10-Stable Isotopes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are applications of stable isotopes in science?
thermometry
palaeoclimatology
tracers
processes
also biological, medical, chemical
What is isotope fractionation?
fractionation refers to the partial separation of two isotopes of the same element, producing reservoirs with different ratios of isotopes.
Differences called isotopic anomalies
2 ways isotopic fractionation occurs:
equilibrium isotope fractionation, due to differences in bond energies of isotopes in compounds
kinetic isotope fractionation, due to differences in average velocity or reaction rates of different isotopes
Both depend only on the mass of the isotope and are called mass dependent fractionation; both will fractionate, say 18O/16O about twice as much as 17O/16O
Strange mechanism is mass-independent fractionation and depends on molecule symmetry
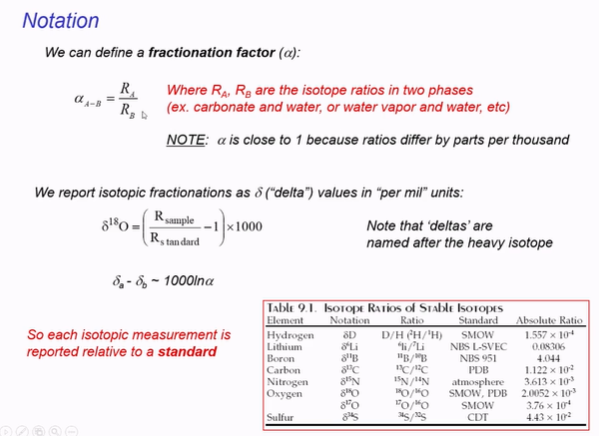
Calibrated - when measured against a standard.
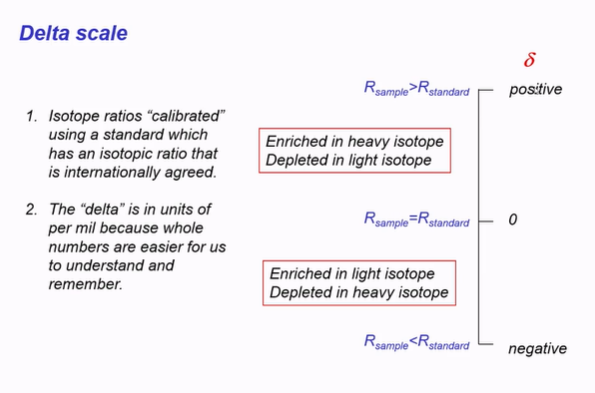
Describe this image:
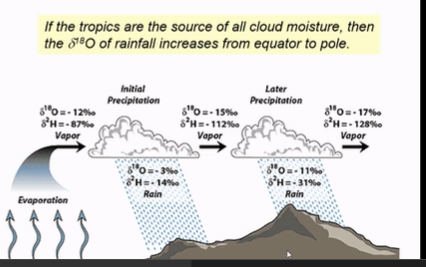
1. Symbols to know
δ¹⁸O = ratio of oxygen-18 to oxygen-16 in water
δ²H = ratio of deuterium (heavy hydrogen) to normal hydrogen in water
Higher δ-values = “heavier” water (more ¹⁸O or ²H)
Lower δ-values = “lighter” water (less ¹⁸O or ²H)
2. Process illustrated
Evaporation at the tropics
Ocean water evaporates → water vapor is slightly lighter (¹⁶O and ¹H evaporate more easily)
Initial vapor has δ¹⁸O = 12‰, δ²H = 87‰
Rainout as clouds move poleward
As clouds move away from tropics → rain falls
Heavy isotopes (¹⁸O, ²H) preferentially fall first → rain has lighter isotopes
Remaining vapor becomes progressively enriched in heavier isotopes
Later precipitation (farther from tropics)
Rain now has δ¹⁸O = -11‰, δ²H = -31‰ (lighter than initial rain)
Vapor now has δ¹⁸O = 17‰, δ²H = 128‰ (heavier than initial vapor)
3. Simple takeaway
Clouds lose heavy isotopes as rain falls
Rain farther from the tropics is lighter (lower δ¹⁸O, δ²H)
Vapor left behind becomes heavier
This is why polar ice has very low δ¹⁸O and δ²H — it comes from tropical moisture that has rained along the way
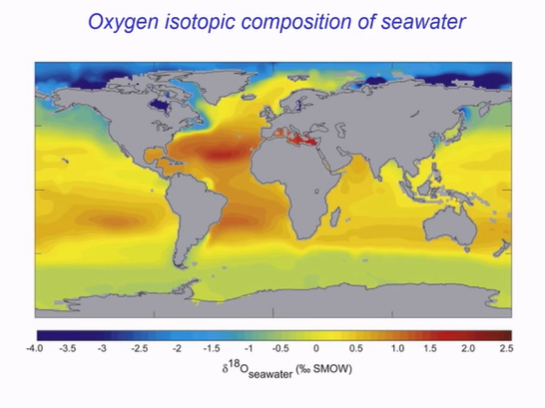
Explain:
Equator evaporation occurs, leaving behind the heavy isotopes, meaning high 18O in high evaporation places, isotopically heavier.
Polar regions, less evaporation. So polar sea water lighter.
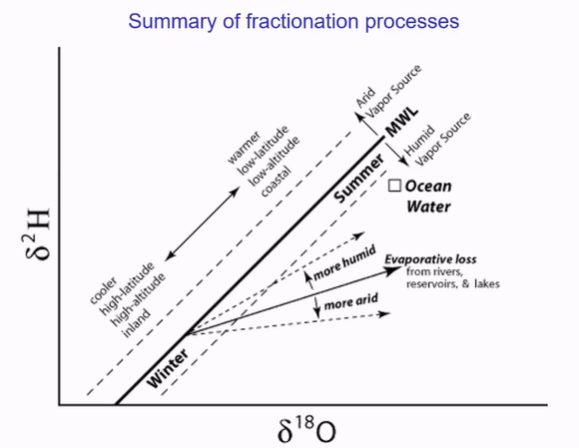
Water heavier in summer, more evaporation. Lower latitudes, isotopically heavier.

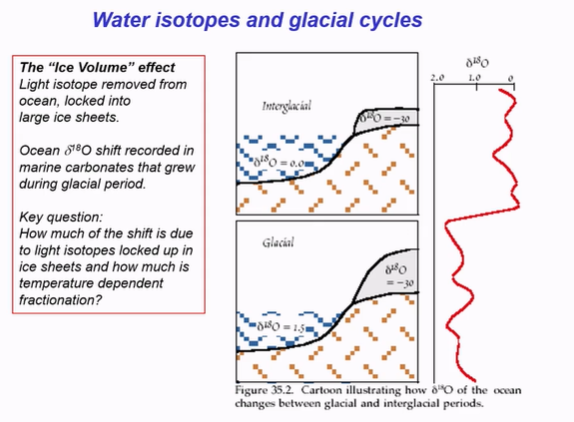
What is the ‘Ice Volume’ effect?
Light isotope removed from ocean, locked into large ice sheets.
Glacial period 18O value more negative, as lighter, and ocean water is heavier.
The standard use for oxygen isotopes in fluids is…
SMOW
standard mean ocean water.
Hydrogen isotope fractionation is much greater than oxygen isotope fractionation because…
Oxygen has smaller mass difference between isotopes
Calcite water fractionation is principally controlled by…
Temperature
If ocean water evaporates to form clouds, isotopically speaking…
Cloud will be lighter and the rain will also be lighter than the ocean
Milankovitch cycles relate to
orbital variation
What is useful for studying Milankovitch cycles?
Groundwater, tree rings, ice cores
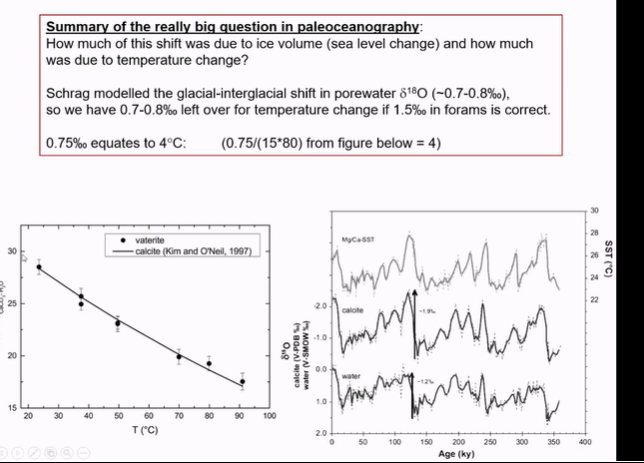
The ice volume effect allows you to calculate
Change in 18O of oceans.
Pore fluids provide independent confirmation of …
d18O of oceans
Foraminifera are problematic as palaeoclimate archives because
-shells might have recrystallised after death
-shells of different ages might get mixed together
-height in water column will affect the ambient temperature
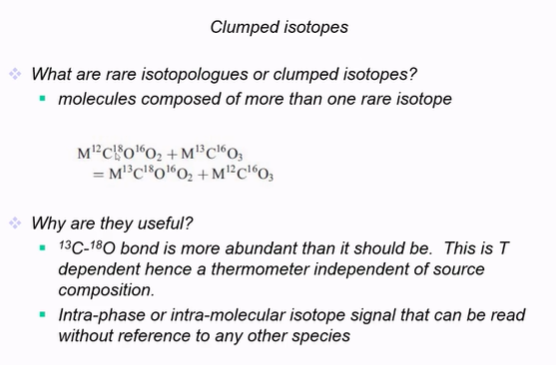
Carbonate clumped isotopes can circumvent problems with interpretation of ‘standard’ stable isotopes because
Temperature is determined by just analysing the carbon and oxygen isotopes.