Immunity to Viruses, Parasites, Fungi, and Prions: Disease Mechanisms and Evasion Strategies
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are the main types of immunity to infection discussed in Chapter 13?
Immunity to viruses, protozoa, helminths and parasites, fungi, and prions.
What is the structure of a virus?
Viruses consist of a nucleic acid genome packaged in a protein coat called a capsid, which may or may not be covered by an envelope.
How do viruses typically enter a host cell?
Viruses enter a host by binding to a host surface receptor.
What is the role of host cells in viral replication?
Viruses depend on host cells for protein translation and virus assembly, as they lack their own protein synthesis machinery.
What are progeny virions?
Progeny virions are new virus particles produced from an infected host cell that can attack nearby host cells.
How do viruses cause disease?
Viruses can cause disease directly by killing host cells or indirectly by inducing immune responses that damage host tissues.
What distinguishes acute viral diseases from chronic viral diseases?
Acute viral diseases are of short-term duration, while chronic viral diseases may persist and cause long-term or recurrent illnesses.
What is an example of a virus that can become latent and reactivate later?
The Varicella zoster virus (VZV), which causes chickenpox in children and shingles in adults upon reactivation.
What is antigenic drift?
Antigenic drift is the rapid and minor modification of viral antigens through random mutations, allowing viruses to evade the immune system.
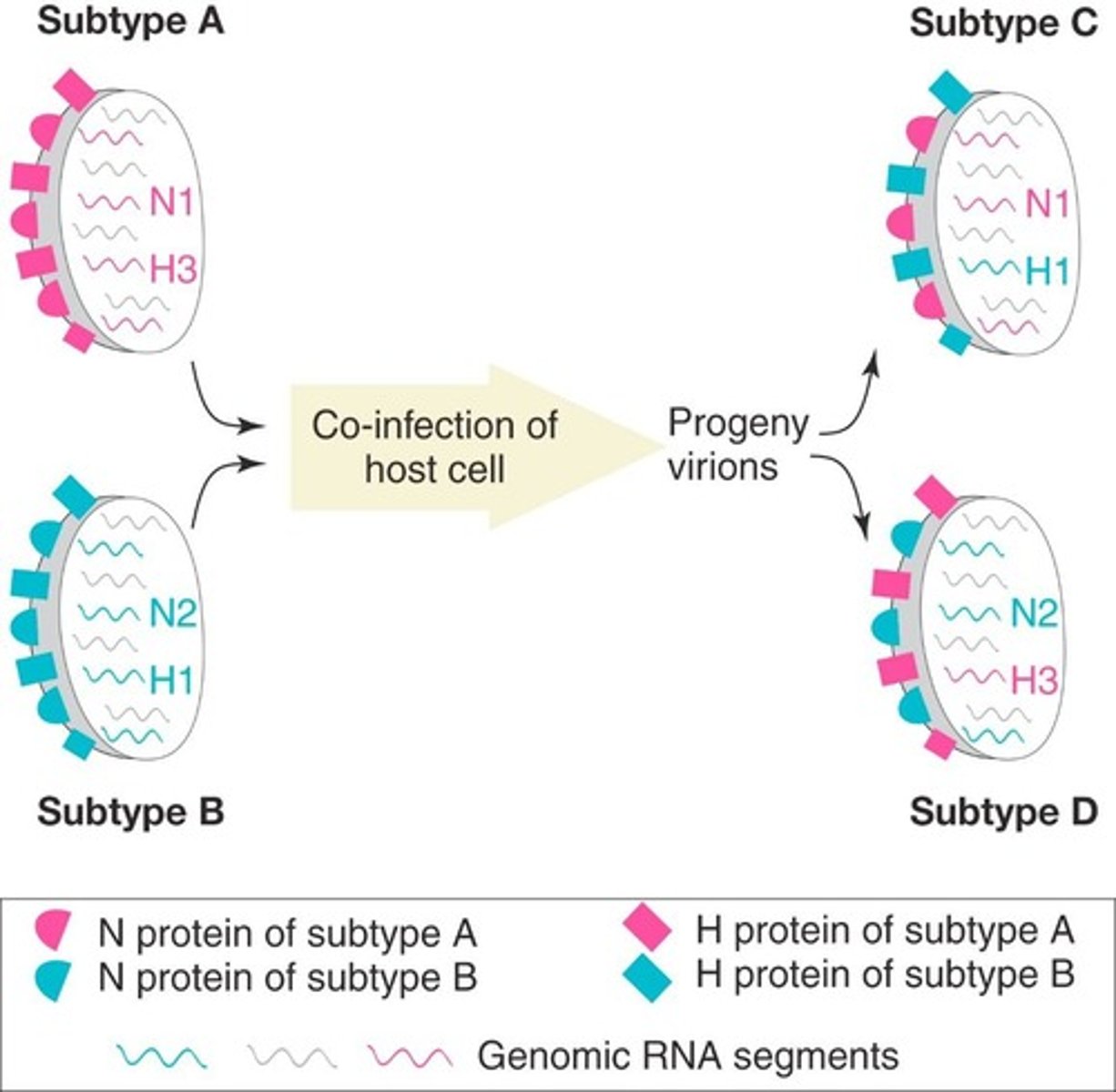
What is antigenic shift?
Antigenic shift is a major change in viral antigens that can occur when two different viruses infect the same cell and exchange genetic material.
What types of organisms do parasites include?
Parasites include unicellular protozoa and multicellular worms.
How do protozoan parasites replicate?
Some protozoans replicate extracellularly, while others replicate intracellularly.
What is a common vector for malaria transmission?
The Anopheles mosquito, which transmits the protozoan parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
What type of immune response do protozoan parasites typically induce?
Protozoan parasites typically induce Th1 immune responses.

What immune response is associated with helminth worm infections?
Helminth worm infections are usually handled by Th2 immune responses.

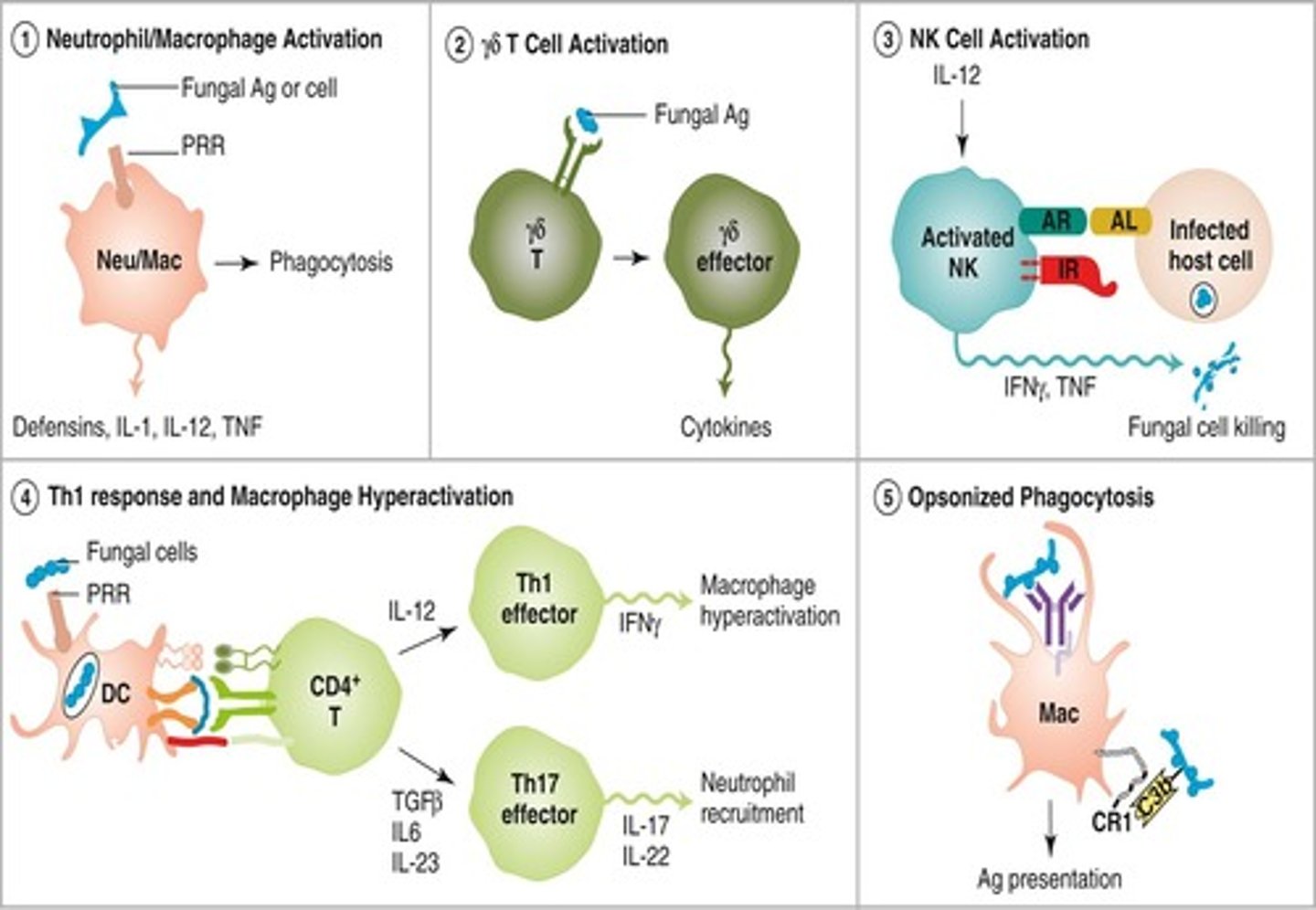
What role do PAMPs play in the immune response to protozoans?
Many protozoan components act as PAMPs that activate immune responses through TLRs.
How do antibodies contribute to the defense against extracellular protozoans?
Antibodies mediate neutralization, opsonized phagocytosis, and classical complement activation against extracellular protozoans.
What is the significance of IFN-g in anti-protozoan defense?
IFN-g is critical for macrophage hyperactivation, which is essential for effective anti-protozoan defense.
What role do hyperactivated macrophages play in combating protozoan parasites?
They produce sufficient levels of reactive oxygen intermediates (ROIs) and reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNIs) to kill the parasites.
What is the significance of TNF secreted by hyperactivated macrophages?
TNF plays an important role in controlling protozoan infections.
What happens if hyperactivated macrophages cannot clear a protozoan parasite?
A granuloma is formed that encompasses the infected host cells and walls off the invader.
What are the anti-protozoan effects of IFN-g?
IFN-g is directly cytotoxic to many parasites, stimulates IL-12 production, induces iNOS expression for NO production, upregulates phagosome maturation, and increases Fas expression on infected macrophages.
How do Th2 cytokines affect susceptibility to protozoan diseases?
Th2 cytokines inhibit IFN-g production and suppress iNOS, making individuals more susceptible to protozoan infections.
What is the role of CTLs in response to protozoan infections?
If a protozoan escapes into the cytosol, CTLs can target the infected host cells presenting antigen via MHC class I.
How does perforin/granzyme-mediated cytolysis relate to protozoan infections?
It is not very effective against acute protozoan infections but becomes important for controlling chronic stages.
What is the importance of TLR4 in the defense against helminth worms?
TLR4 is important for fighting the blood-dwelling trematode Schistosoma mansonii.
What type of immune response is vital for eliminating helminth worms?
Th2 responses are crucial for the elimination of helminth worms.
What are some evasion strategies used by parasites against the immune system?
Avoiding antibodies, avoiding phagolysosomal destruction, avoiding complement, and interfering with host T cell responses.
What are the characteristics of fungi that affect immune response?
Fungi can be unicellular or multicellular, and some are dimorphic, changing forms during their life cycle.
Why are fungi a significant clinical threat to immunocompromised individuals?
They can cause significant harm when invasive, especially species like Aspergillus, Candida, and Cryptococcus.
What are prions and what diseases do they cause?
Prions are transmissible proteins that cause spongiform encephalopathies, such as variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Kuru.
How do prions affect normal prion proteins?
PrPres acts as a template, causing normal PrPc proteins to misfold into additional PrPres.
What is the immune response to prion infection?
Prion infection destroys the brain without inducing a humoral or cell-mediated adaptive response, and T cells are usually tolerant to PrPres.
What is the role of innate defense against prions?
Recent evidence suggests that there is an innate defense against prions that may help slow the progression of spongiform encephalopathies.