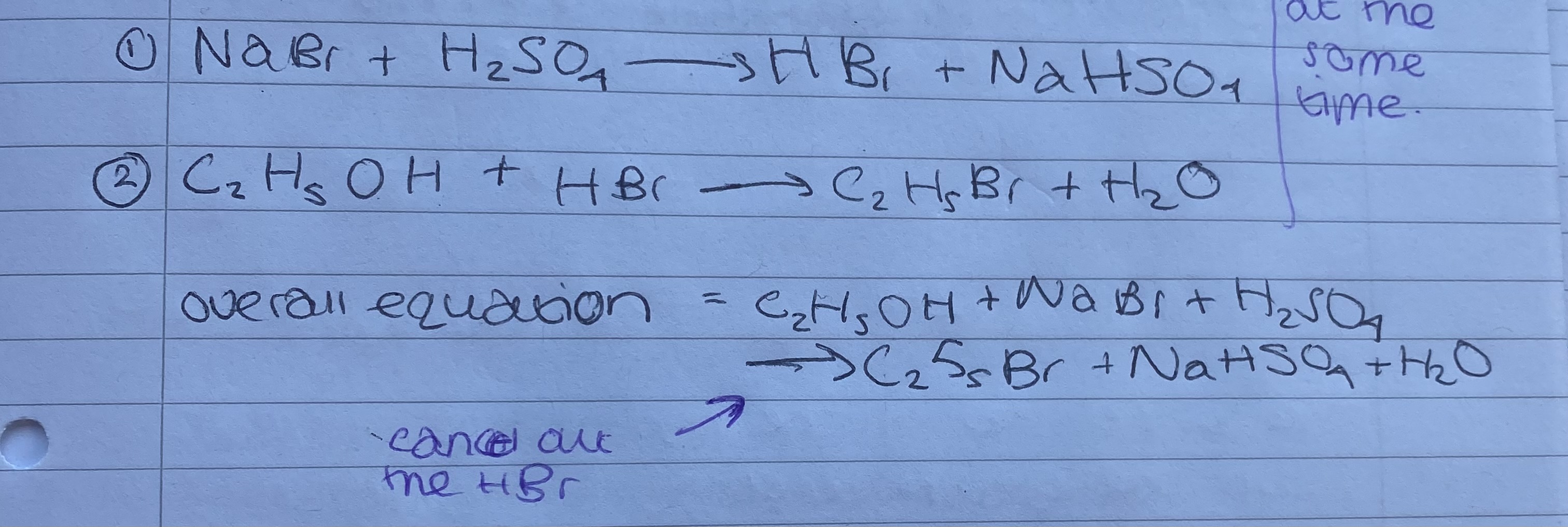Oxidation in alcohols
What are the 3 types of alcohols?
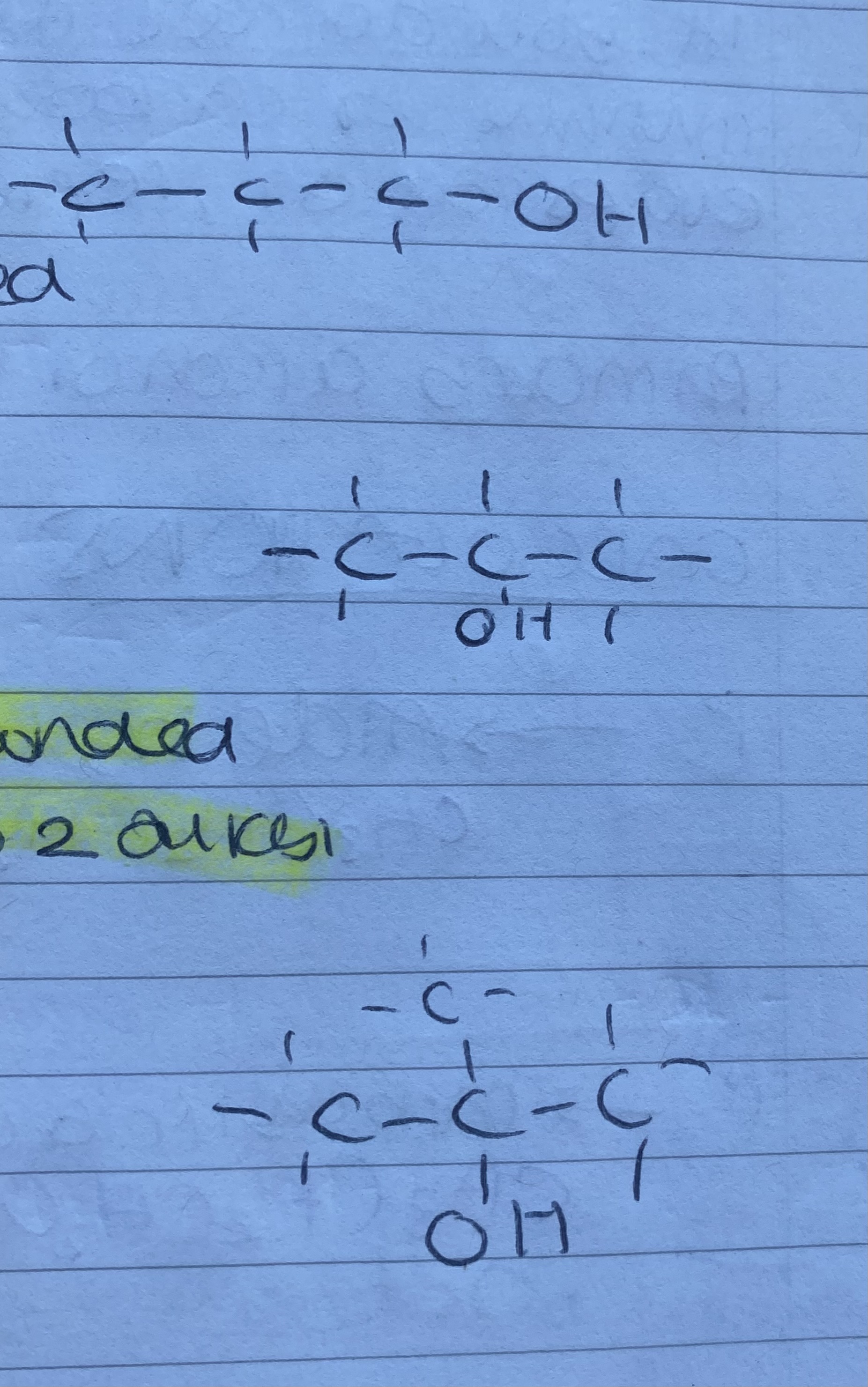
1 degree = OH group is attached to 1 alkyl
2 degrees = OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to 2 alkyl groups
3 degrees = OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to 3 alkyl groups
What can each type of alcohol oxidise into?
2 degree = ketone
1 degree = aldehyde
1 degree = carboxylic acid
aldehyde = carboxylic acid
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the 3 types of alcohols?
1 degree = OH group is attached to 1 alkyl
2 degrees = OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to 2 alkyl groups
3 degrees = OH group is attached to a carbon atom that is bonded to 3 alkyl groups

What can each type of alcohol oxidise into?
2 degree = ketone
1 degree = aldehyde
1 degree = carboxylic acid
aldehyde = carboxylic acid
What is important when showing the oxidation?
The functional groups must be in the same spot in the reactants and products
What is the oxidising agent?
Acidified potassium dichromate
When is distillation and reflux used?
1 degree to aldehyde, you use distillation
1 degree to carboxylic acid, you use reflux
2 degree to ketone, you use reflux
When is water not produced in oxidation?
From aldehyde to carboxylic acid
What is elimination in dehydration of alcohols?
The removal of a small molecule
What does a dehydration of alcohol equation look like?
.
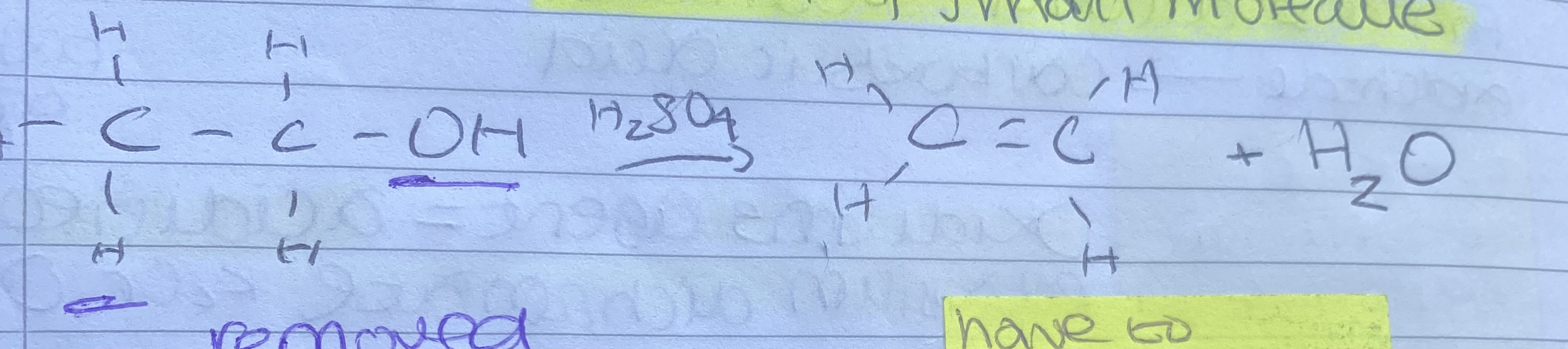
What could the 3 different outcomes of the dehydration be?

What happens during a substitution reaction and what is needed?
Alcohol turns into a haloalkane, a sodium halide and sulfuric acid is need.
What reacts first in the substitution?
The sodium halide and sulfuric acid, creating a hydrogen halide.
What does the substitution react look like?
.