AIS Exam 1
5.0(5)
5.0(5)
Card Sorting
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:06 PM on 2/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
1
New cards
What is the definition of AIS?
system that records, processes and reports on transactions to provide financial and non-financial information to make decisions and have appropriate levels of internal controls for those transactions
2
New cards
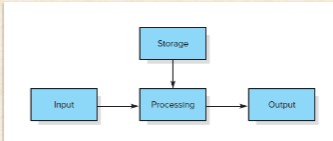
4 elements of of a simple information systems
input, storage, processing, output
3
New cards
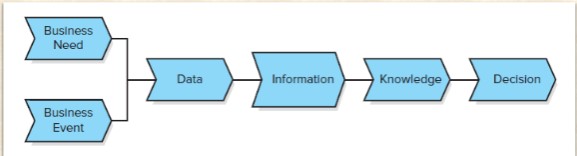
what is the information value chain
The overall transformation from a business need and a business event to the collection of data and information to an ultimate decision
4
New cards
what are the four diff==er==ent roles accountants have
User, manager, designer, evaluator
5
New cards
Describe how business processes affect the firm’s value chain
Primary activities directly provide value to the customer (inbound, operations, outbound, marketing and sales activities, and services). Supporting activities include (infrastructure, HR, technology, and procurement). AIS can add value making each primary activity more effective and efficient
6
New cards
Explain how AIS affects firm value
Making each support and primary activity more effective and efficient
7
New cards
How does AIS assist the firm’s internal business processes
AIS assists in business integration with external parties such as suppliers and customers.
8
New cards
What is a supply chain?
The flow of materials, information, payments, and services from raw materials suppliers, through factories and warehouses. all the wat to the final customers of the firm’s products
9
New cards
What are the 4 AIS strategic roles
Automate: replace human labor
Informate-up: provide info to senior management
Informate-down: provide info to all employees
transform: redefine fundamentals of business processes and relationships
Informate-up: provide info to senior management
Informate-down: provide info to all employees
transform: redefine fundamentals of business processes and relationships
10
New cards
Roles of accounting/finance
1. Finance and accounting processes - pay, cash, report, payroll, treasury
2. Financial close - period end
3. Financial consolidation, reporting, and analysis
4. Providing comprehensive management information
5. People management
1. Using IT to make finance and accounting processes more efficient and effective
\
11
New cards
What is the business process
defined sequence of business activities that use resources to transform specific inputs into specific outputs to achieve a business goal. A business process is constrained by business rules
12
New cards
What is business analysis
The process of defining business process requirements and evaluating potential improvements. Business analysis involves ascertaining, documenting, and communicating information about current and future business processes using business modeling and relating tools
13
New cards
How has SOX made documentation essential
1. Training
2. Describing current processes and systems
3. Auditing
4. Accountability
5. Standardized interactions
6. Facilitating process improvement
\
Well managed businesses
1. Effectiveness
2. Efficiency
3. Internal control
4. Compliance w/ standards and policies
\
14
New cards
What is a business model
A simple, abstract representation of one or more business processes. Typically a graphical depiction of the essential business process information
15
New cards
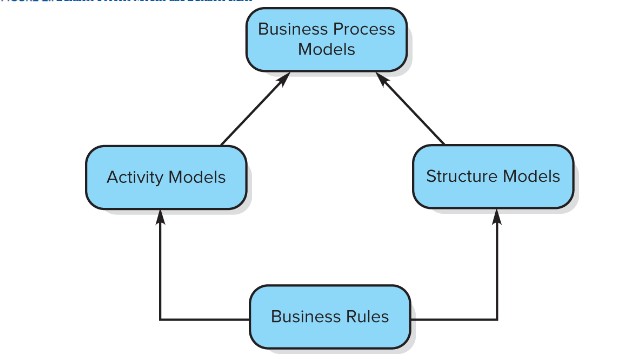
Characteristics of activity models
They describe
1. Events that start, change, or stop flow in the process
2. Activities and tasks within the process
3. The sequence of slow between tasks
4. Decision points that affect the flow
1. Division of activity depending on organizational roles
1. Events that start, change, or stop flow in the process
2. Activities and tasks within the process
3. The sequence of slow between tasks
4. Decision points that affect the flow
1. Division of activity depending on organizational roles
16
New cards
Building Blocks for BPMN
1. Events - start/end
2. Activities - rectangle verb + object
3. Sequence flows - arrow btwn activities
4. Gateways - diamond
5. Annotations - add description
\
17
New cards
What is a pool
BPMN symbols used to identify participants, actors, or persons that perform activities and interact with other participants in a process
18
New cards
What are the lanes
BPMN symbols that provide subdivisions of pools to show, for example, functional responsibilities within an organization
\
\
19
New cards
What are message flows
BPMN represents exchanges between two participants in the same process as message flows which are models as dashed arrows
20
New cards
What is a gateway
Shows process of branching and merging as a result of a decision. Diamond shape
\
\
21
New cards
types of gateways
1. Exclusive - one option (blank diamond or w/ x)
1. Inclusive - one or more (diamond w/ o)
2. Parallel - all (diamond w/ +)
22
New cards
What is an activity
represents specific steps in a business process
23
New cards
Intermediate error
lightening bolt
24
New cards
I+I
subprocess (detailed process hidden)
25
New cards
Message event
envalope
26
New cards
Clock
timer event
27
New cards
Loop w/ arrow
looping (repeat event until satisfy)
28
New cards
3 horizontal lines
sequential (perform task several times at different times)
29
New cards
3 vertical lines
parallel (task performed several times all at same time)
30
New cards
Data object
represents data that is only available for the duration of a process
31
New cards
data store
represents data that is available across processes
32
New cards
association
connects data object/store to an activity. shows direction it flows
33
New cards
purpose of structure models
create a blueprint for the development of a relational database to support the collection, aggregation, and communication of process information
34
New cards
classes
separately identifiable collections of things about which the organization wants to collecct and store information
35
New cards
Associations
\
\
relationship btwn 2 classes
36
New cards
Multiplicities
describe min/max number of times instances can be associated in another class
37
New cards
Best practices for preparing a UML
1. Use common terminology in the organization for class names
2. Link classes on the diagram only when there is a clear business \n purpose for the relationship.
3. Avoid crossing lines where possible
4. Use consistently sized class rectangles
5. Avoid running association lines close together
6. Opt for simplicity
7. Focus first on the accuracy of the content, then address appearance.
1. Use notes to explain more complex situations.
38
New cards
Primary keys + purpose
Attribute or combo of attributes that uniquely identify an instance of a class in a data model or a specific row in a table. Purpose: unique identification
39
New cards
Relationship btwn classes and tables
Each instance of a class maps to a row in a corresponding table. 1:1
40
New cards
Process decision requirements
1. Identify decisions required in the process
2. Describe and document decisions and impact on business objectives
3. Specify decision requirements in terms of information and knowledge required to make the decision
4. Decompose and refine requirements where more are needed
41
New cards
Business rules support process decisions
1. Eligibility or approval
2. Validation
3. Calculation
4. Risk
5. Fraud
6. Opportunity
7. Assignments
8. Targeting
42
New cards
What are business rules
Succinct statements on constraints on business processes. Provide logic of behavior oof the business in a specific situation.
43
New cards
What is a relational data model
Stores information int he form off related two-dimensional tables
44
New cards
Classes in a relational database
Resources, Events, Agents (REA)
45
New cards
Resources (REA)
Cash
46
New cards
Events (REA)
Purchasing
47
New cards
Agents (REA)
Supplier
48
New cards
Tables (relational database)
Store Data
49
New cards
Attributes (relational database)
characteristics, properties, or adjectives that describe each class
50
New cards
Records (relational database)
represents all specific data values that are associates with once instance
51
New cards
What is main purpose of using foreign key
Provides logical relationship or link between two tables
52
New cards
SQL
Computer language designed to retrieve data from a relationship database
53
New cards
FROM \[\]
indicates name of table retrieving from
54
New cards
SELECT \[\]
which columns of table included in query
55
New cards
WHERE \[\]
criteria that must be met to be shown
56
New cards
\*
all columns should be selected
57
New cards
GROUP BY \[\]
aggregate functions based on one or more columns
58
New cards
ORDER BY \[\] ASC/DSC
ASC or DSC
59
New cards
BETWEEN
end points of a range
60
New cards
What is cloud computing
Using redundant servers and multiple locations to host virtual machines
61
New cards
Business activities associated with the sales collection process
1. selling products and services
2. maintaining customer records
3. billing customers
4. recording payments from customers
1. aging accounts and authorizing credit
62
New cards
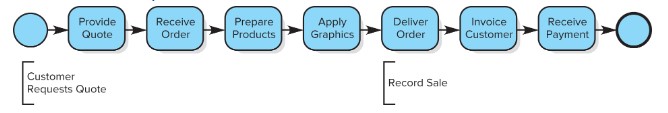
Basic Sales Activity Model
Start > provide quote > receive order > prepare products > apply graphics > deliver order > invoice customer > receive payment > end
63
New cards
Collaboration
BPMN model showing tow participant models and the interactions btwn them in a process
64
New cards
choreogrpahy
science of examining raw data, removing excess noise from dataset, and organizing data w/ purpose of drawing conclusions for decision making
65
New cards
Orchestration
BPMN sequence of activities within one pool
66
New cards
access control
limit who can use and change record in the system
67
New cards
application control
ensure data integrity and an audit trail
68
New cards
What is a type image
Represent management information to help manage a business process. allows process information to be summarized by category
69
New cards
Multiplicities indicate location of foreign keys for
one-to-many associations (primary key of one is foreign key in another)
70
New cards
Multiplicities indicate linking tables for
Many-to-many associations (primary key of both tables used in one table)
71
New cards
Business activities associated with purchasing and payments process
1. buying inventory form supplier
2. maintaining supplier records
3. making payments to suppliers for trade account payable while taking appropriate purchase discounts
72
New cards
Purchases and payments business process
start > request prices and availability > place purchase order > receive items > send payment > end
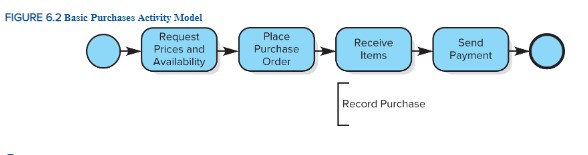
73
New cards
What is the primary objective of conversion process
generates accounting transactions to record the transfer of raw material to WIP and WIP into finished goods
74
New cards
Business activities associated with conversion process
1. Maintaining inventories of raw materials and finished goods
2. Producing finished good form raw material
3. tracking direct labor and direct equiptment costs
4. Apply OH
75
New cards
Basic Conversion Activity Model
start > authorize production > issue raw materials > perform work > complete production > end
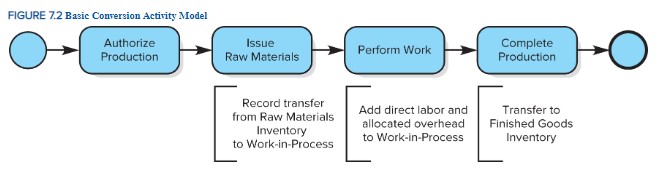
76
New cards
what is an Enterprise System
centralized database that collects data throughout the firm. Integrates and automates business processes across a firm’s value chain within and across organizations.