1: Earth System Science, The Rock Cycle and the Climate System
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Name the Main Spheres of the earth system
Biosphere - all life on earth
Atmosphere - Gaseous envelope around earth including water, aerosols etc
Lithosphere - Upper part of earths surface
Cryosphere - All frozen earth components
Hysrosphere - All water on earth in liquid form
(bio)geochemical cycle
A natural in which elements, chemical compounds and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another.
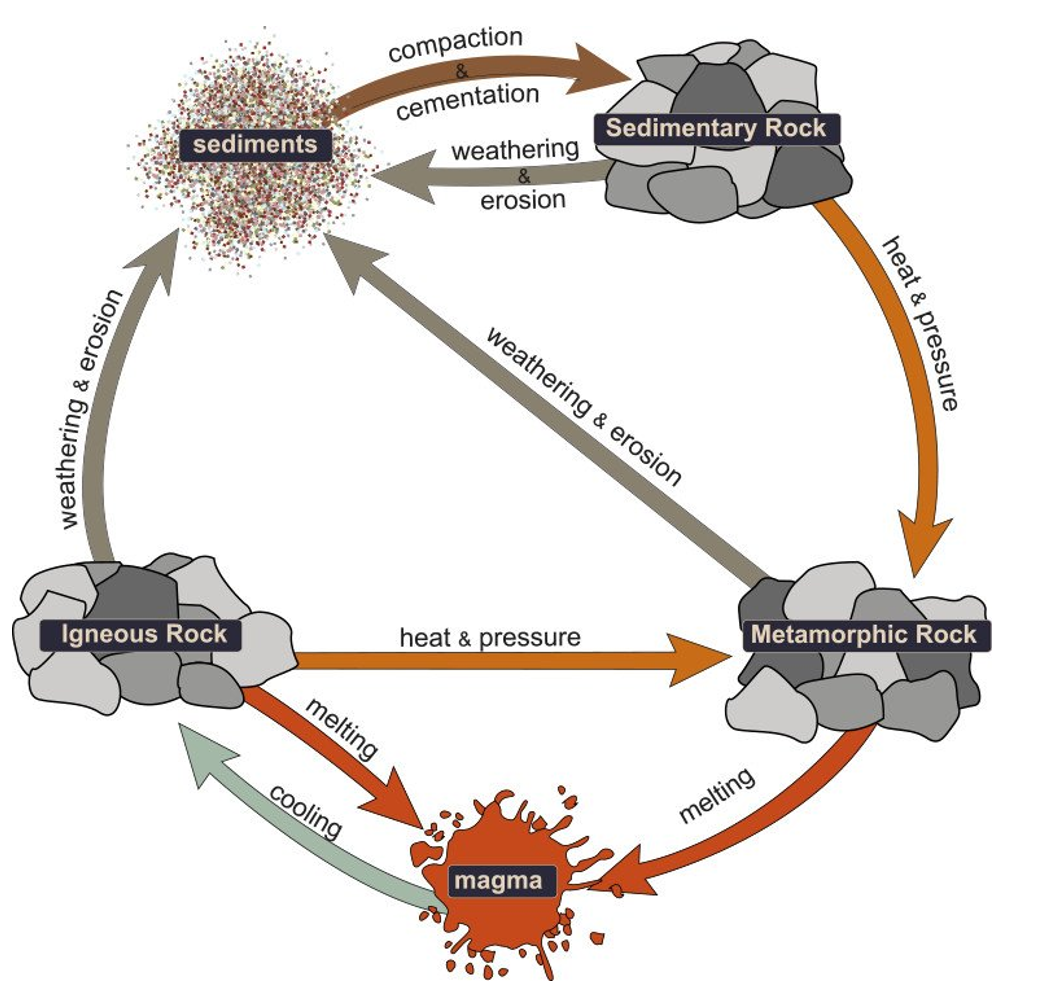
what is the rock cycle
rocks change physical and chemical properties when forced out of equilibrium
changes in T and P, driven by tectonics
aided by hydrological cucle, gravity and life
driven by earths internal heat
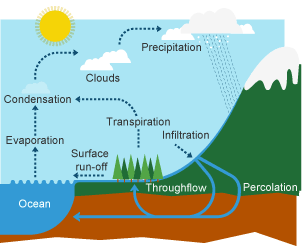
what is the hydrological cycle driven by
suns energy that circulates water through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
explain why energy and mass transfer from one reservoir to another
heat energy is unevenly distributed on earth due to rotation, revolves around sun, tilted, non spherical
mass can be moved into positions where new temp/pressure cause it to become unstable
mass and energy move through gradients
what is earths tilt
23.5 degrees
chemical model of earths differentiation
subdivision of planet based on chem comp
mechanical model of earths differentiation
based omn changes in rheological properties of rock (how squishy or hard)
lithosphere, asthenosphere, outer + inner core
thinning of lithosphere = divergent
thickening of lithosphere = convergent
asthenosphere
part of the upper mantle
weak + undergoes low rates of ductile deformation as result of thermal gradients
lithosphere
rigid outer later of the earth
compromises a number of coherent plates
brittle
Define and give examples of a positive feedbacks in earths climate system
process internal to the earths climate that acts to enhance the original action
e.g. water-vapour feedback:
temp increase = evaporation increase = more vapour in air (GHG) = air temp increase
Define and give examples of negative feedbacks in earths climate system
Process internal to earths climate that counteracts/moderates the original action
e.g. cloud feedback:
temp increase = evaporation increase = more vapour = more clouds = more reflection of solar radiation = decrease in temp
Describe the evolution of the earths atmosphere
repeated melting of eart led to differentiation of internal structure. volatiles were expelled as volcanic gases (N, CO2, H2O, NH3, H2SO4, SO2)
Water vapour condenses along with soluble gases (SO4) as the planet cools, forming the first oceans. this leaves nitrogen and CO2 dominant.
Nitrogen could have also arrived with comets/released by denitrifying bacteria/oxidation of ammonia
describe the origin of carbon
stored as organic matter in limestone (CaCO3)
didnt exist in early precambrian
if all these storehouses were converted to CO2, levels would be 100-1000s x present level (0.04%)
describe the origin of oxygen
photosynthesis from plants and cyanobacteria
other planets lack oxygen and so did the early earth
increase in conc occured ~2.5Ga by around 1-2%
why has the atmosphere remained relatively stable
sustained life requires a consistent temp
higher CO2 in proterozoic led to greenhouse effect then strong cooling as levels decreased
brightness of sun has increased 25-30% during lifetime of earth
Explain and offer hypotheses for the Faint Young Sun Paradox
Feedback between solar radiation and removal of CO2
- CO2 pressure as large as 10 atmospheres?
if sun is stronger, oceans warm = increase evaporation = rainfall increase = more weathering = removal of CO2 from atmospheremethane as much as 100 ppm (currently ~1.7ppm) could have offset the faint sun
Lower albedo (continental area)
Different models for evolution of the sun
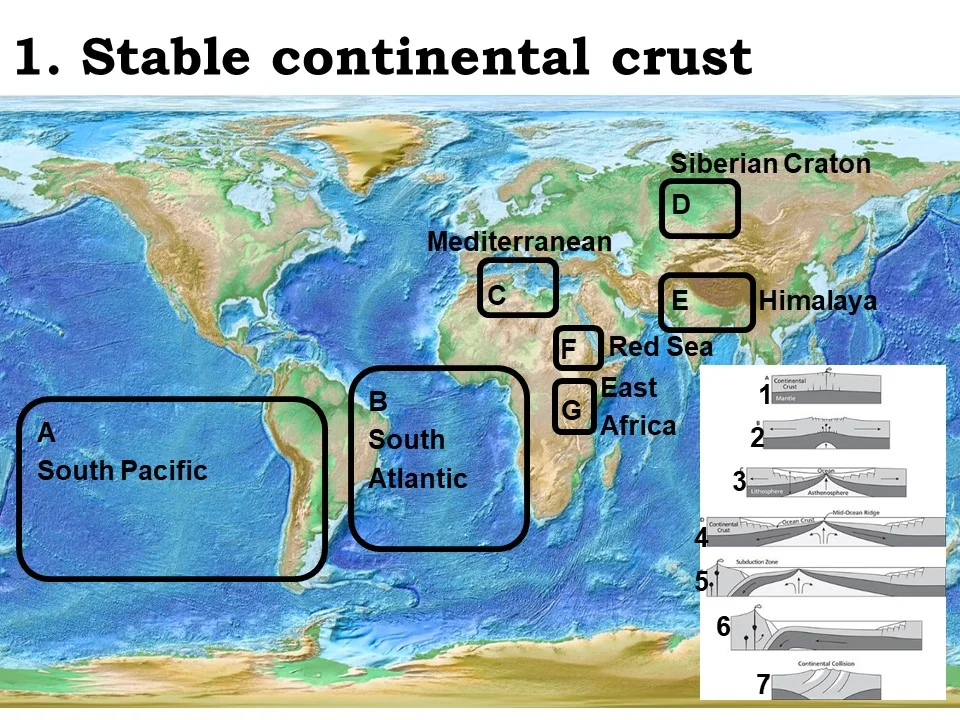
stable continental crust
Siberian Craton
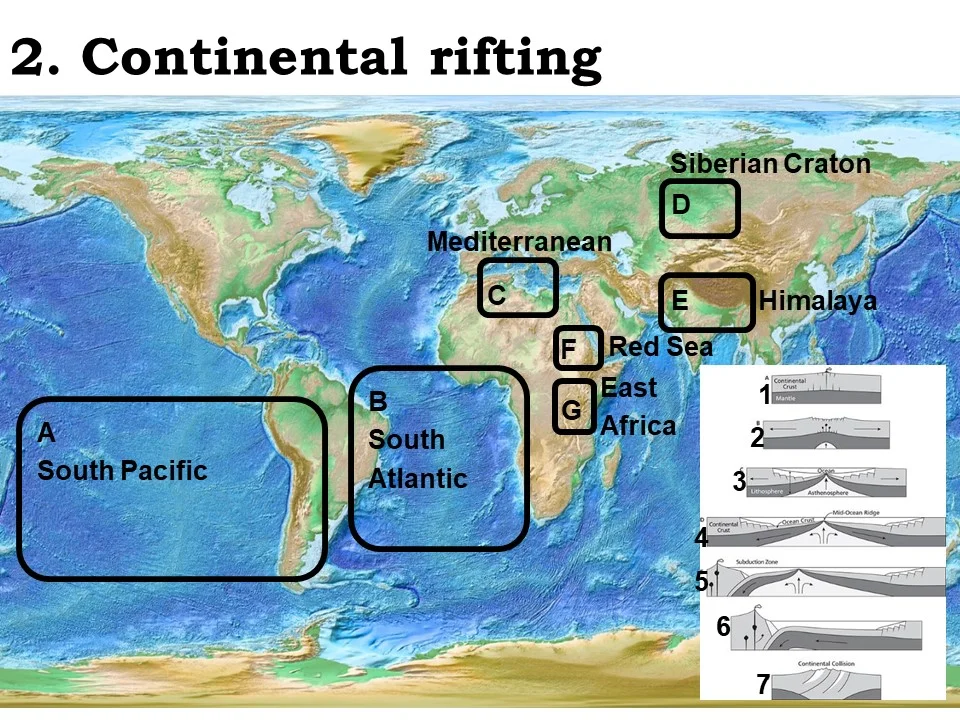
currently undergoing continental rifting
East Africa
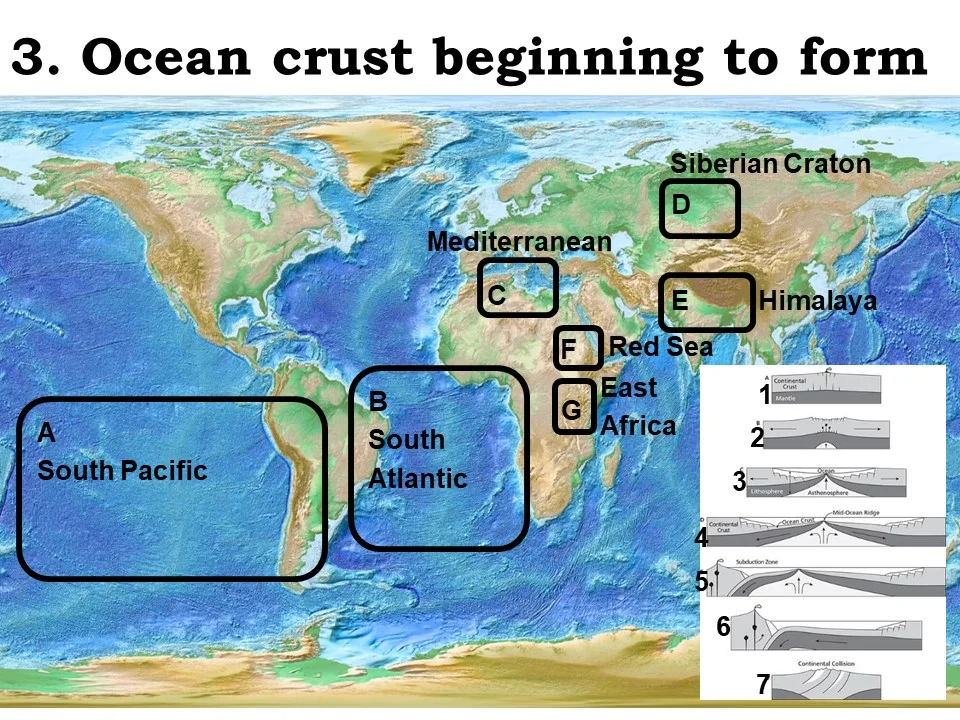
ocean crust beginning to form
Red sea
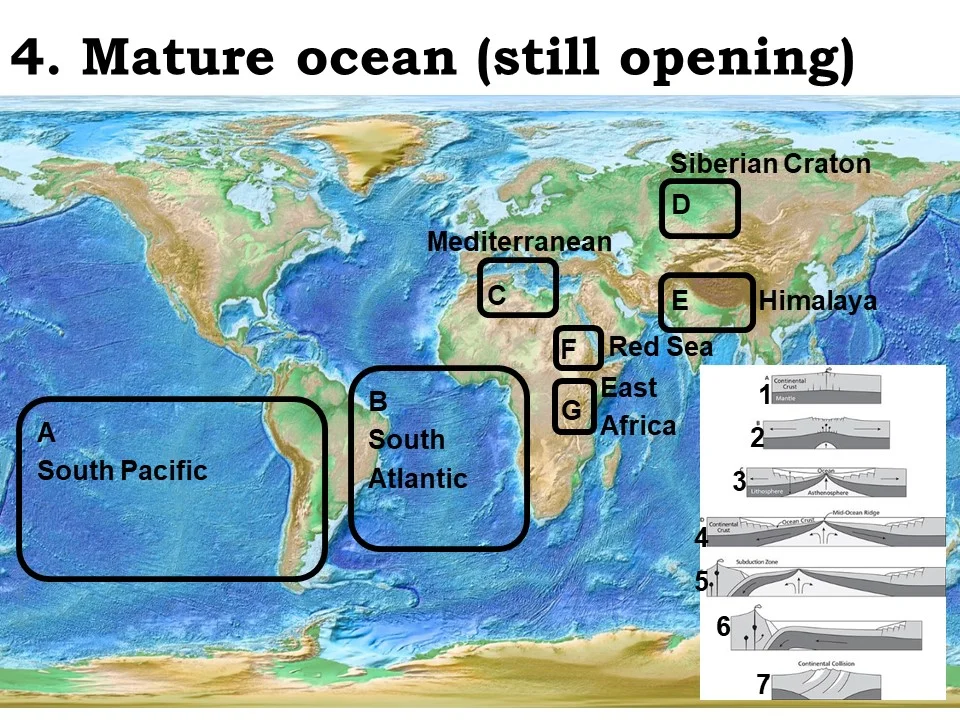
mature ocean (still opening)
South Atlantic
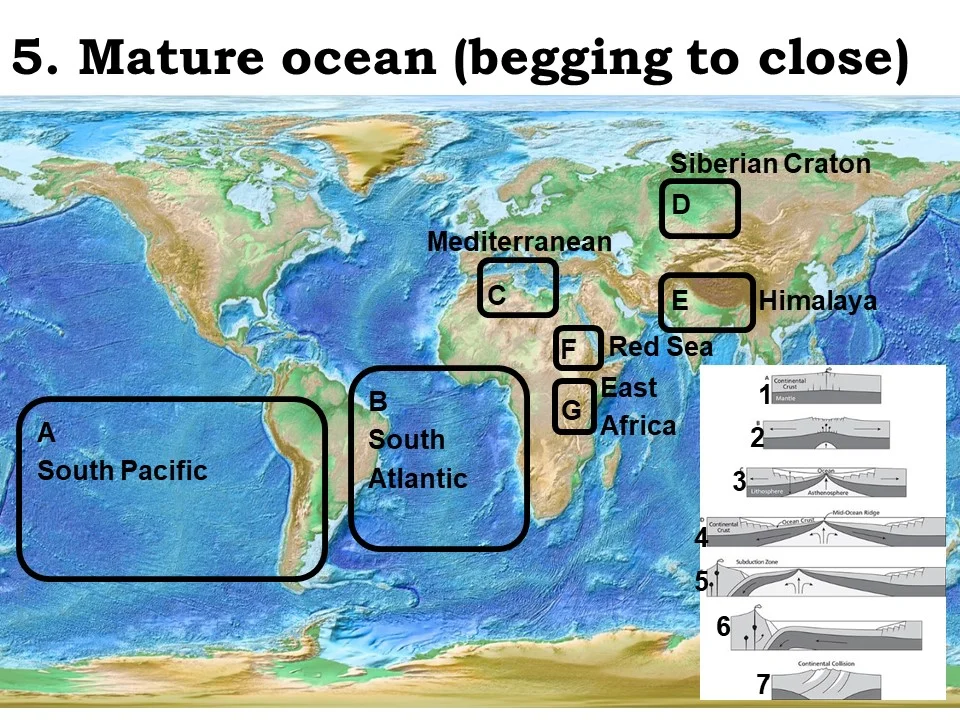
mature ocean (beginning to close)
South Pacific
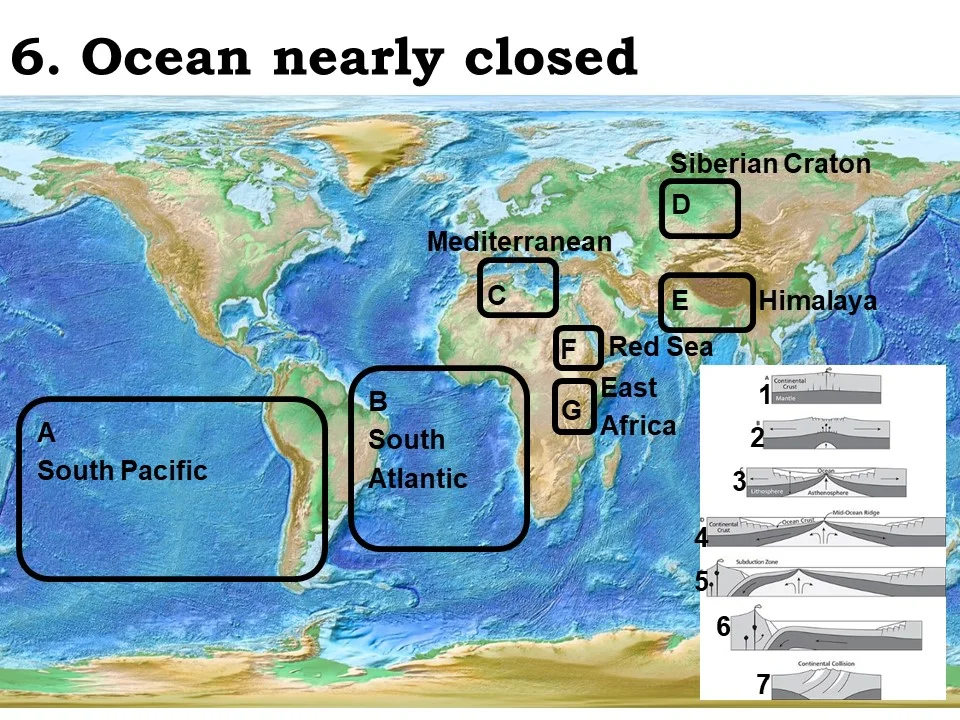
ocean nearly closed
Mediterranean
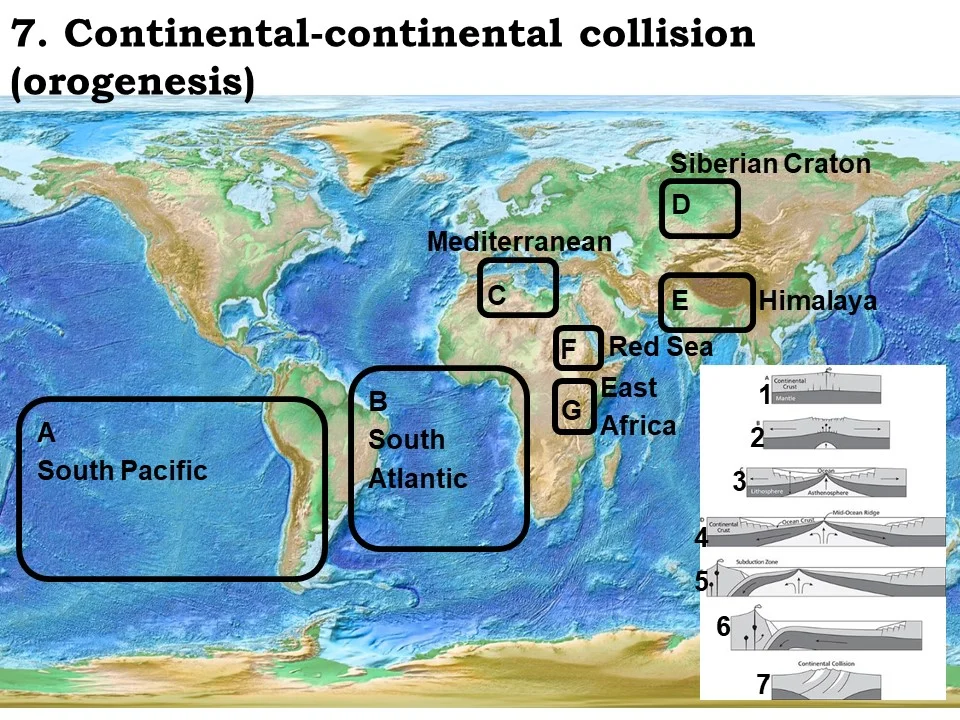
continental-continental collision
Himalaya