Aerobic Resp. , Krebs & Coenzymes
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Where does Krebs take place?
Mitochondrial matrix
How many times does the Krebs Cycle occur?
2
Happens once for every pyruvate molecules, so twice per molecule of glucose
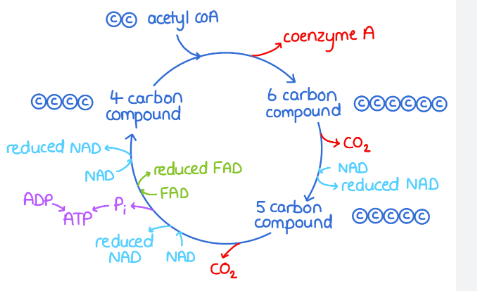
Krebs Cycle process
Acetyl group (2C) combines w. oxaloacetate (4C) to form citrate (6C)
Citrate undergoes decarboxylation & dehydrogenation, producing a red. NAD and CO2
Citrate (5C) undergoes further decarboxylation & dehydrogenation, (4C) producing 2 red. NAD and 1 red. FAD
Substrate level phosphorylation occurs - ADP + Pi = ATP
Inorganic phosphate from matrix
Oxaloacetate is regenerated (from step 3.)
Net products from Krebs Cycle
6x reduced NAD
2x red. FAD
2x ATP
4x CO2
NOTE: Is produced per glucose molecule (each glucose molecule splits to form 2 pyruvates)
Link reaction image
Why are coenzymes needed in respiration?
Required to transfer protons, electrons, & functional groups between the many enzyme-catalysed reactions
Without the coenzymes, electrons & protons can’t be transferred for the redox reactions
NAD
Takes part in all stages of cellular resp.
Accepts 1 H+ to become red. NAD
Red. NAD oxidised at start of ETC, releasing protons & electrons
Red. NAD results in synthesis of 3 ATP molecules (actually varies)
FAD
Only accepts H+ in Krebs Cycle, used in oxidative phosphorylation
FAD accepts 2 H+
red. FAD is reduced further along ETC
red. FAD results in synthesis of 2 ATP molecules (actually varies)