Evolution and Biodiversity
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB Bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
The ability to digest lactose in adulthood appeared due to a mutation in the lactase gene. The frequency of the lactase persistence allele was recorded as 0.8 in present-day European populations and as 0.05 in fossils from populations of their prehistoric ancestors. What could have caused the change in the allele frequency?
Explain natural selection: having the gene was more selected.
Which is an example of evolution by selective breeding (2 animals)?
Dogs & specific traits
Cows that produce lots of milk on a farm.
Which statement best describes how evolution occurs?
Individuals who have traits that help them survive will pass it on to their offspring
The diagram shows a cladogram for part of the animal kingdom. Which group does not represent a clade?
The common ancestor and all of its descendants; know what is and isn’t a clade
The graphs show how the frequency (f) of a trait within a population changes when subjected to selection pressures. Which graph shows stabilizing selection?
The two lines on the graph look basically the same, the same before and after. After natural selection, the same trait is still dominant

The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family. The figwort family has been reclassified and is now much smaller. Why were species such as the foxglove moved into other families?
New DNA evidence. Working hypothesis, constantly changing.
What is a recognition feature for both of the plant phyla indicated? (Filicinophyta vs. Angiospermophyta)
Filicinophyta: Spores
Angiospermophyta: fruits + flowers
They are both vascular pants
Mammals, birds and reptiles have an embryonic tail that may disappear during development.
Evolution, didn’t need a tail after a while;
All vertebrates have a common ancestor.
The graph shows the proportion of a bacterial population of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, displaying resistance to the antibiotic tetracycline. What can be deduced from this graph?
Only stick to what you see in the graph; do not make your own assumptions
Can see: the population of the resistant bacteria increased over time
The plant in the diagram has vascular tissue and reproduces by spores. To which phylum does the plant belong?
Filicinophyta
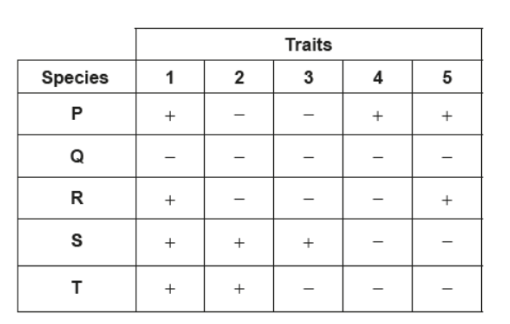
Data regarding the presence (+) or absence (–) of five traits in several different species are shown in the table.
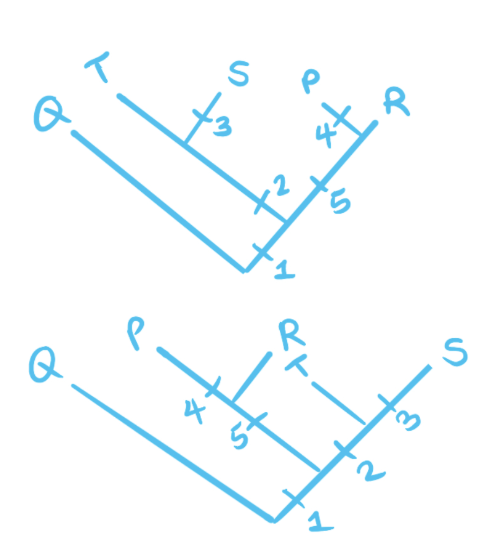
Which cladogram best represents the relationship between the five species?
Draw a cladogram that shows the relationship between the species
Choose the one that is most parsimonious (simplest)
Humans have been improving crop species for thousands of years by cross-breeding plants with desirable characteristics. The photograph shows the changes in dry cobs of corn (Zea mays) over 10 000 years. What is the name of the process that was used to produce modern corn?
selective breeding
Which encircled area shows a clade?
Clade involves common ancestor and all its descendants
The diagram shows features of three plant phyla. Which phyla are represented by R, S and T?
D.
R; filicinophyta (has spores)
S; confierophyta (cone)
T; angiospermophyta (produces fruits and flowers)
Which factor(s) would favour evolution by natural selection?
I. Long lifespans
II. Favourable characteristics acquired by individuals during their lifetime
III. Variation within a species
III. Variation within a species
What could be used as evidence for evolution?
I. Selective breeding of domesticated animals
II. The fossil record
III. Homologous structures
All 3
The pentadactyl limbs of mammals, birds, reptiles and amphibians are examples of which kind of structures?
Homologous
Scientists studying ground finches (Geospiza fortis) on the island of Daphne Major in Galapagos found great differences in the shapes of the beaks. What is the explanation for this variation in beak shape between the birds?
Some finches flew to Mandacasar from the mainland.
Once on the island they adapt to different food sources.
Some develop beaks suited for plants while others develop beaks better suited for nuts.
The image shows the northern sea nettle (Chrysaora melanaster). To which phylum does C. melanaster belong?
Cnidaria ; it’s a picture of a jellyfish
The cladogram shows one theory of how species of hominin evolved. What can be deduced using the information in the cladogram?
**Need to know how to read a cladogram
H. sapiens and P. robustus shared a common ancestor.
To which phylum does the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus belong?
Annelida
Which process results in decreased variation?
Natural selection (since it will kill off those that aren’t good for survival)
A locust is an arthropod. For invertebrate groups, which recognition feature is found only in arthropods?
Exoskeleton and jointed appendages
A dichotomous key can be used to distinguish four types of plant. Which of the plants could be a bryophyte?
Main feature of a bryophyte is it’s Non vascular
On the islands of the St Kilda chain, off the coast of Scotland, there are small birds called St Kilda wrens (Troglodytes troglodytes hirtensis). They look similar to wrens on the mainland of Scotland (Troglodytes troglodytes indigenus), but they are larger and there are differences in the colour of their feathers. What is the most likely explanation for these differences?
C. Gradual divergence
Natural selection; the larger the feather size and color is how you know
Which is an example of speciation?
(Single ancestral species evolves into multiple, distinct and separate species)
E.g. humans and apes
Which evolutionary pathway is most likely to result in the evolution of analogous structures in Species W and Z?
Species V → Species X → Species W,
Species Y → Species Z
The images show a structure found on members of a phylum of green plants. What is the name of the phylum to which the organisms belong?
Chlorophyta
What information can be deduced from the sequence of nodes in a cladogram?
the probable sequence of divergence among species and their relative evolutionary relationships
What are the evolutionary origins and functions of homologous structures?
Same common ancestor, function might not necessarily be the same thing
What process best explains the formation of different pentadactyl limbs?
Adaptive radiation
Natural selection
*Ex: Flyer→wings
What would restrict evolution by natural selection, if a species only reproduced by cloning?
Genetic variation or just variation, population needs variation to evolve and find better suited traits
The offspring would show a lack of variation
An animal has the following characteristics: bilateral symmetry, a mouth but no anus, ribbon shape. Which phylum does the animal belong to?
Platyhelminthes
The cladogram shows some of the groups in the three domains. What domains do X, Y and Z represent?
3 domains:
X = Bacteria (-teria)
Y = Archaea (-philes)
Z = Eukarya (Animals)
Which pentadactyl limb is adapted for flight?
the forelimb
An organism has the following characteristics:
single opening for ingestion and egestion
radial symmetry
tentacles with stinging cells.
In what phylum would it most likely be classified?
Cnidaria
Which organism is a member of the filicinophyta? (Note that these are not to scale)
a fren
Which are examples of homologous structures?
Forelimbs, or motified leaves of plants
Which is an example of natural selection?
(Something that changed/adapted so it’s more likely to survive and pass it onto their offspring)
Development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria

The image shows an organism belonging to the Kingdom Animalia. What feature does this organism have in common with all members of the phylum chordata?
-bilateral semitry
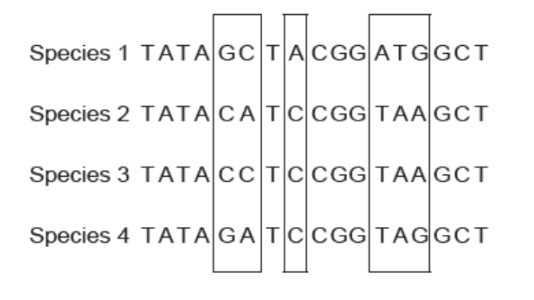
The DNA base sequences in a gene coding for a particular protein in four different species are shown. Locations where mutations have occurred, resulting in changes to the base sequences, are outlined in boxes.
Which cladogram shows the most likely phylogenetic relationship between the four species, based on the data provided?
draw a clotogram with species one as the out group
What is required for natural selection to occur?
I. Acquired characteristics
II. Advantageous characteristics
III. Genetic variation
2: Advantageous characteristics, 3: Genetic variation
If seeds of an unknown species of plant are discovered, what assumption can be made about the species?
Its male gametes are contained within pollen
Conifers and angiosperms (but not angiosperms)
Which phyla have bilateral symmetry?
Arthropoda, Chordata, Annelida, Mollusca, Nematoda, and Platyhelminthes
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of decreasing numbers of species?
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
What is the reason for antibiotics not damaging human cells?
Human metabolism is different from bacterial metabolism
The cladogram shows some major orders of placental mammals and is based on biochemical evidence. Which conclusion can be drawn from evidence in the cladogram?
Cetacea (whales and dolphins) are more closely related to Primates than to Sirenia (manatees and dugongs)
Which is the hierarchy of taxa in order of increasing numbers of species?
species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain
The images show a guinea pig, a mouse, a horse and a whale. Which features support the classification of these four species in the same class?
warm-blooded, having hair or fur at some point in their lives, giving birth to live young (most do), and nursing their young with milk produced by mammary glands
The cladogram shows the relationships of five species I to V. Which species is/are most closely related to IV?
Species II and III
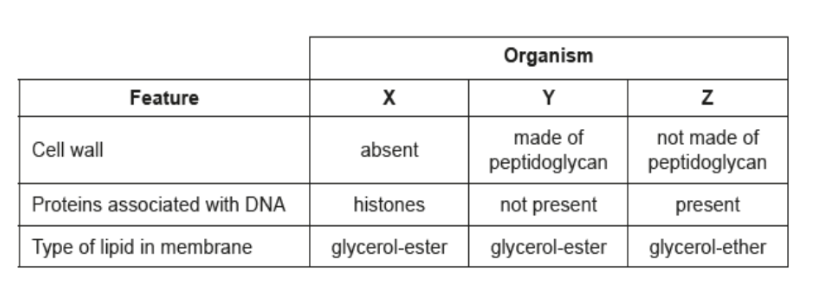
The chart shows features of three organisms X, Y and Z. To which domain does each organism belong?
X= Euyara, Y= Eu bactiral, Z= Archea
Balkan green lizards, Lacerta trilineata, living in mainland Greece eat mostly insects but also small amounts of plants. The same species living on Greek islands (where insects are scarce) show a greater percentage of those physical traits useful for eating plants than the mainland lizards. What is the biological explanation for these observations?
Lizards on the island diverged due to:
Lack of interbreeding with the mainland population
Selective pressure (diet)
Which phylum shows radial symmetry?
Cnidaria and Echinodermata
The cladogram was constructed using DNA base sequences from six species. Which node indicates the greatest difference in base sequences?
he one at the very bottom of the cladogram, also known as the root node
The diagrams show various wings. Which statement describes the relationship between the structures of the wings?
Option A: Homologous structure if wings are pterodactyl
Option B: Analogous structure if from different ancestor with different bone structures
What reduces variation in a population?
Natural selection, cloning, inbreeding
Which invertebrate phylum is characterized by a segmented body and bilateral symmetry?
Annelida and Arthropoda
The figwort family is a large one consisting of many flowering plants that look similar. For what reason have some members of the family been reclassified into a new family?
DNA analysis revealed that the group was not a monophyletic (naturally evolving) one, but was a polyphyletic collection of different lineages that had been mistakenly grouped together due to similar appearances.
Which of the adaptations of flowers would be most successful for the survival of a species?
specific odors for better insect pollination
Prickly pear cactus plants are well adapted to desert conditions. The stems are the flattened structures visible in the image and the leaves are reduced to spines. The white spots in the image are groups of spines.
Which characteristics describes the advantage of those features
Leaves are reduced to spines to lose less carbon dioxide
Flattened stems and spiny leaves conserve more water
Which of these structures is not homologous?
the wing of an insect and the wing of a bird, the fin of a shark and the flipper of a whale, or the leg of a grasshopper and the arm of a human
What causes variation within a population (4)?
Fertilization
Mutation
Crossing over
Independent assortment
Which of the organisms A–D, identified by the key, represents a reptile?
look for the option that talks about the soft eggshells
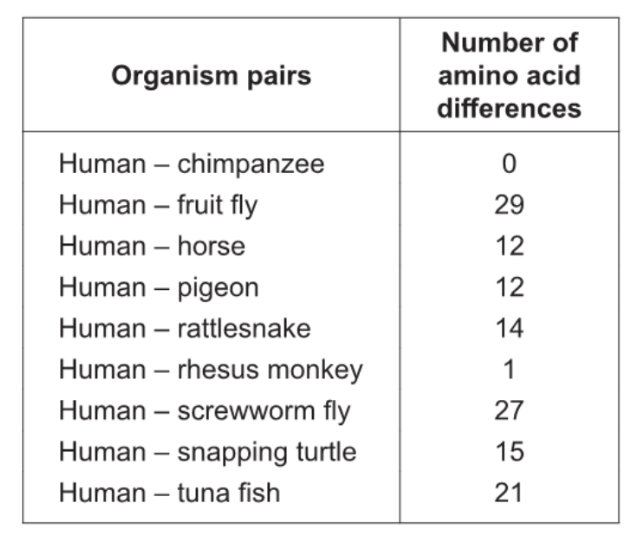
The table shows the number of differences between humans and other selected organisms for the protein cytochrome c oxidase. This protein, consisting of 104 amino acids, is located in the mitochondria and functions as an enzyme during cell respiration.
If the data were used to draw a cladogram, which chordates would be furthest apart from humans?
only look at chordates, so Tuna fish is chordate and has the highest amount of differences
Antibiotics such as penicillin are secreted by fungi and other microorganisms in soil. By secreting them, a microorganism can inhibit the growth of a competitor.
In research published in 2014, nearly 3000 antibiotic resistance genes were discovered in soil microorganisms, giving resistance to 18 different antibiotics. The types of antibiotic resistance gene varied between soil types.
(a) Explain how natural selection could increase the prevalence of an antibiotic resistance gene in a species of soil bacterium.
The ones that don’t have the antibiotic gene will die, while the other ones that do have it will pass it on, until one day all the soil has the antibiotic gene
Antibiotics such as penicillin are secreted by fungi and other microorganisms in soil. By secreting them, a microorganism can inhibit the growth of a competitor.
In research published in 2014, nearly 3000 antibiotic resistance genes were discovered in soil microorganisms, giving resistance to 18 different antibiotics. The types of antibiotic resistance gene varied between soil types.
(b.i) There are viruses in soils that are pathogens of animals. Outline a reason for antibiotics in soil not eliminating these viruses.
Because viuris is not a bacterium and antibiotics are targeted towards bacteria, it won’t affect the virus.
Antibiotics such as penicillin are secreted by fungi and other microorganisms in soil. By secreting them, a microorganism can inhibit the growth of a competitor.
In research published in 2014, nearly 3000 antibiotic resistance genes were discovered in soil microorganisms, giving resistance to 18 different antibiotics. The types of antibiotic resistance gene varied between soil types.
(b.ii) Explain the reasons for antibiotics secreted into soil not harming insects or other animals in the soil.
because antibiotics are targeted towards bacteria and not other organisms
Isolated communities in rural Finland, Hungary and some of the Scottish islands have a high incidence of red-green colour blindness. Describe the inheritance of red-green colour blindness.
Sex linked trait, mainly men inherit it
Isolated communities in rural Finland, Hungary and some of the Scottish islands have a high incidence of red-green colour blindness. Describe the inheritance of red-green colour blindness.
b) The human hand is an example of adaptive radiation. Outline adaptive radiation (5).
Happens in a group of species that evolved from a common ancestor.
Evolution of a structure in different ways, with unique adaptations.
Homologous structures are evidence of adaptive radiation.
e.g. The pterodactyl forelimb: trait of humans, birds, bats. Same structure but different function (lift vs. fly).
Therefore, the human hand has been modified for precision and power grips.
Isolated communities in rural Finland, Hungary, and some of the Scottish islands have a high incidence of red-green colour blindness. Describe the inheritance of red-green colour blindness.
Explain how evolution occurs and which factors can cause the process to be rapid. (7)
Natural selection causes evolution.
Evolution is a change in the inherited traits of a species over time.
These advantageous traits become more common over time.
overpopulation, over-reproduction, more offspring than the environment can support.
competition for resources and mates.
Genetic variation = differences in traits (from mutations and recombinations)
mutation, meiosis, sexual reproduction contributes to variation.
Outline the evidence for evolution provided by selective breeding (4).
E.g. Humans breed dogs to have specific traits.
Those traits that humans want become more common in dogs.
Unlike evolution, the strongest trait isn’t always passed on (e.g. bulldogs wouldn’t survive if natural selection played a role)
Without humans, those traits would be very rare.
Explain the development of antibiotic resistance in terms of natural selection. (6)
Antibiotic will kill bacteria
Some bacteria will be resistant to that antibiotic
Variation is due to a random mutation
Resistant aren’t destroyed by antibiotic
These bacteria are more likely to survive and pass this antibiotic resistant gene onto their offspring (selective advantage)
After several generations, the antibiotic resistant gene will become more common.
Explain how natural selection can cause traits such as drought resistance to develop in wild plants.
If a plant can’t absorb water in a dry environment, it will die.
But some plants will have evolved traits that can absorb and conserve water.
Over time, that trait will become more common amongst the plants.
Variation in genetically inherited characteristics is the basis for evolution.
Explain how genetic variation between the individuals in a species can be generated.
1: genetic mutation = anytime a gene sequence is changed
2: crossing over = (during miosis) when homologous chromosomes exchange information
3: independent assessmen = (during miosis), when homologs line up in pairs, the order will constantly change
4: random fertilization = different egg and sperm cause more variation
Variation in genetically inherited characteristics is the basis for evolution.
Outline the use of analogous and homologous traits in natural classification.
Homologous traits are the only ones used during natural classification.
Homologous traits arise from common ancestors
Analogous traits don’t so therefore they are not involved in natural classification
Define both terms
Explain how natural selection can lead to speciation (7).
- In a population, variation exists due to meiosis and mutations.
- Competition for resources occurs, and the ones best adapted to their environment survive, and pass on their genes to future generations
- Over time, this allele will be more common.
- Speciation is when a single ancestral specie branches into multiple distinct and separate species due to physical and non-physical barriers.
- So, reproductive isolation: temporal, behavioural
- Changes in gene pool
- Interbreeding between new species and parent population and producing fertile offspring becomes impossible
Describe the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
Antibiotics killed bacteria. But some of the bacteria have an antibiotic resistance gene. These bacteria will be more likely to reproduce and pass the gene on to the offspring. And that gene will be more common in the generations to come.
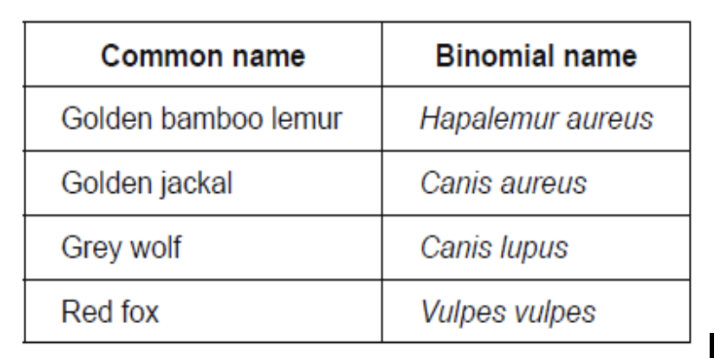
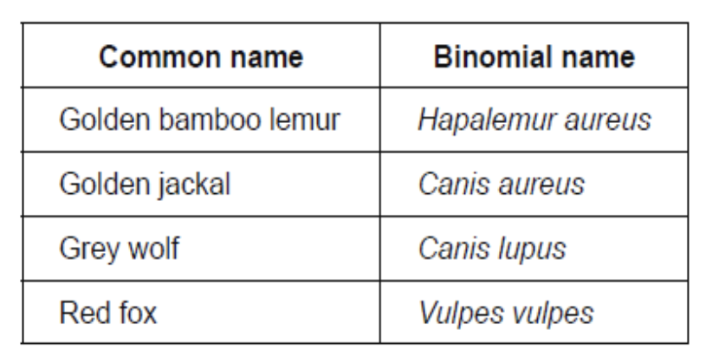
The table gives common names and binomial names for some mammals.
(a) State one feature that characterizes these species as mammals.
Mammary glands
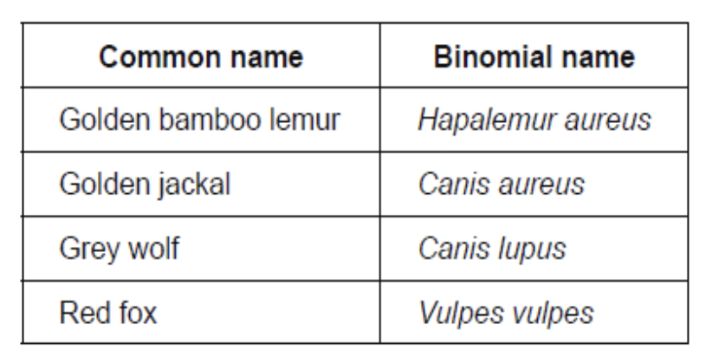
The table gives common names and binomial names for some mammals.
Identify the two species most closely related.
Golden jackal and Grey wolf
The table gives common names and binomial names for some mammals.
Identify two species from the list that are classified in different genera.
Hapalemur and Vulpes
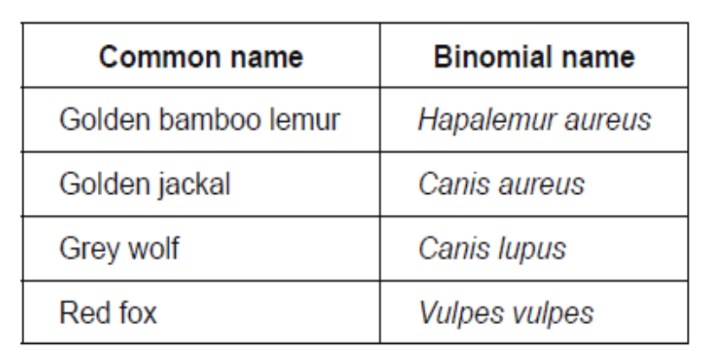
The table gives common names and binomial names for some mammals.
State two features that are found only in mammals.
Mammary glands and fur/hair
Birds, bats and humans are all vertebrates with pentadactyl limbs. Birds and bats use their forelimbs to fly whereas humans can use them to lift and manipulate objects. Outline how the bird, bat and human forelimb can be used to illustrate the concept of homologous structures.
Structures are the same: 5 fingers. But the functions are different. One uses it as fin, one to grab, etc. Different function same structure. Because the common ancestor has this structure, but they evolved to have different functions, which is part of the evolutionary process.
Explain how a newly discovered plant species would be classified and named.
by comparing it to existing species using a hierarchical system (domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) based on its physical characteristics and DNA
Outline how adaptive radiation provides evidence for evolution.
Adaptive radiation happens when one ancestral species quickly evolves into many new species, each adapted to different ecological niches through natural selection
Outline the binomial system of classification.
There’s 2 names: Genus species. The genus name has more to do with how closely related they are to each other. No two species have the same genus and species.
The image shows the wings of an insect, bird and bat.
(a.i) Based on their structure, the insect and bat wings are analogous. Outline what is meant by an analogous trait.
Different structures with the same function. They are all used to fly but they aren’t structured the same.
The image shows the wings of an insect, bird and bat.
The bird and bat wings share homologous bone structures whereas the insect wing does not. Outline the conclusion that can be drawn about the evolution of these wings, based on homologous structures.
The bat and the bird shared a common ancestor that they didn’t share with the insects.
The image shows the wings of an insect, bird and bat.
Explain how cladistics can be used to investigate evolutionary relationships.
Uses common ancestry to determine rather than just how it looks
They are looking at DNA structures
The image shows the wings of an insect, bird and bat.
Cladistics and other evolutionary evidence suggest that mammals and birds have a more recent common ancestor than mammals and amphibians. Draw a cladogram to show the relationships between mammals, birds and amphibians.
Amphibians are the out group, Birds and mammals are closer, or creating a clade
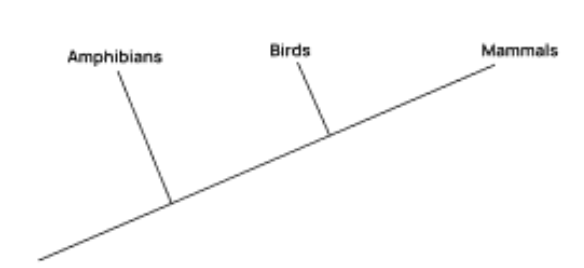
Describe what is shown in a cladogram.
Common ancestor
All of its descendants
The images show parts of plants belonging to two different phyla.
State the phylum of plant X and of plant Y.
Just look at the plant and be able to identify what phylum they belong to
Outline the types of evidence that can be used to place a species in a particular clade.
Common ancestry
DNA similarities
(all the things you can’t see on the surface)
The cladogram includes four marsupial (non-placental mammal) families. Deduce the family that is most closely related to the Diprotodontoidea.
The family most closely related to the Diprotodontoidea is the one that branches from the same node as it — they share the most recent common ancestor.