3.8 Plant Reproduction
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Reproduction in Angiosperms
gametophytes are in flowers
female gametophyte is enclosed structure - ovule
double fertilization produces embryo & endosperm
ovary tissues form fruit
animal pollination is common
Reproduction in Gymnosperms
gametophytes on separate cones
female gametophyte is on bracts of female cone
single fertilization produces naked seed
wind pollination more common
Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms
occurs in flower fertilized by pollen
Perfect or hermaphroditic Flowers
Both Male and Female Parts
Monoecious
separate male & female flowers on same plant
Dioecious
separate male & female plants
Flowers
produced by mature sporophyte
house gametophyte generation
modified stems w/ modified leaves
Flower Structure
flower whorls from outside to inside
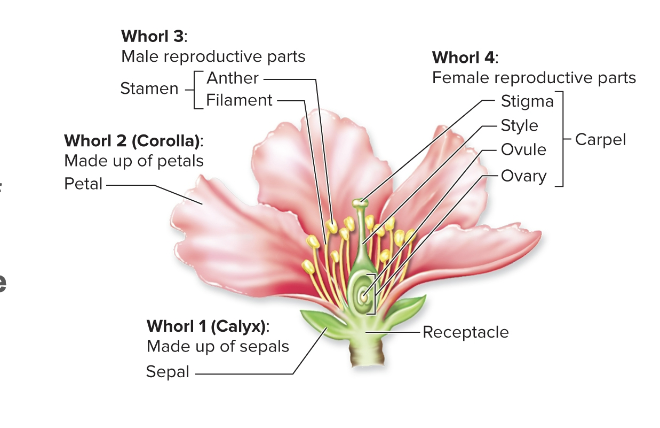
Flower Structure - Calyx
outermost whorl made of sepals help to protect the bud
Flower Structure - Corolla
second whorl made up of petals
Flower Structure - Androecium
third whorl w/ male reproductive structures
Flower Structure - Gynoecium
innermost whorl w/ female reproductive structures
Flower Reproductive Structures - Carpel
female part of flower
ovary - contains ovule
stigma - tip for pollen landing
style - neck or stalk leading to ovary
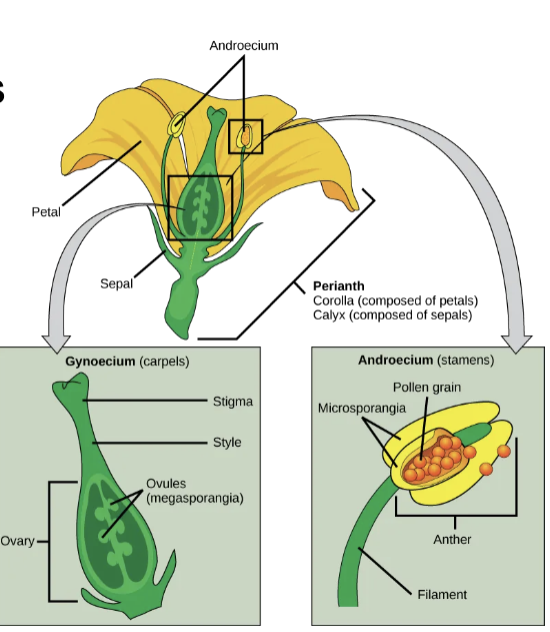
Flower Reproductive Structures - Stamen
male part of flower
anther - contains pollen grain
filament - supports anther
Types of Flowers - Complete Flowers
all 4 whorls are present
not a perfect flower
Types of Flowers - Incomplete Flower
missing at least one whorl
Types of Flowers - Perfect Flower
contains both male & female parts
Perfect flower = Complete flower
Types of Flowers - Imperfect Flower
identified by structures that are present in the flower
Staminate - only male structures are present
Carpellate - only female structures are present
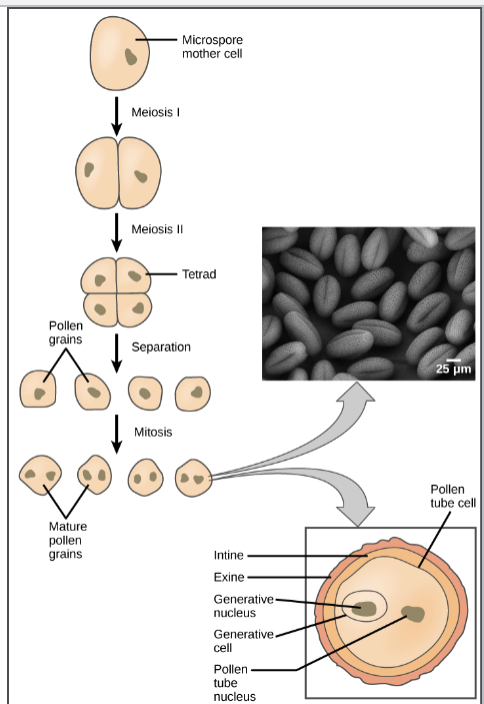
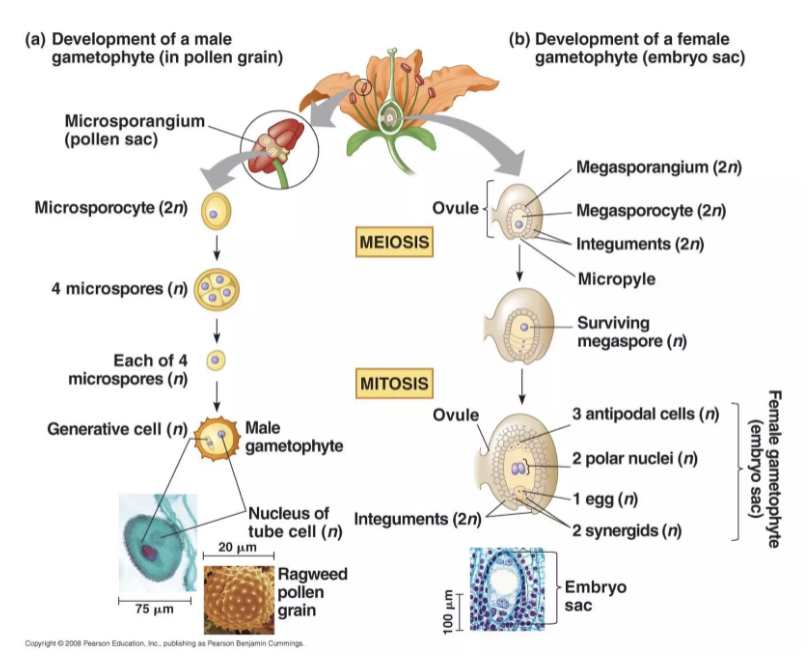
Male Gamete Production
Microsporogenesis undergoes meiosis
Microgametogenesis divide via mitosis
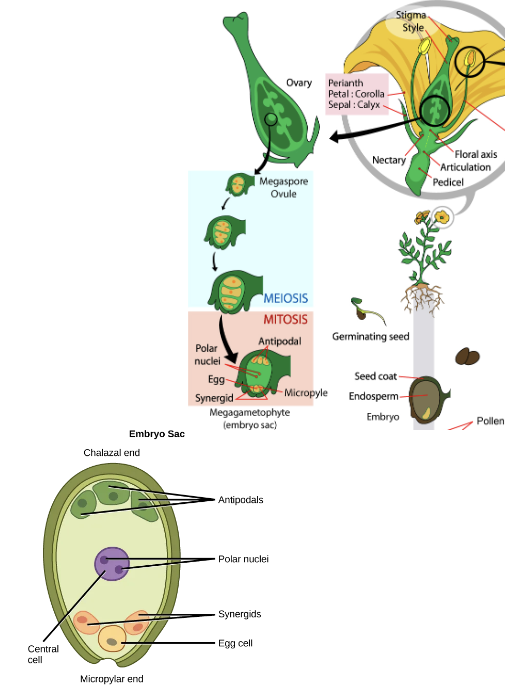
Female Gamete Production
megasporogenesis via meiosis > 4 megaspores (3 small, 1 large)
megagametogenesis via mitosis to produce 8 nucleate, 7 celled gametophyte
Gamete Formation
sporogenesis occurs via meiosis to produce spores
gametogenesis occurs via mitosis to produce gametes
Pollination
transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
pollen grain grows pollen tube
Fertilization
one sperm fuses w/ egg nucleus = diploid zygote
one sperm fuses w/ two nuclei in central cell = triploid endosperm
Pollination - Self Pollination
plant does not need to produce nectar for pollinators
Pollination - Insects
shape of flower suits pollinator
Pollination - Bats
flowers are large & bright
Pollination - Birds
plants are sturdier than those pollinated by insects
Pollination - Wind
flowers emerge before leaves
The Seed
seed coat protects embryo
endosperm stores food for developing embryo
The Seed - Embryo Structure
cotyledons: leaves
radicle: roots
hypocotyl: stem
The Seed - Micropyle
stays open as a pore for gas exchange
The Seed - Hilum
scar on seed coat from attachment to ovary wall
The Embryo
zygote develops from a single cell into an embryo
Monocot & Eudicot(dicot) Seeds
Monocot: one cotyledon
Eudicot (dicot): two cotyledons
Fruit Formation
fruits = dispersal of seeds
Fruit
thickened walls of ovary
seed dispersal
True Fruits
develop from ovary
Accessory or False fruits
develop from other parts of flower
Fruit Structure
Pericarp = all tissue outside of seed coat
Exocarp: skin/ outer covering
Mesocarp: middle
Endocarp: inner layer
Types of Fruit
True Fruits: develops from ripened ovary of a flower
Accessory or False Fruits: develops from ovary or other parts of flower
Simple fruits
develops from a single ovary of a single flower
Berries
simple fruit where two innermost tissue layers are fleshy
Pepos
type of berry with hard rind
Hesperidium
type of berry w/ leathery rind
interior separated into segments
Drupes
Simple fruit where endocarp forms hard enclosure/pit
Multiple Fruits - Accessory Fruits
formed as result of fused ovaries & other structures
Aggregate Fruit
forms from one flower w/ many carpels (female)
Pomes
accessory fruit formed from receptacle
Achenes
dry fruit that does not split open
Seed Growth
Germination - resumption of growth and development after a period of seed dormancy
Plant Growth
enzymes break down the endosperms starch into sugars
cellular respiration
cell division at apical meristem
Asexual Reproduction in Angiosperms
via mitosis
offspring genetically identical to each other and parent
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Apomixis: asexual repro to produce seeds w/out fertilization
Self Propagation via
stolon
tuber
plantlets
Plant Life Spans
senescene: aging
annuals
biennials
perennials
Plant Life Spans - Monocarpic
flower only once in lifetime and die soon after
Plant Life Spans - Polycarpic
flower many times