Meiosis, Genetic Diversity, and Cell Death Processes
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Somatic
Relating to the body, excluding the reproductive cells.
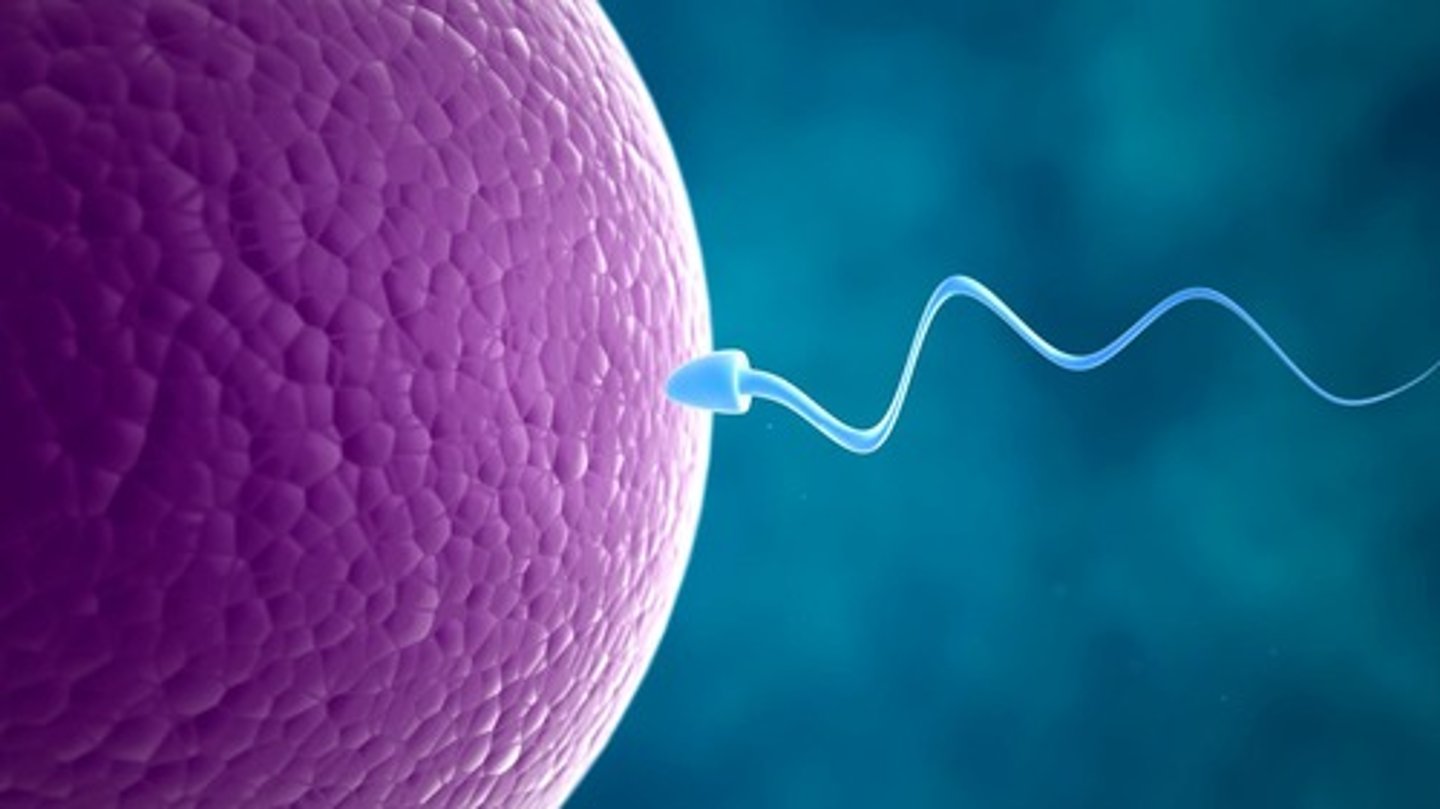
Gamete
Haploid (1n) germ cells created by meiosis; each parent contributes one gamete to an offspring.
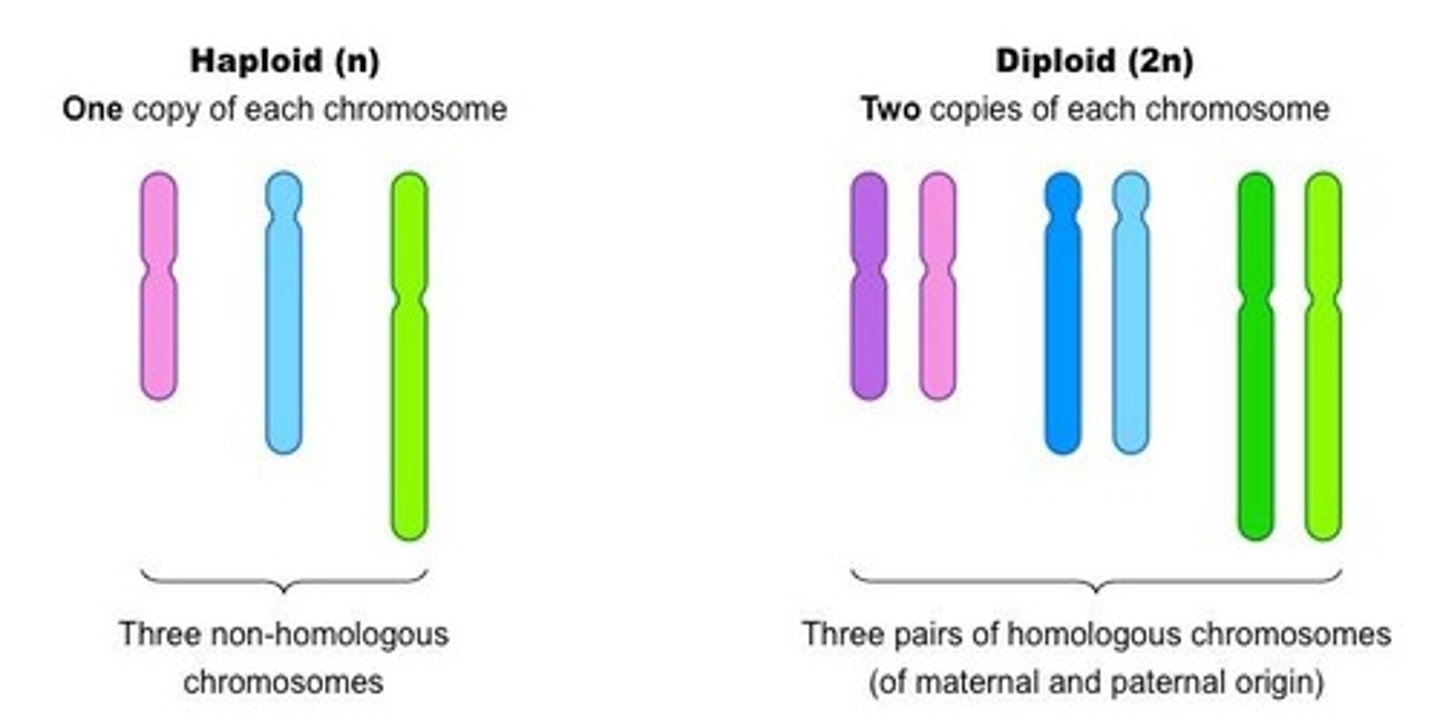
Diploid
Contains 2 copies of every chromosome (i.e. homologous chromosomes).
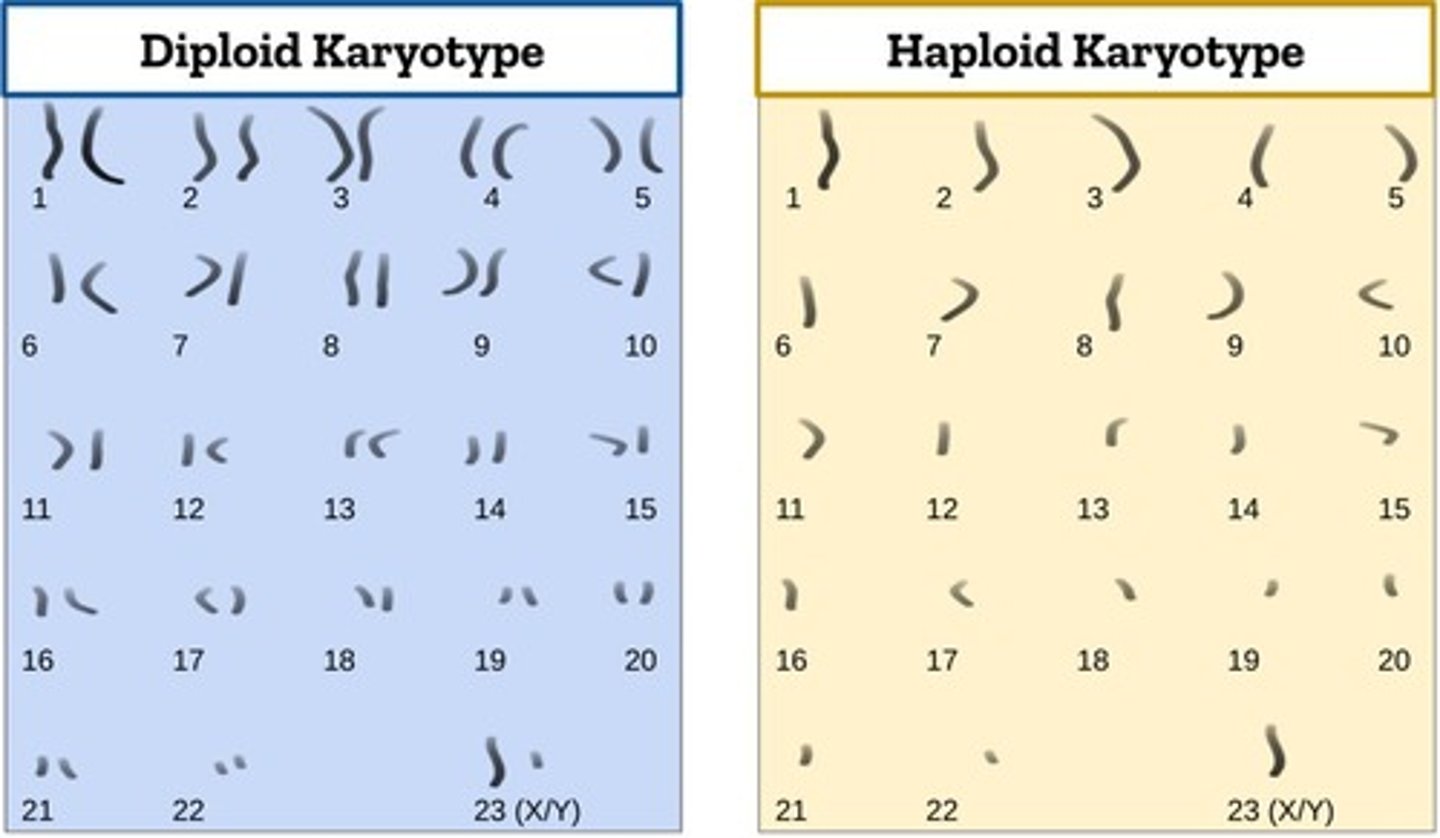
Haploid
Contains 1 copy of every chromosome (1n).
Aneuploid
A condition in which the number of chromosomes is not an exact multiple of the haploid number.
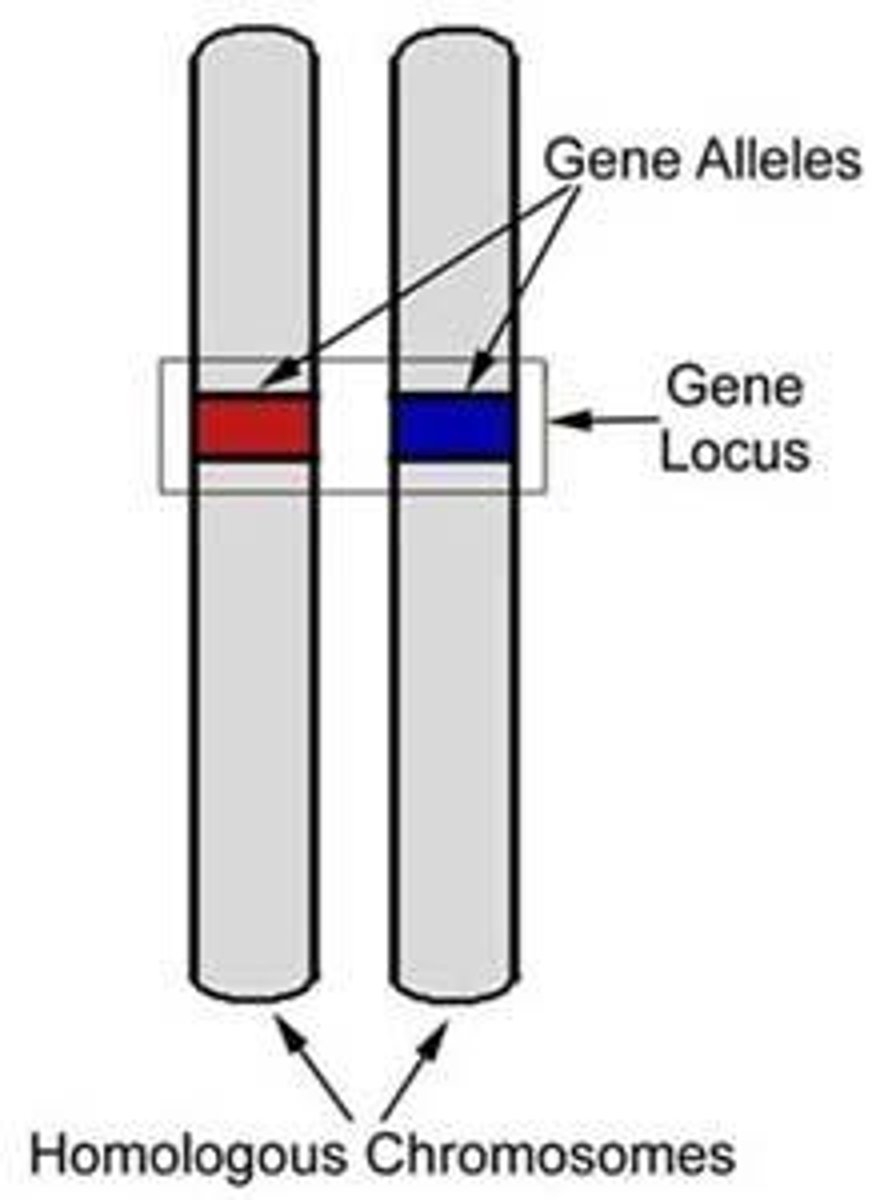
Allele
Different versions of a gene that may exist at a specific locus on a chromosome.
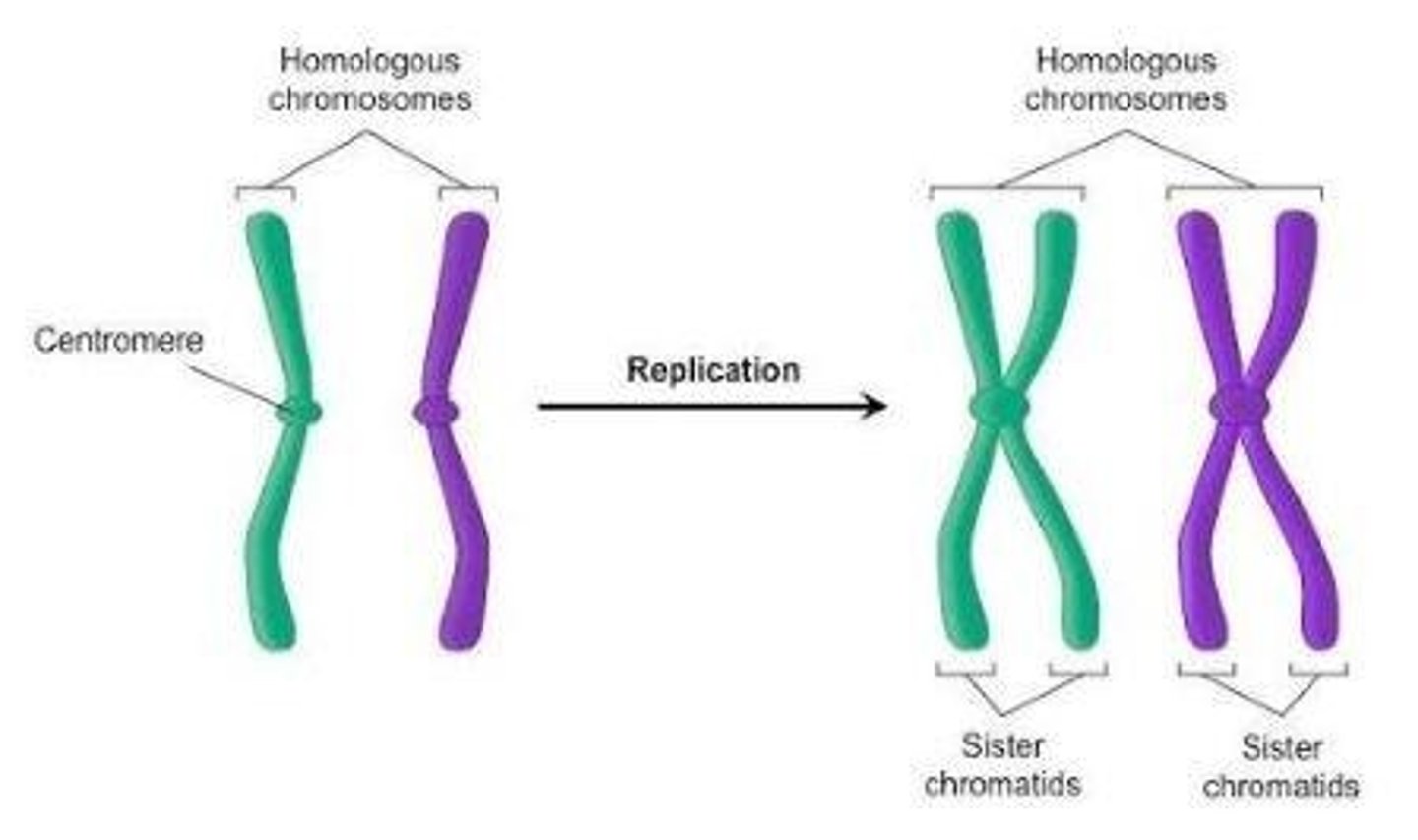
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosome pairs that have the same genes but may have different alleles.
Sister chromatid
Identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a common centromere.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
Polyploidy
A condition in which a cell has more than two complete sets of chromosomes.
Meiosis
A specialized type of cell division used for sexual reproduction that reduces the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
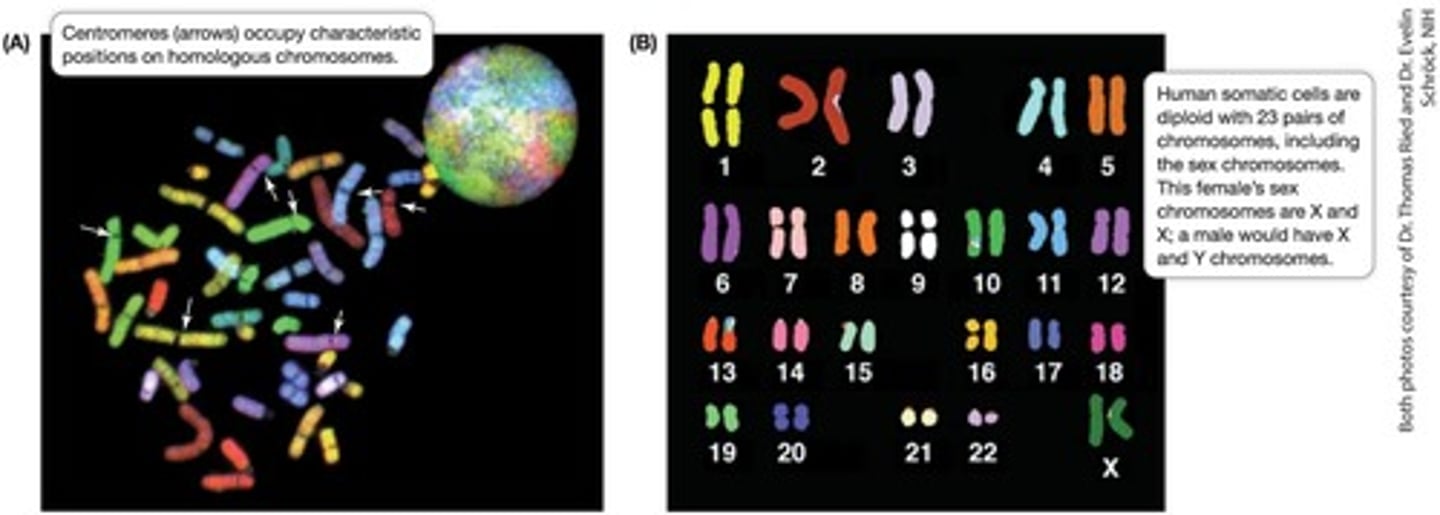
Karyotype
The number, shapes, and sizes of all chromosomes of a cell, used to diagnose abnormalities.
Zygote
The diploid cell formed when two gametes fuse during fertilization.
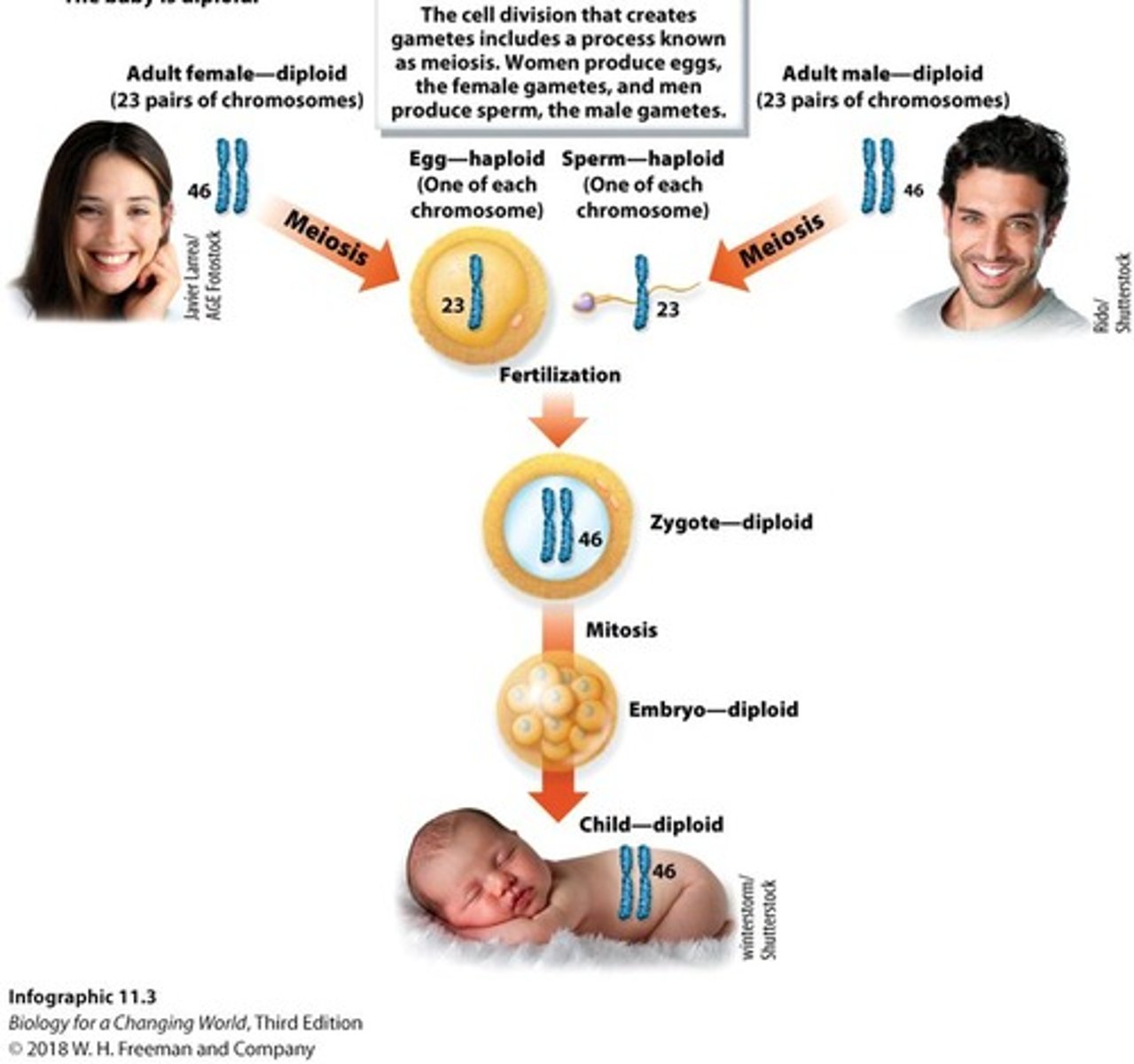
Fertilization
The process where two haploid gametes fuse to form a zygote.
Apoptosis
A process of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms.
Necrosis
The process of cell death caused by injury or disease, leading to inflammation.
Chromosome number reduction
Meiosis reduces the chromosome number from diploid (2n) to haploid (n).
Genetic diversity
The variation in alleles and genes within a population, generated through meiosis.
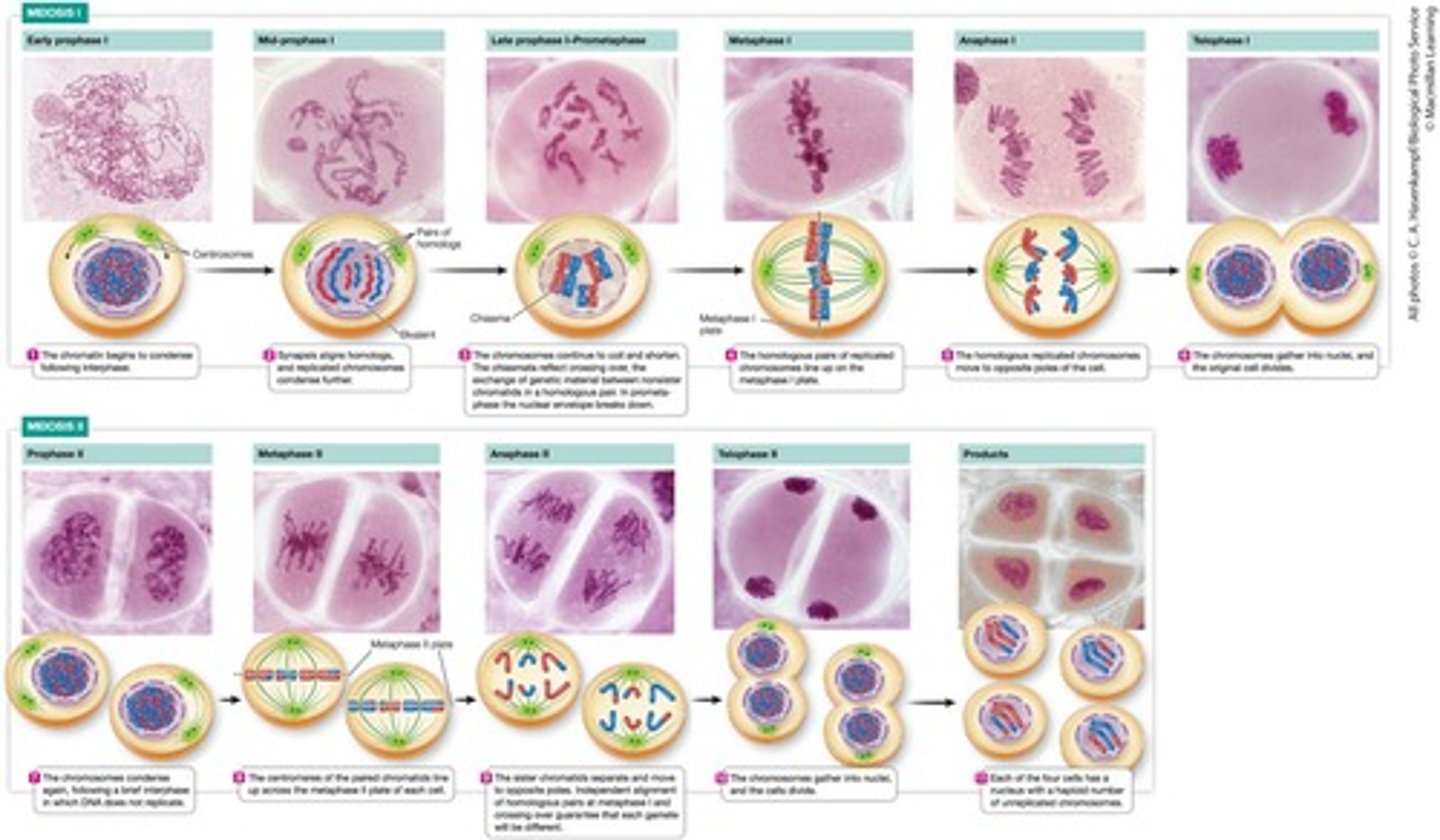
Meiosis I
The first division in meiosis where homologous chromosomes separate, but sister chromatids remain together.
Meiosis II
The second division in meiosis where sister chromatids separate.
Sexual reproduction
Produces offspring that are not identical to the parents through the fusion of gametes.
S phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated before meiosis.
Haploid Nuclei
Two haploid nuclei result, each with half of the original chromosomes (one member of each homologous pair).
Prophase I
In Prophase I, the nuclear envelope dissolves, centrosomes move to the poles and form the spindle apparatus, chromosomes condense and form homologous pairs, and homologous chromosomes pair (synapsis) and form a tetrad or bivalent.
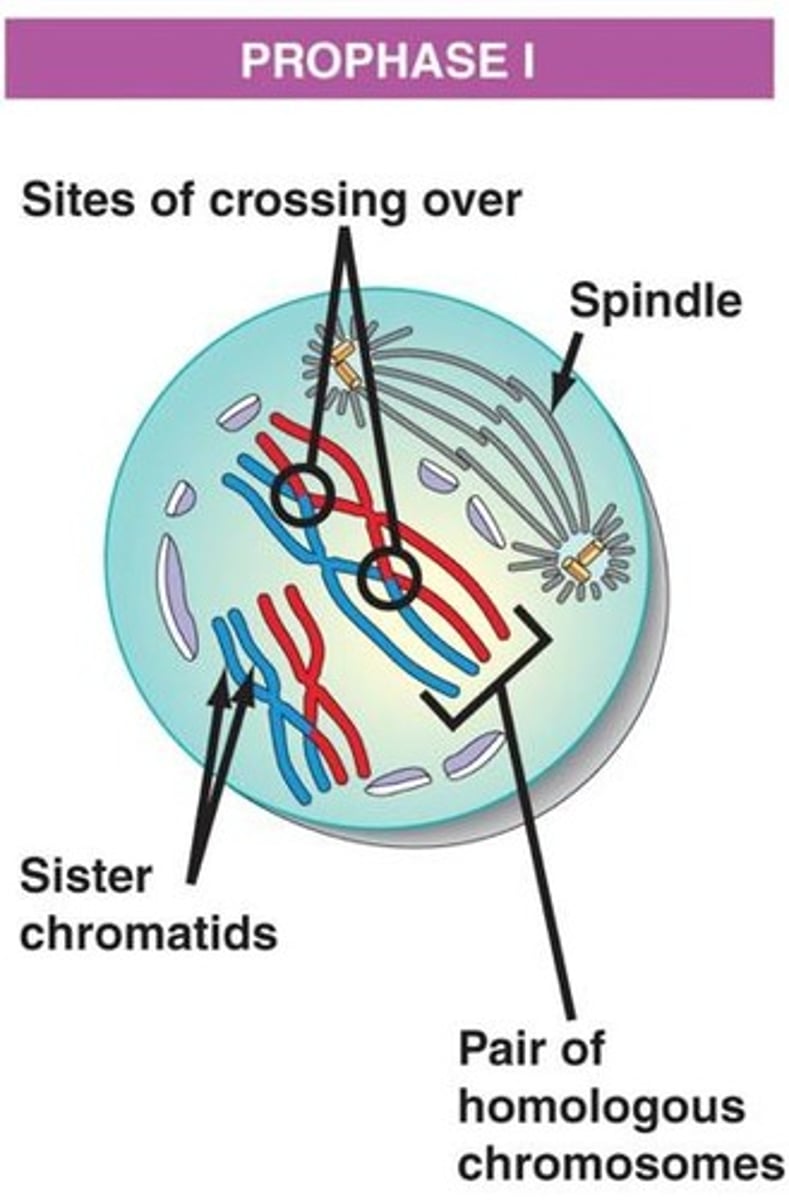
Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids (homologous pairs) at the chiasmata, regions of attachment that form between non-sister chromatids.
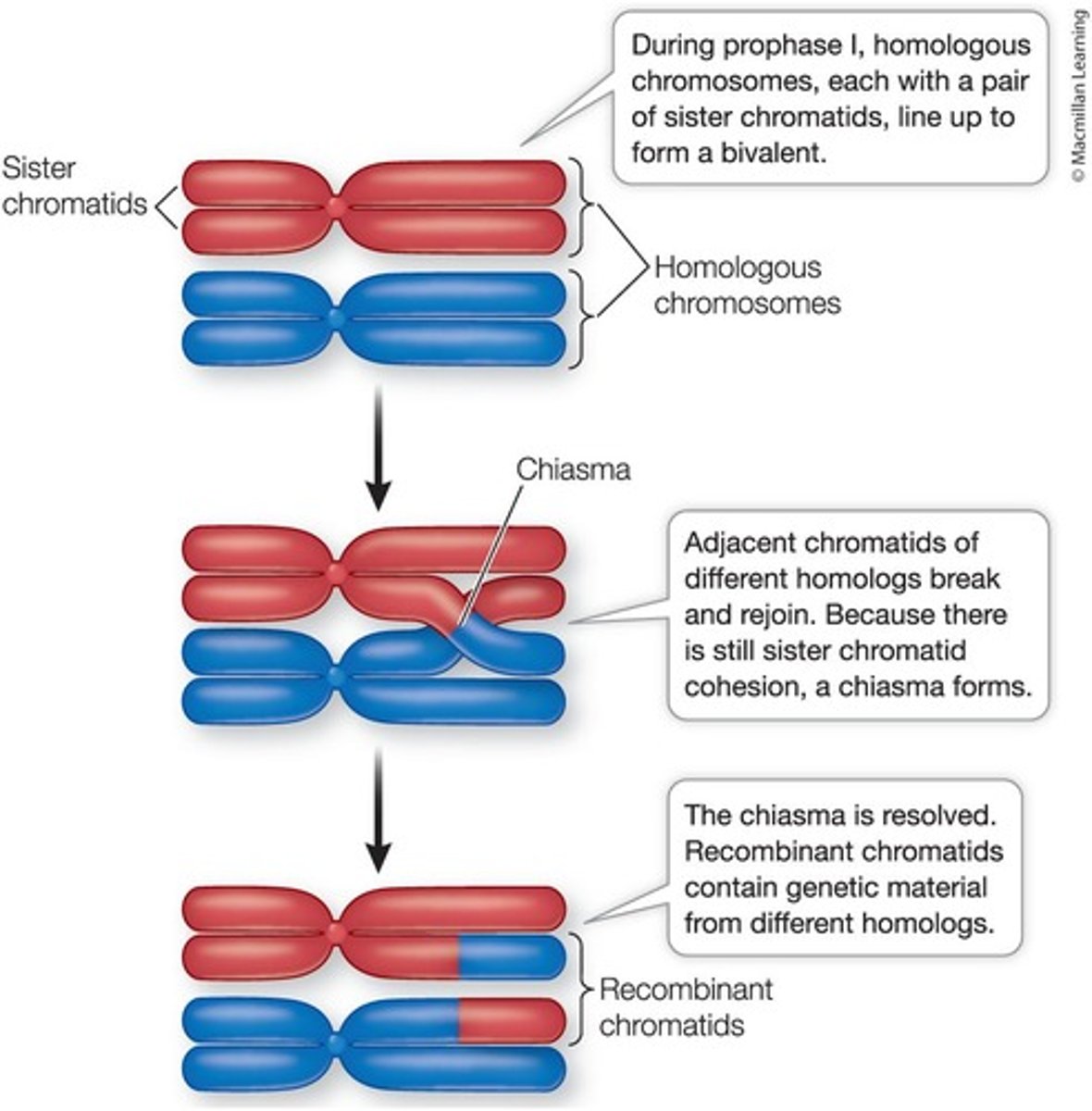
Genetic Diversity from Crossing Over
Crossing over results in recombinant chromatids and increases genetic variability of the products.
Metaphase I
During Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up in the center of the cell, and homologous pairs can line up in any order (independent assortment).
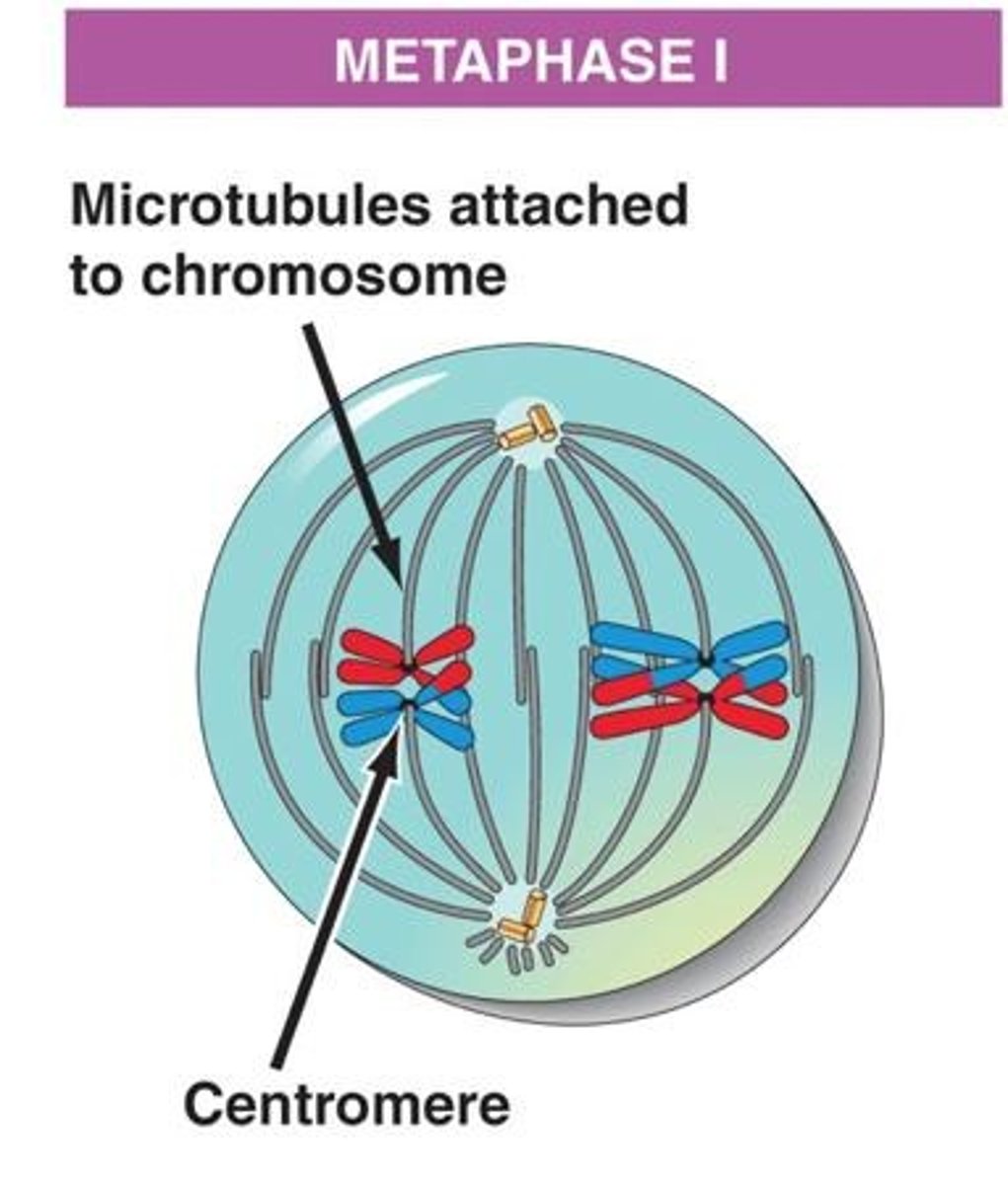
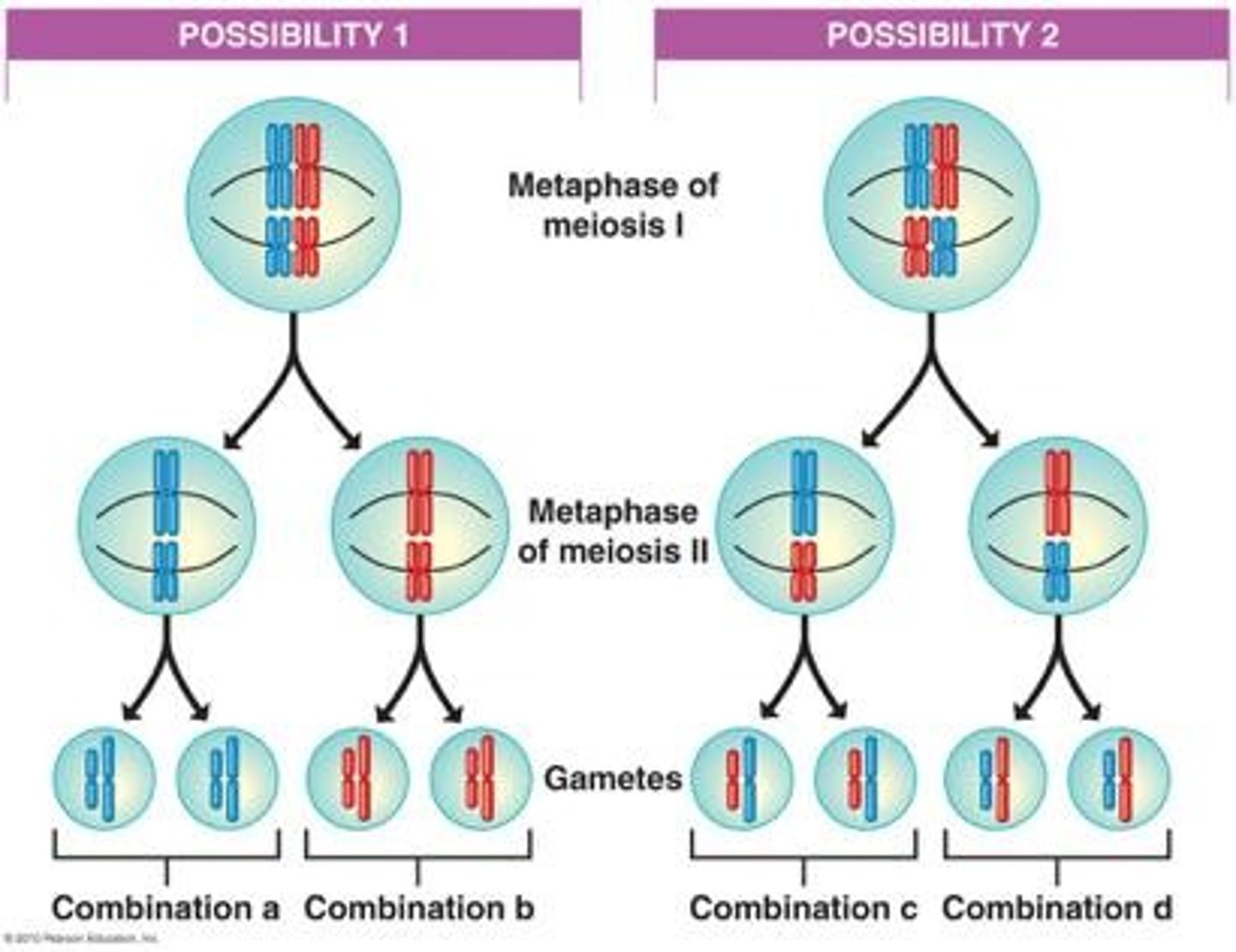
Independent Assortment
Independent assortment is when homologous chromosome pairs align at the metaphase plate, allowing for different alignments each time meiosis occurs, causing the mixing of alleles in gametes.
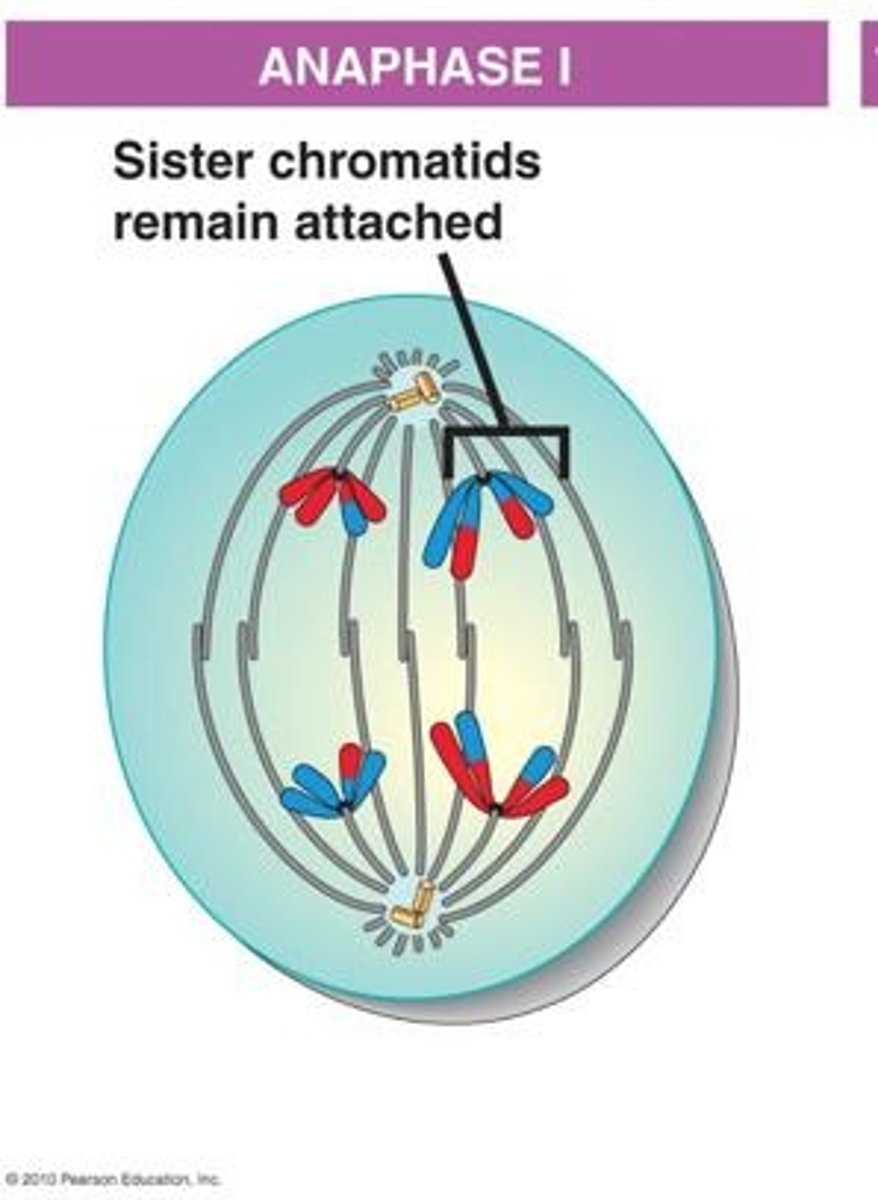
Anaphase I
During Anaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell, while sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere.
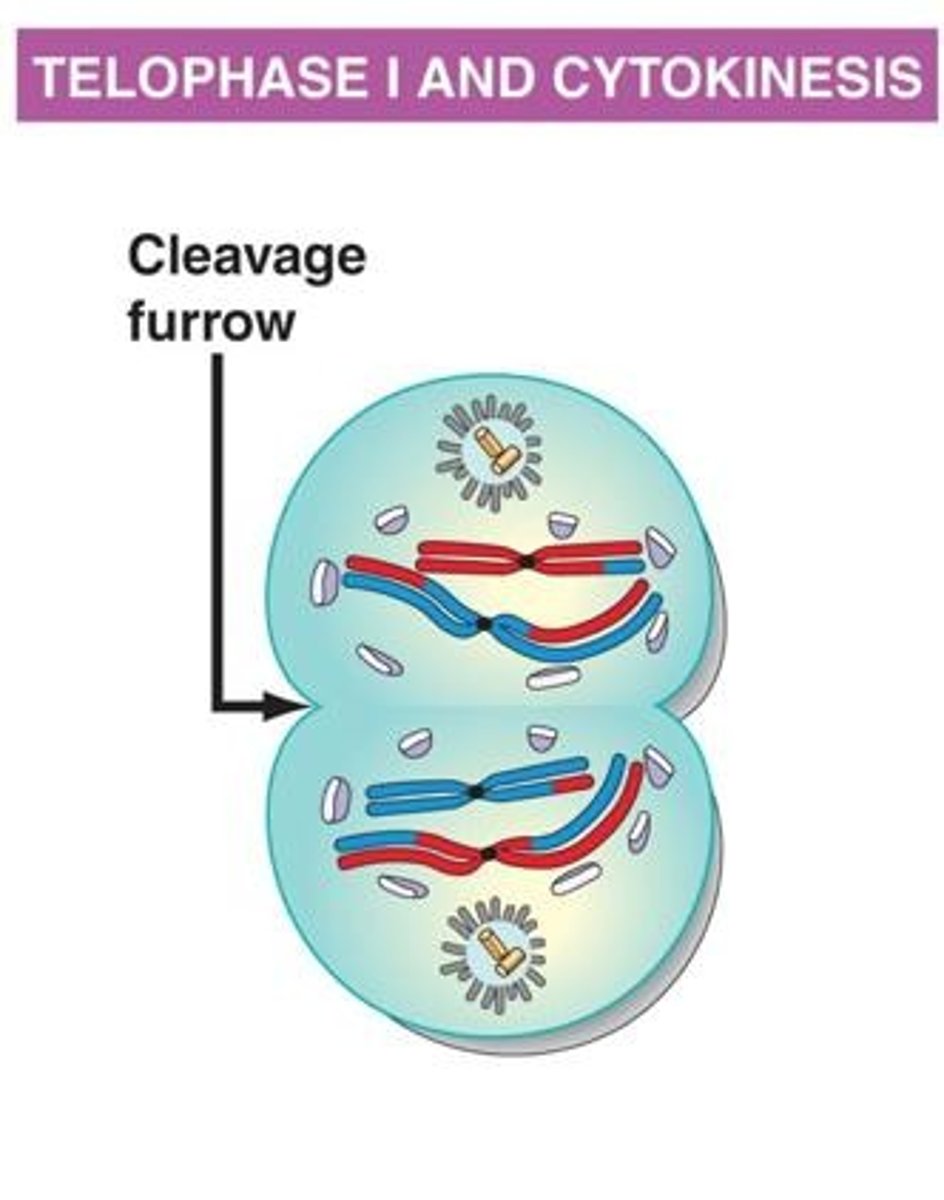
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
During Telophase I, the nuclear envelope reforms, the spindle apparatus dissolves, and the chromosomes unwind, resulting in two haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis II
Meiosis II is not preceded by DNA replication, sister chromatids are separated, and the final products are four haploid daughter cells (n).
Prophase II
During prophase II, chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope dissolves, and the centrosomes move to the poles and form the spindle.
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell in single file just like in mitosis, with no pairs present.
Anaphase II
During anaphase II, the cell elongates, and sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase II and Cytokinesis
During Telophase II, the nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes unwind, and the spindle apparatus dissolves, ending with four haploid daughter cells.
Crossing Over Occurrence
During Metaphase I, crossing over occurs.
Homologous Chromosome Alignment
During Metaphase I, homologous chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell.
Nuclear Envelope in Metaphase I
During Metaphase I, the nuclear envelope breaks up.
Centrosome Migration
During Metaphase I, centrosomes migrate to opposite poles.
Sister Chromatids in Metaphase
During Metaphase II, sister chromatids line up single file in the middle of the cell.
Cells After Telophase I
Upon the completion of Telophase I and cytokinesis, there are two haploid cells.
Independent assortment
The process during meiosis where homologous chromosome pairs are randomly distributed into gametes.
Crossing over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Fertilization
The process of combining two distinct genomes to form a zygote.
Aneuploidy
Cells with an incorrect number of chromosomes, either lacking or present in excess.
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosome pairs or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
Down syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by trisomy 21, characterized by developmental delays and physical features.
Patau Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by trisomy 13, leading to severe intellectual disability and physical abnormalities.
Edwards Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by trisomy 18, associated with a high rate of infant mortality.
Warkany Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by trisomy 8, which can lead to various physical and developmental issues.
Turner's Syndrome
A condition resulting from a missing or incomplete X chromosome in females (XO).
Klinefelter's Syndrome
A condition in males characterized by the presence of an extra X chromosome (XXY, XXXY, etc.).
Trisomy X
A genetic condition in females where there is an extra X chromosome (XXX).
Jacob's Syndrome
A genetic condition in males characterized by an extra Y chromosome (XYY).
Polyploidy
The condition of having complete extra sets of chromosomes (e.g., 3n, 4n).
Triploid
An organism with three sets of chromosomes, often sterile and unable to undergo meiosis.
Necrosis
The process of cell death due to damage or lack of nutrients, leading to cell swelling and bursting.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death that occurs in normal development and removes unnecessary or damaged cells.
Blebs
Membranous lobes formed during apoptosis that break into fragments.
Signal transduction pathways
The processes by which signals are transmitted through cells to initiate responses such as apoptosis.
Mitochondria
Organelles that can be affected during apoptosis, leading to increased membrane permeability and cell death.