capacitance
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is a capacitor?
device that stores charge, and therefore energy, on its two plates when a potential difference is applied across it
what is proportional in a capacitor?
charge and p.d
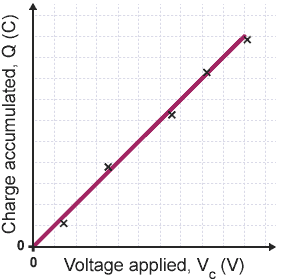
capacitance graph
gradient = charge stores per unit p.d (coulombs per volt)
area under graph = energy, ½ V C
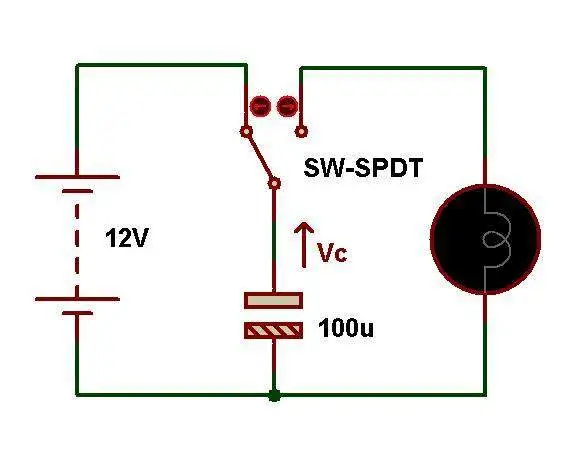
what does the switch in a capicitance device do?
allow you to change from charging to discharging a capacitor
charge of a capacitor
Q = V C
energy of a capacitor
½ Q V
½ C V2
½ x Q2 / C
why is a variable resistor used in a capacitor?
to allow us to keep the charging current constant, which we can use in Q = I t
what is the capacitor potential difference when fully charged?
same as the battery / power supply
what is the capacitor potential difference before its fully charged?
the pd will be taken up by the resistor in the circuit
how do you usually discharge a capacitor?
using a resistor
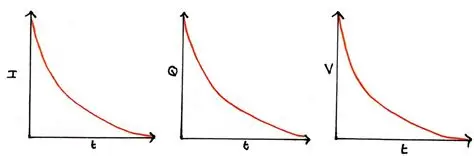
how does a capacitor discharge?
V , Q and I all discharge exponentially, like in decay
what is the equation for capacitor discharge?
Q / Q0 = I / I0 = V / V0 = e-t/RC
ratio of current value compared to the initial, ratio between 0 and 1
V0 = maximum pd when fully charged
R = resistance of resistor
C = capacitance
how much of the initial [Q , I , V] do we have left? its a ratio
how does a capacitor charge?
graph is inverted for V and Q, but not for I (current still decays when charge increases)
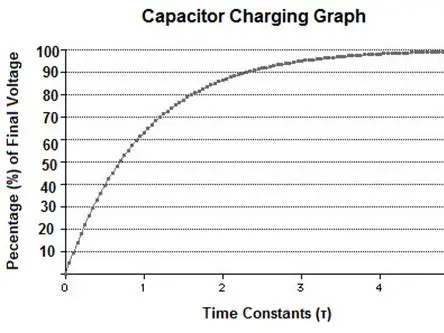
what is the equation for capacitor charge?
V / V0 = 1 - e-t / RC
how do you rearrange a charging / discharging equation for t , R , or C?
taking logs, then making a graph of -log (V / V0) or ln (V0 with ln V0 as the y-int, in which the gradient magnitude = 1 / RC
what is the time constant used for?
to compare capacitors , the time taken such that the fraction of PD left is e-1 which is 0.37, 37% , which is only true when tc = RC, so RC = time constant
how do you find the time constant?
on a decay graph, find 37% of the initial value, and the time it takes to do that is the time constant which = R C
what is the structure of a capacitor?
two plates that become oppositely charged when a pd is applied. no charge should flow directly between the plates. they are separated by an insulating layer called a dielectric and usually these foils are wound into cylinders
what is capacitance proportional to?
the area of the those plates, C ∝ A ε / d
A = plate area (m2)
d = separation of plates (m)
ε = permittivity (Fm-1) , ε0 (permittivity of free space) when the area between is a vacuum or a vacuum, if there’s anything else between then its ε0 x εr (relative permittivity of the material, no unit, > 1)
what is permittivity, ε ?
a measure of how easy it is for an electric field to be produced in the space between the two plates
what is capacitance inversely proportional to?
the separation between the plates (m)
how can we increase the capacitance?
inserting a dielectric (an insulating material that contains polar molecules) between the plates, which increases the permittivity which increases the capacitance
why does a dielectric increase capacitance?
the polar molecules in the dielectric line up along the electric field lines, creating an opposing electric field, which reduces the pd across the plates, meaning the same amount of charge is stored at a lower potential difference (can be represented by a positive and negative delta opposite to the plate its near)
its like the polar molecules create their own electric field which reduces the net electric field and therefore reduces the pd needed to store the same amount of charge
how will changing plate area, ε, or distance between plates affect capacitance when capacitance is decreasing?
if still connected to battery, V constant, Q decreases, E decreases where E = ½ C V2
if not connected to battery, Q constant, V increases, E increases where E = ½ Q2 / C
what happens when a dielectric is removed?
εr decreases, therefore C decreases
what happens when removing a dielectric?
work is done to remove it as its charged edges are attracted to the plates. the work is added to the energy stored if the capacitor is disconnected from the battery
εr and therefore C decreases