Bovine Review - VST 221 Knowt
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Working on it.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Bos taurus
temperate-climate cattle
Bos indicus
heat-tolerant cattle of hot regions
Cattle serve?
industry: milk, beef, hides, draft power, and sacred roles in some cultures
Pelvic bones prominent
Nutrition shunted to milk
udder wide, four quarters
6–7 gallon/gal day⁻¹ capacity
Large heart girth + long thin legs
high milk yeild
Holstien
Milk Volume: Highest
Fat %: Low
Notes: Black and white, Al Breeding
Guernsey
Milk Volume: Moderate
Fat %: High
Notes: Golden, Thick Milk; High in Protein and Ca²⁺
Stanchion Barn
Individual barn, rubber mat + straw
Free-stall
separate feed & rest areas
Loose housing / pen
group pens with bedding
Automatic milkers
-> Bulk tank -> chilled and tested
Twice-daily milking
365 days a year, except 60 d dry period
Heifer
female never calved
Cow
female that had calved > once
First calving =
24 months
Beef Cattle Confirmation
Stocky, muscular, small udder (females), short thick limbs
Some dual-purpose breeds give moderate milk
Angus
Black, Polled (naturally hornless)
Hereford
red & white, polled strain popular
Polled Hereford
Hornless at birth
Minimal confinement
roof + drop-down sides for weather
Pasture-rearing
planted forage (increases) muscle mass.
Open pasture
native plants, vast area, lower hygiene risk
0-6 Months
nursing and weaning
6-15 months
Graze open pasture
15 months+
Feedlot - High protein pellets
Cattle sorted:
age and size
Close quarters
(higher risk) for disease transmission and hygiene issues.
All cattle have a:
four chambered stomach; the rumen is the largest.
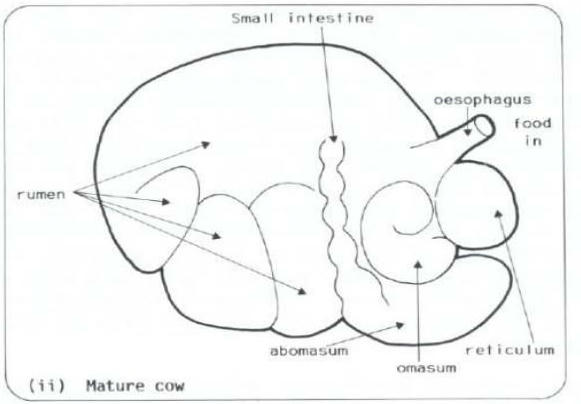
Food flow of (bovine) stomach:
oesophagus → rumen → reticulum → omasum → abomasum → small intestine. The abomasum works like a monogastric stomach.
Dental pad:
replaces upper incisors, lower incisors nip grass
Tongue:
gathers forage → bolus swallowed with little chewing.
Cud regurgitation:
repeated chewing + saliva breakdown
Microbes:
in rumen (bacteria and protozoans) ferment cellulose.
Class: Beef
Roughage: Hay, Silage, Pasture
Supplements: Occasional protein
Class: Dairy
Roughage: controlled ration
Supplements: Grains, pellets, minerals, vitamins adjusted for pregnancy & lactation stage
Water and Minerals
Up to 50 gallons water a day.
Salt/mineral blocks supply Na⁺, Ca²⁺, P to balance grass diets
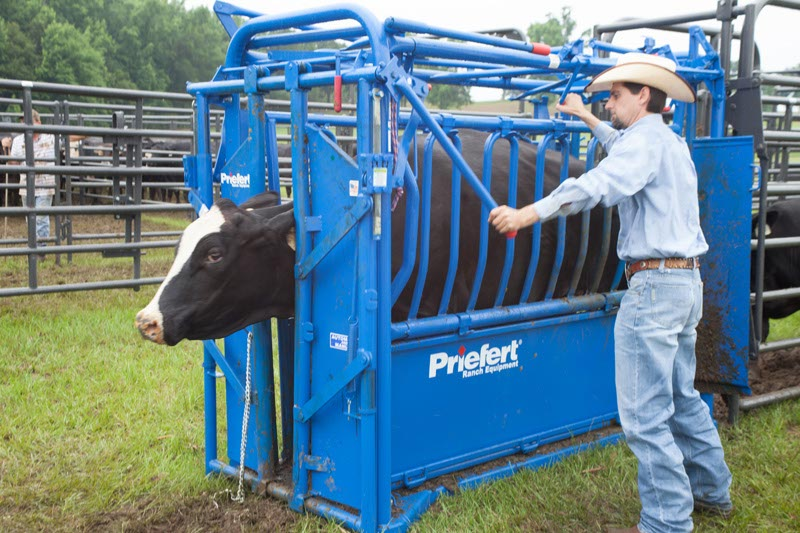

Squeeze Chute:
the primary restraint device, featuring a head gate to secure the animal's neck. The septum piercing area is particularly sensitive and allows for control when handling cattle.
Types of facilities:
Holding corrals, Sorting chutes, Loading chutes, Head gates

Holding corral:
temporary containment

Sorting chutes:
separating animals

Loading chunks:
transport
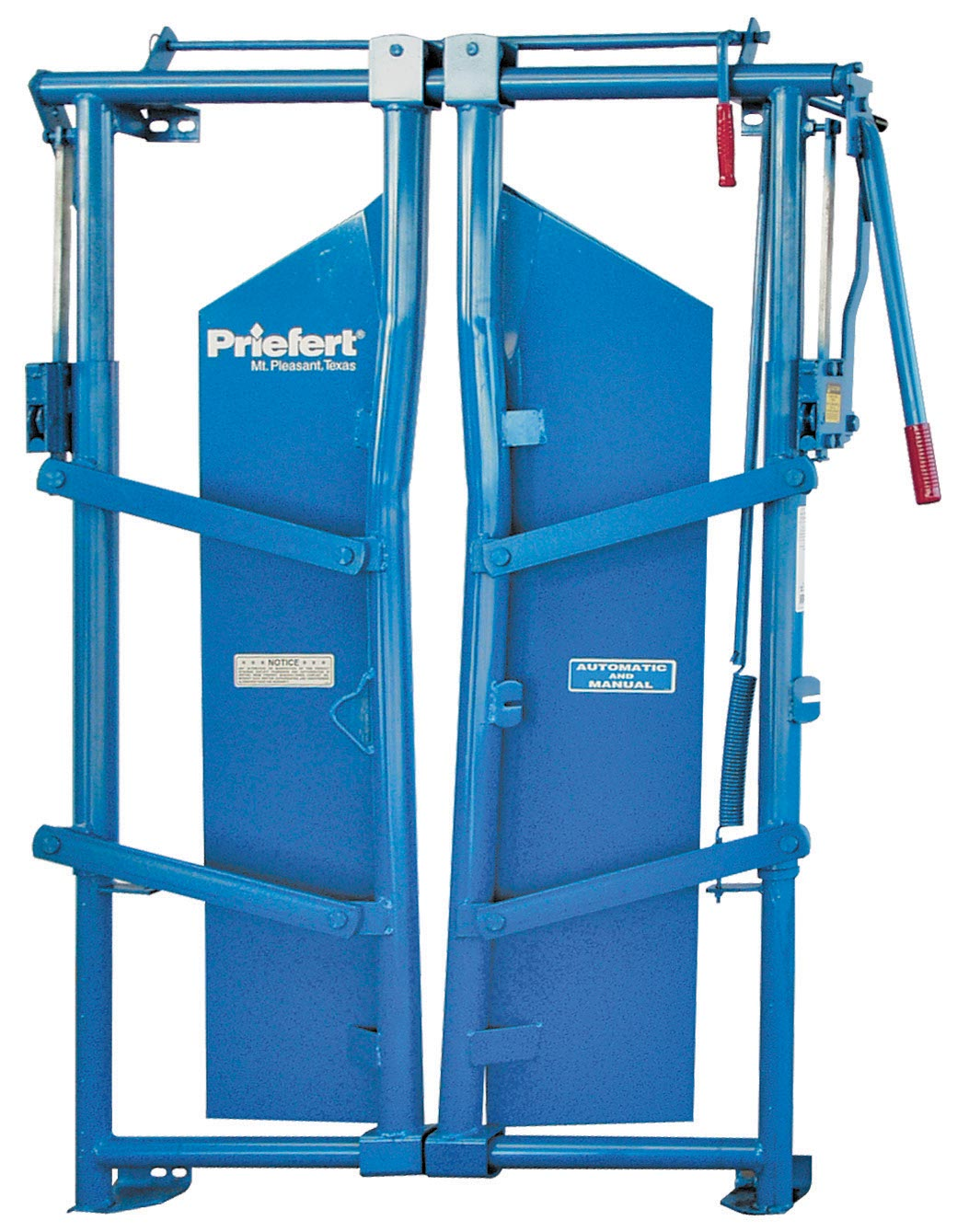

Head gates:
individual restraint
Alternative restraint methods:
Rope leading, Casting, Nose tongs, Tilt tables
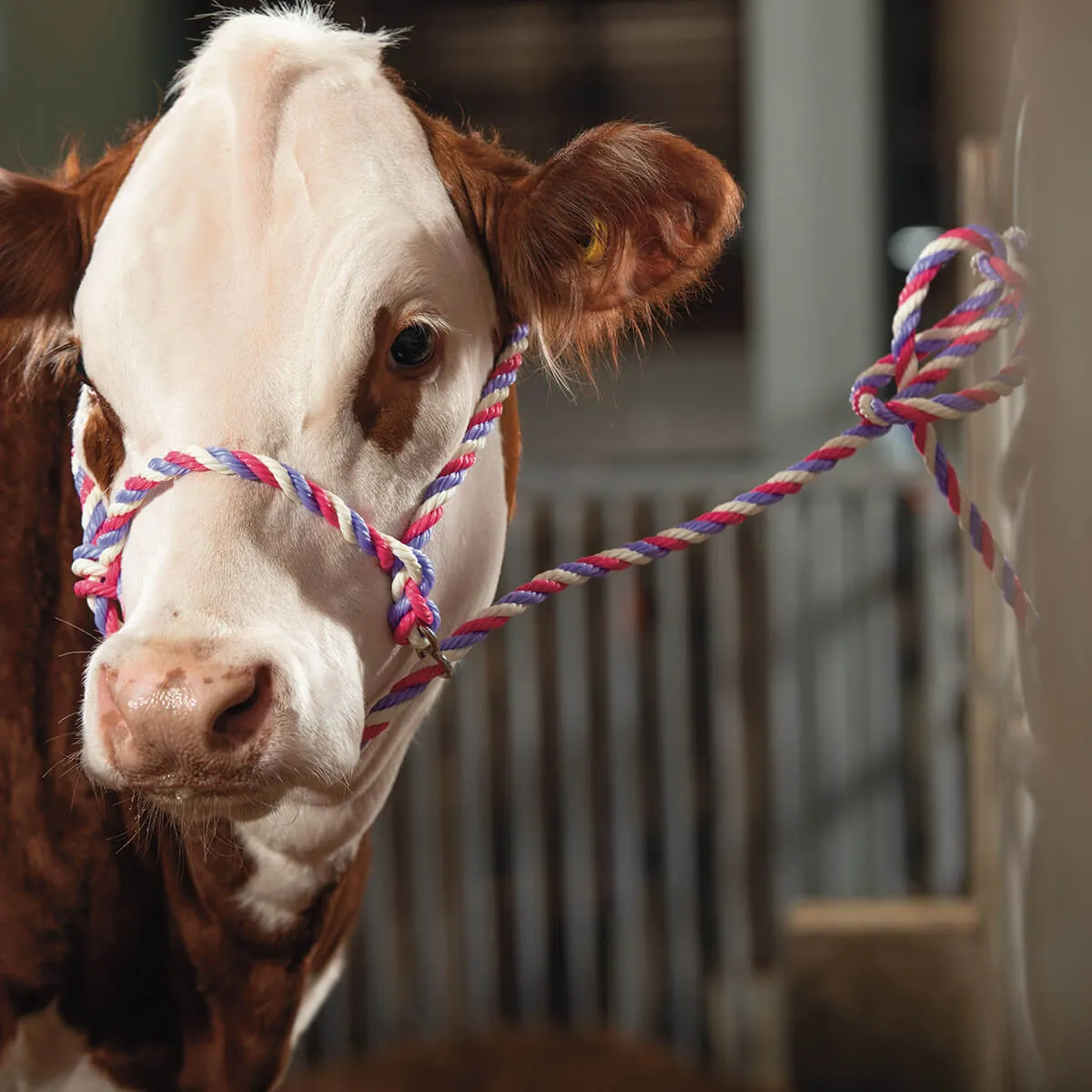

Rope leading:
Dairy cows
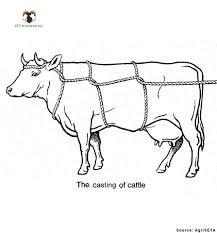
Casting
using ropes to lay cattle down.
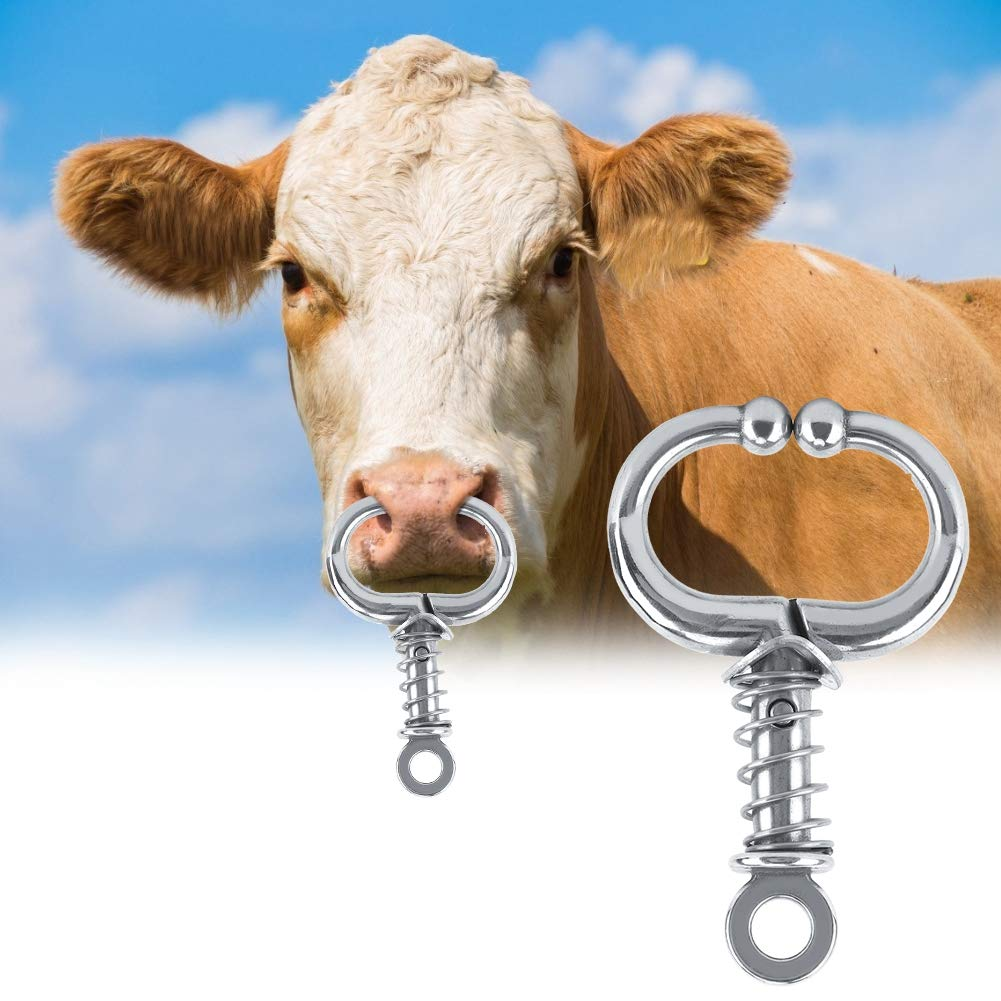

Nose tongs:
Additional control.
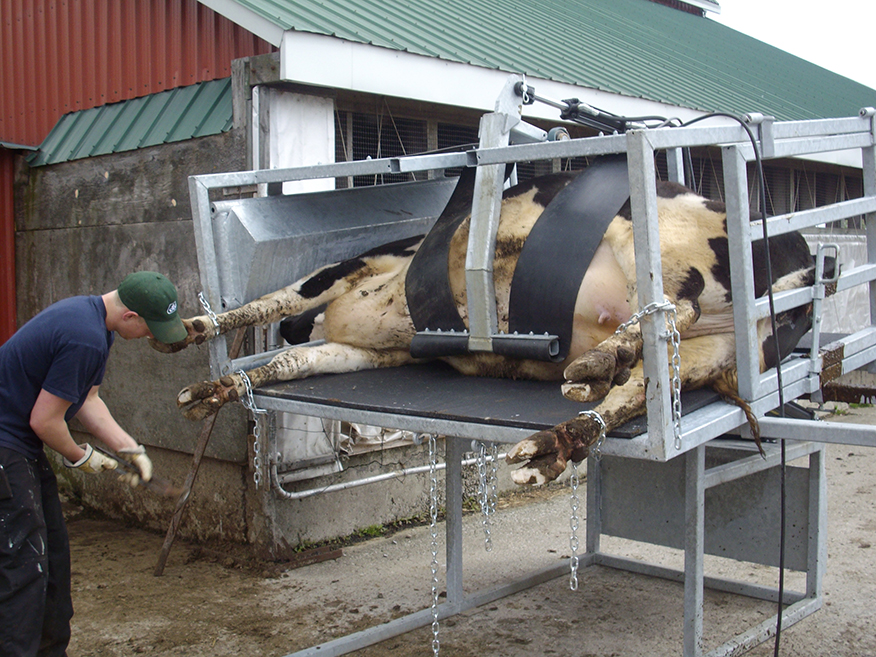

Tilt tables:
for hoof care (minimum twice yearly)
Individual identification
crucial for reproductive management and disease control. Dated tags help monitor vaccine schedules.
Tag types:
Visual Tags, Electronic RFID Tags
Visual Tags:
identification only.
Electronic RFID Tag:
store/track database information
Ear anatomy considerations:
Two large veins run parallel from head to ear tip - avoid piercing
Avoid cartilage ridges in middle ear to prevent infection or deformation
Dehorning should occur:
before 8 weeks of age for safety.
Electric dehorning is preferred;
other methods work for older animals by crushing blood vessels.
Castration methods:
Surgical, Emasculatome
Surgical:
remove scrotum portion, crush spermatic cord with emasculator
Emasculatome:
non-surgical, crushed cord with scrotum.
Benefit of Emasculatome:
The emasculatome crushes the spermatic cord, cutting blood/nerve supply. Testicles atrophy and become non-functional. This humane procedure causes less pain than surgical castration with no open wound or infection risk.
Bull:
Mature male for breeding.
Cow:
Female that has given birth (dairy).
Steer:
Young castrated male
Heifer:
Young female not given birth.
Cattle cycles:
Polyestrus, Puberty, Gestation, Estrus
Polyestrus:
21 day cycles.
Puberty:
before 1 year, but breed at 15 months.
Gestation:
lasts 9 months.
Estrus:
lasts 18 hours, ovulation occurs 12 hours after.
Breeding methods:
Dairy, Beef, Rebreed, Goal
Dairy:
almost exclusively artificial insemination.
Beef:
natural servicing.
Rebreed:
2 months after parturition.
Goal:
One calf per year.
Llamas have a reticulum.
False (They’re the only one that don’t have the reticulum)
Newborn calf requirements:
Shelter from elements
2 quarts colostrum within first 6 hours (provides antibodies and vitamins)
After day 1: dairy cows machine-milked, calves fed by pail or bottle
Milk letdown process:
Stimulated by udder washing or calf nuzzling
Pituitary releases oxytocin → teat muscle contraction → milk expression
Stripping: examine first milk squirts for blood, debris, flakes (signs of mastitis
Mastitis prevention:
Antibacterial teat dip after milking.
Infected cows milked last to prevent bacterial spread.
Mastitic milk discarded from food supply.
Parasite control:
Ectoparasites: flies, lice, mosquitoes, ticks, mites → spray, dust, fog, dip.
Endoparasites: worms, bacteria → oral medications.
Withdrawal interval: 14 days post-medication before slaughter.
Required testing:
Tuberculosis - still present in U.S.
Brucellosis - rare but causes abortion storms, highly contagious.
Mastitis diagnosis:
California Mastitis Test using centrifuge methodology.
Intramammary antibiotic infusion for treatment.
Core vaccines cover:
Bacterial diseases
Respiratory diseases
Bovine viral diarrhea
Brucellosis (females only)
Vaccine schedules vary state by state.
Displaced abomasum:
Common in high-producing dairy cattle.
"Ping" sound on abdomen examination.
Abomasum fills with gas and rises from floor.
Hardware disease (traumatic reticulopericarditis):
Caused by sharp objects piercing stomach wall.
Object migrates through reticulum to heart area
🐮 Cattle Health Issues.
Prevention:
Remove all wires, nails, and metal scraps from cattle feeding areas.
Clinical signs:
Head and neck extension
Weight loss
Pain
Decreased appetite
Arched back
Grunting
Treatment: Antibiotics and magnet to collect metal material.
Hardware disease occurs when?
cattle ingest sharp metal objects that penetrate the reticulum, causing peritonitis and systemic illness.
Photosensitization
"Sunburn" - skin sensitivity to sunlight
Ringworm
Dermatophytosis - fungal skin infection
Papillomatosis
Fibropapillomas - warts caused by viruses
Cellulitis
Subcutaneous abscesses
White Muscle Disease:
Cause: Selenium deficiency
Function: Required for normal growth, fertility, and disease prevention
Appearance: White streaks in striated muscle
Prevention: Injections of Vitamin E and selenium
Milk Fever:
Cause: Calcium deficiency due to insufficient dietary supplementation before calving.
Timing: Generally occurs within 24 hours post-calving, can extend to 2-3 days.
Compounded by: Calcium loss during lactation.
Small ruminants include:
all livestock except cattle, oxen, and buffalo.
Ungulates:
Hooved mammals walking on digit tips (camels, deer, rhinoceros).
Cattle:
Stomach Chambers: 4 (rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum)
True Ruminant? (YES!!)
Llamas:
Stomach Chambers: 3 (rumen, omasum, abomasum).
Common Features:
Split hooves
Dental pad (no upper front teeth)
Horizontal pupils
Flock:
Group of Sheep.
Ram:
Adult Male.
Ewe:
Adult Female.