Galvanic cells
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Galvanic cell
is a type of electrochemial cell in which chemical energy is converted into electrical cells
An electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy or vice versa.
Battery
a combination of galvanic cells connected in a series
Purpose of the two half cells
The two half cell seperate oxidation and reduction, thus prevent contact between reactants, allowing electrons to be forced to travel through the external circuit connecting the two half cells, allowing the chemical energy to be converted into electrical energy
Electrodes
Electron conducting rods where oxidation/reduction occur allowing current to flow
Electrolytes
a non reactive solution that enables the flow of ions and help maintain electrical neutrality and complete the internal circuit
Salt bridge
Salt bridge connect the two electrolytes of the two separated half cells where It completes the cell’s electrical circuit by allowing the flow of ions, thus maintaining electrical neutrality.
This prevents the accumulation of charge in cells by providing cations that move towards the cathode and anions that move towards the anode.
Salt bridge is an electrical connection between the two half cells in a galvanic cells where it is usually made from a material satured in electrolyte solutions.
In order for a salt solution to be suitable for use in a salt bridge, it must be very soluble in water, unreactive and will not form an insoluble compound (precipitate with half cells)
Will be spectator ions
Most common salt brdige is KNO3
External circuit
Refers to the wire that connects the two electrode together allowing electron to flow from anode to cathode, allowing chemical energy to be converted into electrical energy.
Anode
The site of oxidation
Substance at the anode is the reductant and produces electrons through the external circuit
Electrons flow from here
Has negative charge in the galvanic cells
Cathode
The site of reduction
Substance at the cathode is the oxidant and receives the electrons through the external cirucit
Electrons flow to here
Have a positive charge in the galvanic cell.
Explain the significance of the increase in temperature of the solution
Not all of the chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy. Some of the chemical energy stored in the reactants is released as heat energy
Potential difference
Potential difference measures the tendency to push electrons into the external circuit. It is the electromotive force between two points in the circuit
Standard conditions for measuring potential difference
A pressure of 100kPa
1M concentration of solution
Potential difference are usually measured at 25C
Standard electrode Potentials
The half cell should be constructed at standard conditions (gas pressures of 100kPa, concentration of 1M) and the temperature of 25C.
The cell is connected to a standard hydrogen electrode to form a galvanic cell and the potential difference is measured with a voltameter.
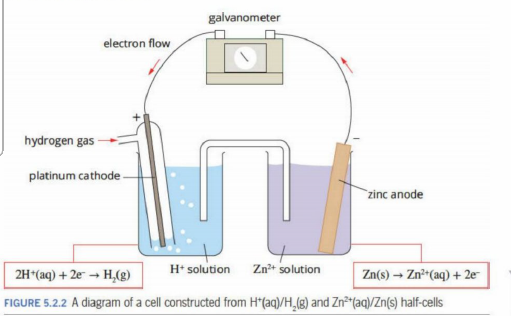
A standard is used because
When the conditions are not standard. the order of half reactions in electrochemical serieis may be different.