Prehistoric and Ancient Societies: Key Archaeological Sites and Cultures
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Blombos Cave
100,000 - 70,000 BP, South Africa
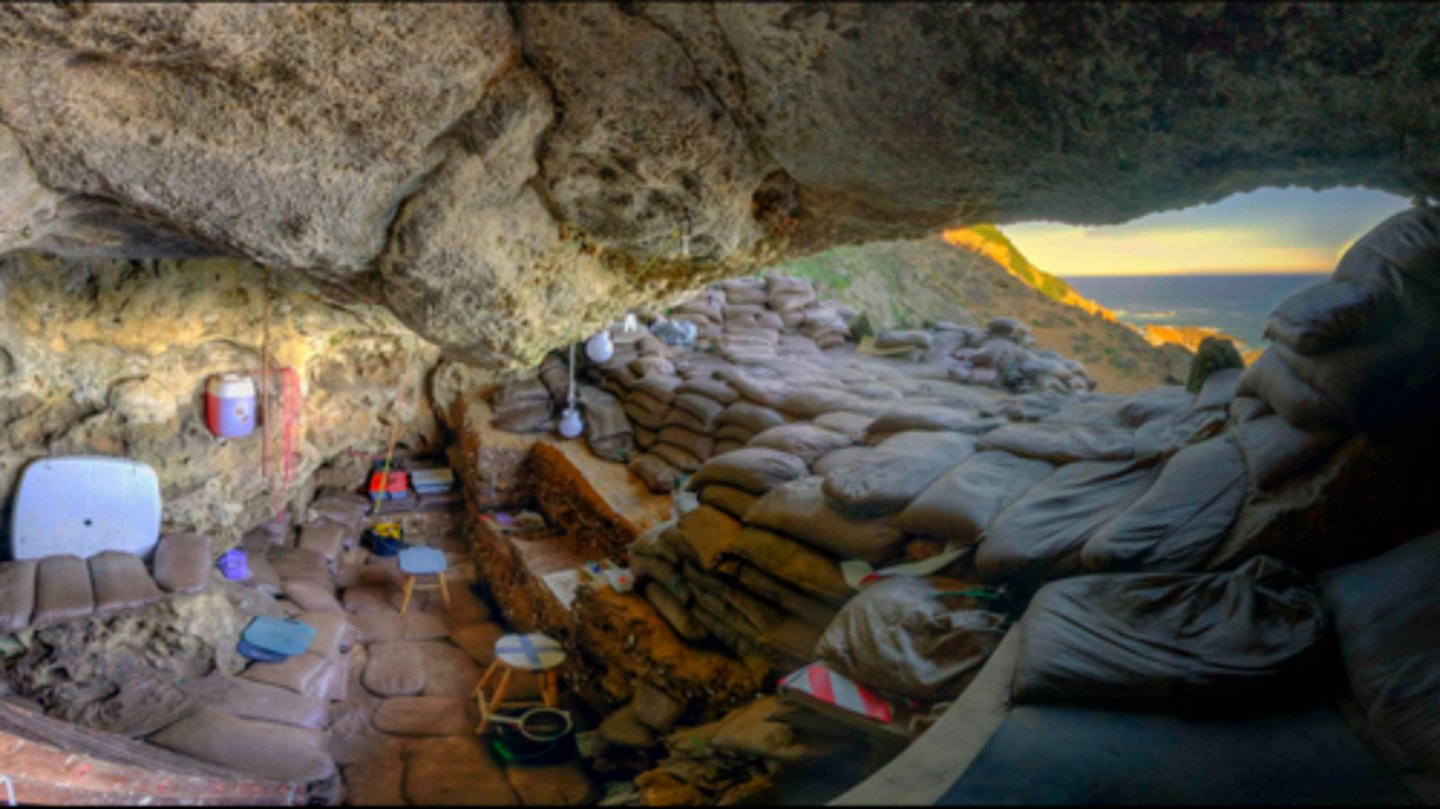

Rhino Cave
70,000 BCE, Tsodilo Hills, Botswana
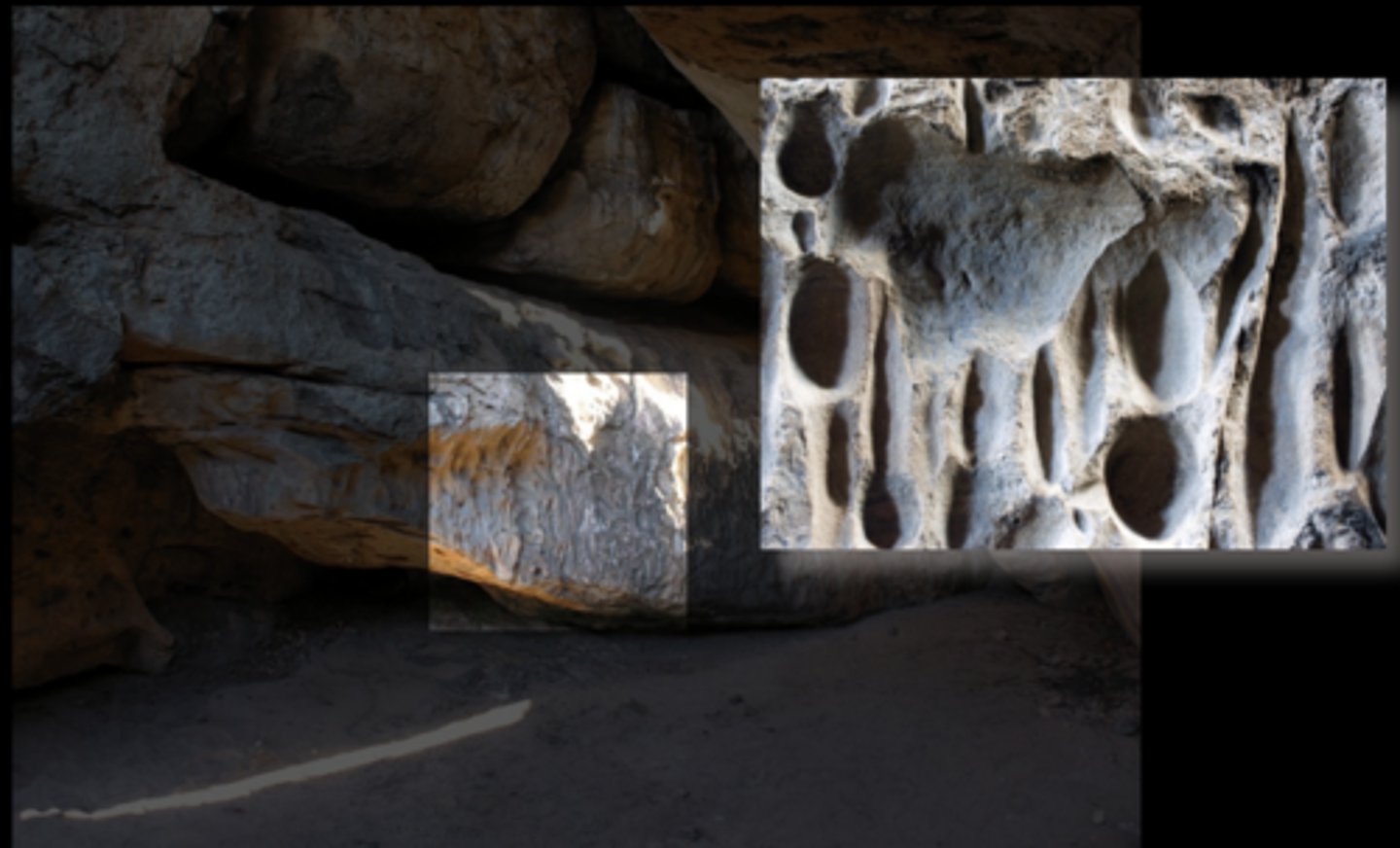

The Social Package, 100,000 BP
tools
ochre
symbolic expression
sacred landscapes
dance
bands, or kin-based groups
Social package: tools, knapping
Sharpening object by breaking off pieces/where stones can be found in landscape
Social package: ochre
"Paint," often applied to caves and clothing, used during death rituals, ex blood, vitality, birth, and menstruation
Social package: symbolic expression
Engraved stones showing an expression
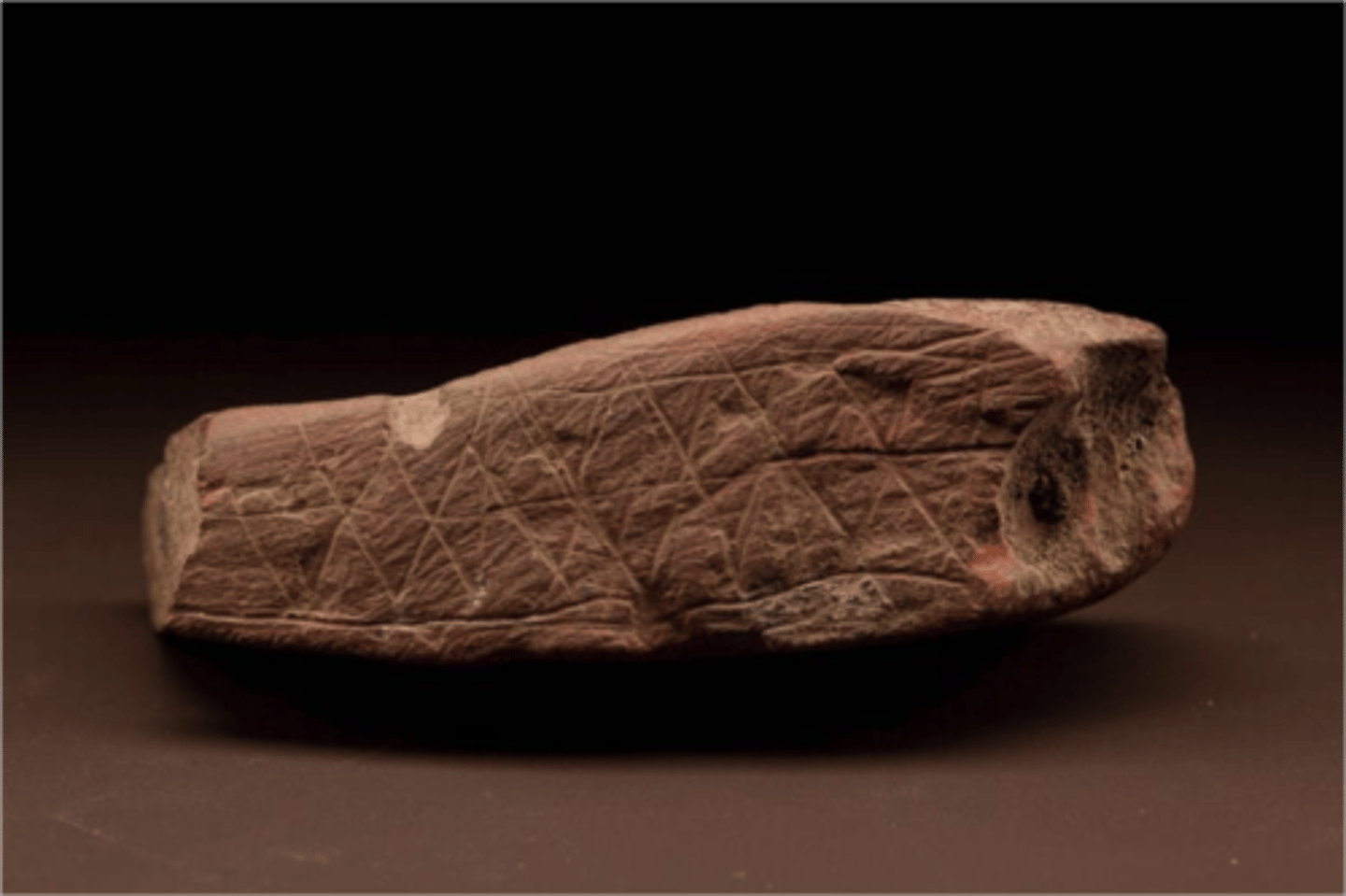

Social package: sacred Landscapes
Defines the relationship between nature and humans, animals and humans, living and the dead.
Social package: dance
Defines relationships, may last for days even months
Social package: Bands, or kin-based groups
40% of their time hunting, gathering, and hut building
60% of their time socializing, dancing, resting
First societies
did not change or shift to agriculture
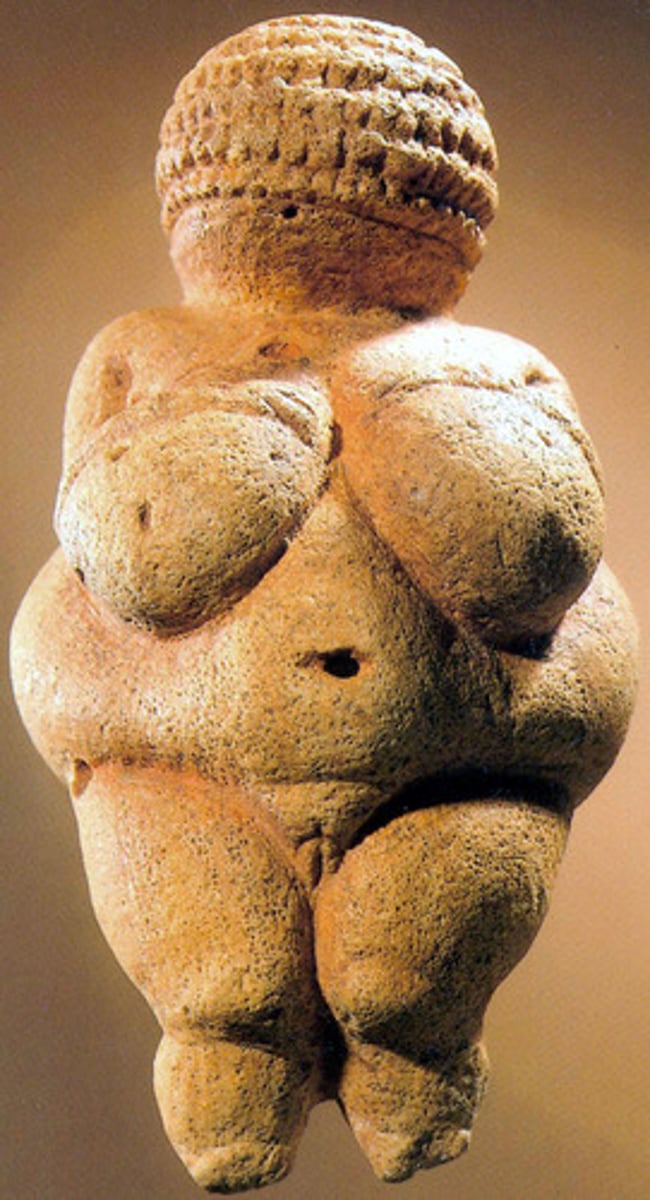
Venus of Willendorf
A figurine from Willendorf, Austria, dated 24,000-22,000 BCE.

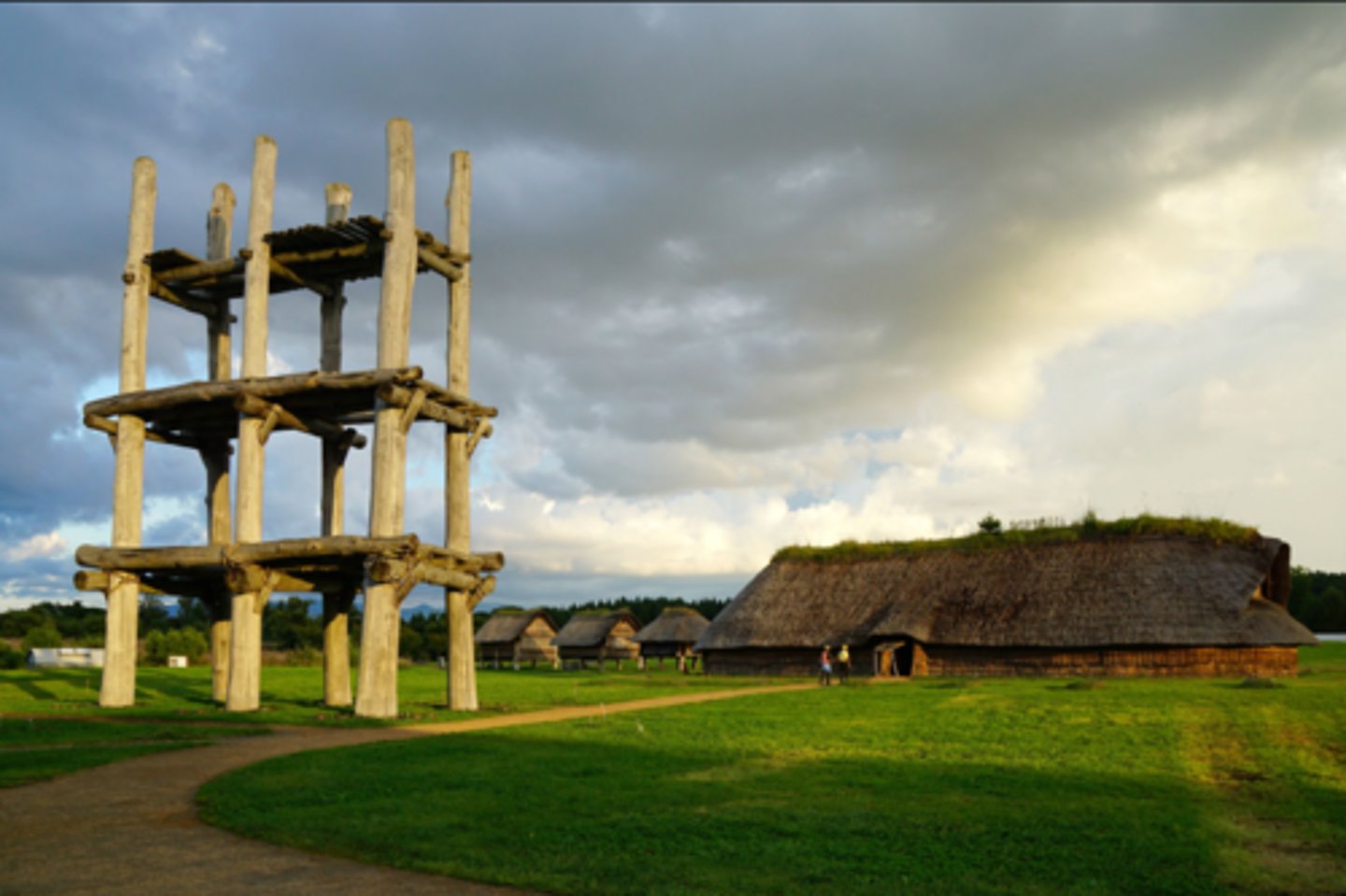
Sannai-Maruyama Site
Japan, 4,000 to 2,000 BCE

First society: Savanna and Scrubland Societies
!Kung populations today
First society: Gravettian Culture and Steppe Cold-Weather Hunting Societies
Hunted mammoths, reindeer, and horses
Women created warm clothing and footwear for the hunting men
Venus figurines
Bear cults and worship
Likely presence of shamanism, enters altered state of consciousness to interact with the spirit world
Sami in Sweden and Norway, Goahti, and Lavvu
Plains Indians in the US belonged to this group until the nineteenth century
First society: Forest and river societies
Rivers supported farming, trade, and permanent settlements. Forests provided resources leading to villages, social hierarchies, and early religion
Gravettian Culture
33,000 - 20,000 BP
Last Glacial Maximum (LGM)
A period from 26,000 to 20,000 BP.
Holocene
Began 9700 years ago after the last ice age, marking the warming of the climate and rise of agriculture.
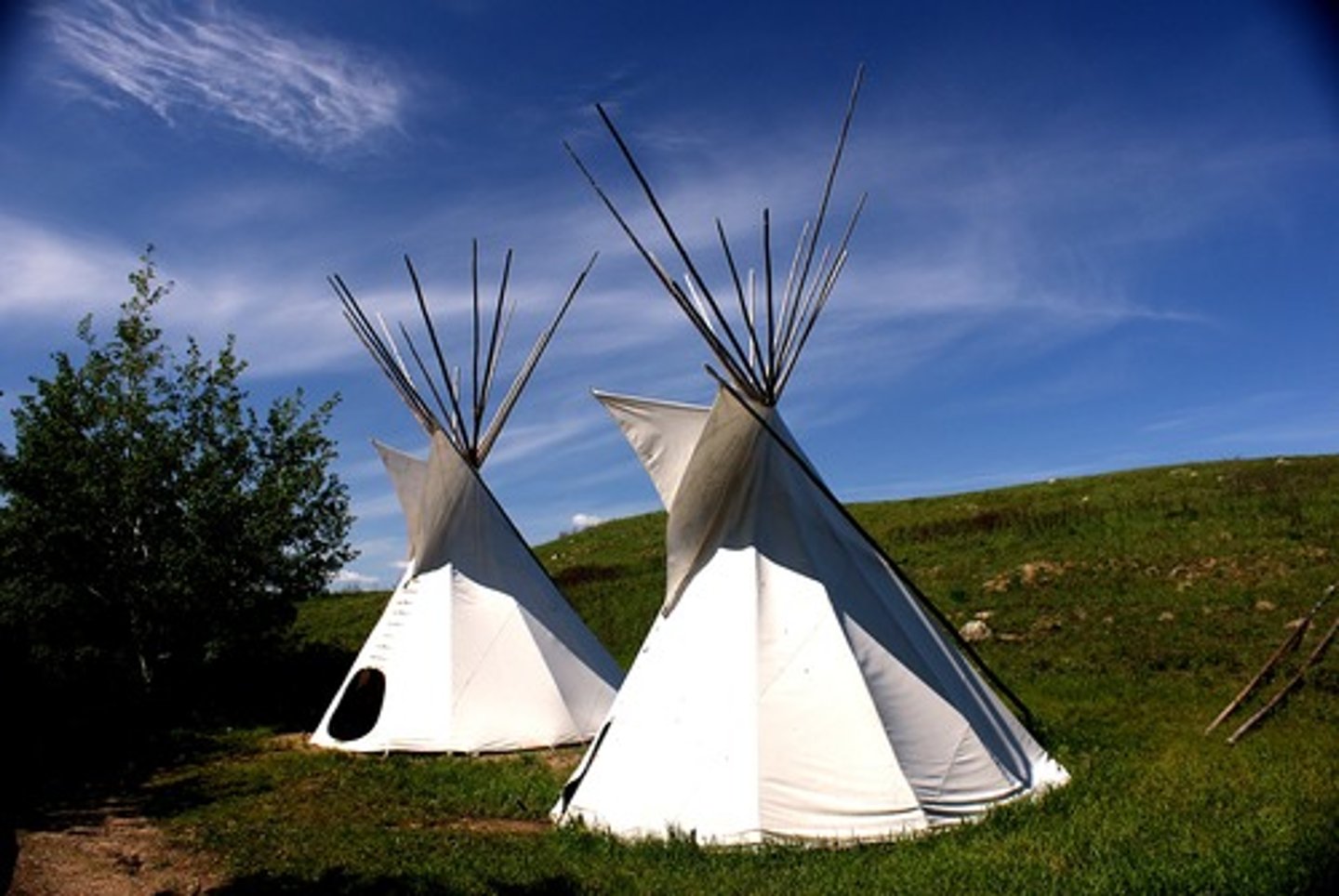
Tipi
Tilting structure allows for better temperature control
Animal skin binds pieces together
Poles tied at top to keep rain out
Easily portable
Reusable elements

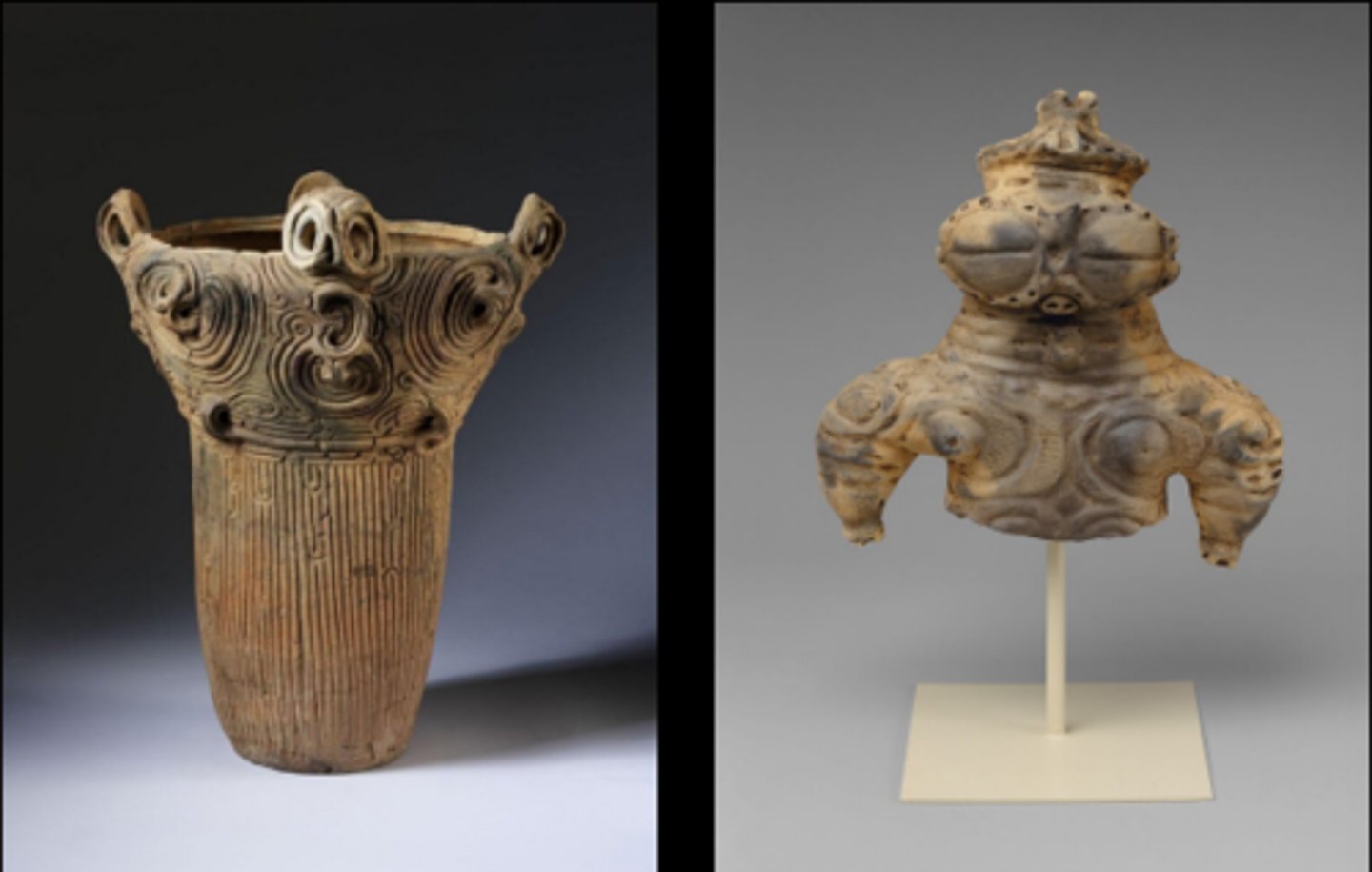
The Jomon
14,000 - 300 BCE, salmon-oriented along rivers and seacoasts, small communities in pit houses, survived by hunting, fishing, and gathering.
Known for their pottery, including simple jars and bowls, later figurines

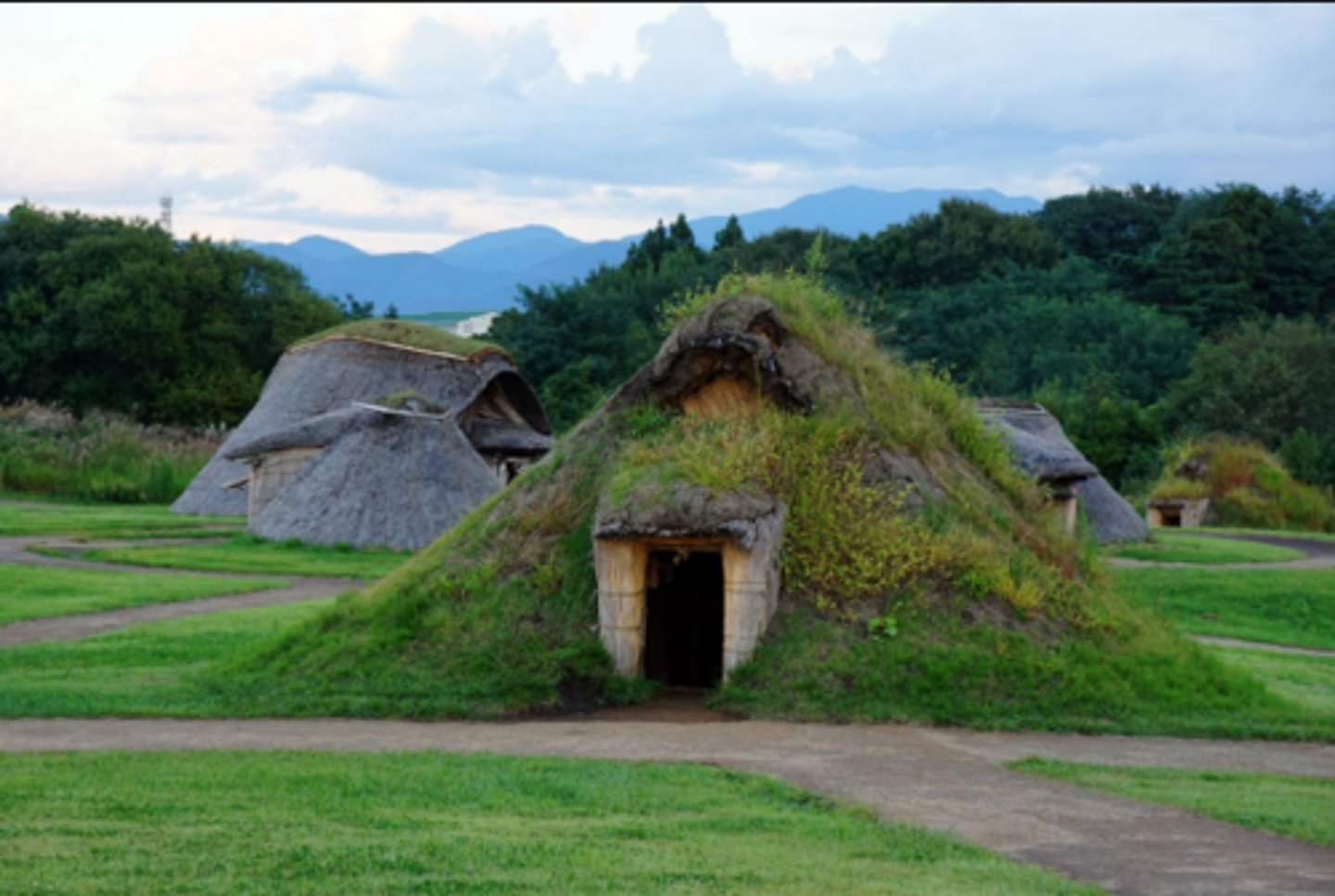
Pit House
A dwelling in which the floor level is below the surrounding ground level.

The Haida
North American people of Haida Gwaii
Economics based on fishing (salmon, halibut, and cod) and hunting
Plentiful annual salmon supported the tribes artistic and ceremonial pursuits
Known for their art and architecture that creatively used wood
Potlatch
A ceremonial feast used to display rank
Pastoralism
Social organization based on livestock raising as the primary economic activity
Agropastoralism
8,000 BCE
A way of life based on the growing of crops and raising of livestock as a primary economic activity
Plant Selection
A small handful of plants tended to in first societies became modern plants
In Africa and Eurasia...
Modern plants included taro, millet, sorghum, rice, oats, wheat, and barley
In the Americas...
Modern plants included squash, potatoes, corn (originally teosinte), and tomatoes
Maasai
Speakers of Maa, an eastern sundanic language
Nomadic, wandering in bands and subsisting on almost entirely meat, blood, and milk of their herds
Their kraal consists of a large circular thornbush fence around a ring of muddung houses, which hold four to eight families and their herds.
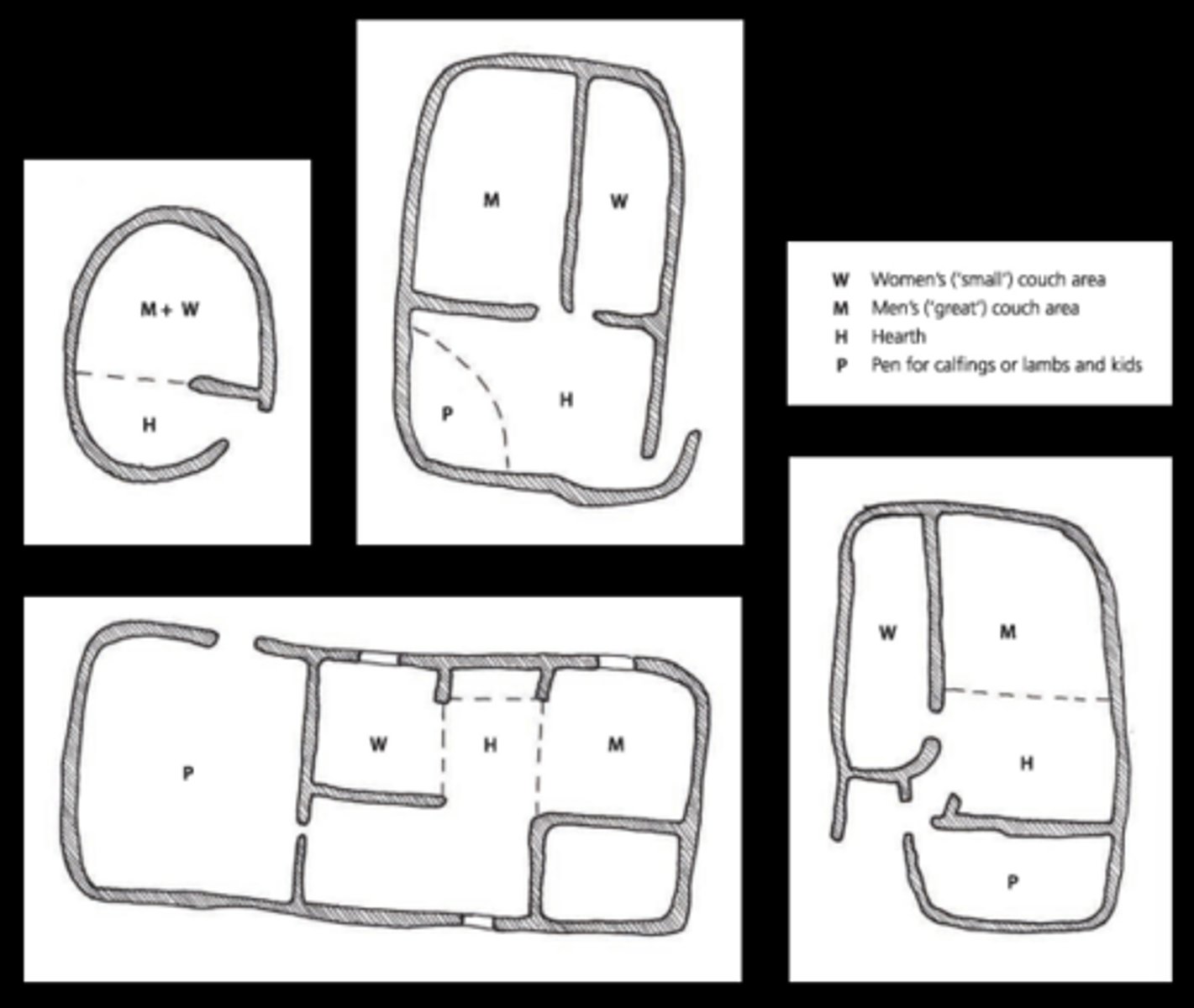
Kraal
An enclosure or group of houses surrounding an enclosure for livestock.
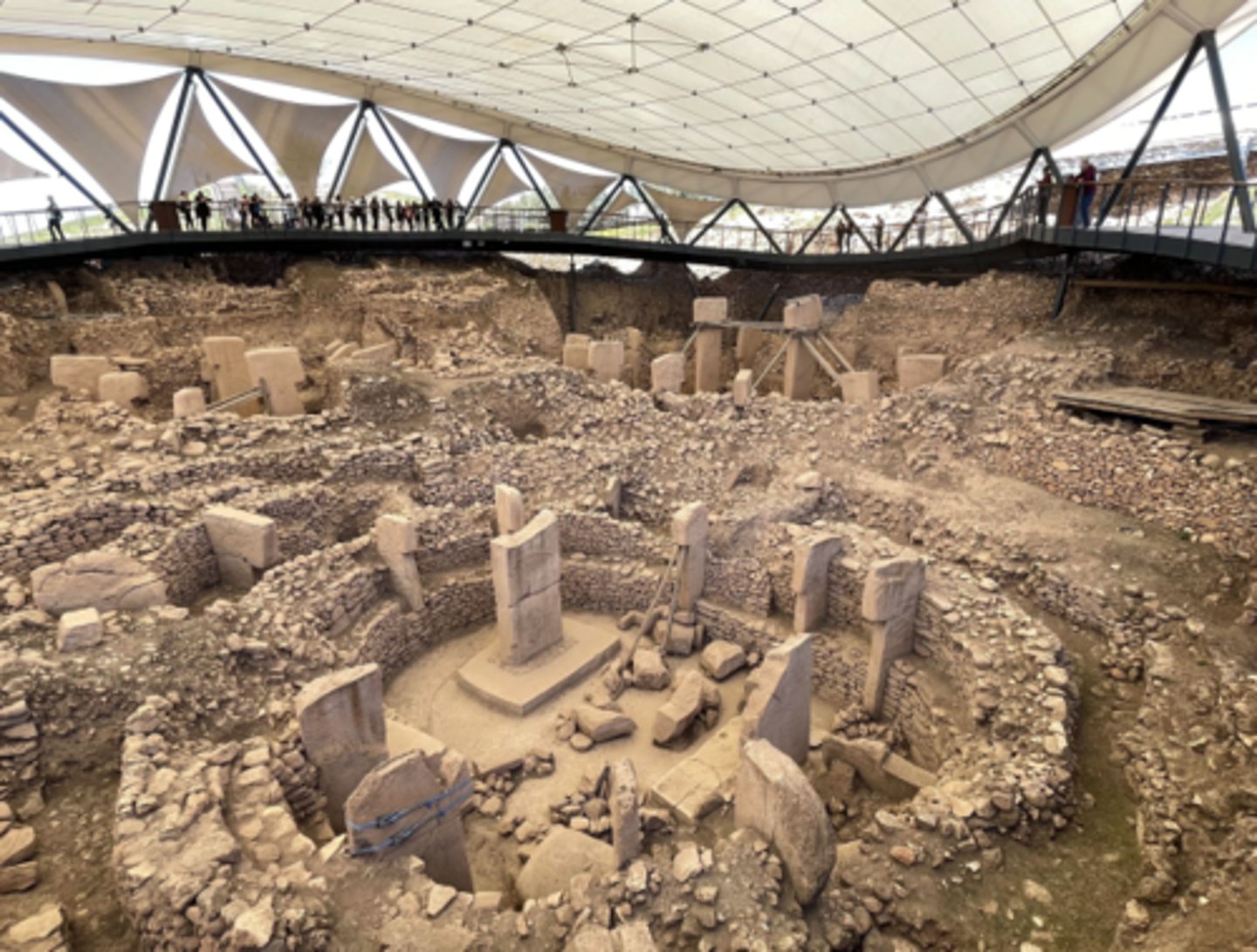
Göbekli Tepe
Turkey, 9,000 - 7,500 BCE

Stele
Upright stone slab or column with a commemorative inscription or relief design, often serving as a gravestone.
Excarnation
The exposure of human corpses to the elements to facilitate the decomposition of the flesh before the bones are buried.
Second burial
Period of waiting between the first burial and a second burial that often coincides with the duration of decomposition.
What is the importance of a second burrial?
To create a passage from the visible society of the living to the invisible one of the dead
Elements of the Emergent Agropastoral World
Plants and animals
- grain (bread), milk, and meat
manufactures
- pottery, leather, (obsidian) tools and weapons
rituals
- ritual centers, animal/grain worship
Çatalhöyük
Turkey, 7,400 to 5,500 BCE
Tell es-Sawwan
Iraq, 6,000 to 3,500 BCE
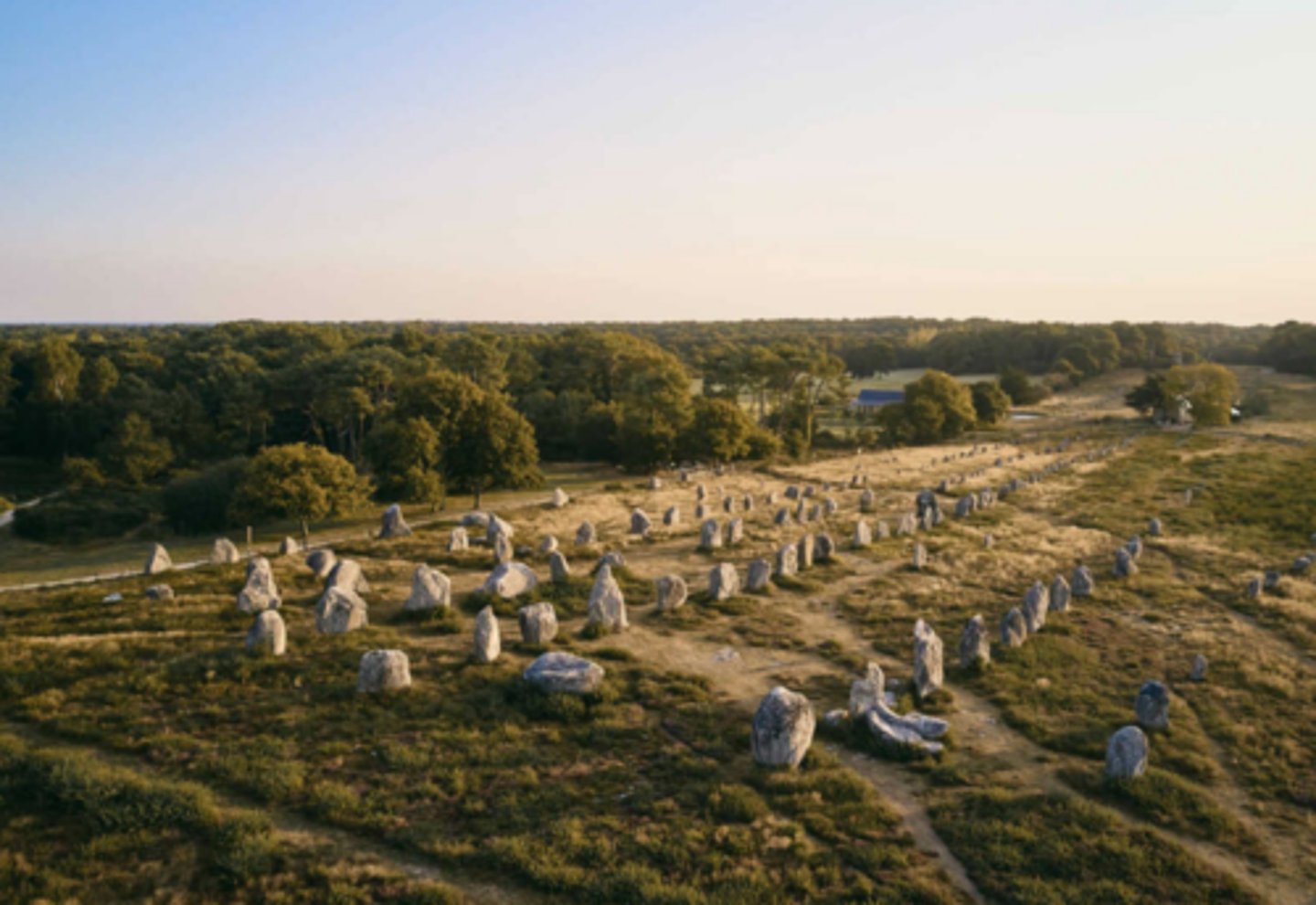
Carnac stones
Brittany France, 3,500 BCE

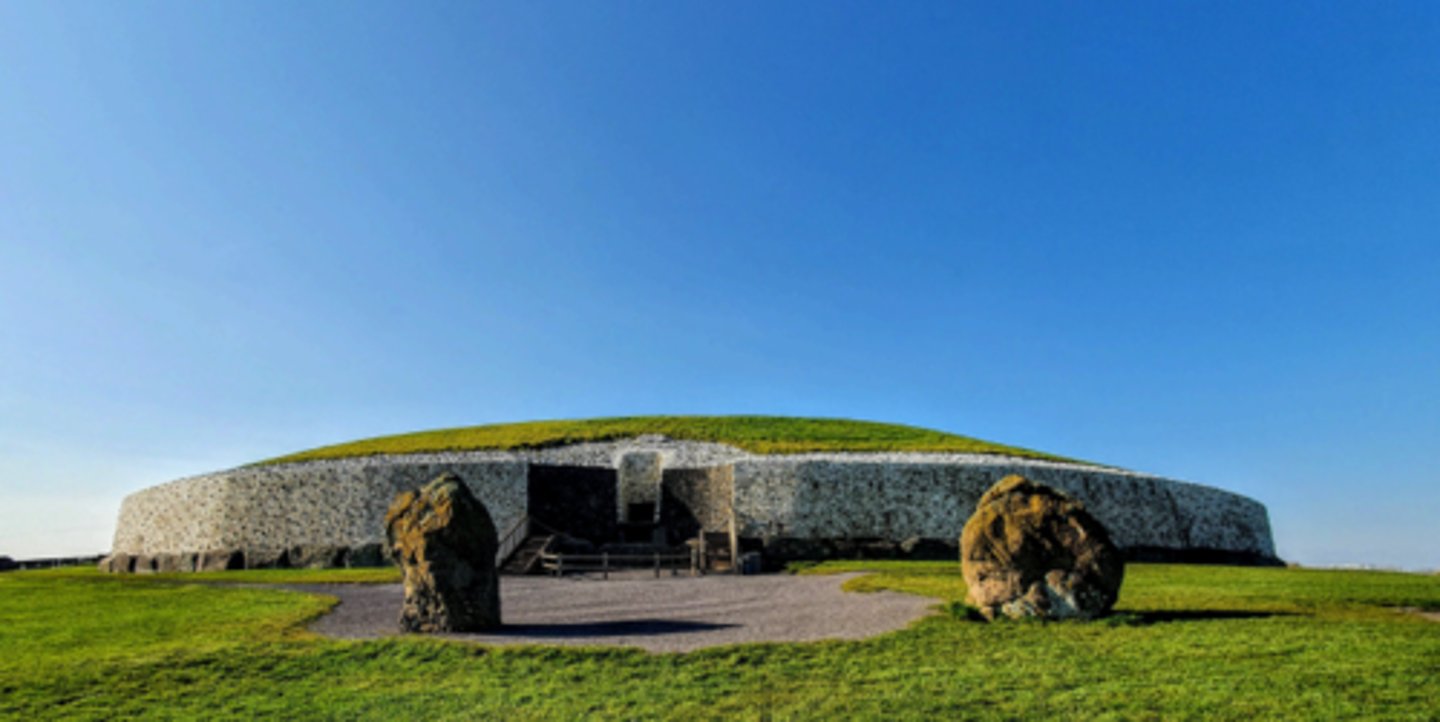
Newgrange
County Meath, Ireland 3,200 BCE

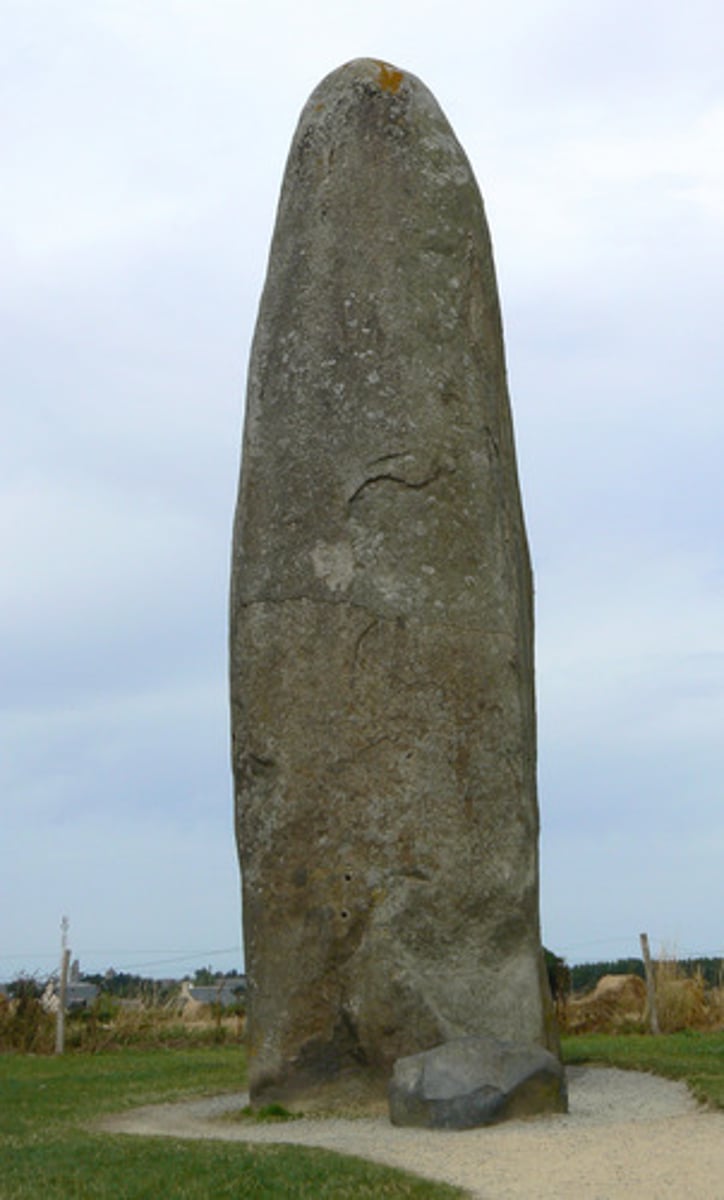
Menhir
Large standing stone found as a single upright monolith or in a group.

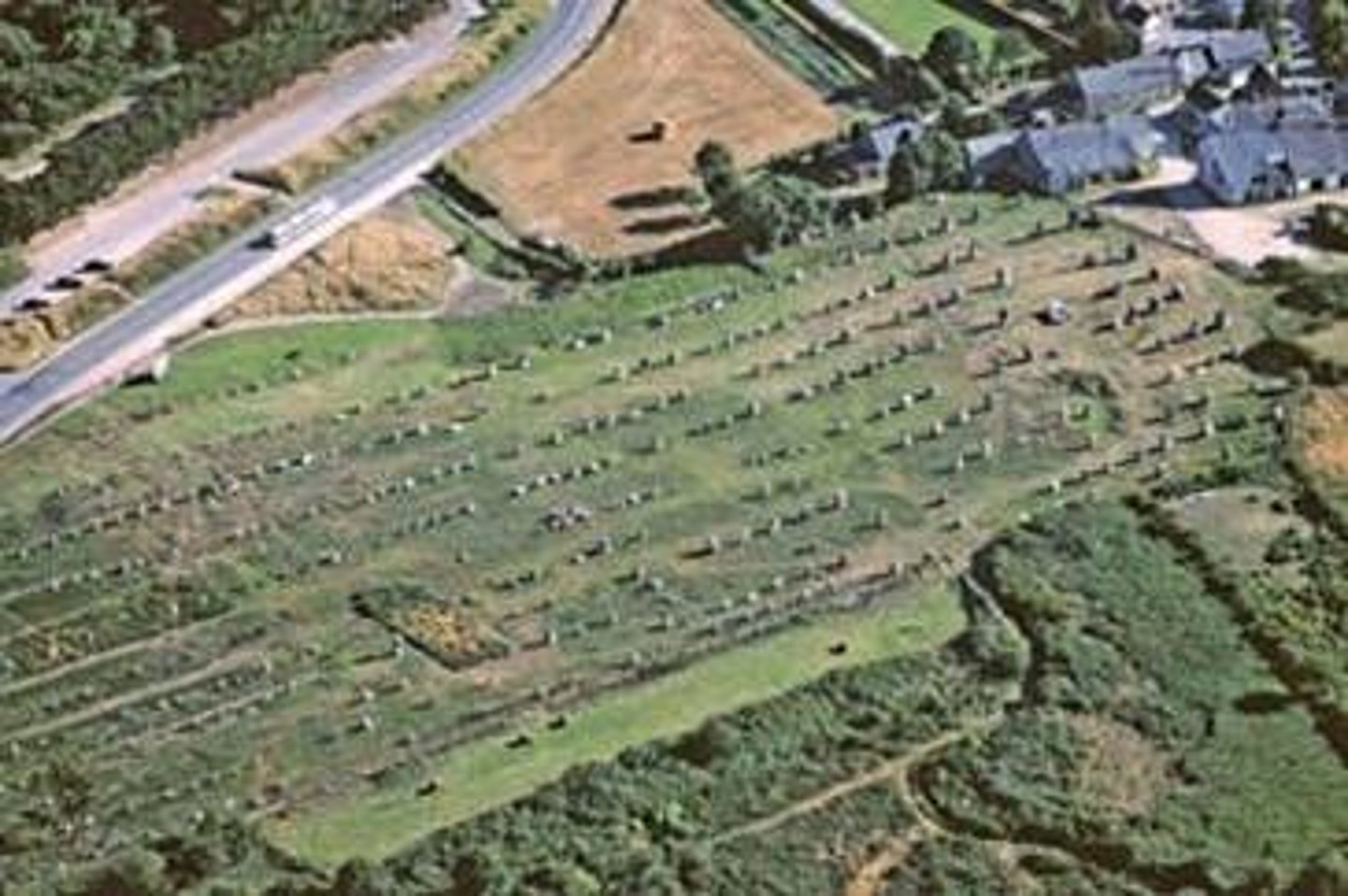
Alignments
Either large stones with wide spaces and smaller stones with more closed spaces.

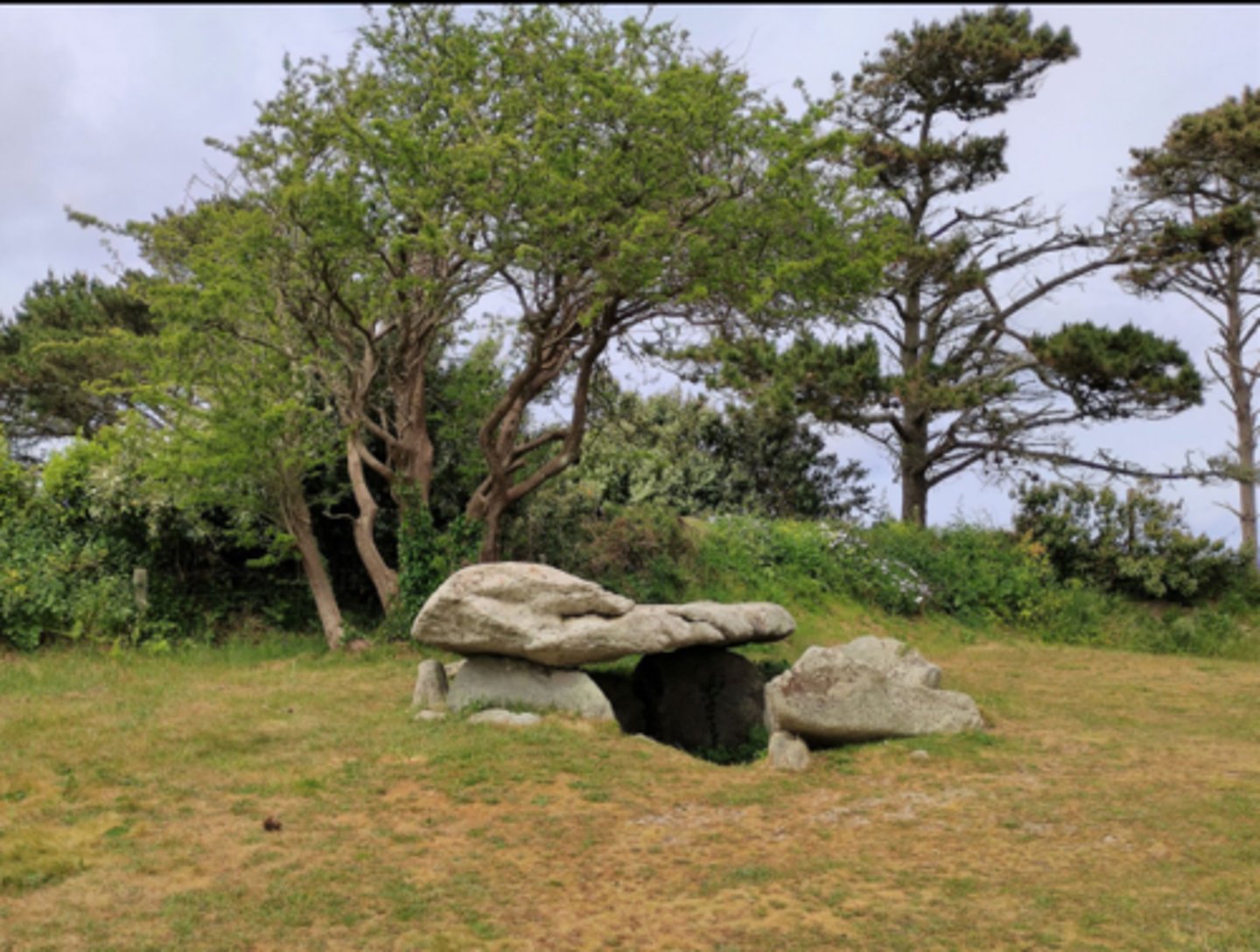
Dolmen
Structure of upright stones supporting a horizontal capstone, partial tomb.

Tumulus
If a dolman is covered with earth or small stones, don't always have a tomb within.
Cursus
Avenue-like construction defined by ditches that crosses the landscape, stretched for several kilometers, found in England.
Henge
Circular arrangement of stones, timber posts, or ditches.

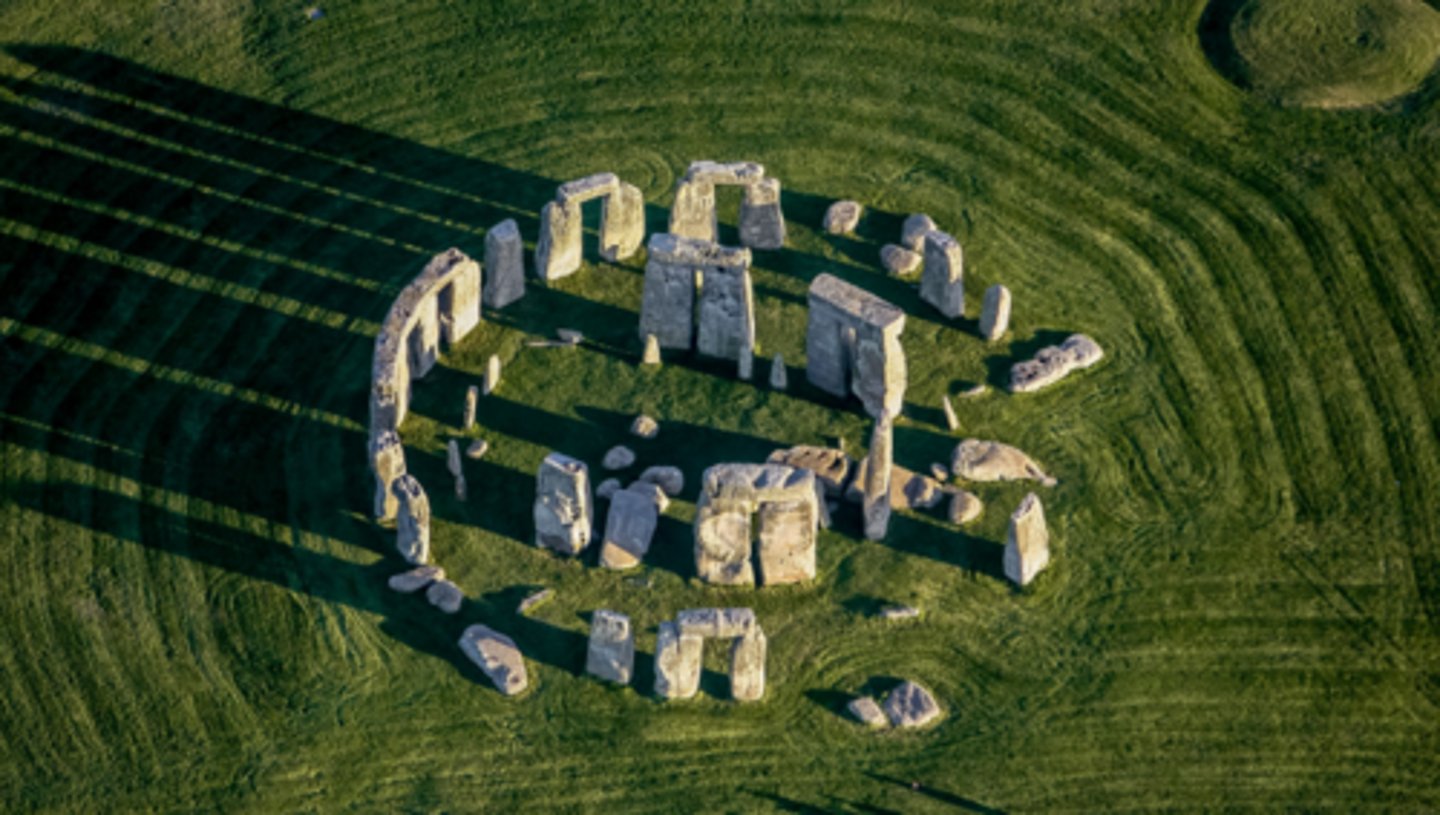
Stonehenge
Wiltshire, England, 3,000 BCE.

Megalithic Temples of Malta
Malta, 3,600 - 2,500 BCE.
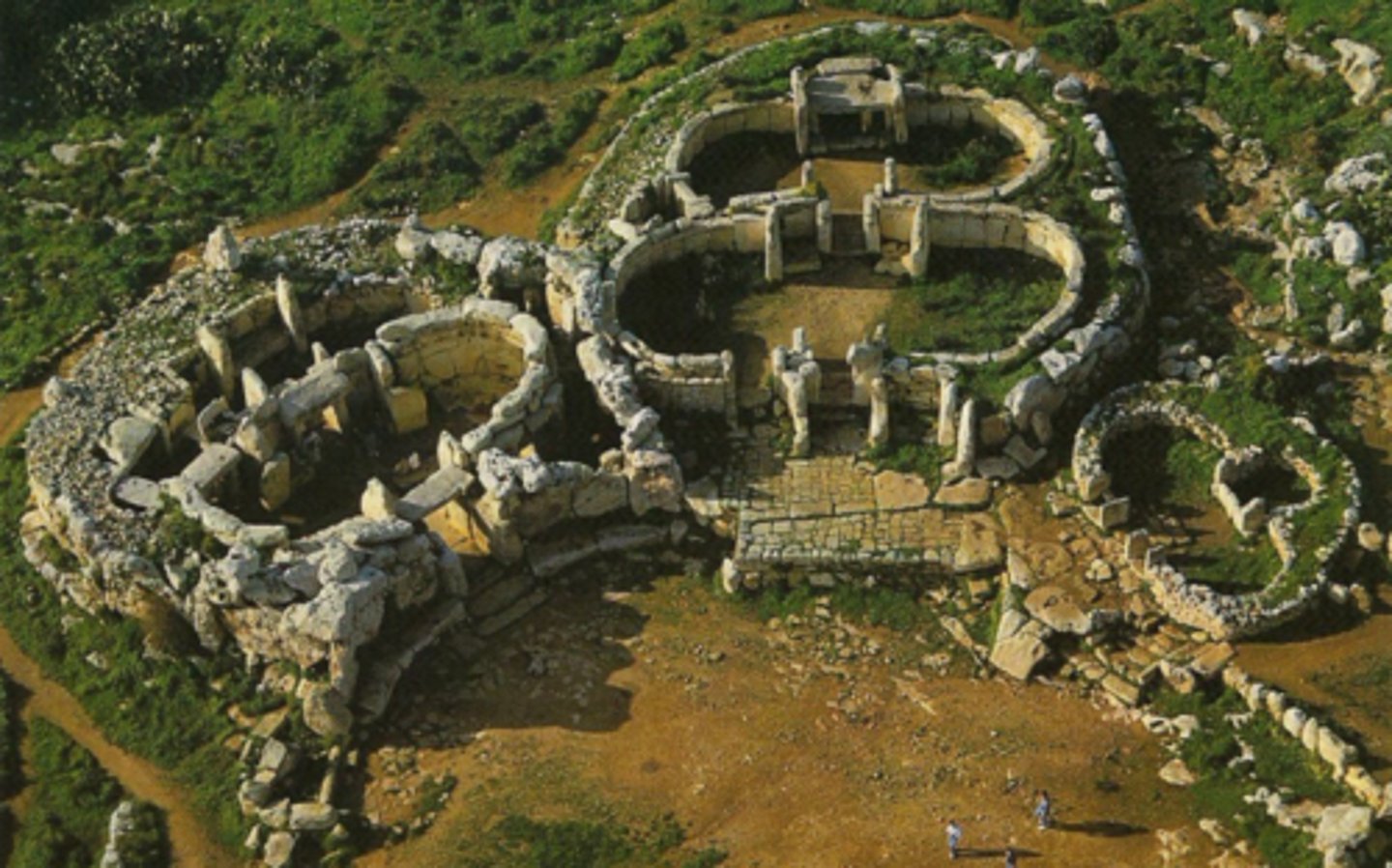

Elements of the Megalithic world in Malta
Oracular pronouncements, sleep-based trances, a mother goddess cult, sacred landscape, temples built for visitors created temple-based tourism.
Sumer (Sumerians)
Earliest known civilization, southernmost part of Mesopotamia (Iraq), settled 4500 - 4000 BCE by Ubaidians.
Ubaidians
The first civilizing force in Sumer, draining the marshes for agriculture, developing trade, and establishing industries like weaving, leatherwork, metalwork, masonry, and pottery.
Eridu
Iraq, 4500 - 3800 BCE.
White temple
Uruk, Iraq, 4000 BCE.
Elements of the first cities of Mesopotamia
Irrigation efforts to control flooding, grain production, hierarchically organized with powerful rulers with institutions that allow them to exert their power, such as temples, pantheon of gods, bureaucracies and armies
The Akkadian Empire (akkadians)
The name Akkad was founded by Semitic Conqueror Sargon 2300 BCE
Sargon united the city-states and extended his rule to encompass Mesopotamia which stabilized this region
Development of art, literature, science, agricultural advances, and religion
After Sargon's fall in 2150 BCE, the central Iraq region was ruled by Sumerians and Akkadians
Empire
Major political unit where a single authority controls large territories or multiple peoples, either formally or informally.
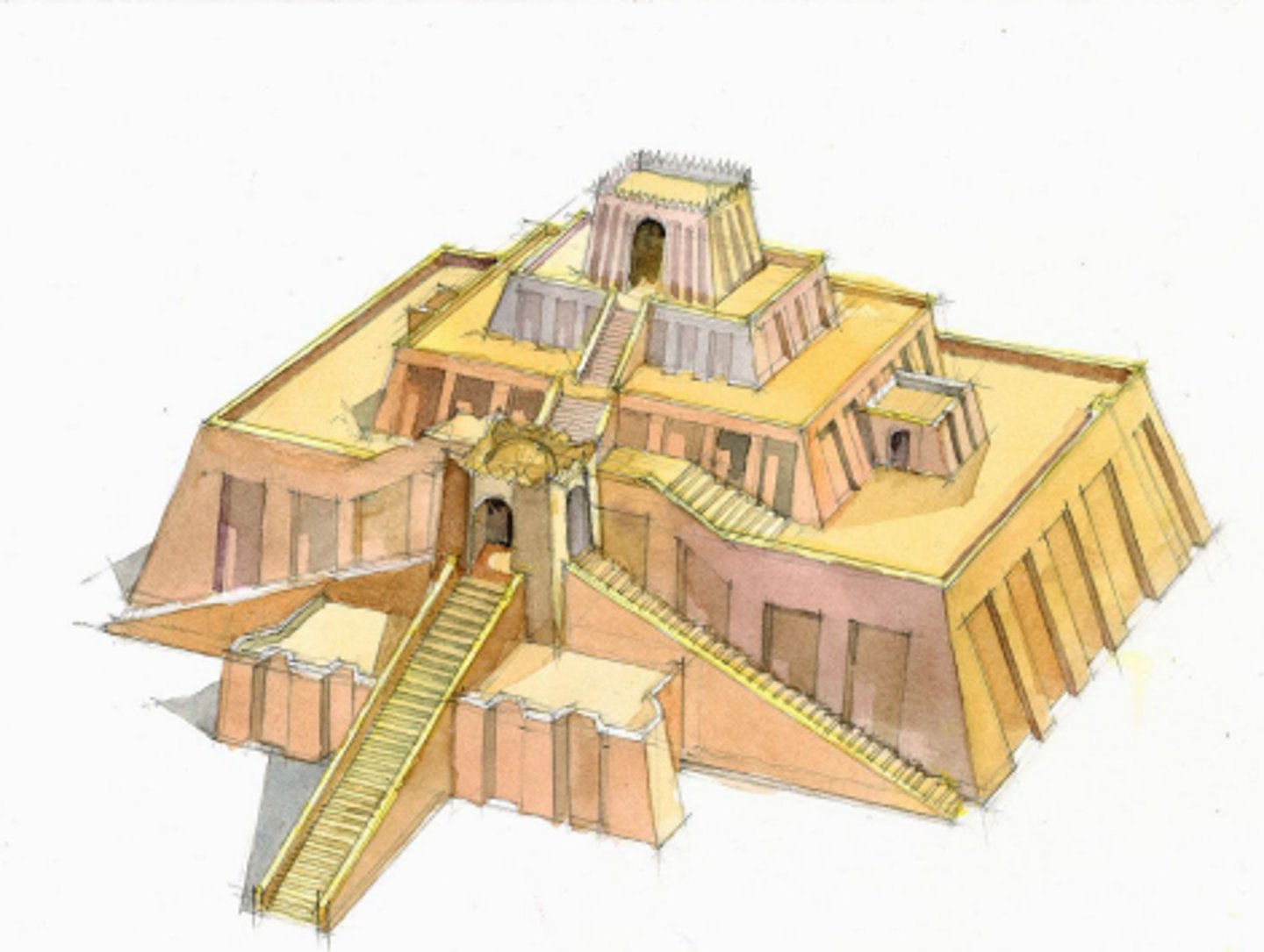
Great Ziggurat at Ur
Ur, Iraq, 2100 BCE.
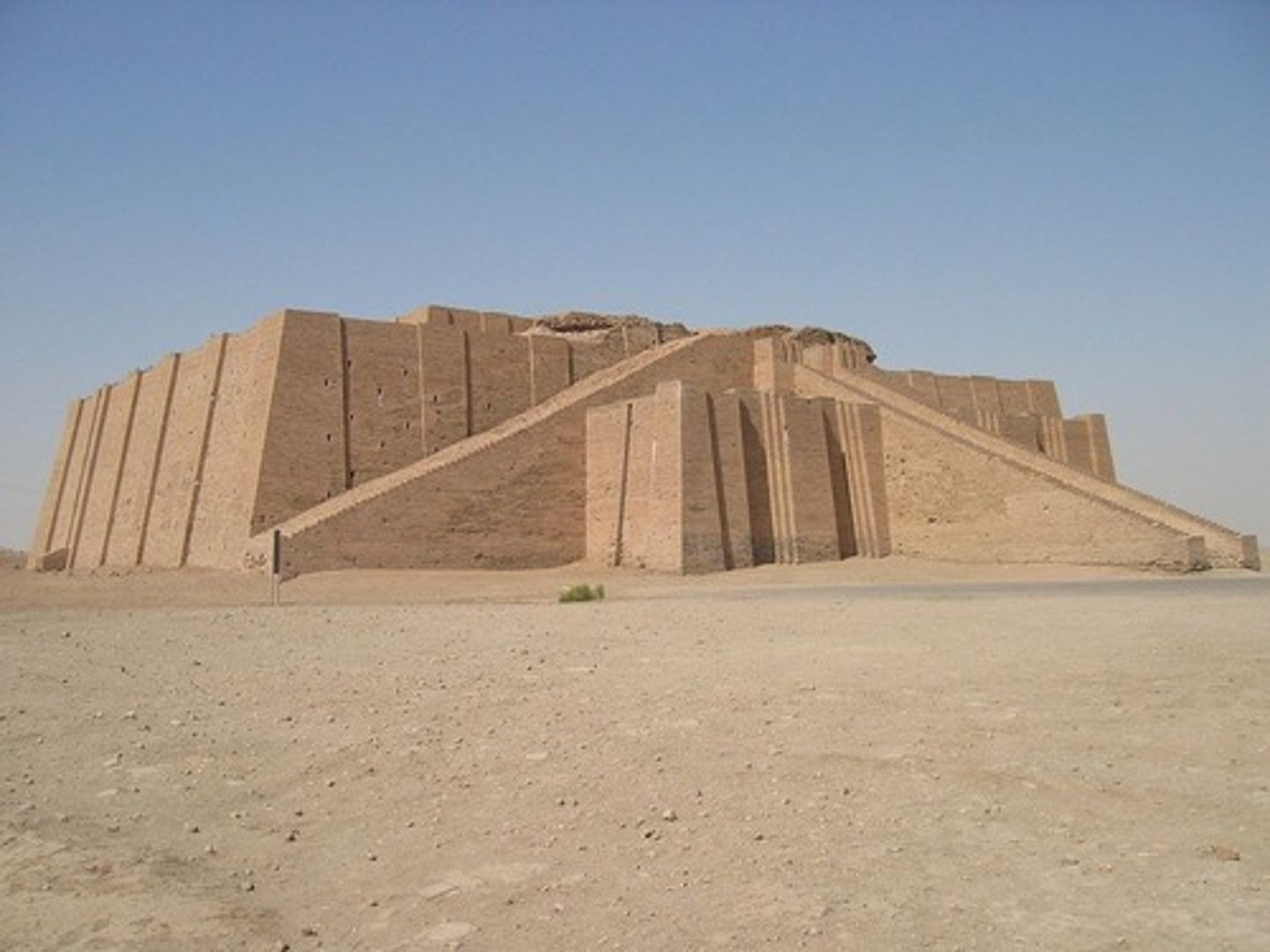

Ziggurat
Ancient Mesopotamian staged temple-tower of pyramidal form in which each successive stage is smaller than that below it, leaving a terrace all around it
What did they trade in Mesopotamia?
Wood: build houses
Baked bricks: construct temples and palaces
Copper: Increased rulers' prestige
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Obsidian tools/weapons
7000 BCE
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Copper tools/weapons
5000 BCE
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Casting of bronze
3600 BCE
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Invention of the wheel
3600 BCE
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Invention of writing
3200 CE
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Centralization of power
3000 BCE (ex. Kings)
Intensifiers of the Agropastoral world: Domestication of camels
2500 BCE
Mari
on the Euphrates, Syria, 2200 - 1800 BCE
Mastaba
ancient-Egyptian mausoleum, the exterior of which has battered sides, a flat roof, and plain with a tomb chamber underground
Ka
ancient-Egypt belief that the spiritual part of a person or God that survived after death and dwells in the statue
Step Pyramid of Djoser (Zoser)
Saqqara, Egypt 2650 BCE
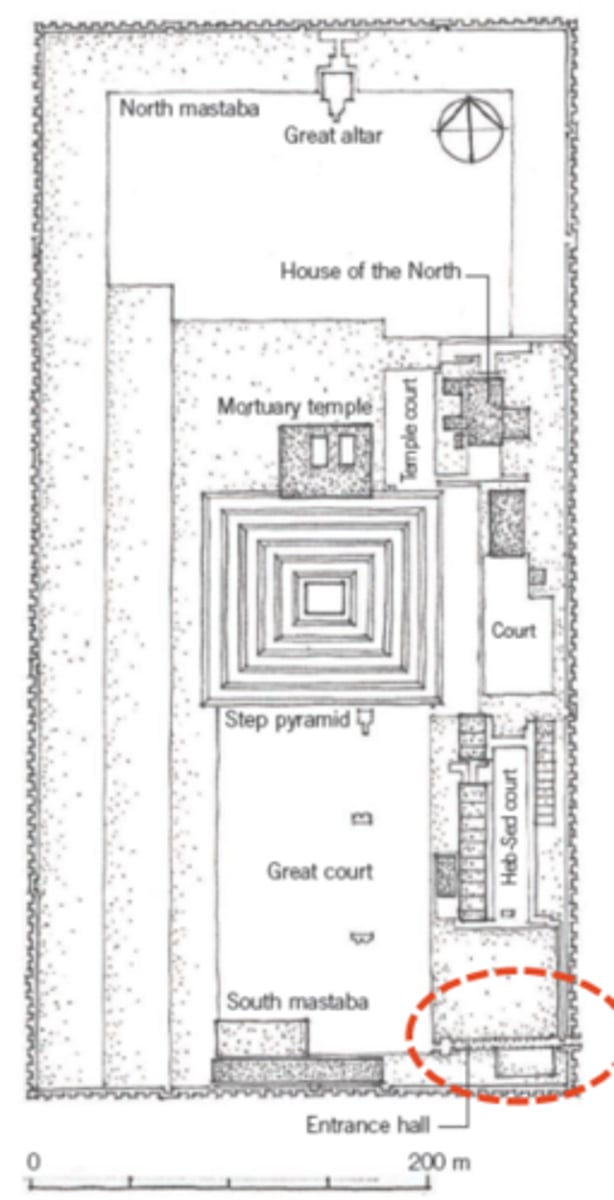
Serdab (ka-chapel)
narrow chamber of ancient Egyptian mastaba, accessible by a narrow passage and containing a statue of the deceased
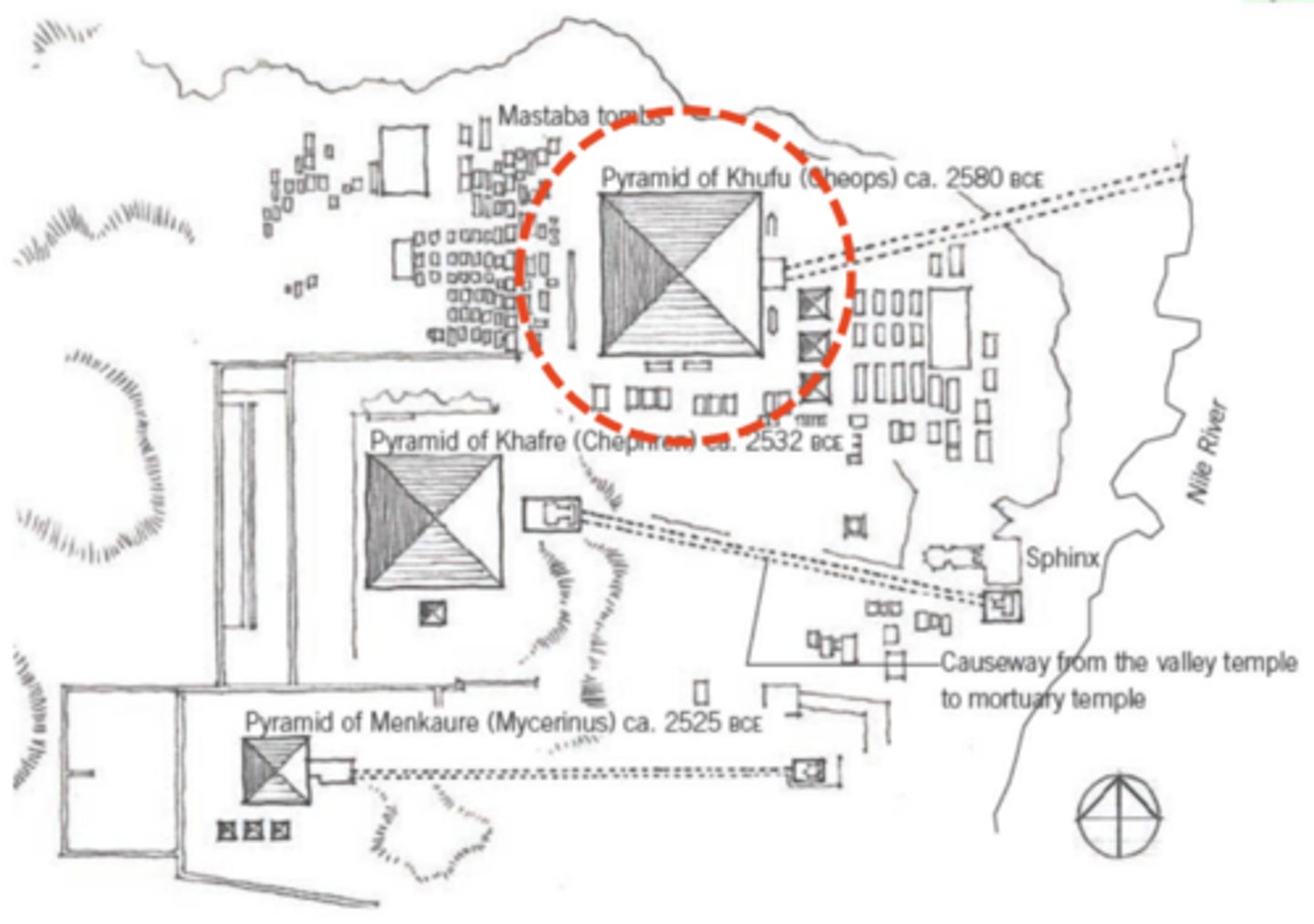
The Pyramids at Giza
Giza, Egypt, 2580 - 2525 BCE
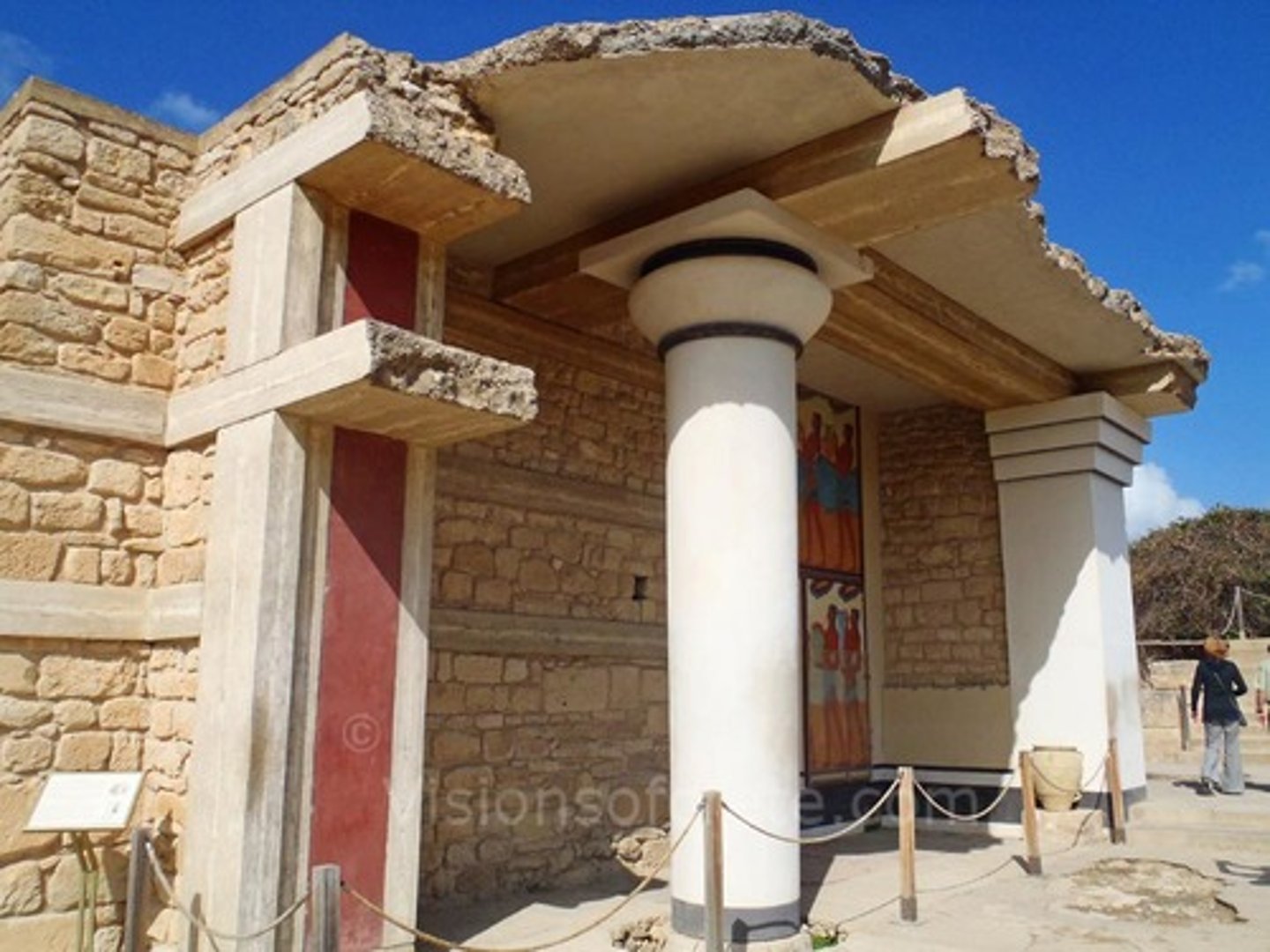
The Minoans (Minos)
Bronze age civilization of Crete that flourished 3000 - 1100 BCE, peaked in 1600 BCE, its known for its great cities, palaces, trade, and writing. Sophisticated art included seals, pottery (light on dark style) and vibrant frescoes
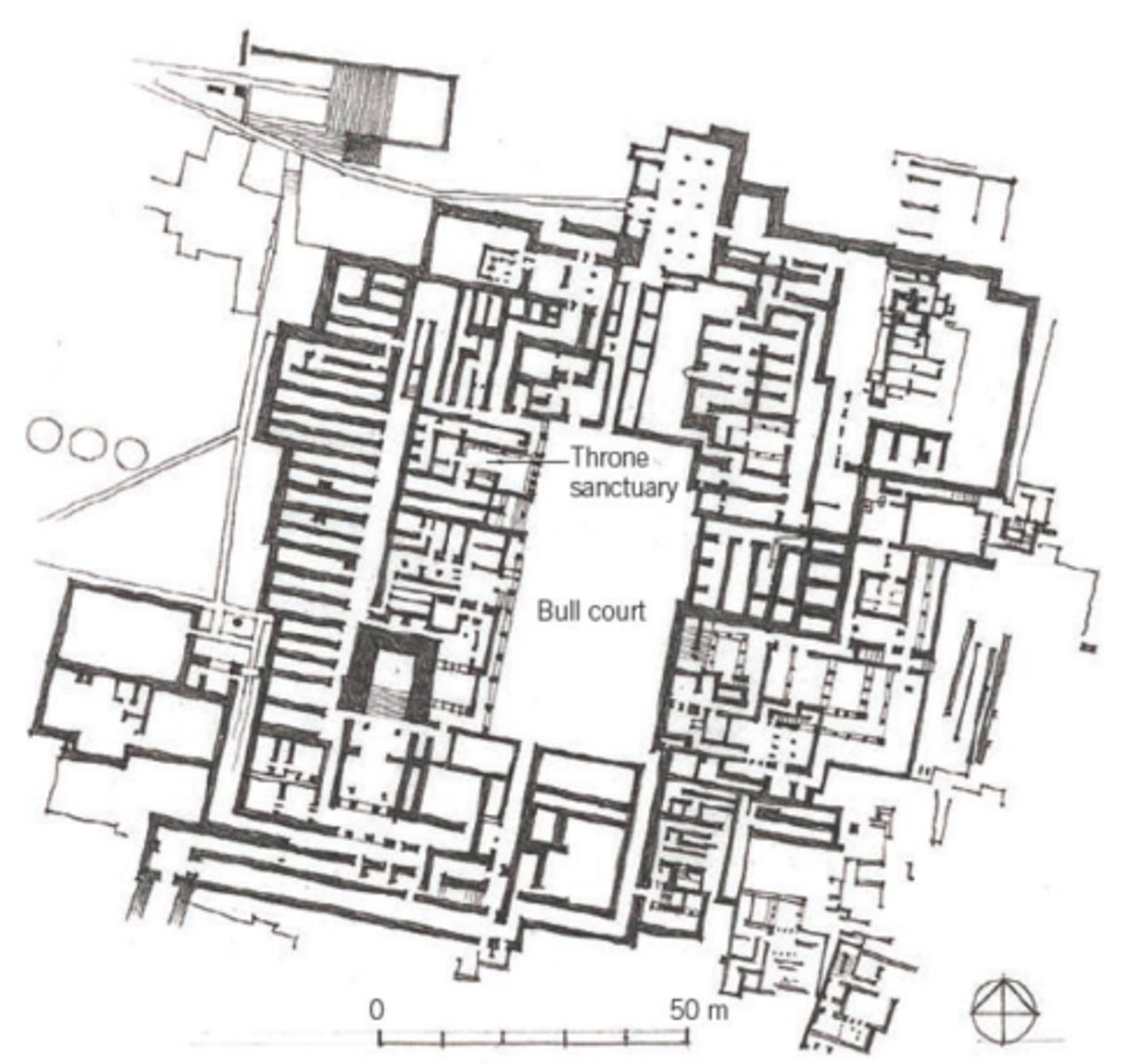
Temple/palace at Knossos
Knossos, Crete, 1700 - 1400 BCE
The Mycenaeans
Group of warlike Indo-European peoples who entered Greece in 1900 BCE and established a bronze age culture on the mainland. Dependent on the Minoans who politically dominated them, then threw off Minoan control in 1400 BCE till invaded in 1150 BCE
Propylon
outer monumental gateway standing before main gateway

Megaron
square/rectangular room with raised center and columns supporting the roof
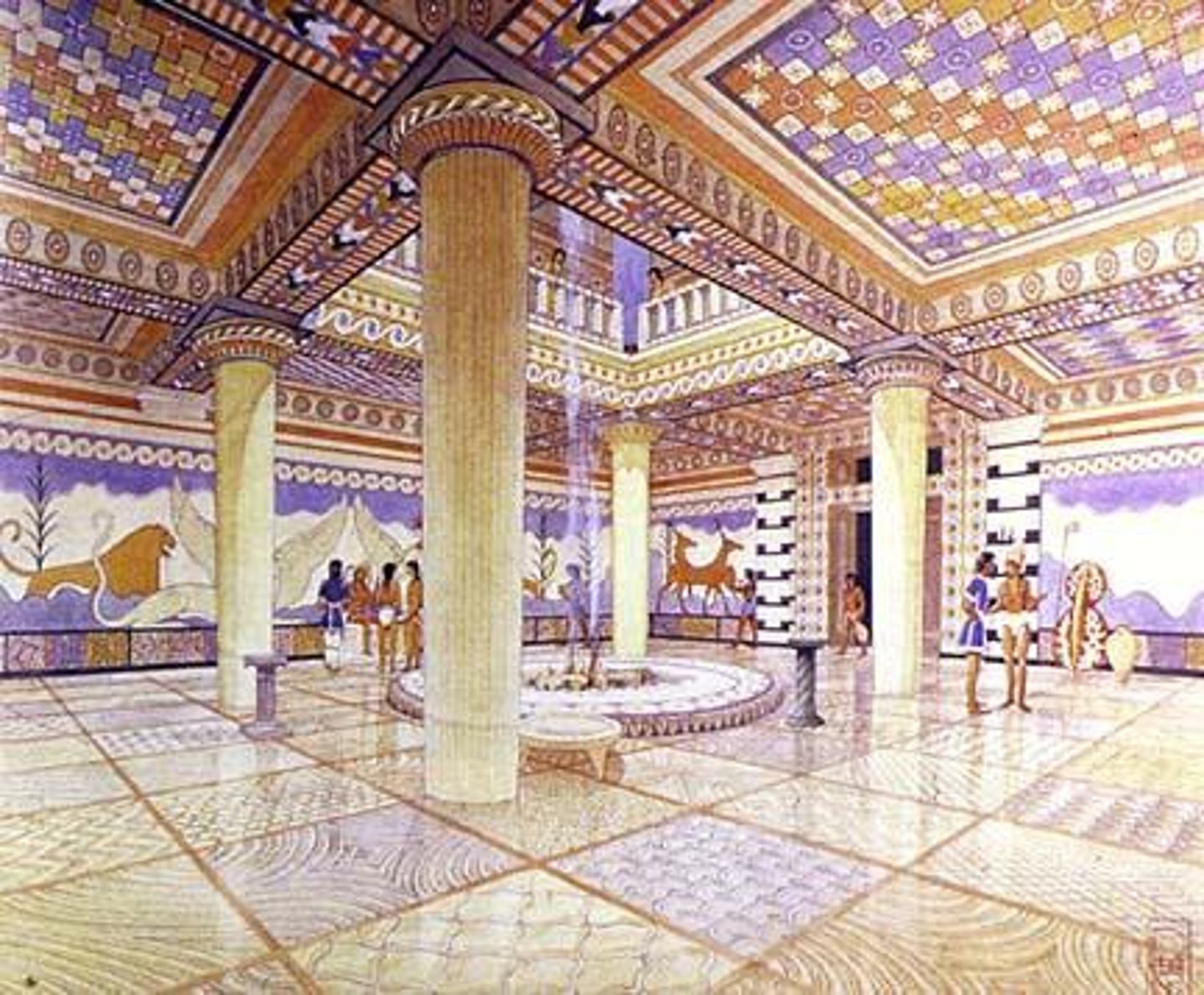

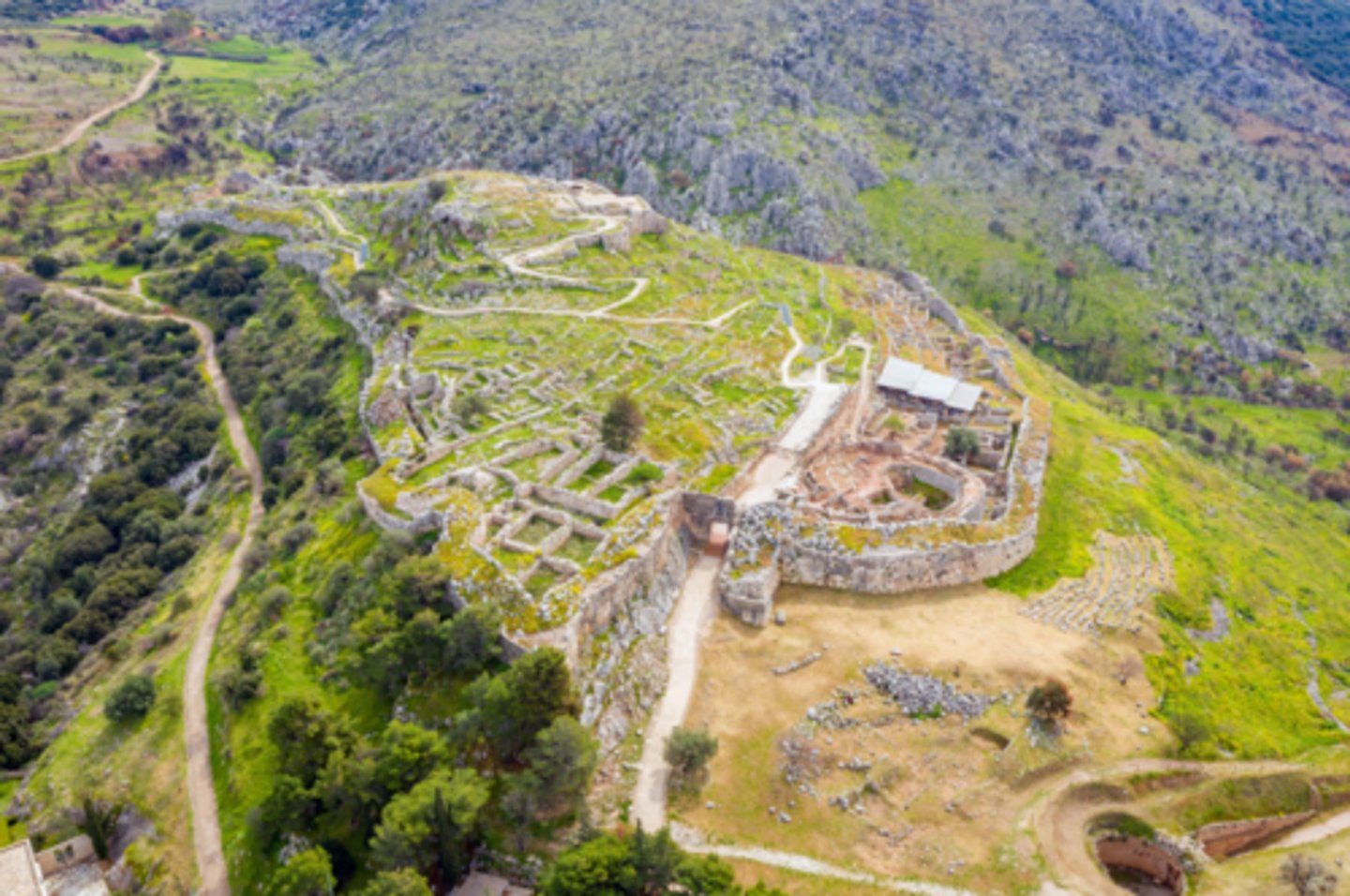
Mycenae
Greece, 1600 - 1000 BCE

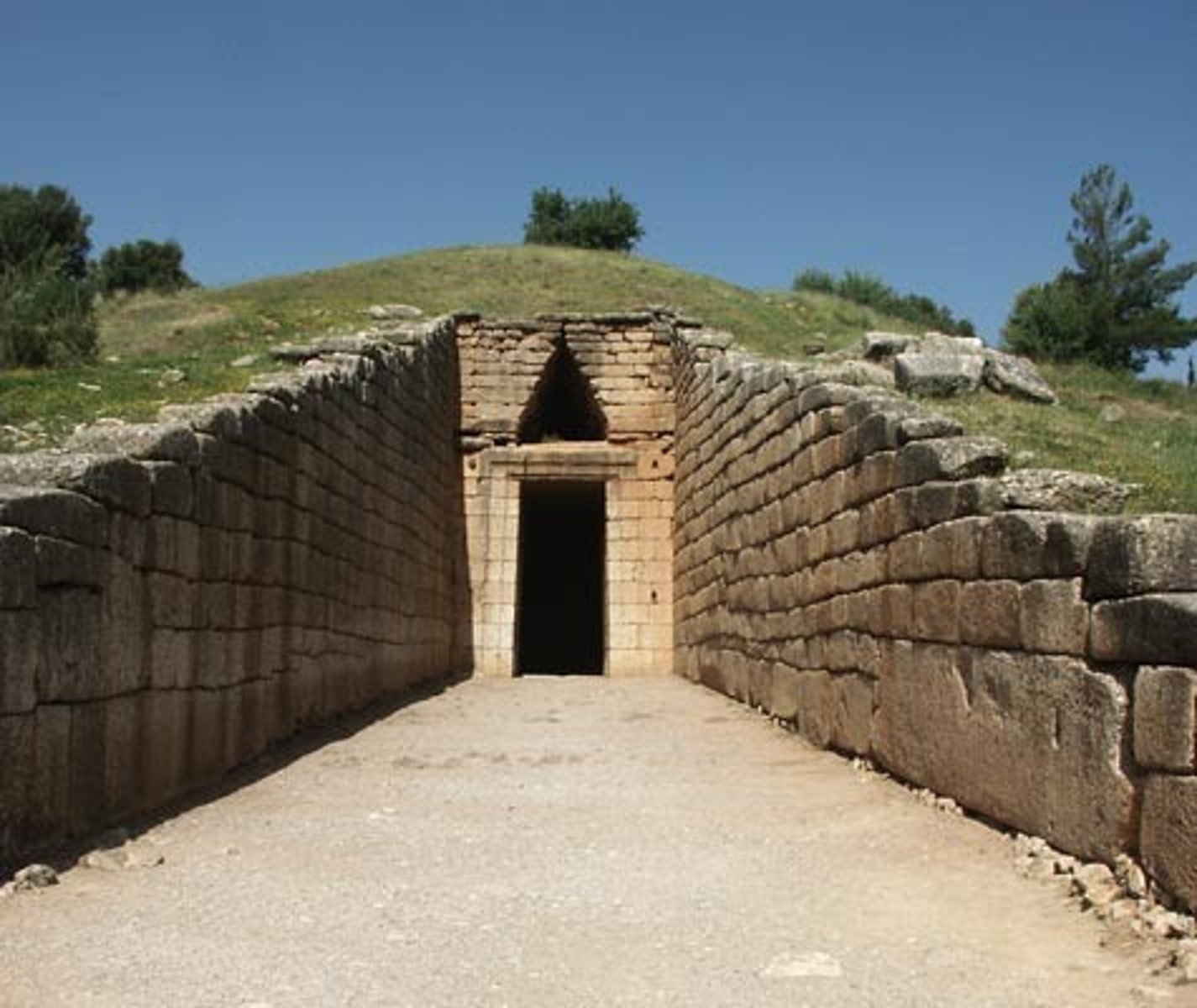
Treasury of Atreus
Mycenae, Greece, 1250 BCE
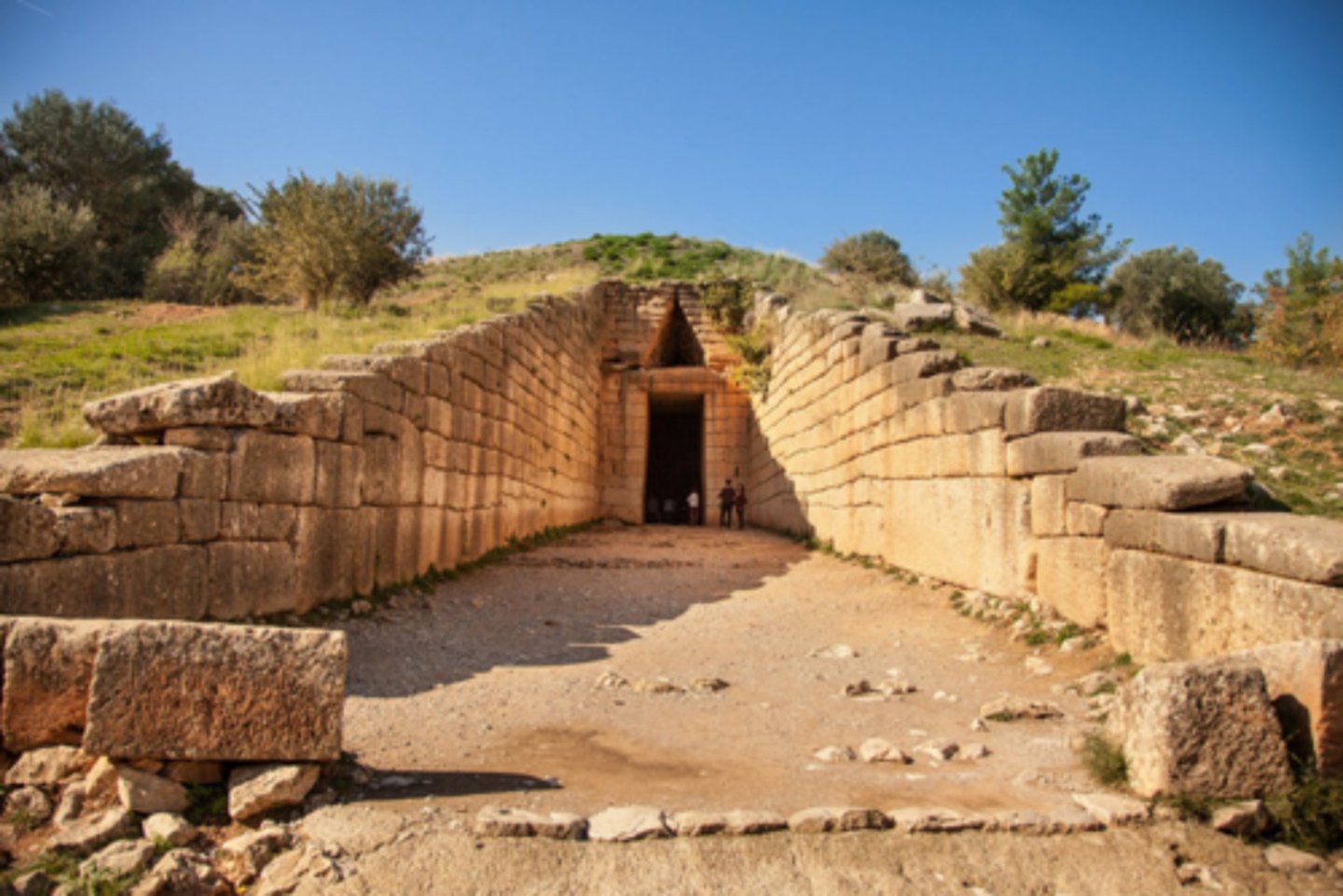

Tholos
circular building with a conical domed, vaulted roof
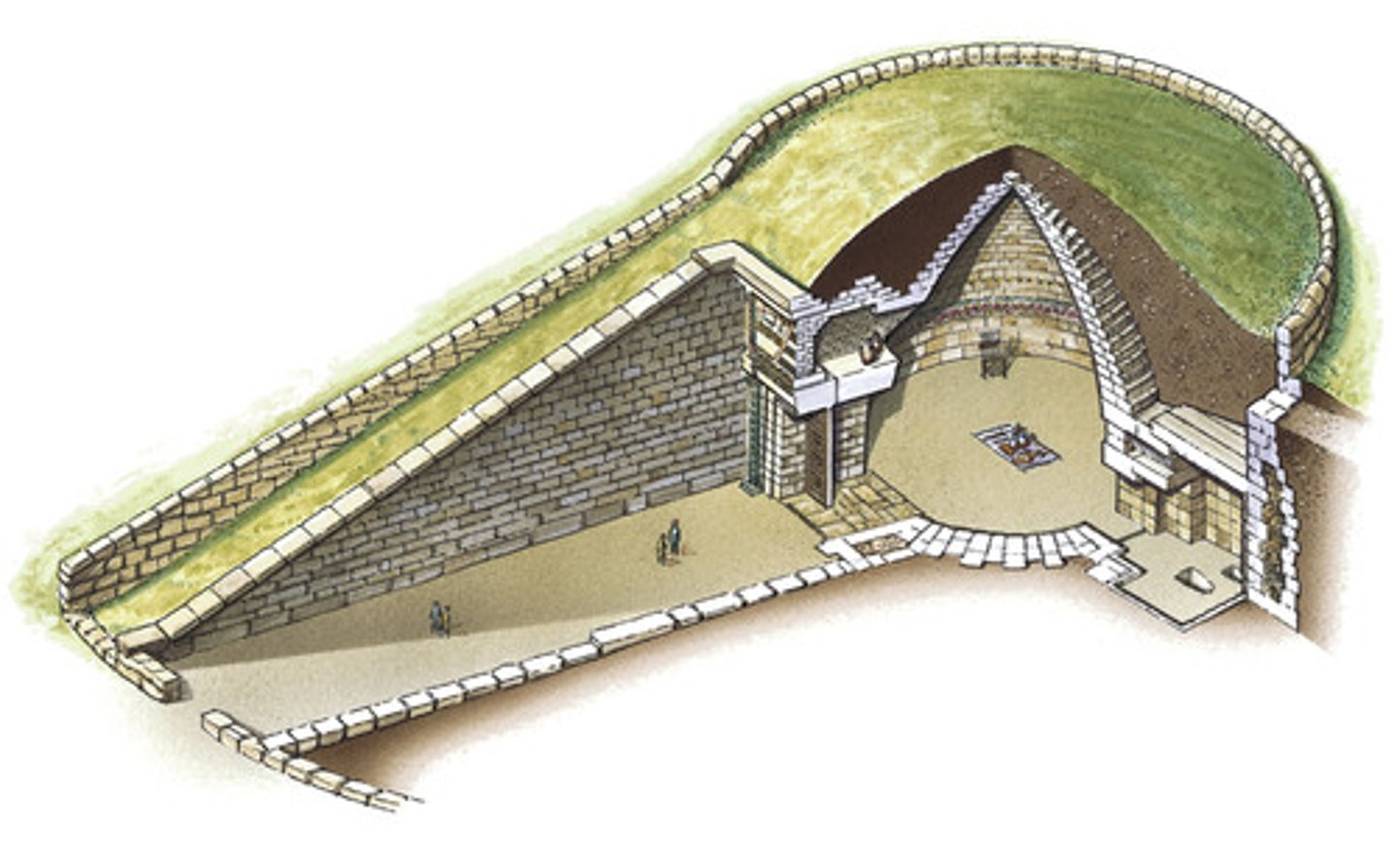
Dromos
long, narrow passage, partly open and within a mound giving access to tholos tombs.

The Hittites
1400 - 1200 BCE, established one of the great empires of the ancient Middle east. The empire encompassed Central Turkey, Northwestern Syria, and upper Mesopotamia.
Famous for skills in building, using chariots, and the use of iron
Hattusas
Bogazkoy, Turkey, 1600 BCE
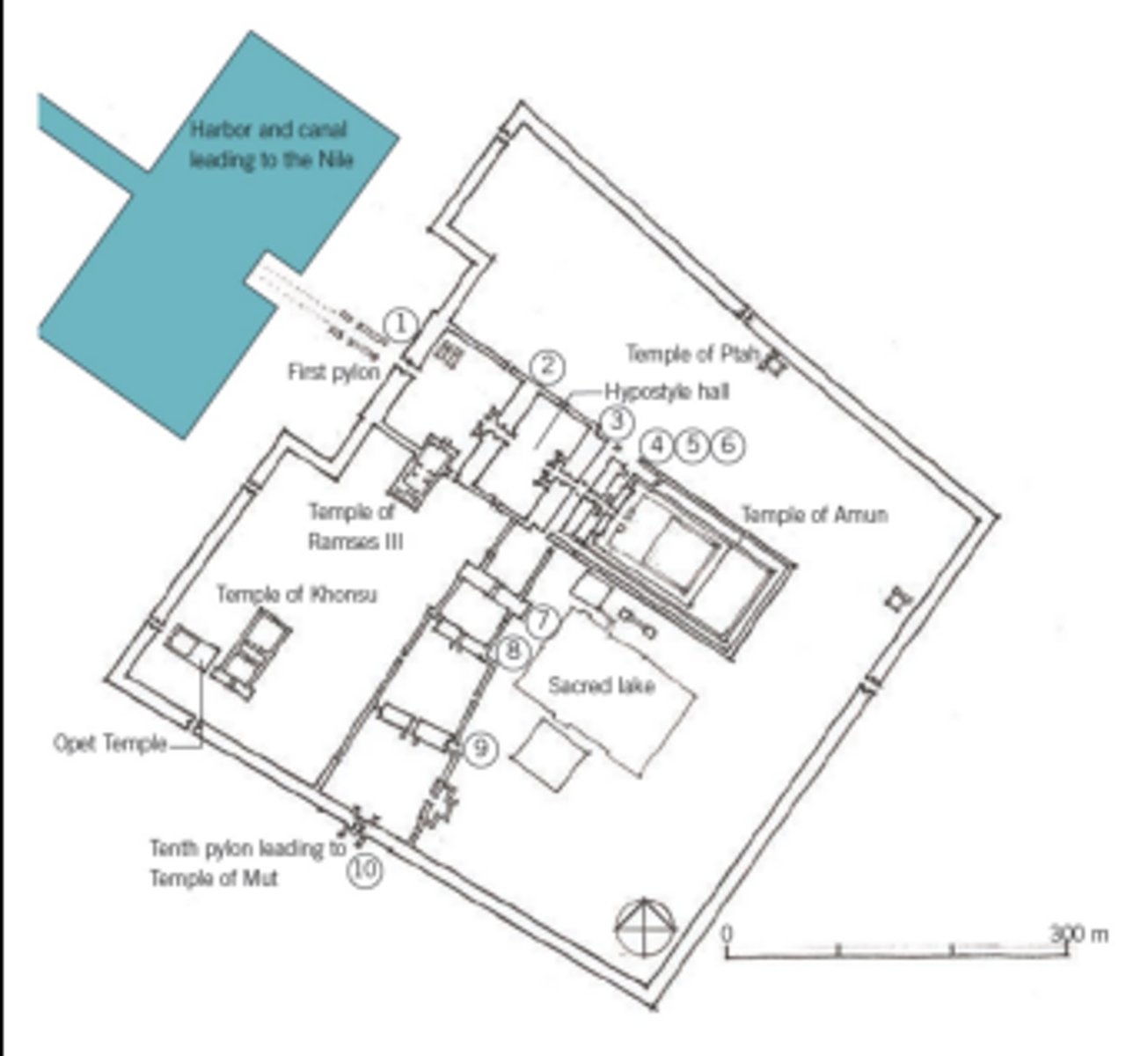
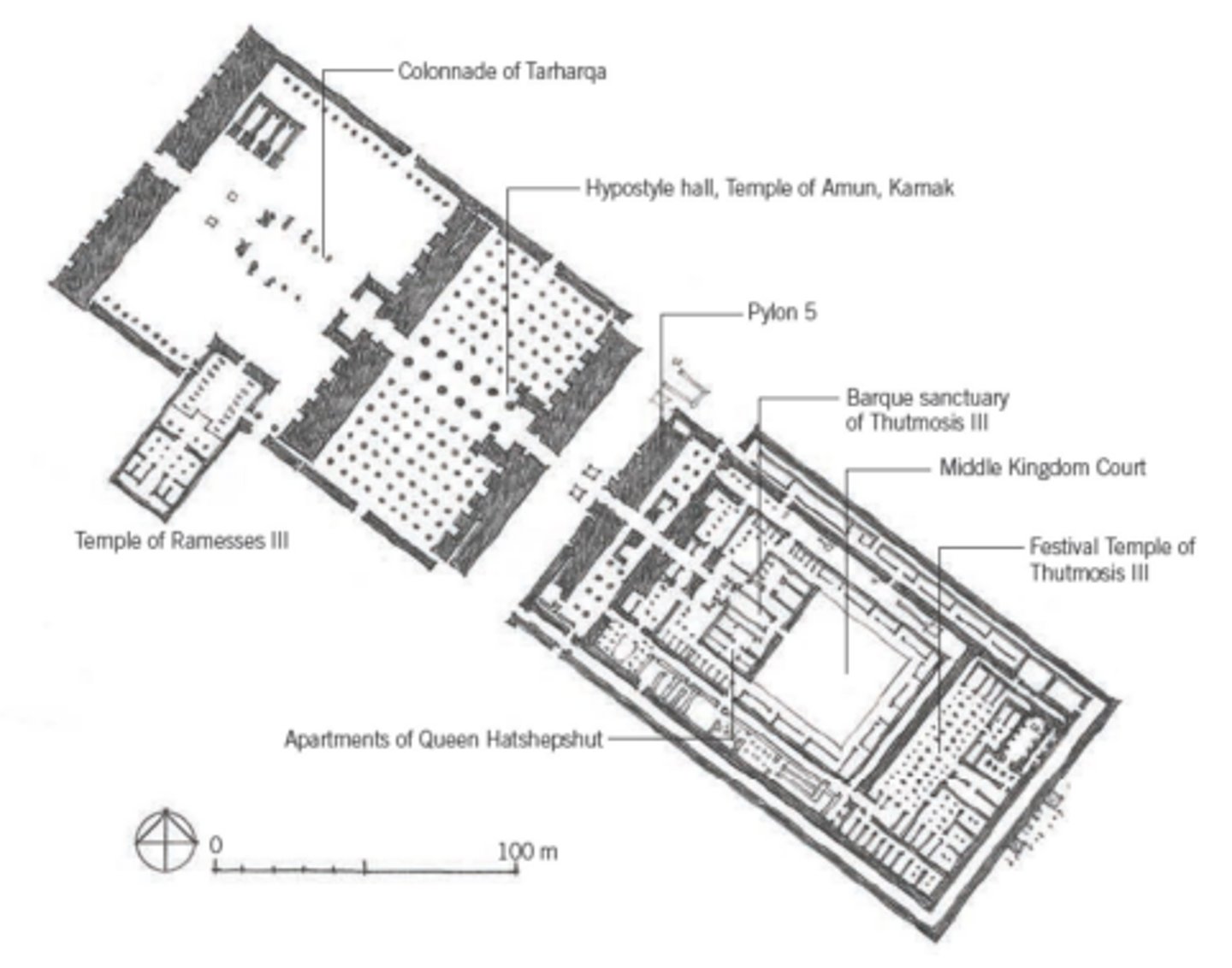
Temple Complex of Karnak
Thebes, Egypt, 1550 BCE
Temple of Amun-re
Pylon
portal of an ancient-Egyptian temple with two decorated battered towers
Hypostyle hall
large room with a flat roof carried on many columns in rows
Old kingdom
Emergence of mortuary complexes, mortuary complex of Djoser at Saqqara and Pyramid of Khufu
Pharohs are in complete control
Religion and preparations for the afterlife are reserved for the elite
Mortuary Temple of Queen Hatshepsut
outside Thebes, Egypt, 1470 BCE