testes (cooler than rest), occur in seminiferous tubes. Near outer wall of tubes; spermatogenia, (germinal epithelial cells) that can undergo either mitosis/meiosis at any time.
Mitosis to replenish numbers (start puberty and continue in life), meiosis→spermatozoa
1 spermatogenia → 4 equal sized small spermatozoa →flaggelum+acro develop in tubes, released during ejaculation in semen, millions a day
Oogenesis: ovaries, 4 end product cells, but 3 polar bodies (useless; has chromosome.)
4th haploid → ovum(ova), start pub, end menopause, released in ov, 1 egg per productio
D3.1.16 Blastocryst
After fertilisation: zygote divides → embryo of identical cells → cells: more but smaller: all cytoplasm from og. cell. Hence, for embryo to grow in size: ball of cells (modula) that start to differentiate into a blastocyst. Occurs in oviduct. Blastocyst is hollow ball. Inside will become fetus (inner cell mass), outside (trophoblast) → placenta + amniotic sack.
Blastocyst hatches out of zonapellucia; implanted/embedded into endometrium/uter wall
Now, internal organs + external structures form. Heart+blood: day 16, pumo: day 20. Most organs done by week 10, except brain which develops long. After week8: fetus
D3.1.18 Placenta
Disc shape structur, embedded in uterus wall, develops about 4 weeks after conception. How the fetus is nourished. Forms from trophoblast(blastocyst) + mothers tissue. One side blood vessels mom, other side blood vessels fetus/embryo.
On foetal side: umbilical cord: 3 blood vessels. 2 carry blood into plac: deox RBC+ waste
Exchange material w maternal blood: 3rd ves returns good blood to foetus
No blood exchanged:
out: CO2, Urea, Water, Hormon
in: O2, nutrient, H2O, Hormon, alcohol/nicotine if used…
D3.1.13 Puberty
Puberty:sequence of changes in transition from childhood → sexual maturity, rate/timing varies per person.
Fem: breast, pubic/arm hair, growth spurt, period, change body shape; oogenesis
Mal:dick grow, scrotum/testes grow, pubic/arm/face hair, voice, growth; spermatogenesis
Triggered by hypothalamus; secrete GnRH → travel to pituitary → cascade of rea → secrete FSH and LH → testes/ovaries → bin to transmembr receptor → puberty → testosterone(LH)/oestradiol(FSH)/progesterone(FSH)
D3.1.19 Hormones pregancy + childbirth
Progesterone; maintain preg + signal birth: produced by corpus luteum/placenta, less progesterone produced full term → birthing. Prevent ovulation, maintain endometr, stop period…
INHIBIT OXYTOCIN production by pituitary: keep uter muscle relax: prevent early labour
Childbirth is triggered by drop in prog levels: oxytocin rises; stimulate contraction muscle:
positive feedback: pushing of baby to uterine wall nerve impulse more oxytocin produced
→ more/heavier contractions until child is born
D3.1.20 HormoneReplacementTherapy
Menopase: women stops menstrual cycle permanently oestradiol/prog decrease.
No oestr → symptoms: hot flash, sweat, reduces sex drive, vaginal dryness.
Can get medication of oestrad/progest→reduce ❤-dis in post-meno/ reduce symptoms
D3.1.8 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants
Gametes of flowering plants are made in = ovules (fem), pollen grains (male).
Meiosis makes them, mitosis makes gametes in these haploid structures.
Hermaphroditic: make both mal/fem structures: can self-pollinate. (orchid, sunflower)
Self-pol & fertilization: sexual reproduction: gamete by mitosis, fusion of gametes
Disadvantage of self-pol: loss of genetic variation bc same individual: copies
Cross-pollination: transfer of pollen of 1 plant to another plant. Use shapes, markings, colours, smells, to attract pollinating animals and hope that they help with pollinating
D3.1.8 Process of sexual reproduction in plants
Pollen develops in anthers in smart position so pollinators can contact wo. realizing it.
Pollen will move to diff structure (same/diff plant): stigma: upright in fem. part of flower: sticky, pollen stay
Pollen moves through pollen tube to ovules: 1 pollen = 2 gametes
One of gamete fertilise one of gametes in ovule (has 3) → zygote
Other pollen gamete + 2 other ovule gametes → endosperm tissue: 3n: triploid: grows and is nutrients that nourish early plant embryo
D3.1.10 Increasing cross polination
Transfer pollen from anther of 1 to stigma of another plants flower. Need outside agent to transfer pollen: wind or animal. Leads to genetic variation → evolution: needed when environment is changing.
Many plants hermaphrodite: both male/fem gamete production: self-pol possible: inbred
In animals: lead to miscarriages and genetic disease. Increase rare rec allele frequency
Plants cross pol usually strong/healthy: natural selection favours them.
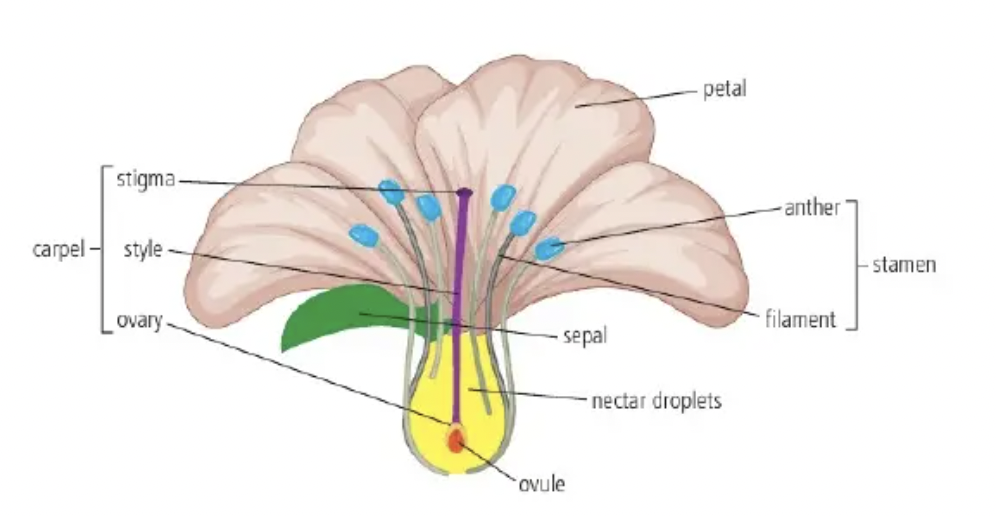
D3.1.9 Insect pollinated flowers
Bees, wasps, flies, butterflies, moths. flowers are large brightly coloured/strong scent; offer reward in form of nectar: base of flower. Stamen deep inside flower: insect touch pollen grains (adhere sticky/spiky). Stigma also sticky: pollen transferred ins→stig
Sepal: protect developing flower
Petal: colourful, attract pollinators
Stamen: male part:
Anther: make pollen
Polen: contain male nuclei (2) for fertilization
Filament: hold anther up
Carpel: fem part:
Stigma: sticky top of carpel; pollen lands
Style: carpel supporting stigma
Ovary: base carpel; ovule(s)
Ovule: chamber w ovary: fem nuclei (3) develop
D3.1.11 Self-incompatibility
Plants avoid self-polination to try get genetic diversity: healthier. differs per plant, either:
1. fail to germinate
2. germinate but no enter through stigma into style
3. tube enters ovule but pollen degenerates before fertilization
4. fertilization occurs but plant embryo degenerates earlily
D3.1.12 Seed dispersal + germination
seeds transported long distances from parent plant: seed dispersal.
By wind. Sycamore has wings, cranesbill is explosive, budock has hooks for animal
D3.1.12 Process of plant grows/development
Pollination: pollen → ovule
Fertilization: fuse to form zygote
Seed dispersal: zygote/seed is spread and waits until good conditions (water,temp…):
Germination: sprouting of seed into embryo → plant.