Supply Schedules & Supply curves
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is a supply schedule
table that shows relationship between price and quantity of a product (table format)
What is a supply curve
relationship between price of product and quantity of the product supplied (graph)
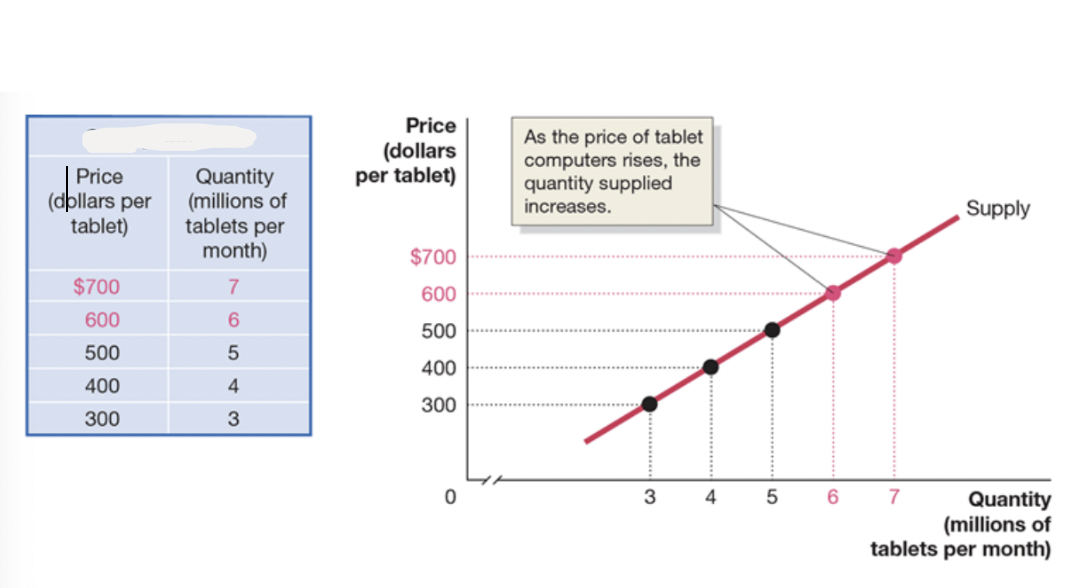
Which is the supply schedule and which is supply curve?
The table is the supply schedule, and the graph shows the supply curve
What is the law of supply?
holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied
How it works: plan output, given the price, to enable them to make as much profit as possible + firms will sell out more + more resources of production is needed which increases marginal cost
What are variables that shift market supply?
Prices of inputs
Technological change
Prices of substitutes in production
Number of firms in the market
Expected future prices
What are prices of inputs
an input is anything used in the production of a good or service - e.g. price of a component of tablet computers, such as flash memory rises, the cost of producing computers will increase + tablets will be less profitable at every price
influences supply
Technological change
ability of a firm to produce an output with a given quantity of inputs (able to produce more output using same amount of inputs)
more profitable for firm
Prices of substitutes in production
Prices of substitutes in production refer to the costs associated with producing alternative goods that can replace another product using the same resources.
Example: if price of smartphones increases relative to tablet price, smartphones will be more profitable, and Apple, Samsung and other firms making smartphones will shift their productive capacity from tablets to smartphones
Number of firms in the market
change in the number of firms in the market will change supply
Example: when new market firms enter a market, the supply curve shifts right, and when existing firms leave, the supply curve shifts left
Expected future prices
if a firm expects product price will be higher in the future than it is today, it has incentive to decrease supply now and increase it in future , supply curve will shift to left
-e.g. price of laptops are low - due to economic downturn - the company can store some production to sell later on when prices are expected to be higher
What is change in supply?
shift of supply curve - change in one of the variables other than product price
What is change in quantity?
movement along the supply curve?
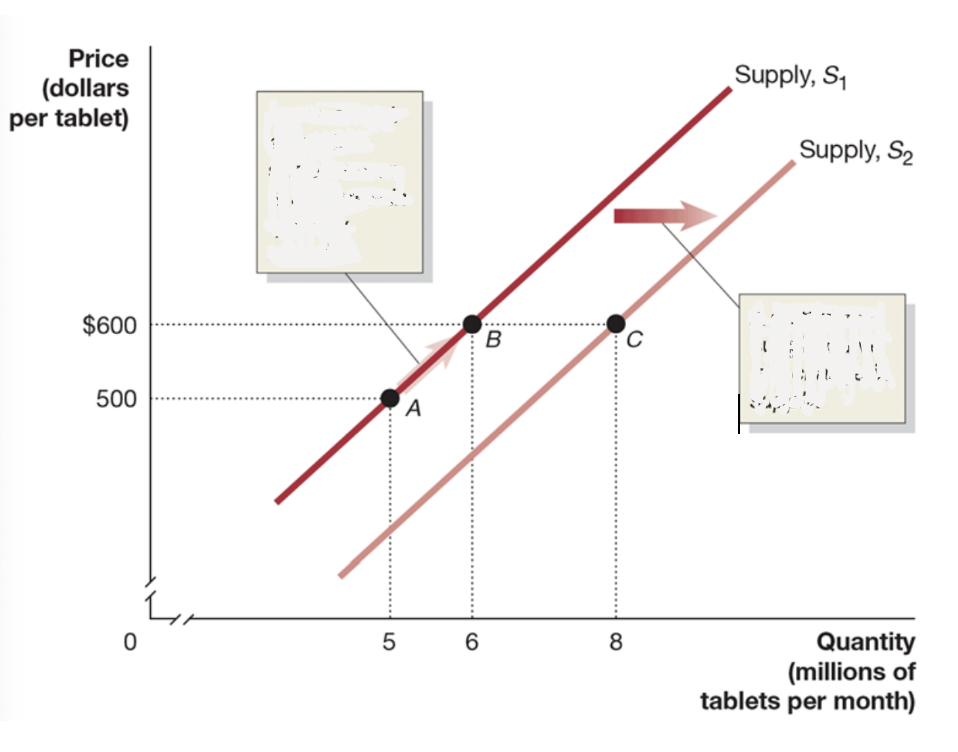
Which is change in supply and change in quantity
points are change in quantity supplied
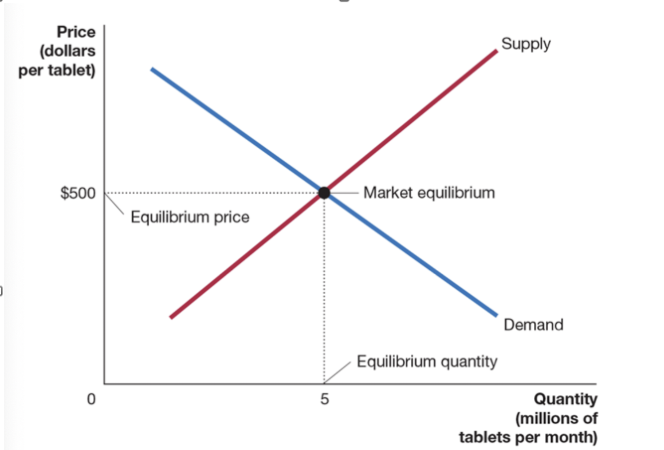
What is Market Equilibrium?
Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity of a product that consumers want to buy is equal to the quantity that producers want to sell. At this point, the market price is stable, and there is no surplus or shortage of the product.
What is a market surplus?
A market surplus occurs when the quantity supplied of a product exceeds the quantity demanded at a given price. This situation often leads to downward pressure on prices as sellers try to sell their excess inventory.
What is market shortage
A market shortage occurs when the quantity demanded of a product exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price. This situation often leads to upward pressure on prices, as consumers compete to buy the limited supply available.