Energy Transfer & Conservation
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yr 9 - Term 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Energy efficiency
A measure of how much of the input energy is useful energy.

Energy Transfer
The movement of energy from one object or place to another.

Energy Transformation
The conservation of energy from one form to another.

Gravitational Potential Energy
Energy stored when an object is raised above the ground.
Hydropower
Electricity generated from flowing water.

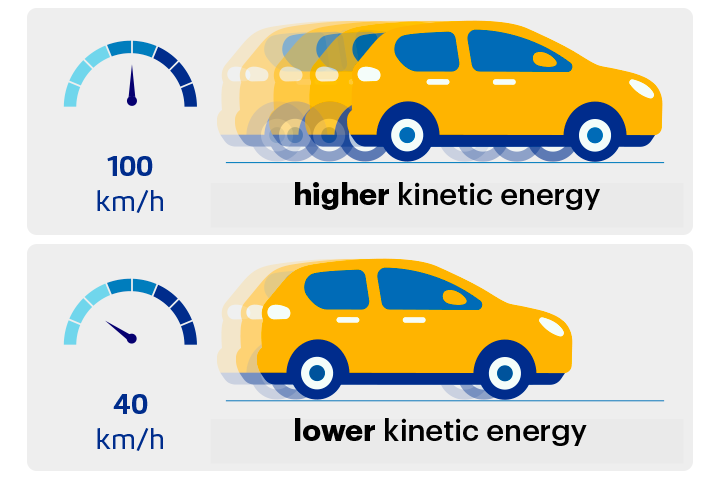
Kinetic Energy
The energy of movement.

Law of conservation of energy
The statement that asserts that energy can not be created or destroyed.
Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
Potential Energy
Energy that is stored.

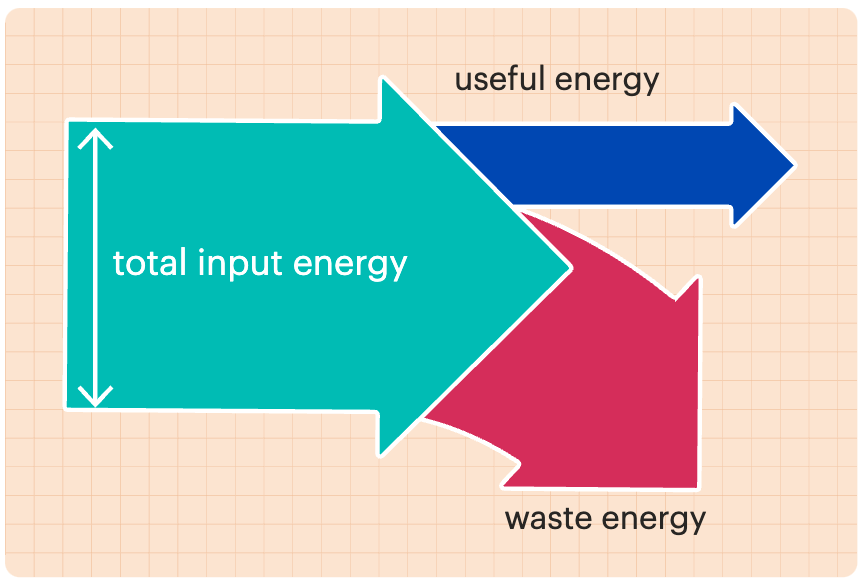
Sankey diagram
A model that uses arrows of varying thickness to show changes in a system.
Speed
The rate of change in an object’s position.
Useful energy
The output energy that is put to the intended use.
Waste Energy
Output energy that is not put to the intended use.
Absorption
The transfer of light energy into an object.
Colour
A property of visible light that depends on its frequency.
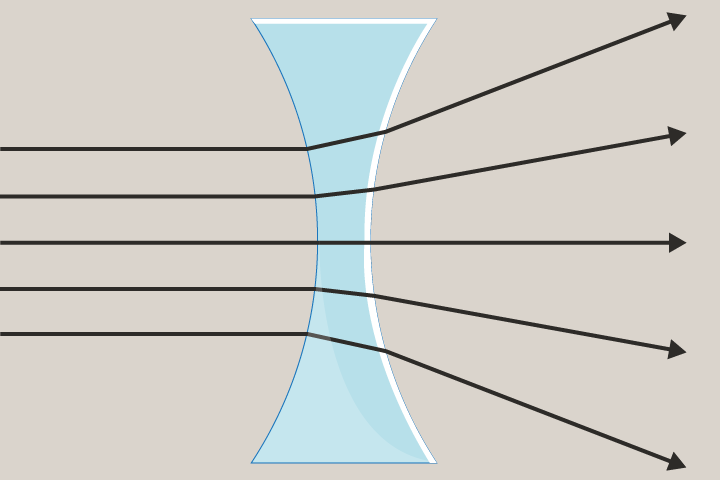
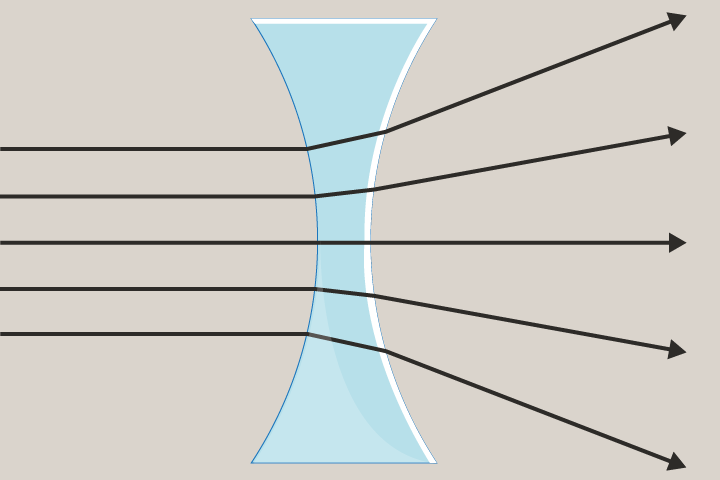
Concave Lens
A lens that is curved inwards and is thinner in the middle. Concave lenses cause light light rays to diverge and produce smaller images.
Converge
To get closer together.
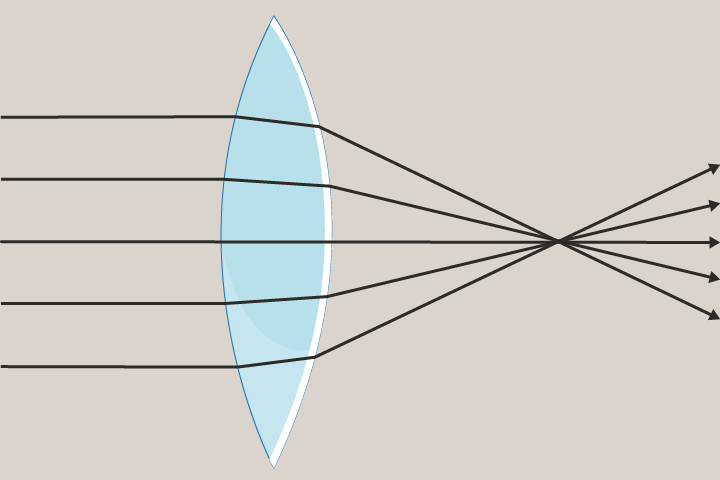
Convex lens
A lens that is curved and is thicker in the middle. Convex lenses cause light rays to converge and can produce either bigger or smaller images.
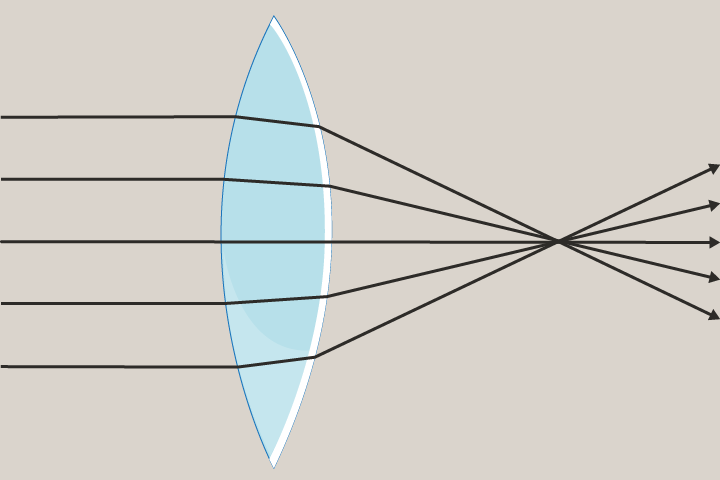
Diverge
To get further apart.
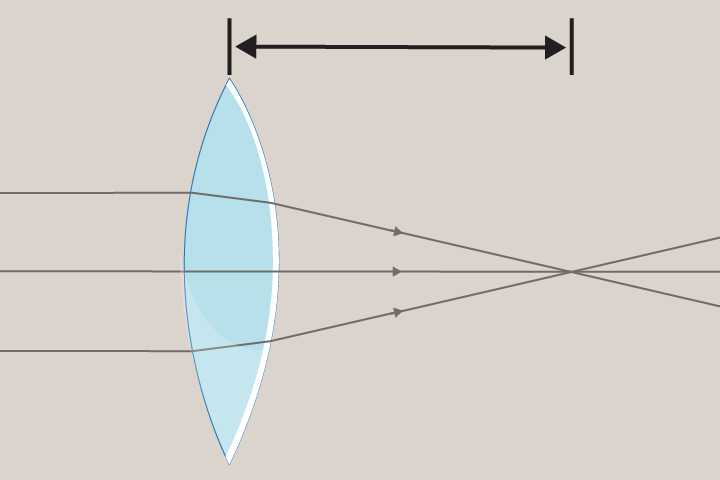
Focal Length
The distance between the centre of lens and its focal point. The focal length depends on how strongly the lens refract light.
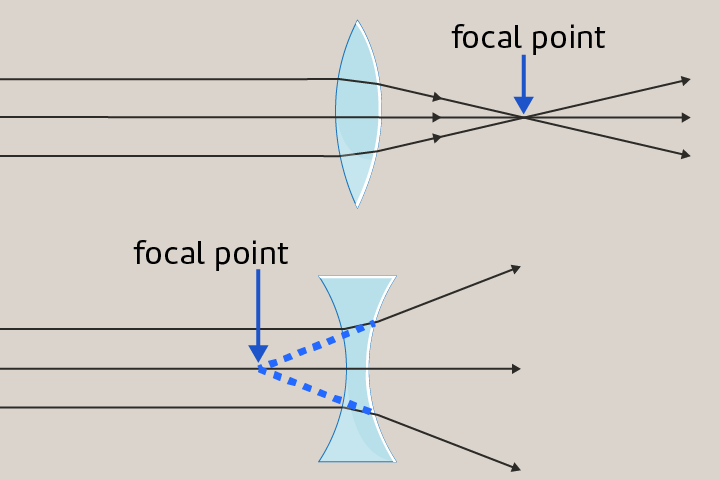
Focal Point
A place where light rays either converge to or diverge from. The focal point is located behind a concave lens and in front of a convex lens.
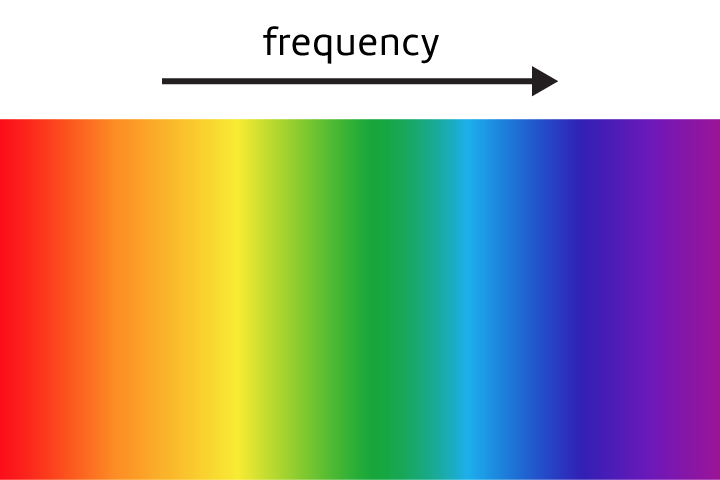
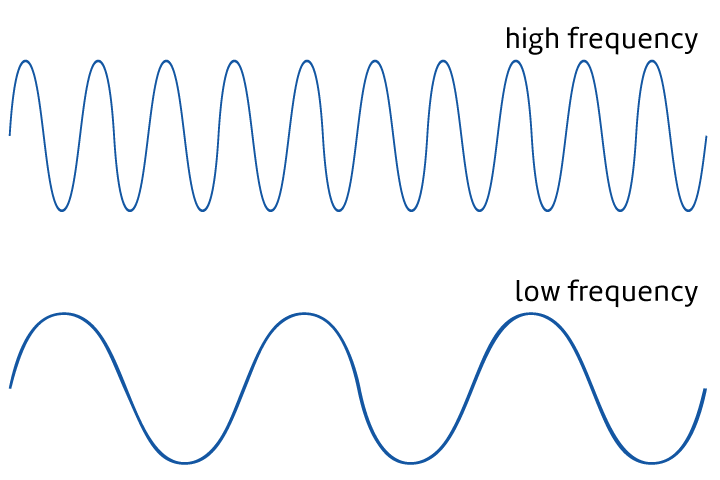
Frequency
The number of waves that go by in one second.
Lens
A curved piece of transparent glass or plastic that refracts light.

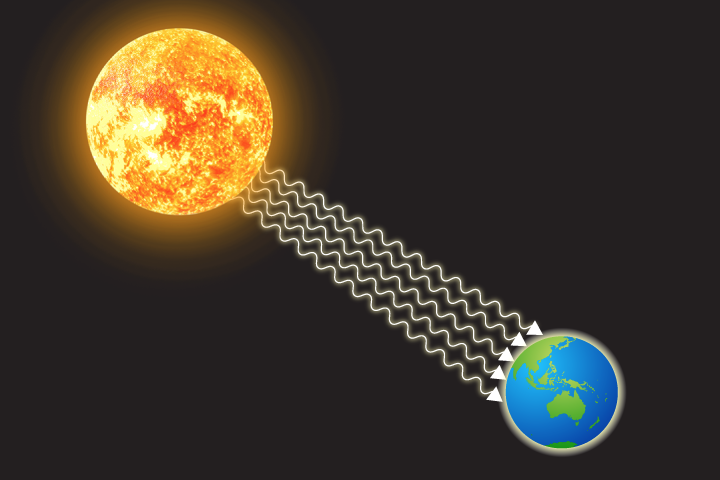
Light
A type of energy that travels in electromagnetic waves.

Magnification
A measure of a lens ability to increase the size of an image.

Opaque
Not allowing light to pass through.

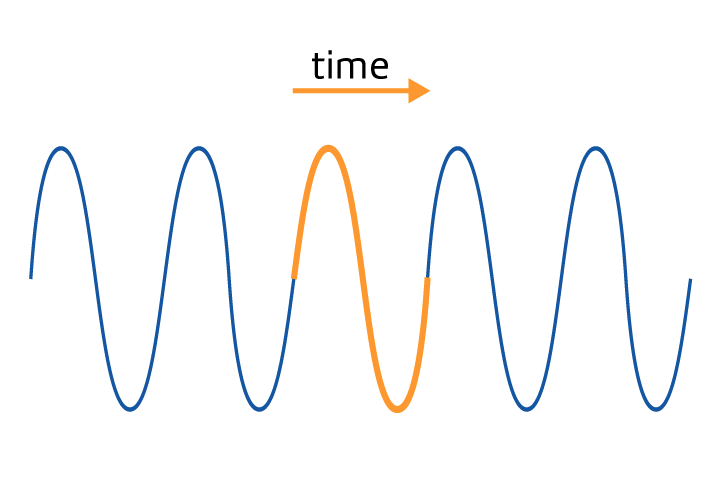
Period
The time it takes a wave to go through its full motion.
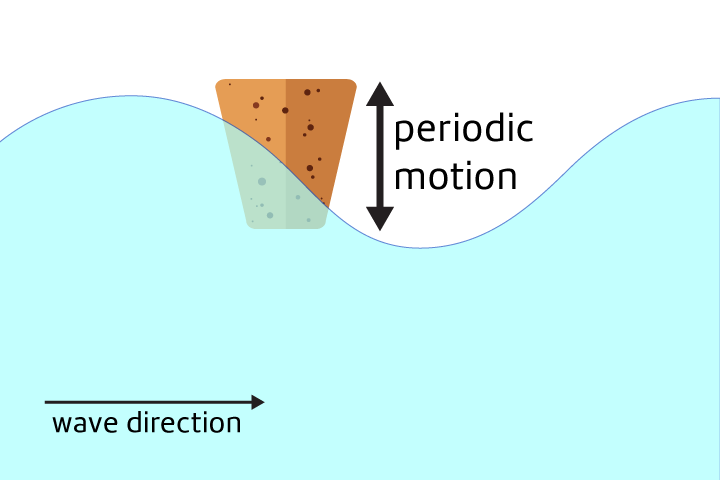
Periodic Motion
Movement that is repeated at regular intervals.
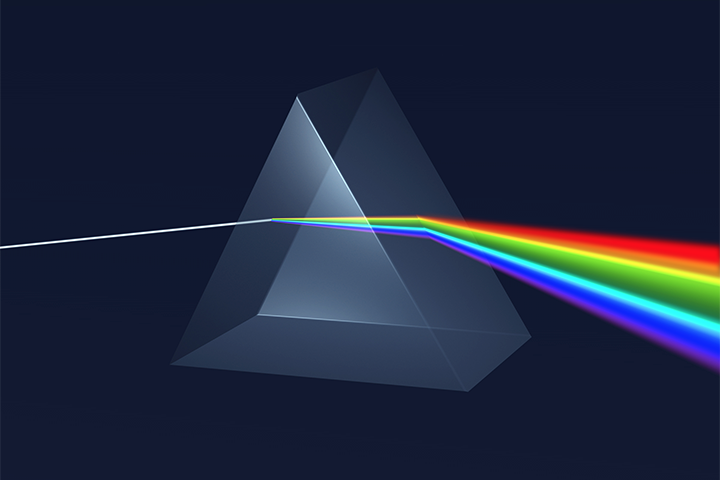
Prism
A transparent object with flat surfaces, which refract light.

Reflection
The bending of light as it bounces off a surface.
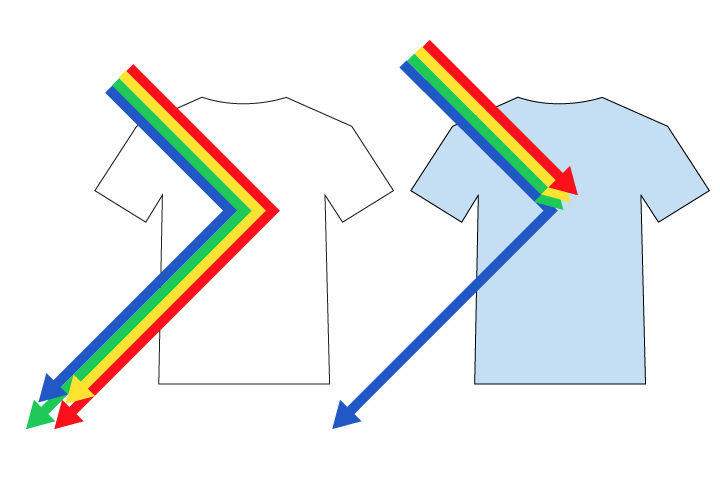
Refraction
The bending of light as it passes into a new material.
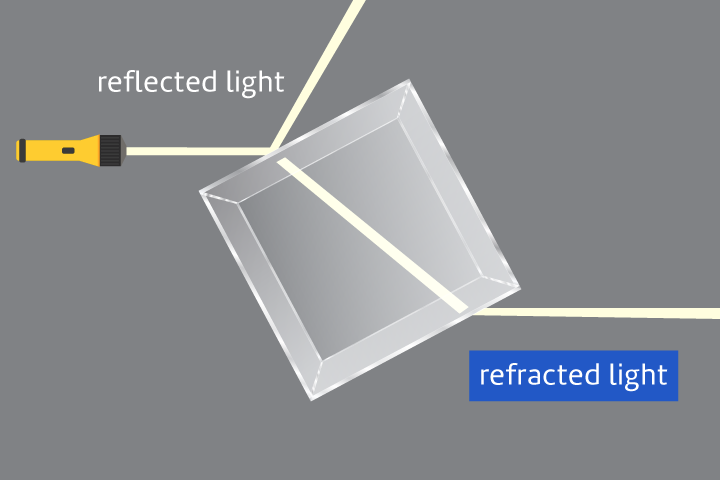
Translucent
Allowing only some light to pass through.
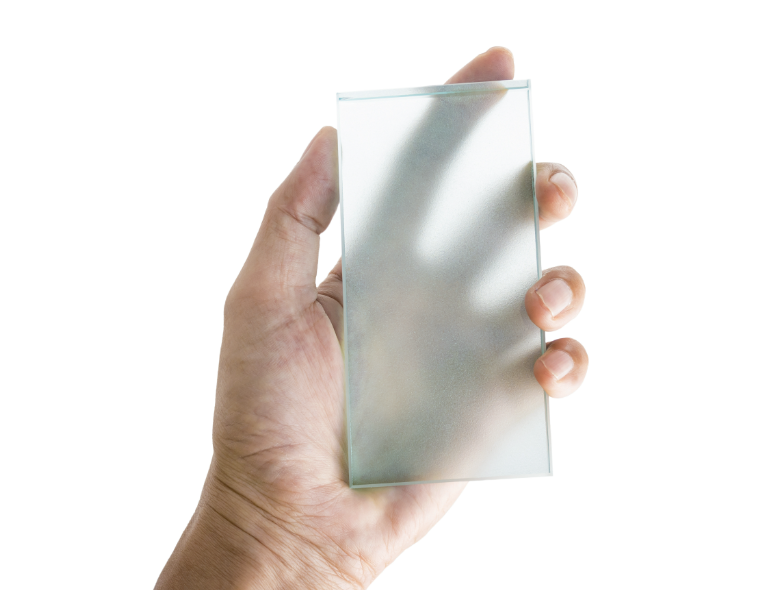

Transmission
The passing of light through a material.
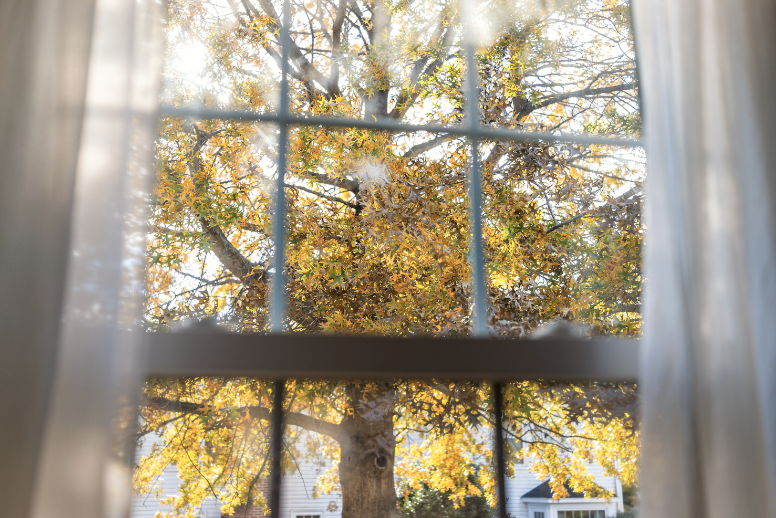


Transparent
Allowing nearly all light to pass through.

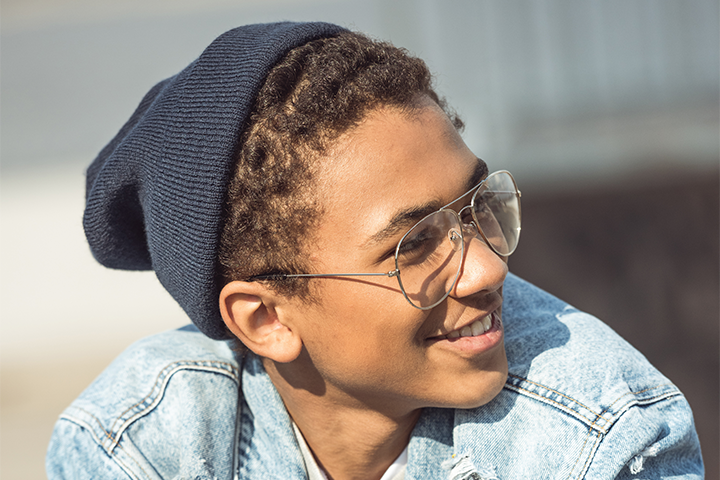
Visible Spectrum
The spectrum of light frequencies we can see.

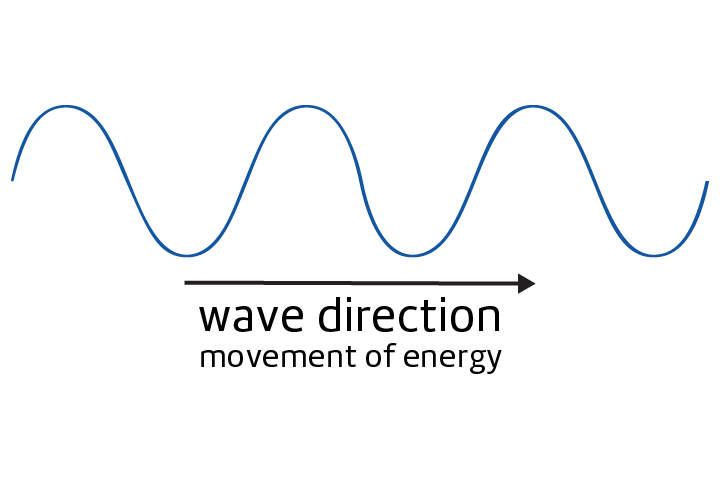
Wave
A repeated motion that transfers energy.
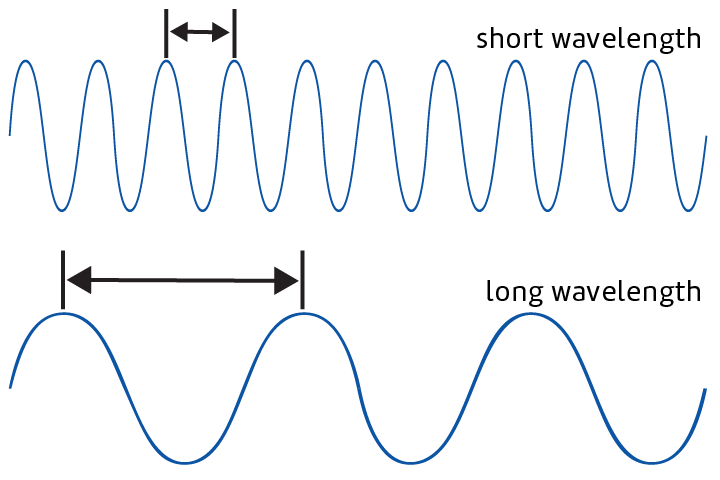
Wavelength
The distance between one crest of a wave to the next.
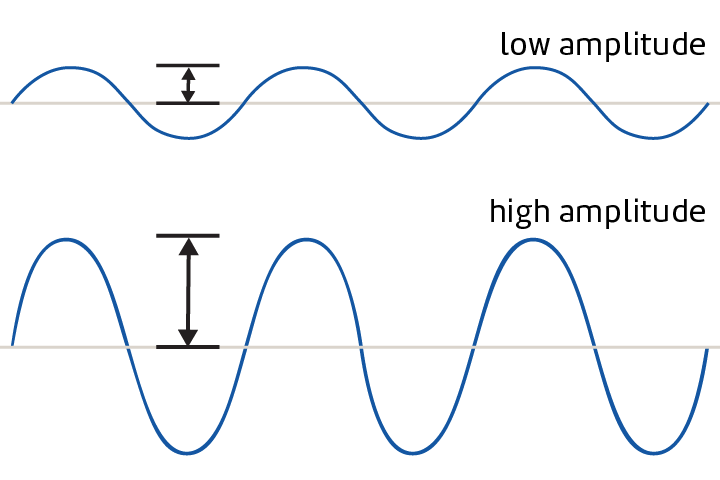
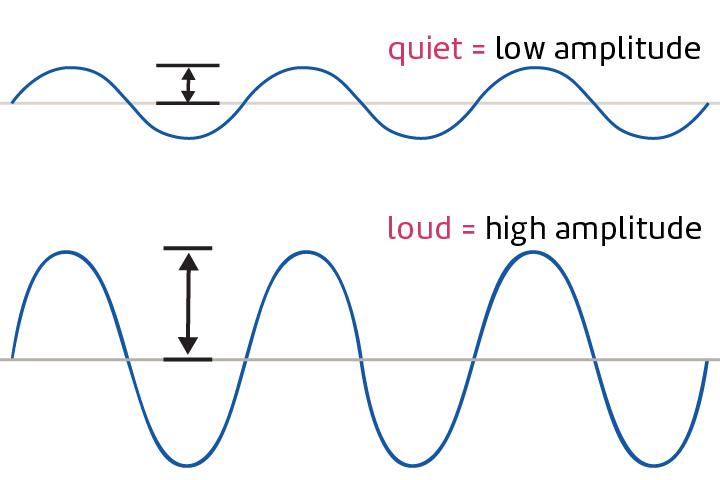
Amplitude
The distance between the midline of a wave and the top or bottom.
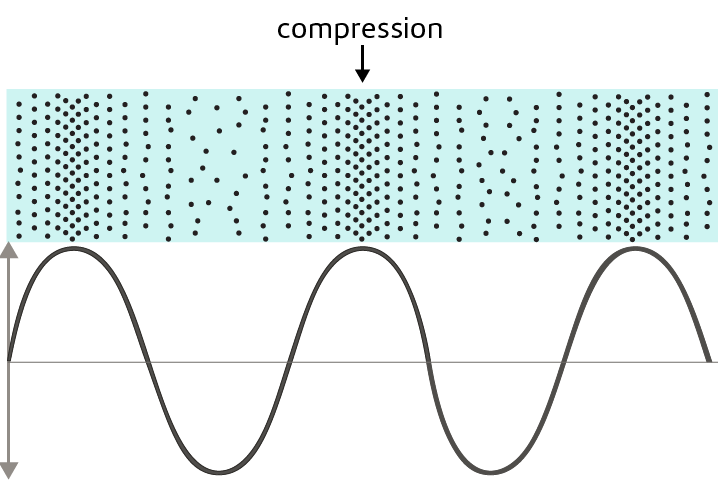
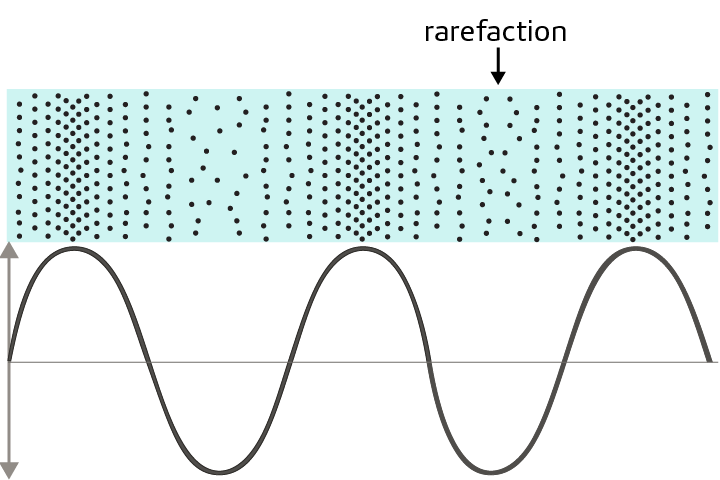
Compression
Part of a sound wave where particles are closer together.
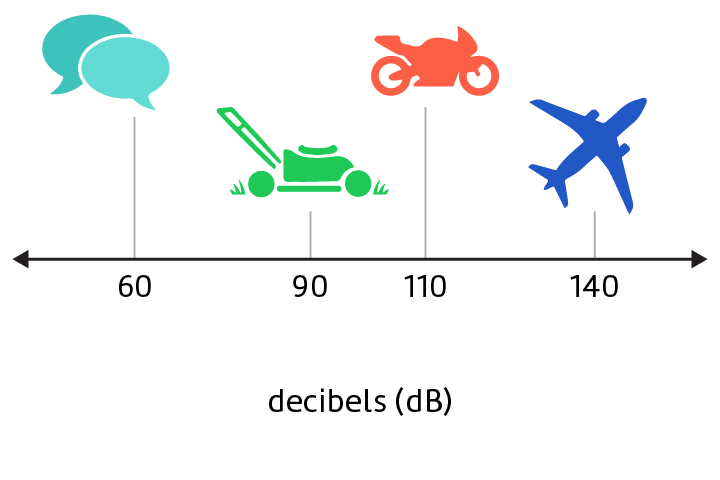
Decibel
A unit used to measure loudness.
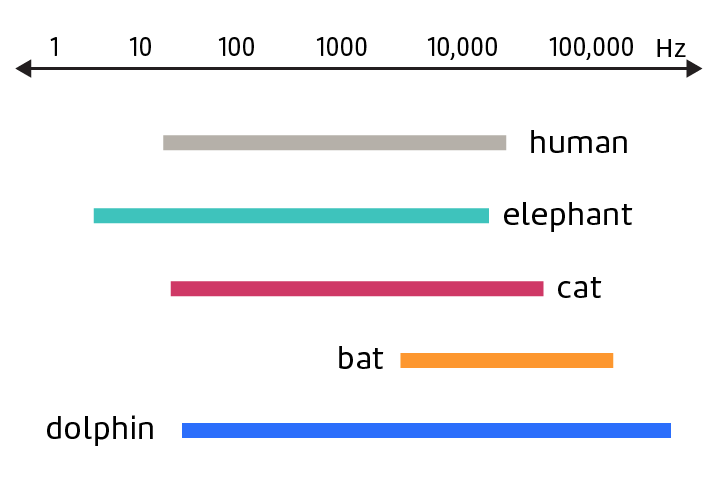
Hearing Range
The range of frequencies that can be heard by a human or animals.
Hertz
The standard unit of frequency.

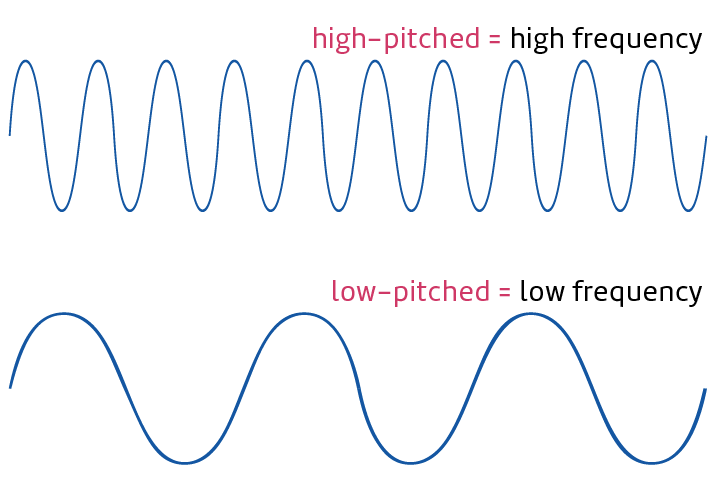
High Pitched
The quality of sounds produced by waves with high frequency.

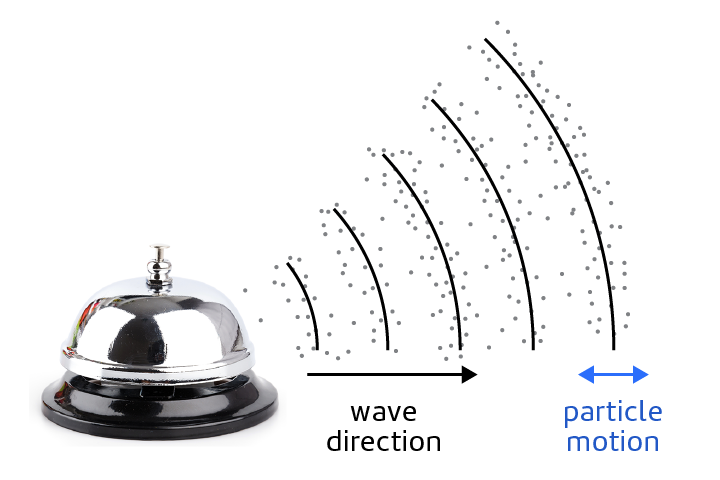
longitudinal wave
A wave in which particles move back and forth in the wave direction.
loudness
A quality of sound that depends on the amplitude of the sound wave.
low-pitched
The quality of sounds produced by waves with low frequency.

Medium
A substance that a wave can travel through.

Pitch
The quality of sound depending on the frequency of the sound of the wave.
Rarefaction
Part of a sound wave where particles are further apart.
sound
A type of energy transmitted by vibrating particles.

Sound wave
A vibration of particles that transfer energy.
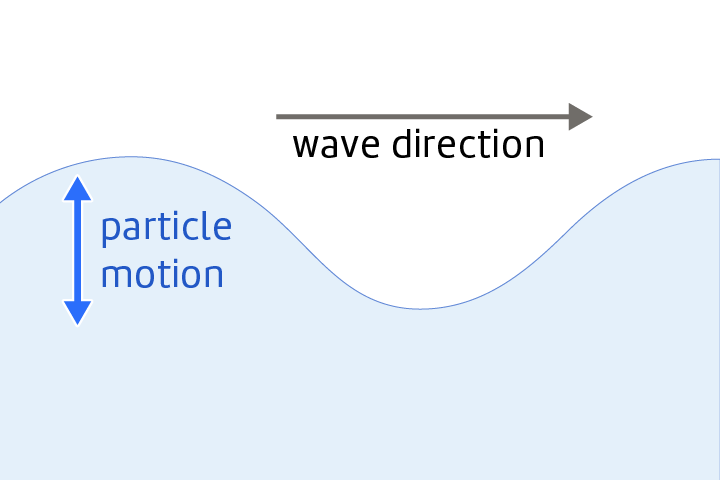
Transverse Wave
A wave in which particles move at right angles to the wave direction.
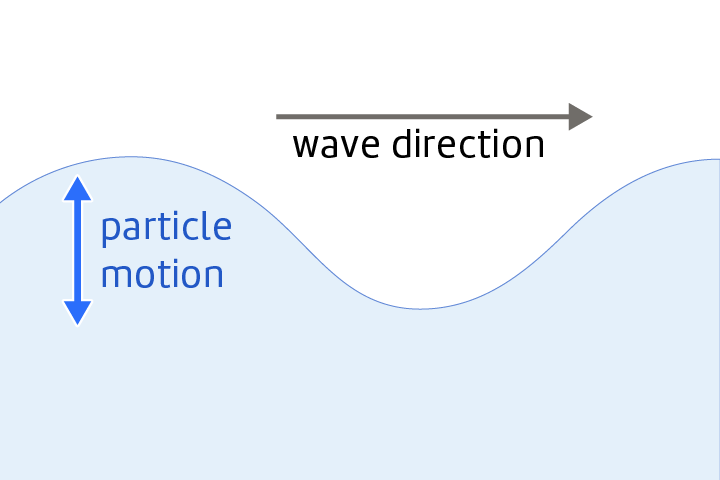
Wave
A repeated motion that transfers energy.