BIO EXAM 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
coral reefs, Arthropods, Mollusks, Echinoderms CHESNES
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
Location of coral reefs
Indo-pacific region, between equator
2
New cards
Location coral reefs degrees
30N 30S
3
New cards
Constraints to Coral reefs
Warm water from the South
4
New cards
hermatypic corals need
68 degrees
5
New cards
Requirements of Coral reefs
Full salinity, Clear water, photic zone, poor nutrients, low sediments
6
New cards
Types of Reefs
Fringing, Barrier, Atoll, Patch Reef
7
New cards
Fringing Reef
shoreline
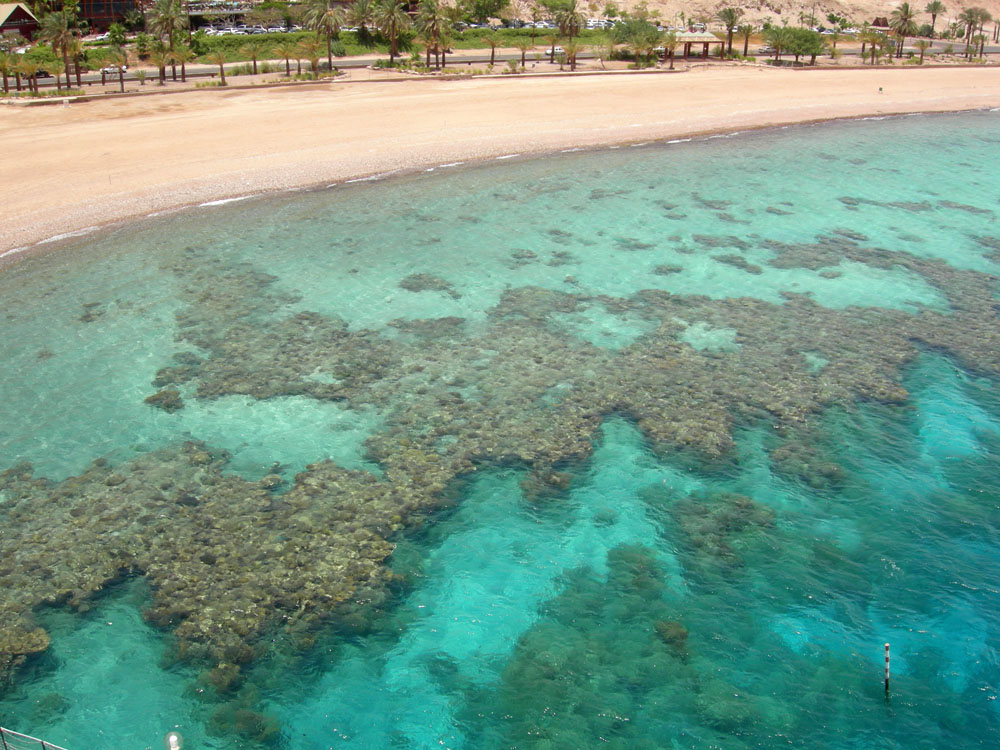

8
New cards
example of fringing reef (P)
Red sea
9
New cards
Barrier Reef (L)
border shoreline
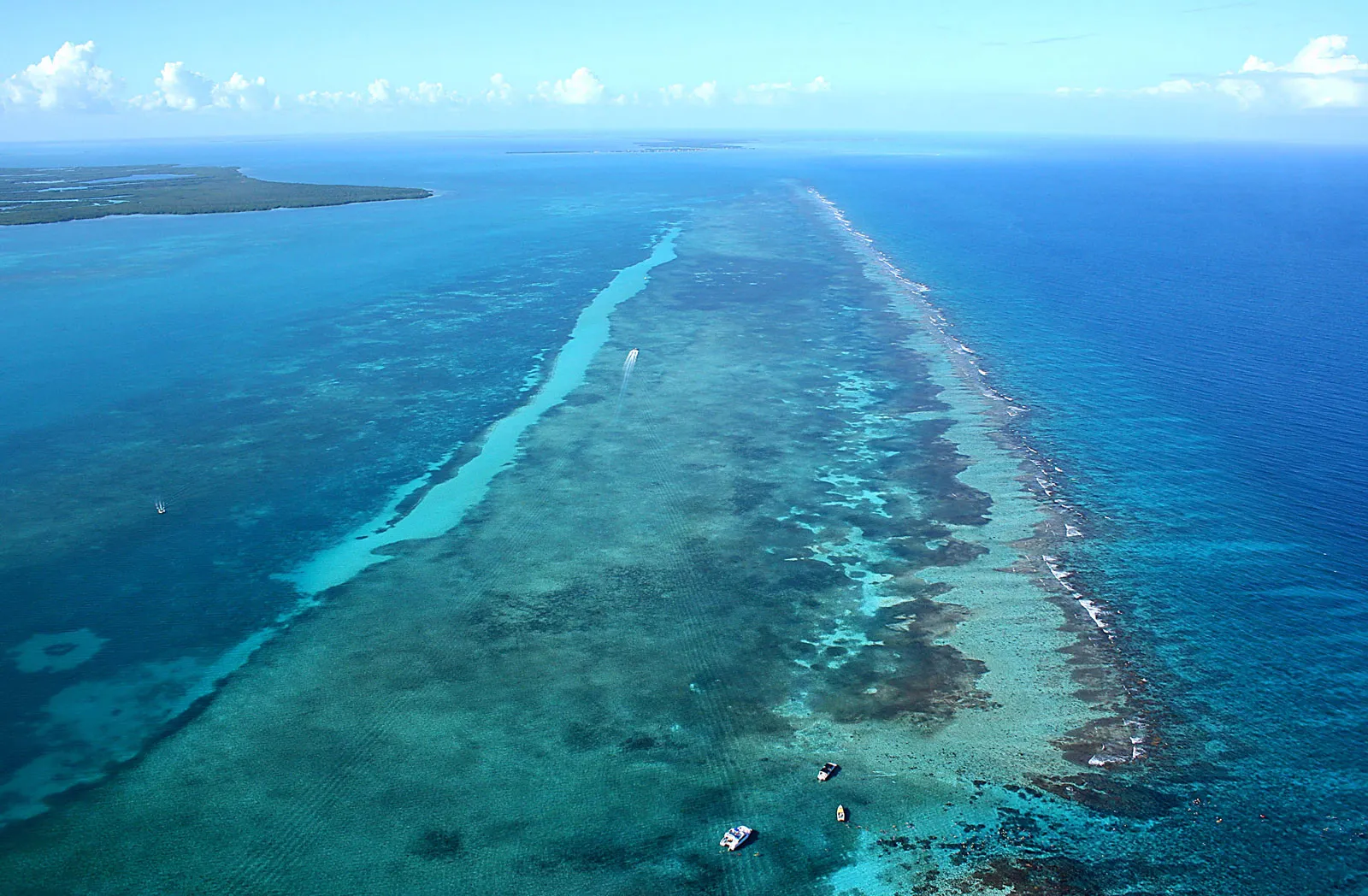

10
New cards
example of barrier Reef
Great Barrier Reef, Meso American Reef
11
New cards
Atoll Reef (pacific)
ring shape
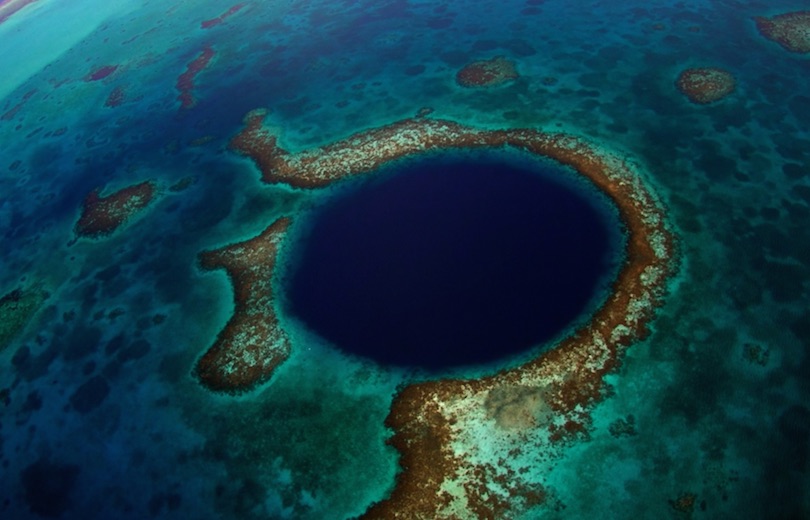

12
New cards
Atoll reef example
Maldives, Atafu
13
New cards
Patch Reef
isolated outcrop

14
New cards
Coral Reef Evolution
A, B, F
15
New cards
coral reefs occur because of
erosion
16
New cards
REEF ZONES
Lagoon zone, Reef flat, Back reef, Reef crest, Buttress zone. Fore Reef zone, Deep fore reef
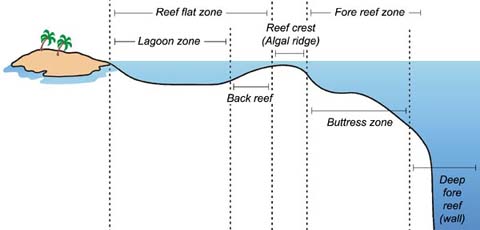
17
New cards
lagoon zone
shallow area, near shore
18
New cards
Reef flat zone
inner reef
19
New cards
Back reef
shallow, exposure to UV radiation
20
New cards
Reef crest
most WAVE energy, find stony organism
21
New cards
Fore reef
reef slope
22
New cards
Buttress zone
deeper area
23
New cards
Deep fore reef
lowest area, slow growing organisms
24
New cards
coral structure
when corals die, they lose polyp and leaves behind a new location for others.
25
New cards
corals build walls of
limestone
26
New cards
Coral reproduction
Asexual and Sexual
27
New cards
Coral Asexual Reproduction
budding and fragmentation
28
New cards
Budding asexual reproduction corals
corals produce buds
29
New cards
Fragmentation asexual reproduction corals
polyp breaks off and forms a new colony of individuals
30
New cards
nematocyst
cell containing venomous threads which are projected for self-defense.
31
New cards
Coral competition
corals compete for space
32
New cards
Christmas tree worms
sedentary, filter feeders
33
New cards
orang-loing sponge
filter feeder
34
New cards
father duster
worm, sedentary, filter feeder
35
New cards
fireworms
errant, stinging cells, predators
36
New cards
Long-spined urchin
algae eaters
37
New cards
calcareous algae
sponge, arrow crab, fix calcium carbonate, builds reefs
38
New cards
parrot fish
feed on microorganisms, pieces of reef
39
New cards
Importance of Coral Reefs
Important fishery and nursery areas, erosion control, tourist attractions
40
New cards
Threats to coral reefs
overfishing, acidification, temperatures, pollution, invasive species,
41
New cards
coral diseases
yellow band diseaseye
42
New cards
yellow band disease cause by
rising temperatures, stress and lack of zooxanthellae
43
New cards
Arthropods meaning,
Jointed-foot
44
New cards
what makes arthropods unique
metamerism, chitinus exoskeleton
45
New cards
metamerism
linear body with segments
46
New cards
chitinus exoskeleton
chitin= complex carbohydrate, molting periods
47
New cards
(arthropods) Subphylum Chelicerata
no antenna
48
New cards
(chelicerata) class merostomata
horseshoe crab
49
New cards
horseshoe crabs uniqueness
no antenna, fully Dioecious
50
New cards
Horseshoe body
carapace, cephalothorax, abdomen, telson
51
New cards
cephalothorax
fused head and thorax
52
New cards
Horseshoe reproduction
Dioecious
53
New cards
Horseshoe blood
copper, has antibacterial ability
54
New cards
(arthropods) Subphylum crustacea
mainly marine based
55
New cards
what makes crustaceans unique
pair of antennas
56
New cards
crustaceans reproduction
Dioecious, meroplankton
57
New cards
meroplankton
only planktonic larvae and turn into either benthic or pelagic organisms
58
New cards
crustaceans shell
period of molting, soft shell period
59
New cards
(Subphylum crustacea) Class copepoda
copepods, holoplanktonic, parasitic, one eye

60
New cards
importance of copepoda (copepods)
bottom of food chains
61
New cards
(Subphylum crustacea) Class cirripedia
barnacles, cirri
62
New cards
Barnacles (cirripedia) has
cirri: extensions outside of shellre
63
New cards
(cirripedia) Barnacles reproduction
dioecious
64
New cards
(cirripedia) Barnacles decide..
where they will live their entire life when in larvae form and then stay there forever.
65
New cards
(Subphylum crustacea) Class malacostraca
shrimps, lobsters, crabs. 3/4 of all crustaceans
66
New cards
(Class malacostraca) Order stomatopoda
thumb splitter shrimp, chromatophores, wh
67
New cards
at makes stomatopoda (class malacostraca) uniqe?
velocity and extending apondages
68
New cards
(Class malacostraca) Order Euphasiacea
southern krill
69
New cards
Euphasiacea (class malacostraca) are found in
giant schools
70
New cards
(Class Malacostraca) Order Decapoda
shrimps, lobsters, crabs, crayfish
71
New cards
difference in decapoda lobster
florida small, normal lobster, large
72
New cards
(Class Malacostraca) Order Mysidacea
small shrimp-like organisms
73
New cards
(class malacostraca) Order isopods
isopods
74
New cards
uniqueness in isopods (Class malacostraca) is...
they are dorsoventrally compressed
75
New cards
(Class malacostraca) Order Amphipoda
Amphipods, laterally compressed
76
New cards
Molllusks (mollusca)
bilateral symmetry, gills, cilia ci
77
New cards
cilia
hair like projections that move water through gills
78
New cards
feeding types
filter feeders (usage of cilia) and grazers with radula (tongue)
79
New cards
mollusks predators
conesnail
80
New cards
conesnail
has extending venomous barbs
81
New cards
(Mollusca) Class Gastropoda
snails, sea slugs
82
New cards
Class Gastropoda uniqueness (Mollusca)
torsion
83
New cards
(Gastropodas) subclass prosobrancha
Common marine snails
84
New cards
(Gastropodas) subclass opistrobrancha
No shell snail
85
New cards
(Gastropoda) pulmonata
Land snail
86
New cards
(Mollusks) Class mono(2)placophora
one shell
87
New cards
example of monoplacophora
Neopilina (living fossil)
88
New cards
(Mollusks) Class Polyp(many)placophora
chitons, eight plate shells
89
New cards
(Mollusks) Class A(no)placophora
no shell, spicules covered body(
90
New cards
(Mollusks) Class bi(2)valvia
two shells, clams
91
New cards
(mollusks) Class scaphopoda
tusk shells, benthos
92
New cards
(Mollusks) Class Cepha(head)lopod(foot)a
nautili, cuttlefish, squids, OCTOPODS
93
New cards
primitive forms
lots of arms, lack suckers
pri
pri
94
New cards
primitive forms examples
nautil, cuttlefish
95
New cards
Advanced forms
lack arms, ink sacks, advanced eye
96
New cards
Advanced form examples
squids, octopus
97
New cards
cephalopods all have
venomous bite
98
New cards
Echinoderms
spiny skin, salt water
99
New cards
pentaradial symmetry
5 points
100
New cards
adult starfish is in the stage of
pentaradial symmetry