Chapter 22 - Enthalpy + Entropy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
lattice enthalpy
enthalpy change of of the formation of one mole of an ionic compound from its gaseous ions
K+ (g) + F- (g) → KF (s)
-is exothermic = more exothermic → more stronger ionic bonds
standard enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements under standard conditions
Na (s) + ½ Cl2 (g) → NaCl (s)
first ionisation energy
enthalpy change when 1 electron is removed from each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
-always endothermic = energy supplied to remove negative electron from the attraction to positive nucleus
-second ionisation energy is more endothermic as electron is closer to nucleus so greater attraction
standard enthalpy change of atomisation
enthalpy change of formation of 1 mole of gaseous atoms from element in its standard state under standard conditions
½ Cl2 (g) → Cl (g)
-is always endothermic = energy needs to be supplied to break bonds between molecules into atoms or into a gas
first electron affinity
enthalpy change when 1 electron is added to each atom in 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form gaseous 1- ions
-is exothermic = electron being added is attracted in towards the nucleus
-BUT second electron affinity is endothermic = negative electron being added to negative ion so energy required to overcome repulsion
method for Born-Haber Cycle
lattice enthalpy:
g = a-b-c-d-e-f
-need to multiply values by 2 if there are 2 moles of a substance
factors that affect LATTICE ENTHALPY + HYDRATION
-greater ionic charge
-smaller ionic size/radius
-both lead to stronger attractions between the ions or H2O so leads to a more negative/exothermic value
standard enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solute completely dissolves in water under standard conditions
MgBr2 (aq) + aq → Mg2+ (aq) + 2Br- (aq)
-energy is taken in to break ionic bonds, new attractions formed between ions and water, cations and S- dipole of H2O, anions and S+ dipole of H2O
-overall endothermic = more energy being taken in to break bonds than released to make bonds
-overall exothermic = vice versa
standard enthalpy of hydration
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions react and dissolve in water to form aqueous ions
-always exothermic = energy is released when attractions to water molecules are made
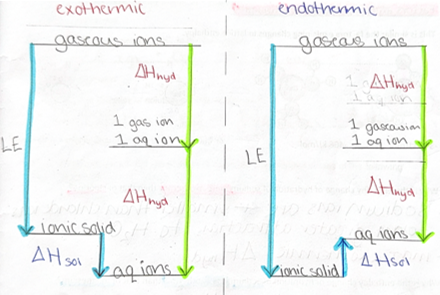
calculation for enthalpy change of solution cycles + experiment
sum of lattice enthalpy + solution = sum of the enthalpy changes of hydration
Q = mcT
entropy
a measure of the dispersal of energy in a system which is greater, the more disordered a system
symbol = S
units = J K-1 mol-1
order of states of entropy
solid < liquid < gas - increases in disorder of particles so increase in entropy
effect of temperature on entropy
higher temp so particles move around more so more random arrangement of particles so higher entropy
entropy value
-if system becomes more random, energy spread out more so entropy value is positive
-if system becomes less random, energy is concentrated so entropy value is negative
effect of gas molecules on entropy
-increase in number of gas molecules = increase in entropy = positive change
-decrease in number of gas molecules = decrease in entropy = negative change
standard entropy
entropy change = sum of products - sum of reactants
factors that affect feasibility
-temperature
-entropy change
-enthalpy change
free energy change equation
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
ΔG = free energy change
ΔH = enthalpy change
T = temperature
ΔS = entropy change
-predicts feasibility, units = kJ mol-1
ΔG value for feasibility
-must have a negative value to be feasible
1) positive ΔH, negative ΔS = always positive so not feasible
2) negative ΔH, positive ΔS = always negative so feasible
3) both negative ΔH and ΔS = only negative at low temperatures
4) both positive ΔH and ΔS = only negative at high temperatures
limitations of using free energy change
-reaction may have high activation energy
-very slow rate of reaction