yr 9 physics
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
vacuum
sound cannot travel through this
Microwave
Electromagnetic waves that have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves.
x-rays
form of em radiation, with high energy and short wavelength
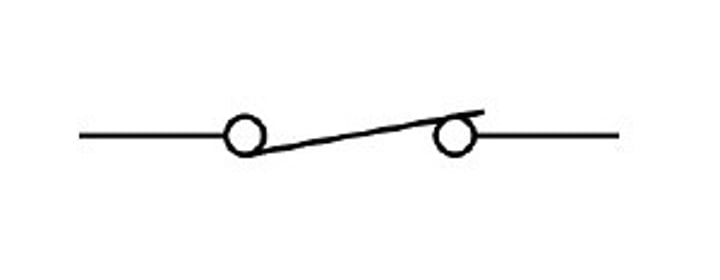
closed switch
allows current to flow
Parallel circuit
When components are connected in branches adjacent to one another.
Insulator
A material that does not conduct electricity.
Resistance
A measure of how difficult it is for current to pass.
Measured in ohms (Ω).
Ohms
Unit for resistance
Fuse
A wire of high resistance; it will melt if too much current flows in the circuit.
decibel
unit used to measure amplitude
matter
sound requires this to be transmitted
Conduction
The transfer of heat between substances that are in direct contact.
Convection
the transfer of heat in liquids/gases where warmer portions of the fluid rise, while cooler, more dense portions sink.
Non-luminous
An object that does not release or emit light.

Shadow
A dark area where light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object.
Violet
High frequency / high wavelength light waves.

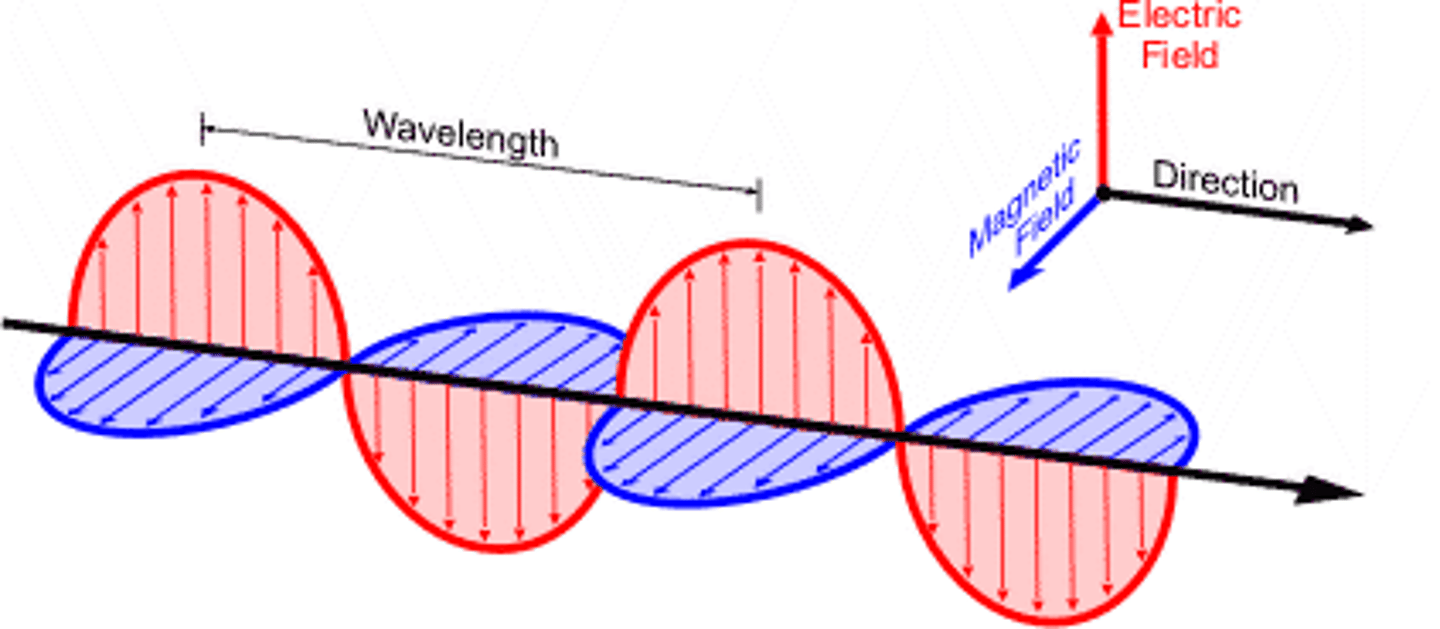
Transverse (electromagnetic) wave
Light is this type of wave.
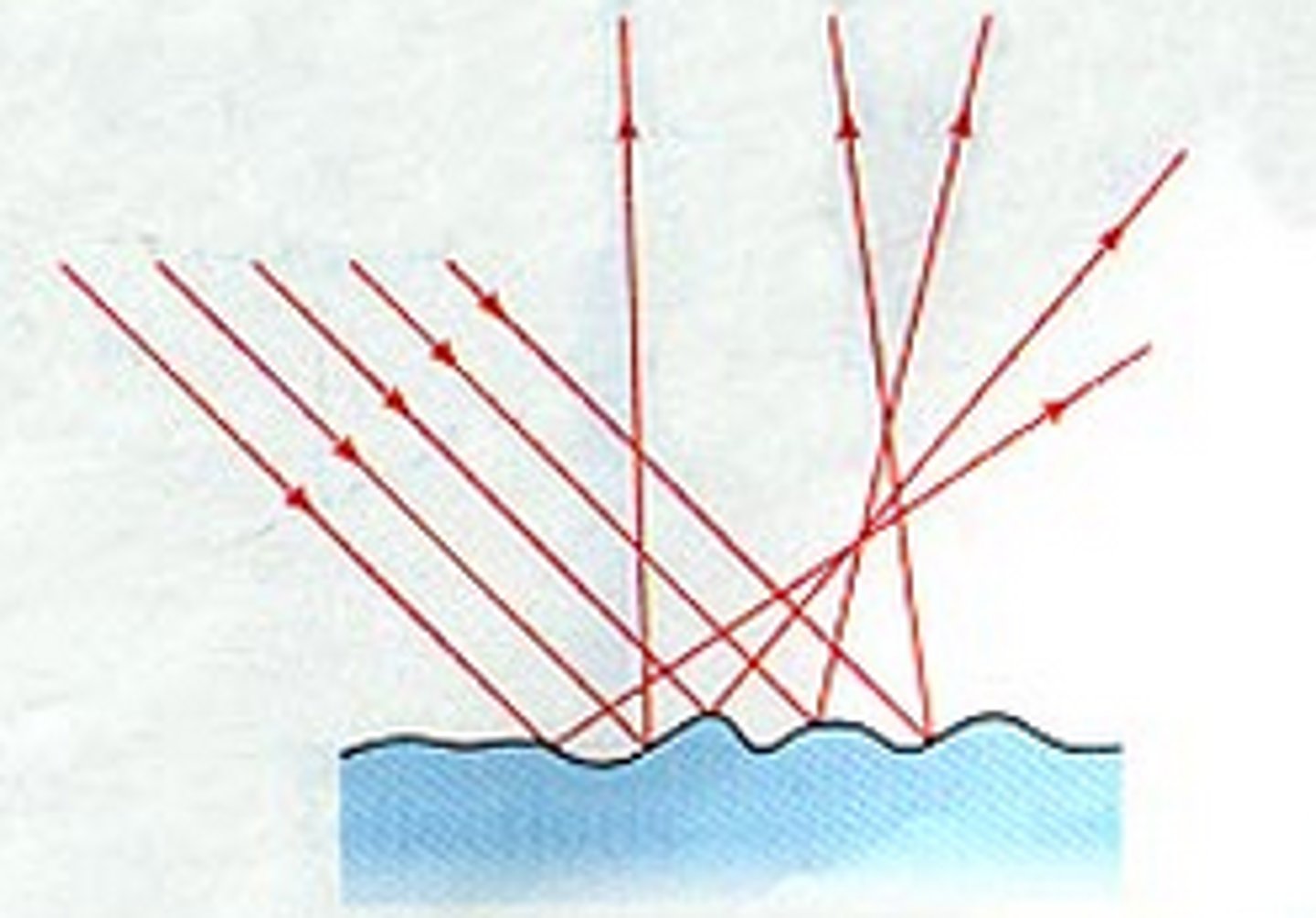
Regular reflection
When light reflects off a smooth surface (such as a glass or a window) it produces a clear reflected image.

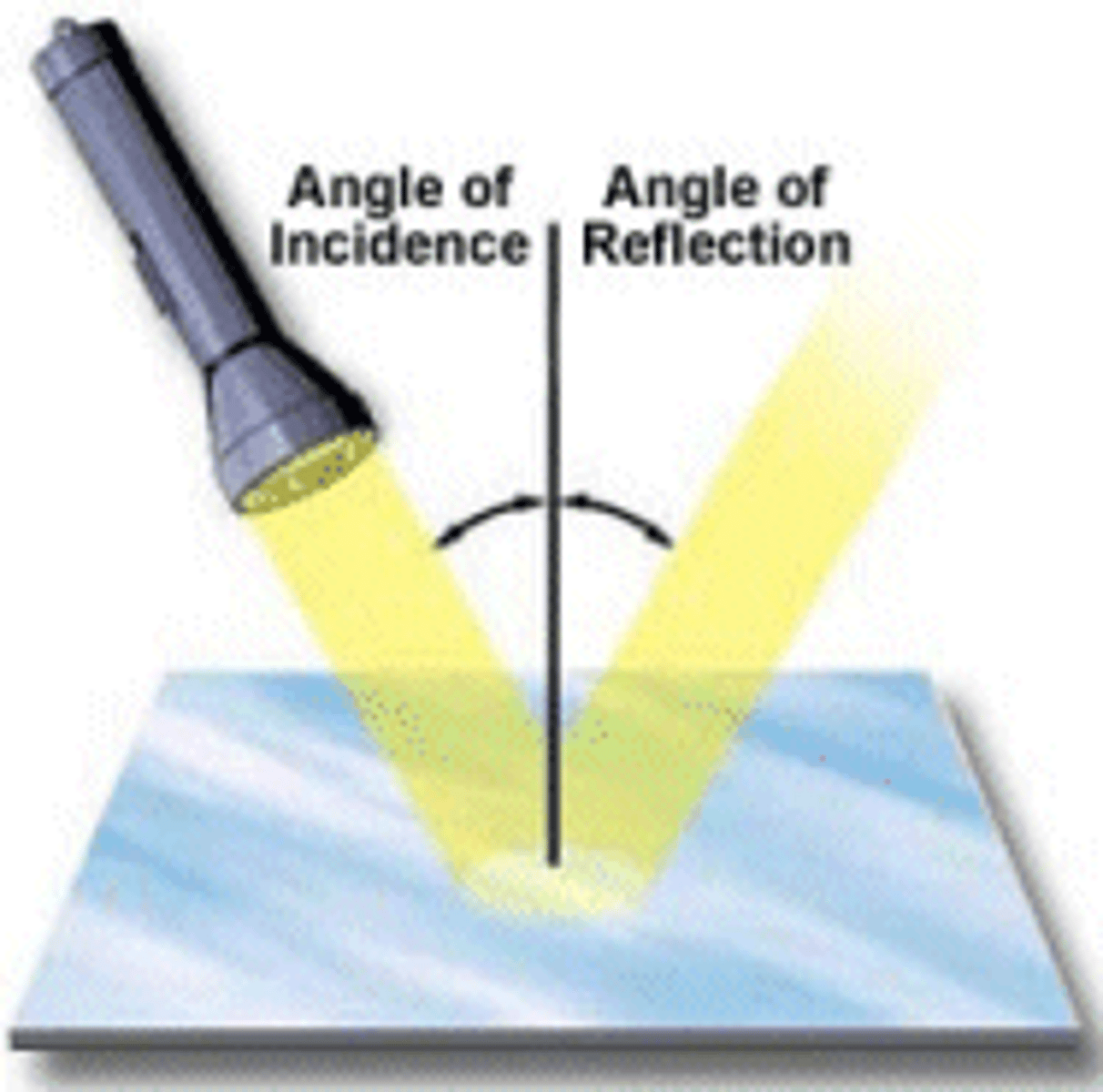
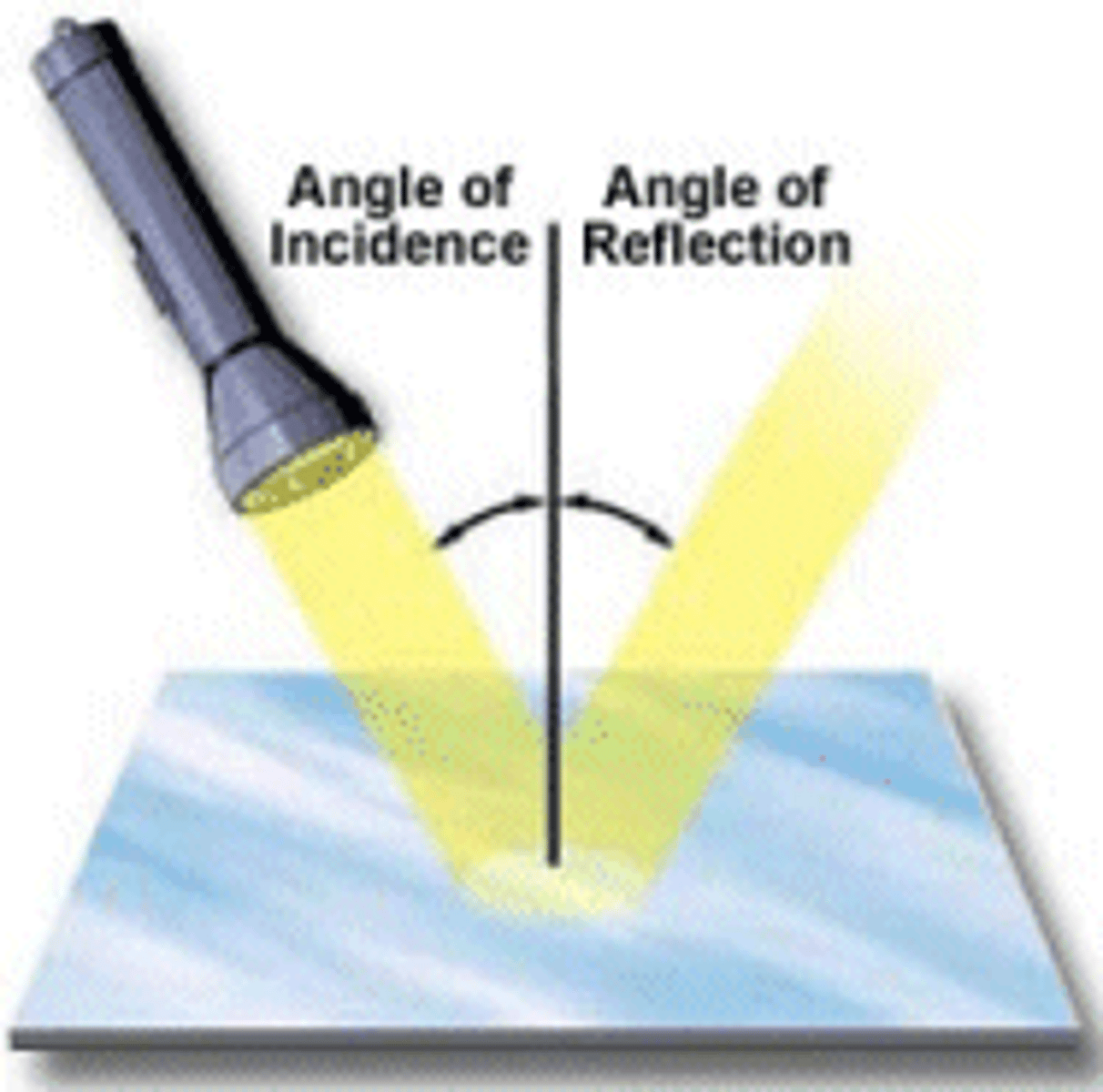
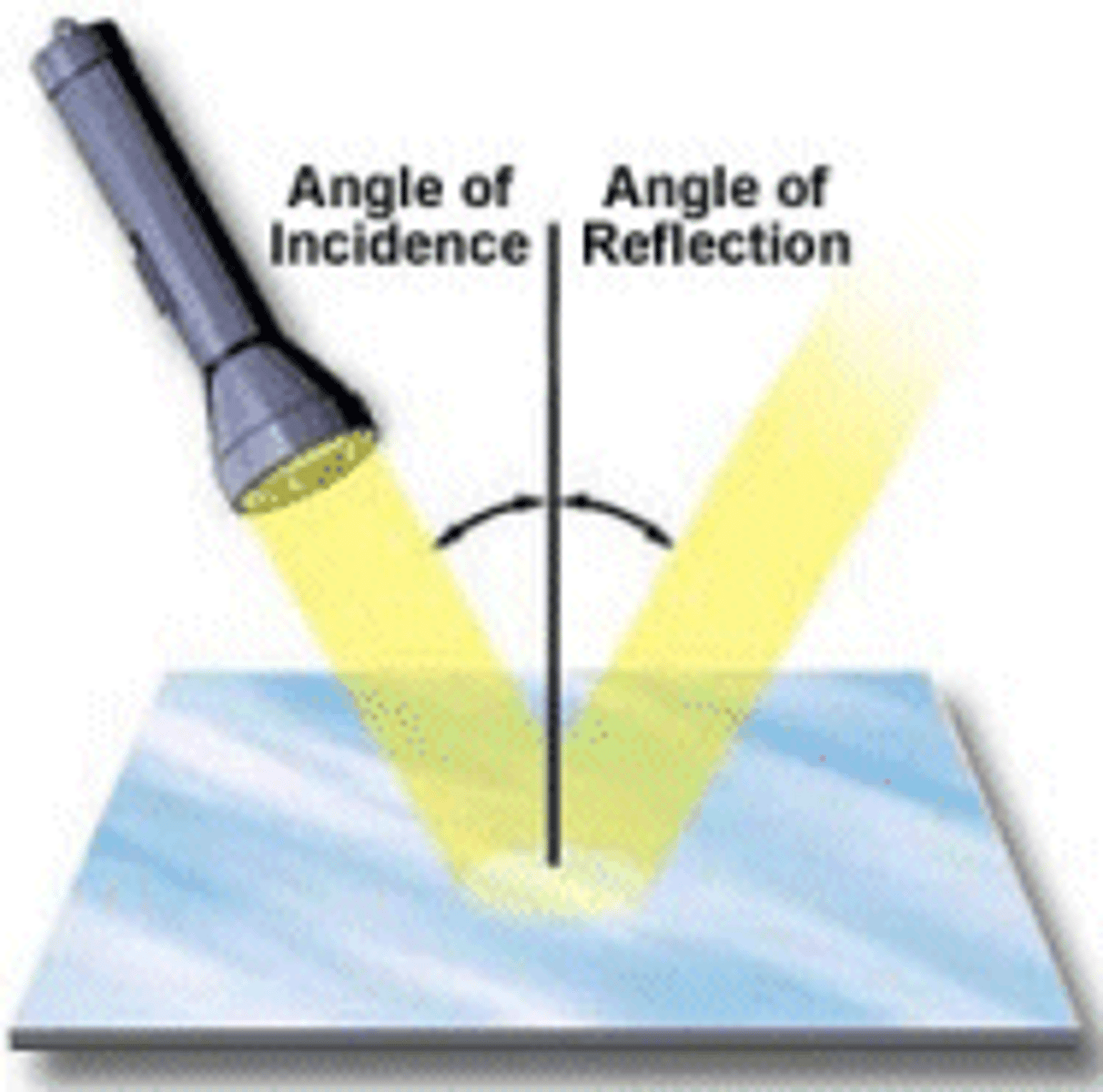
Angle of incidence
The angle an incoming ray makes with the "normal".
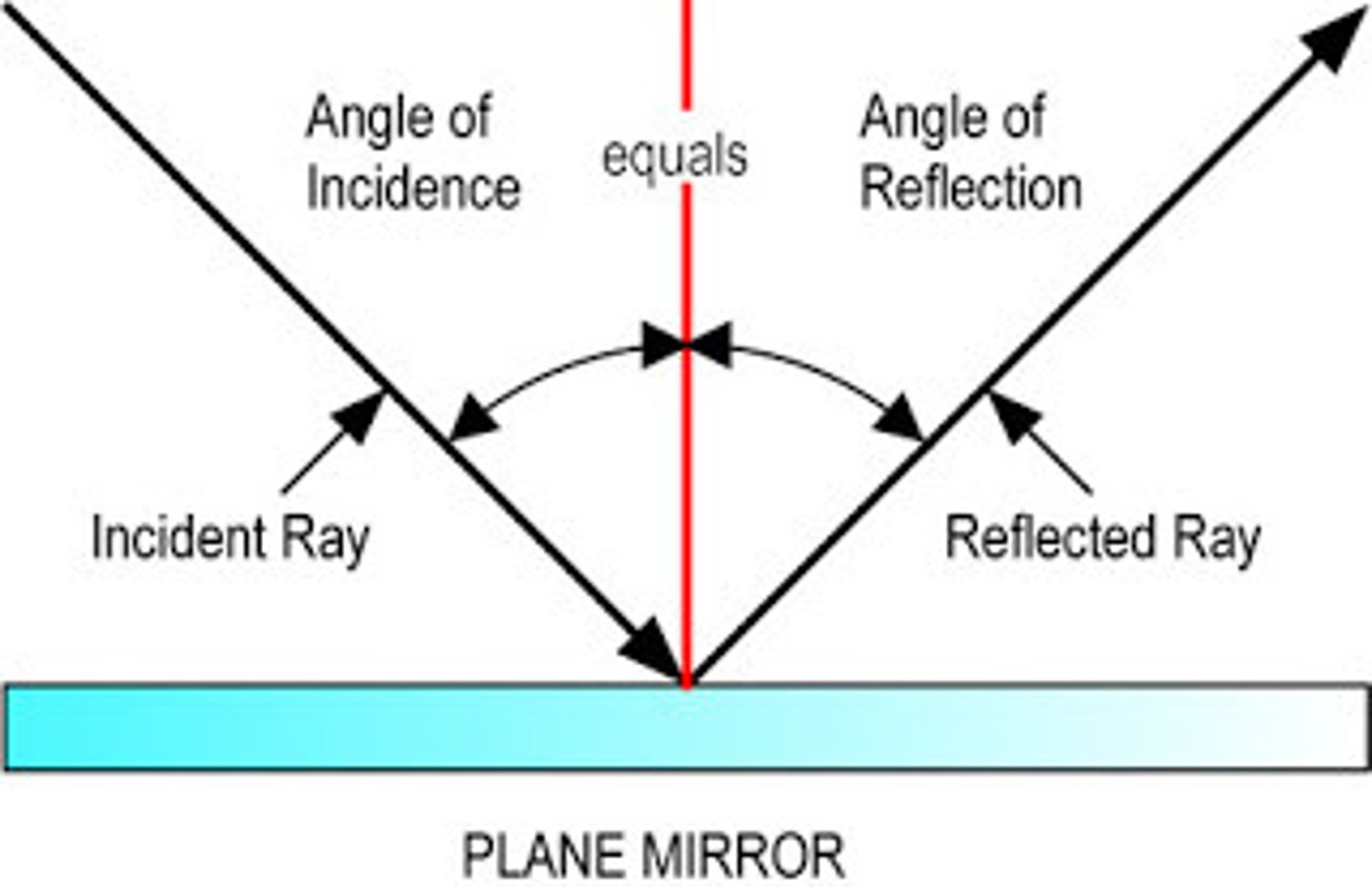
Angle of reflection
the angle a reflected ray makes with the "normal".
Concave mirror
Mirror that causes light rays to point inwards. This can produce an upright and diminished image as well as an inverted magnified image depending on distance.

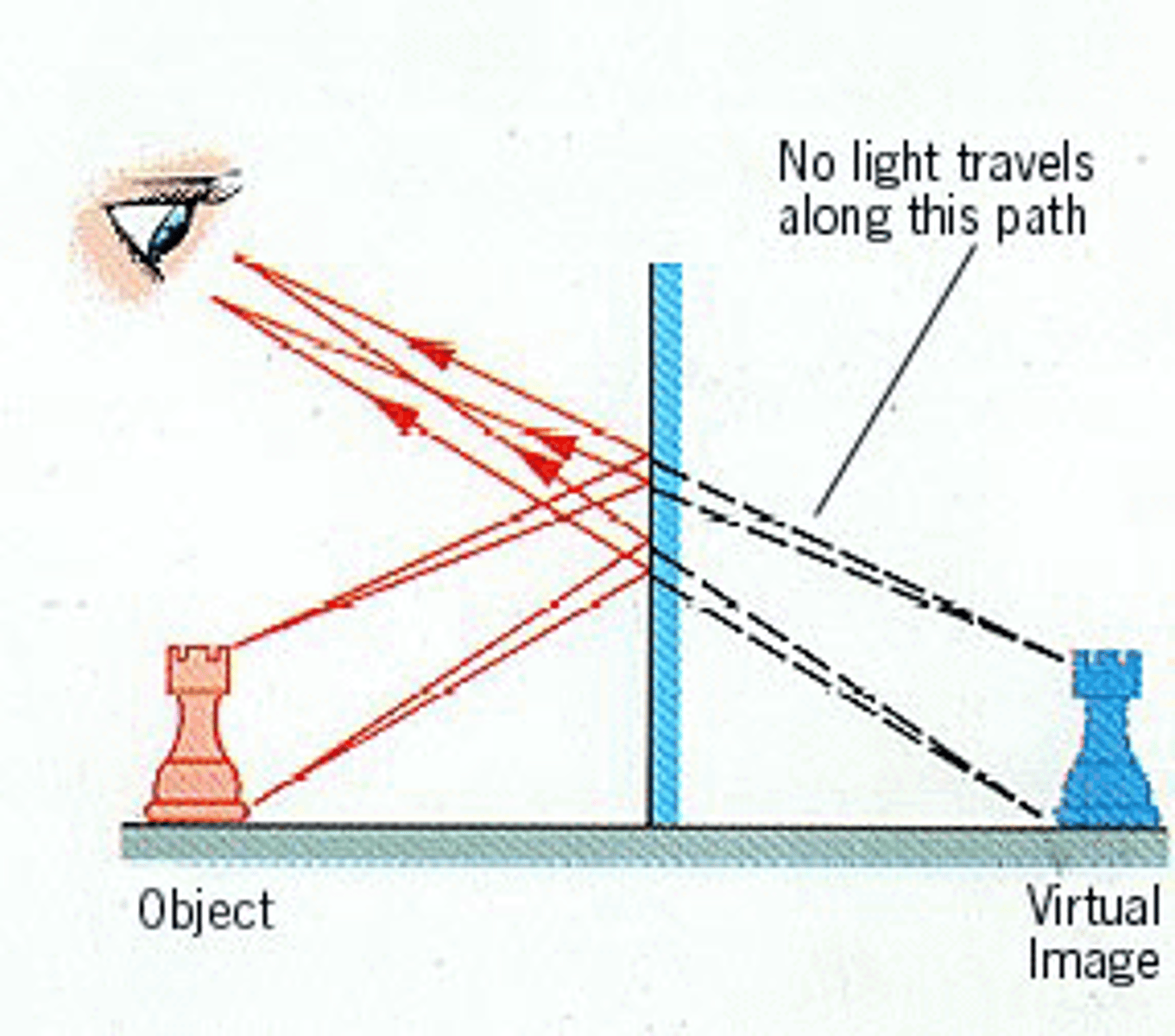
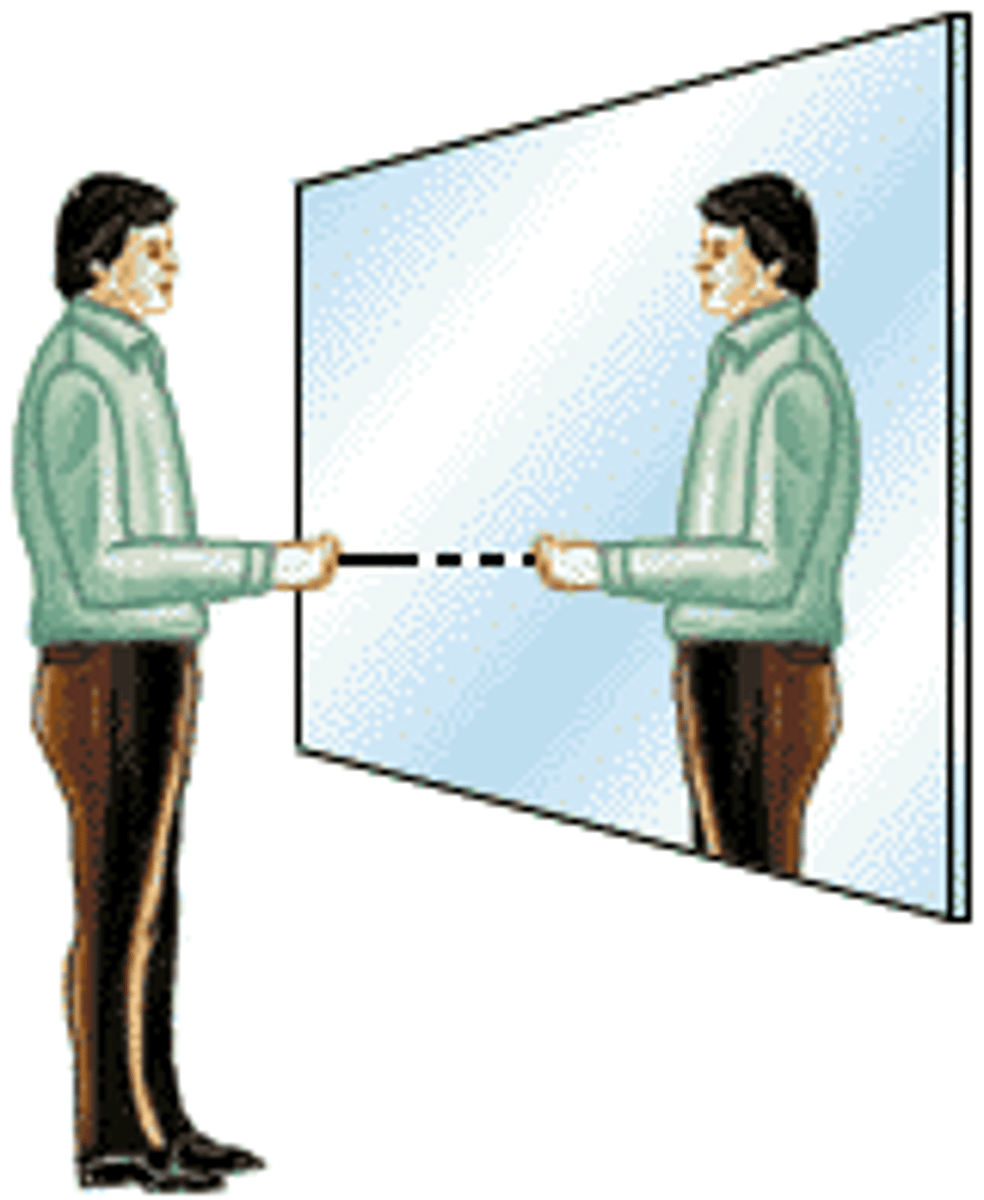
Virtual image
Image that appears in a mirror
Reflection
When light bounces off a surface at an angle relative to the angle of incidence.
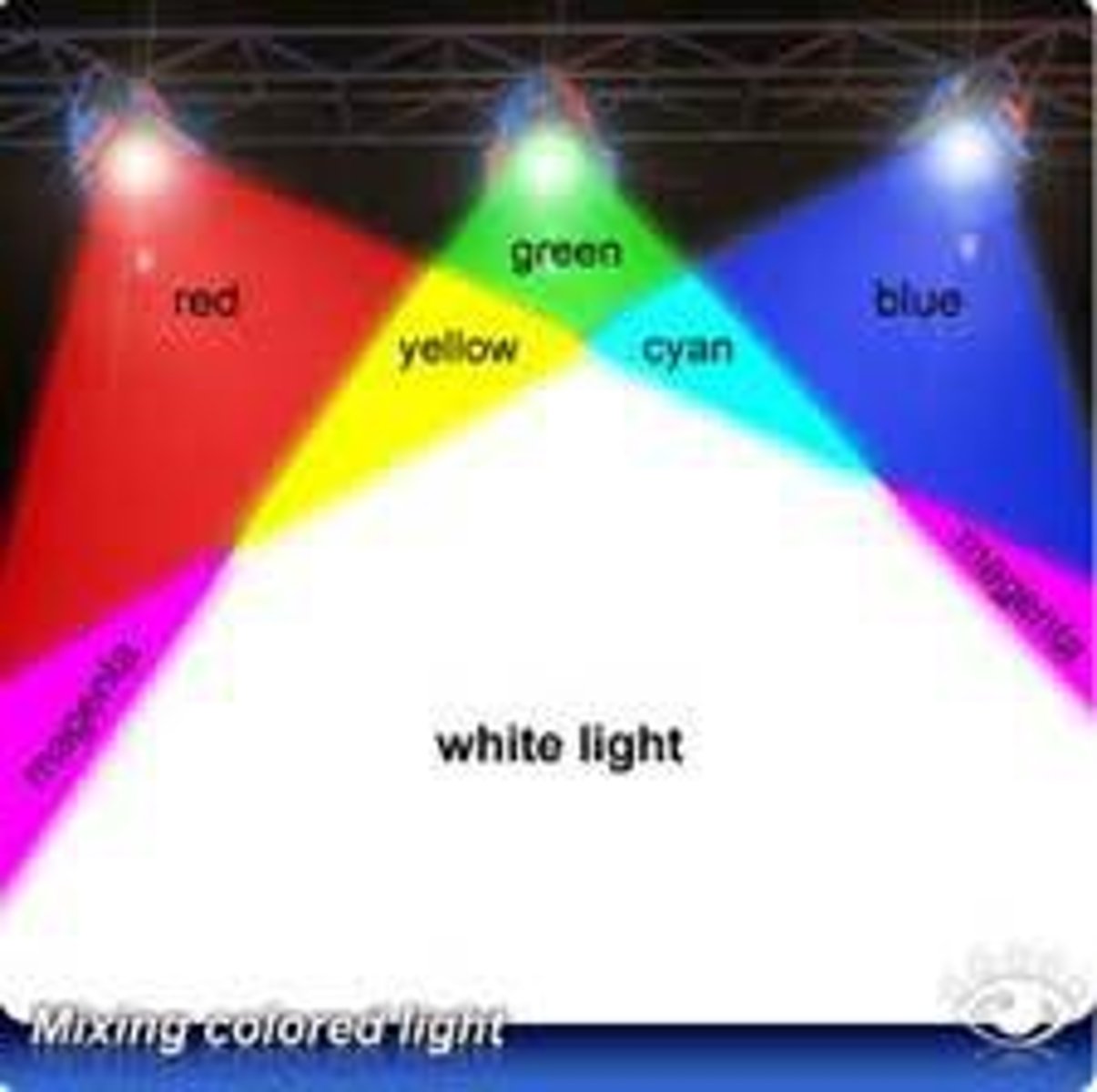
White Light
This light is a mixture of many different colours, each with a different frequency.
Dispersion
When white light passes through a prism, each individual frequency of light is bent, or refracted, a slightly different amount.
Polarisation
Light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane.
Infrared
Electromagnetic waves of frequencies lower than the red of visible light.
Uses for microwaves
Heating food in a microwave oven or transmitting information from one place to another.
Uses for x-ray
primarily used for medical imaging as it can penetrate substances such as skin and muscle (eg. diagnostic radiography)
Red
Longest wavelength of visible light
amplitude
total distance a wave moves up and down from its resting position
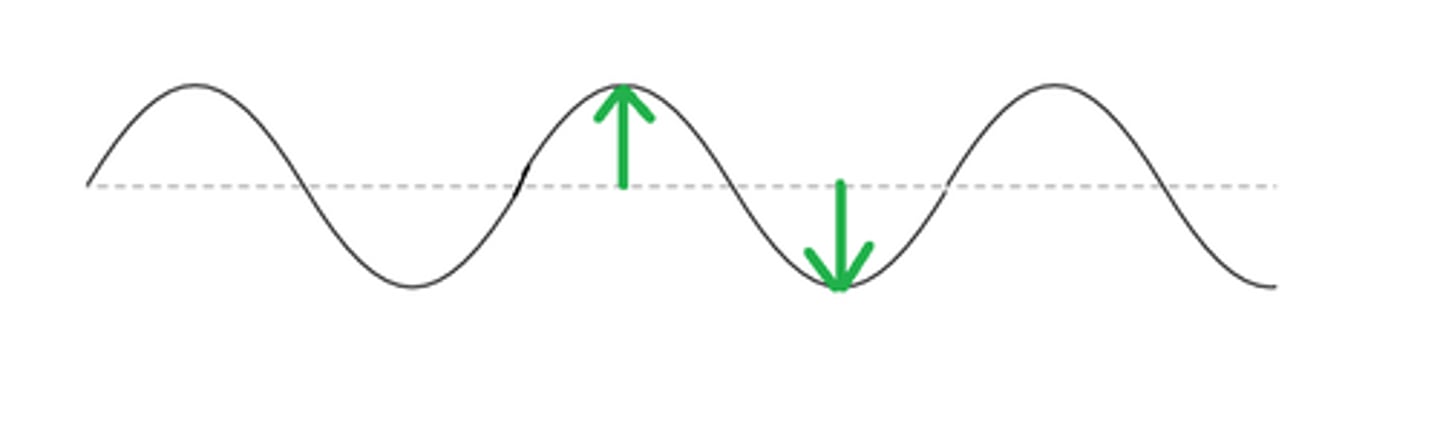
wavelength
distance from any point on one wave to a corresponding point on the next wave, such as crest to crest or trough to trough
transverse wave
a wave that moves perpendicular (up and down) to the direction that it travels
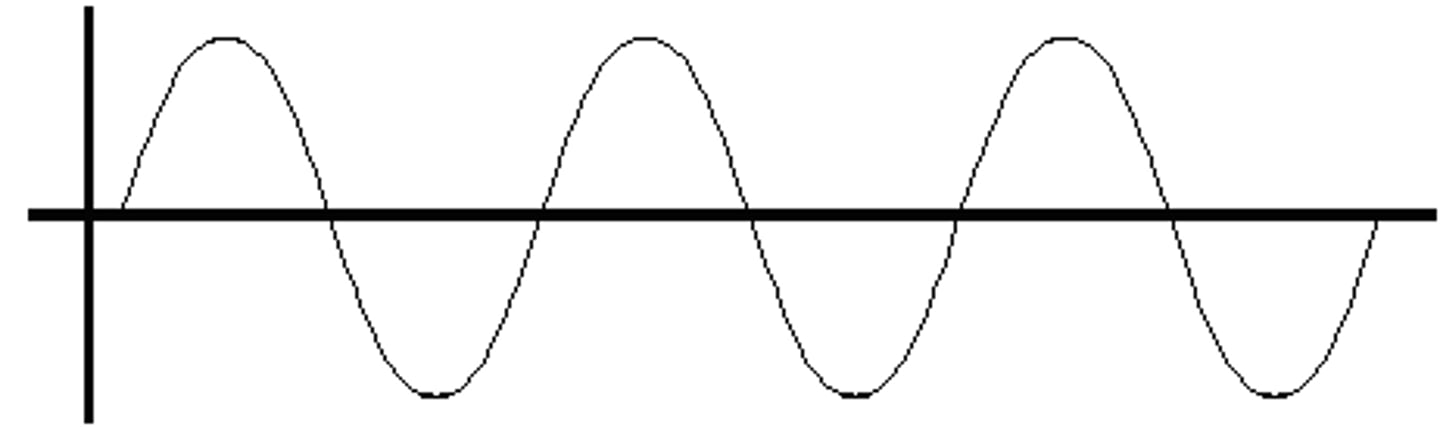
Period
The time for one complete cycle of a wave.
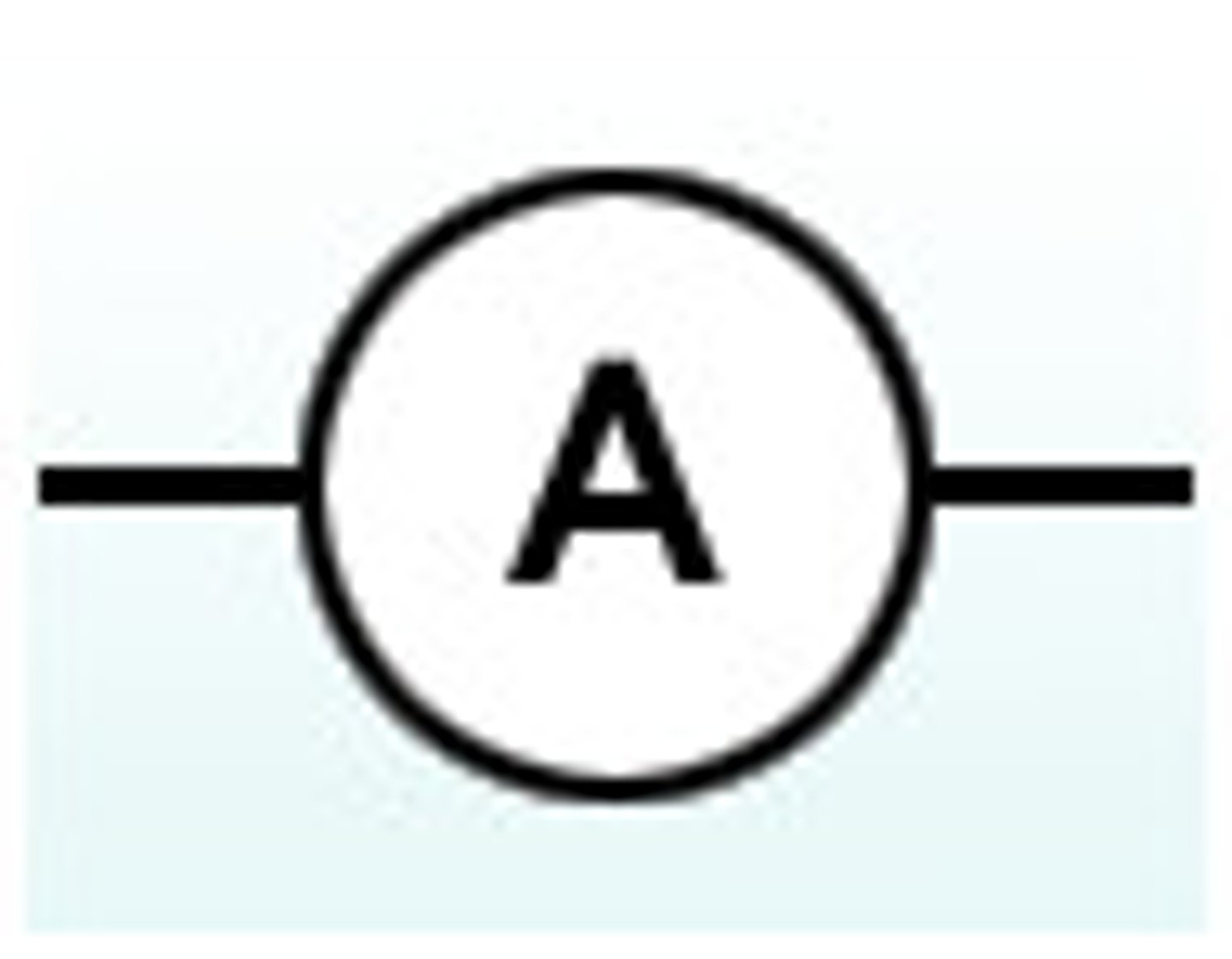
ammeter
An instrument that measures current.
Conductor
A material that allows a current to pass through it.
transverse wave
a wave in which the vibration is at right angles to the direction the wave is travelling.
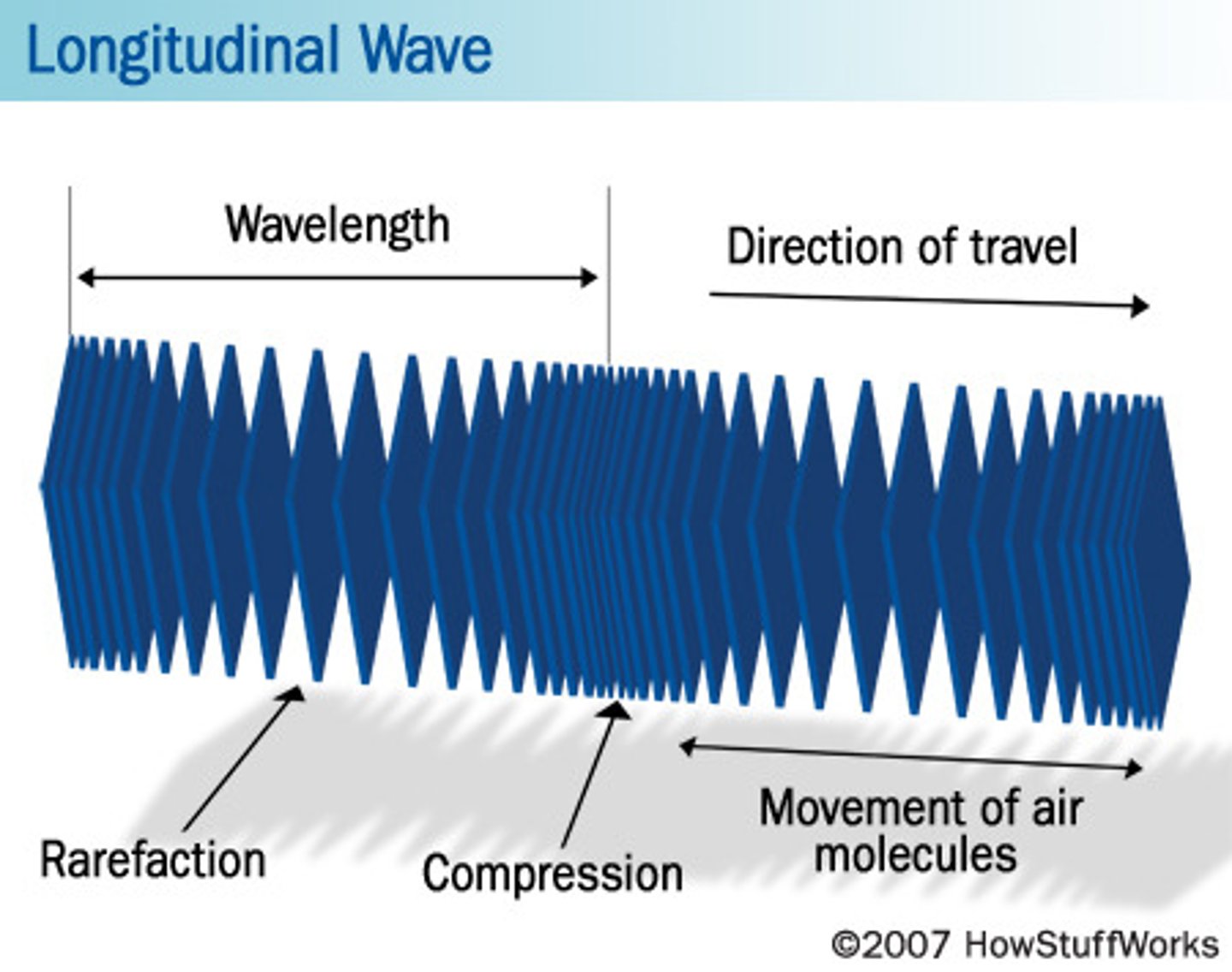
wavelength
the distance from one peak to the next or one compression to the next.
compression
a region of high pressure where particles are close together.
echo
a sound that is reflected and heard a second time
frequency
the number of waves passing a point every second
Hertz
the unit used to measure frequency
longitudinal wave
a wave in which the vibration is in the same direction that the wave is travelling
rarefraction
a region of low pressure, in which particles are far apart.
sound wave
regions of high and low pressure originating from a vibrating object and transmitted through a medium.
pitch
the way we hear frequency
(measured in Hertz).
vibration
how sound is created
wave
transfer energy without a transfer of matter
metres
units used to measure wavelength
solids
the medium in which sound travels fastest
gases
the medium in which sound travels slowest
Radiation
The transfer of heat through a vacuum and to an object by electromagnetic waves.
White
Colour that reflects most radiation.
Black
Colour that absorbs most radiation.
Insulator
A poor heat conductor, heat energy does NOT pass through it easily.
Heat
The transfer of energy.
Thermal Energy
The total energy of all the particles within an object.
Joules
Units used to measure heat.
Hot to cold
Heat is always transferred in this direction.
Thermometer
Device used to measure temperature.
Degrees Celsius
Units used to measure temperature.
Temperature
Average energy of all particle within an object (°C).
Metal
Example of a good conductor of heat.
Plastic, wood
Examples of bad heat conductors
Luminous
An object that releases or emits light.

Opaque
When light is either reflected or absorbed into the substance.

Translucent
Some light is reflected. Some light passes through but it is scattered.

Transparent
Almost all light is transmitted through this substance.

Speed of Light
300,000,000 meters per second
Electromagnetic wave
Light wave consisting of alternating electric and magnetic fields. This can also be described as a transverse wave.
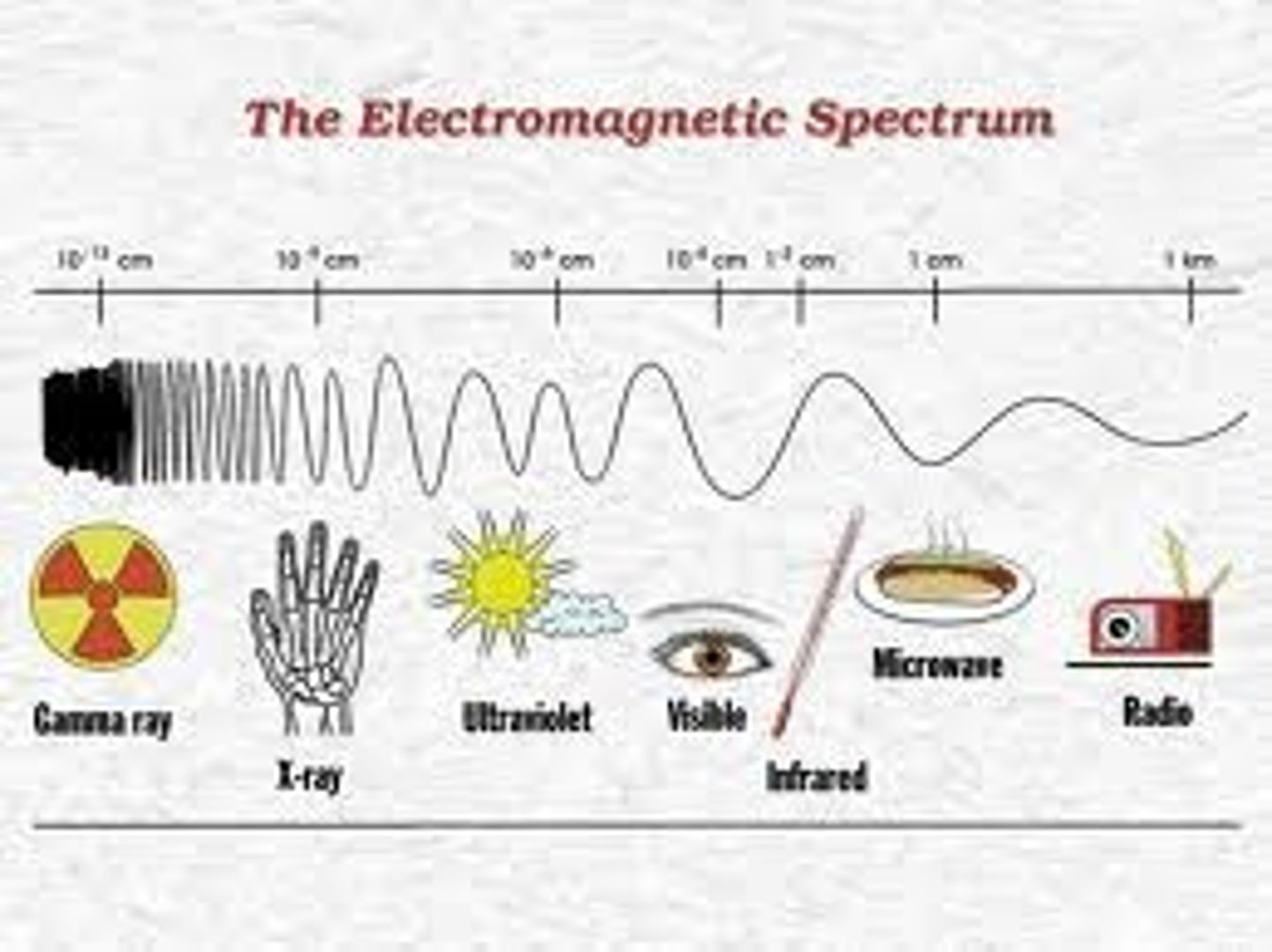
Colour
The way we see the frequency of the light waves.

Red
Low frequency / low wavelength light waves.

Diffused Reflection
Although they may appear smooth, the surfaces of most objects are rough close up. These surfaces reflect light in many directions and do not form an image.
Normal
An imaginary line that is drawn at right angles to a surface that a light is hitting (incident on).
Law of reflection
The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (incidence = reflection).
Plane mirror
Mirror that produced an upright, laterally inverted virtual image.
Convex mirror
Mirror that causes light rays to radiate outwards, resulting in an upright and diminished image.
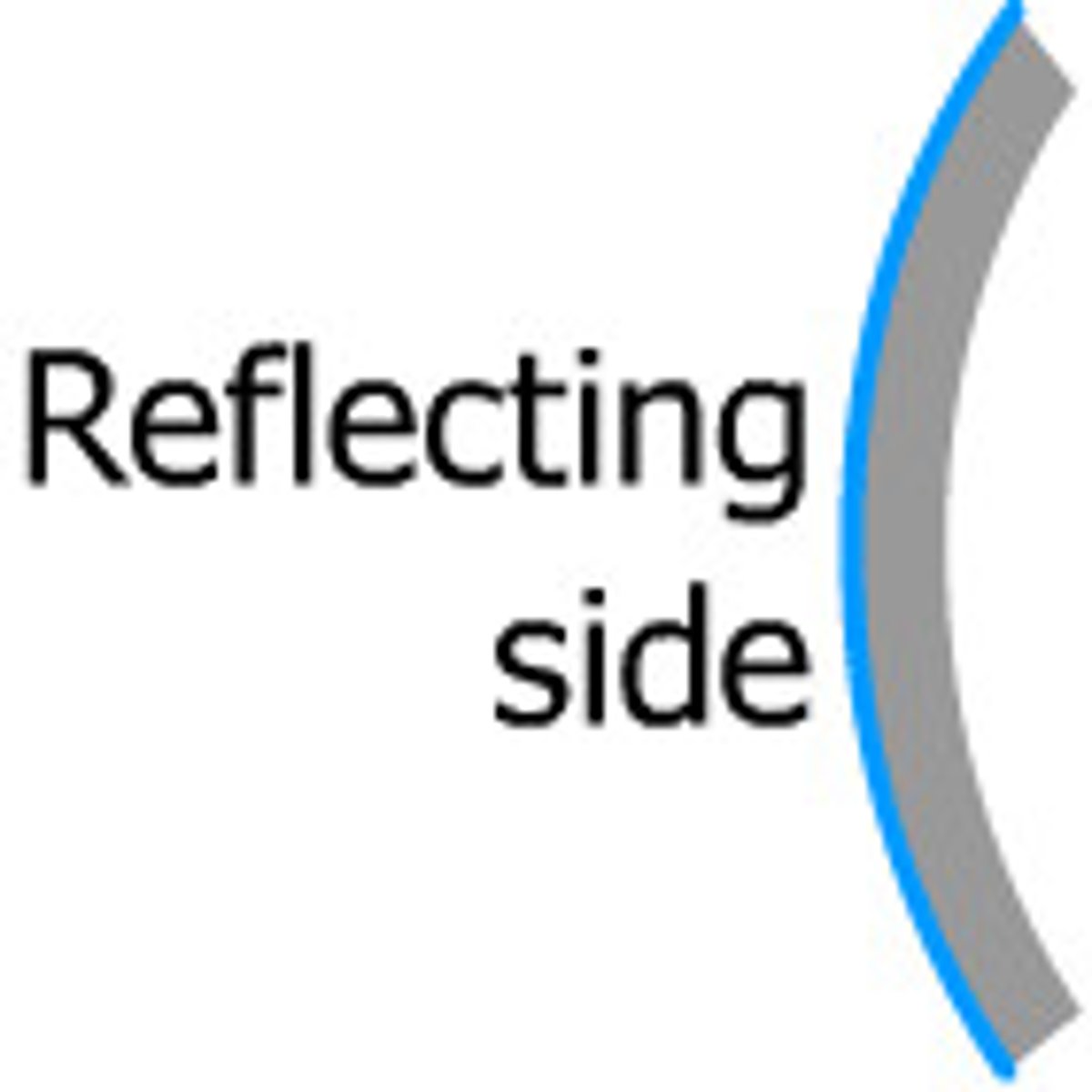
Real image
Image that appears in the real world. Concave mirrors in projectors create images.
Refraction
The bending of light as it enters or leaves different substances at an angle.
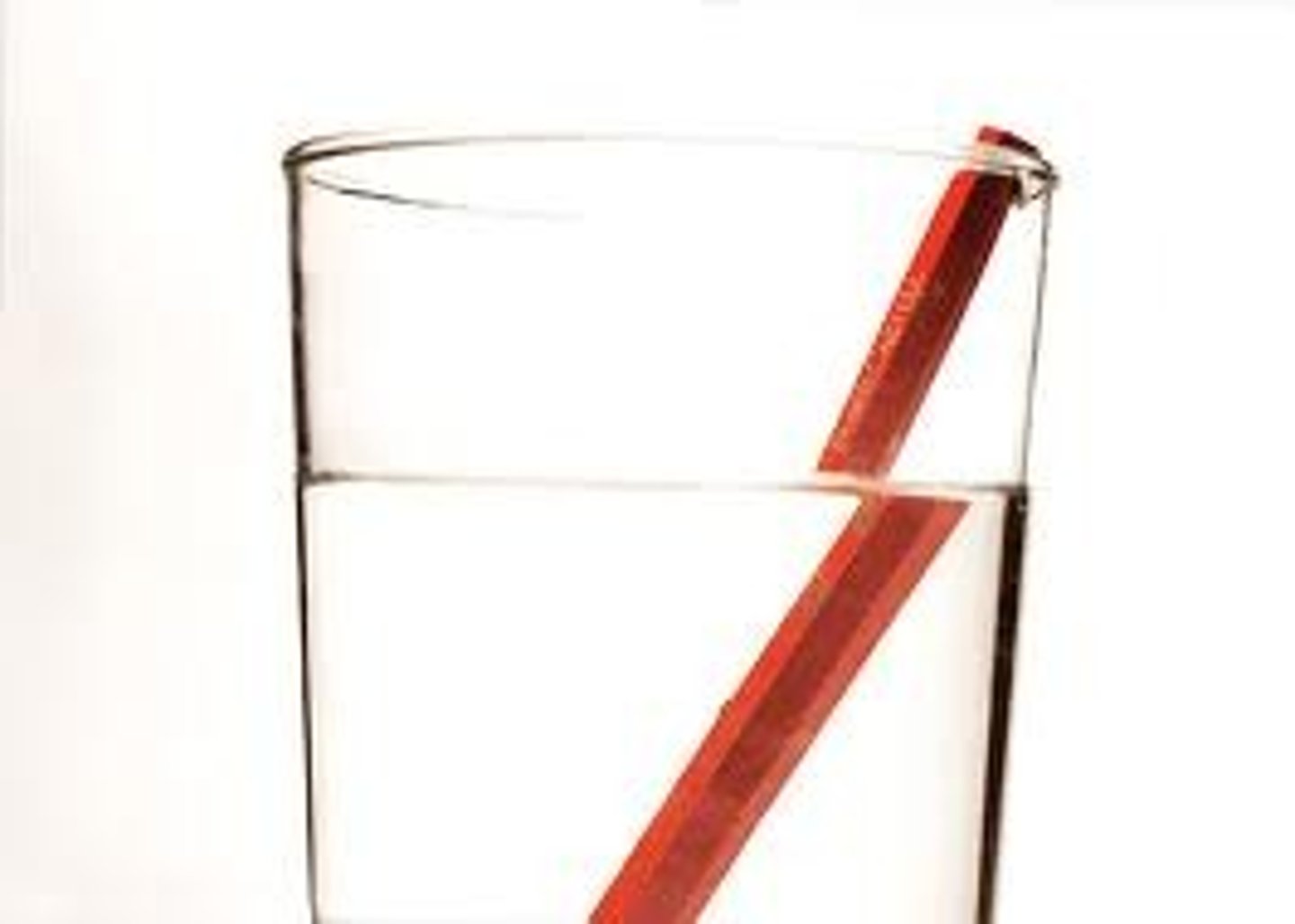

Depth Illusion
The bending of light rays from air to water can make objects appear closer than they really are.
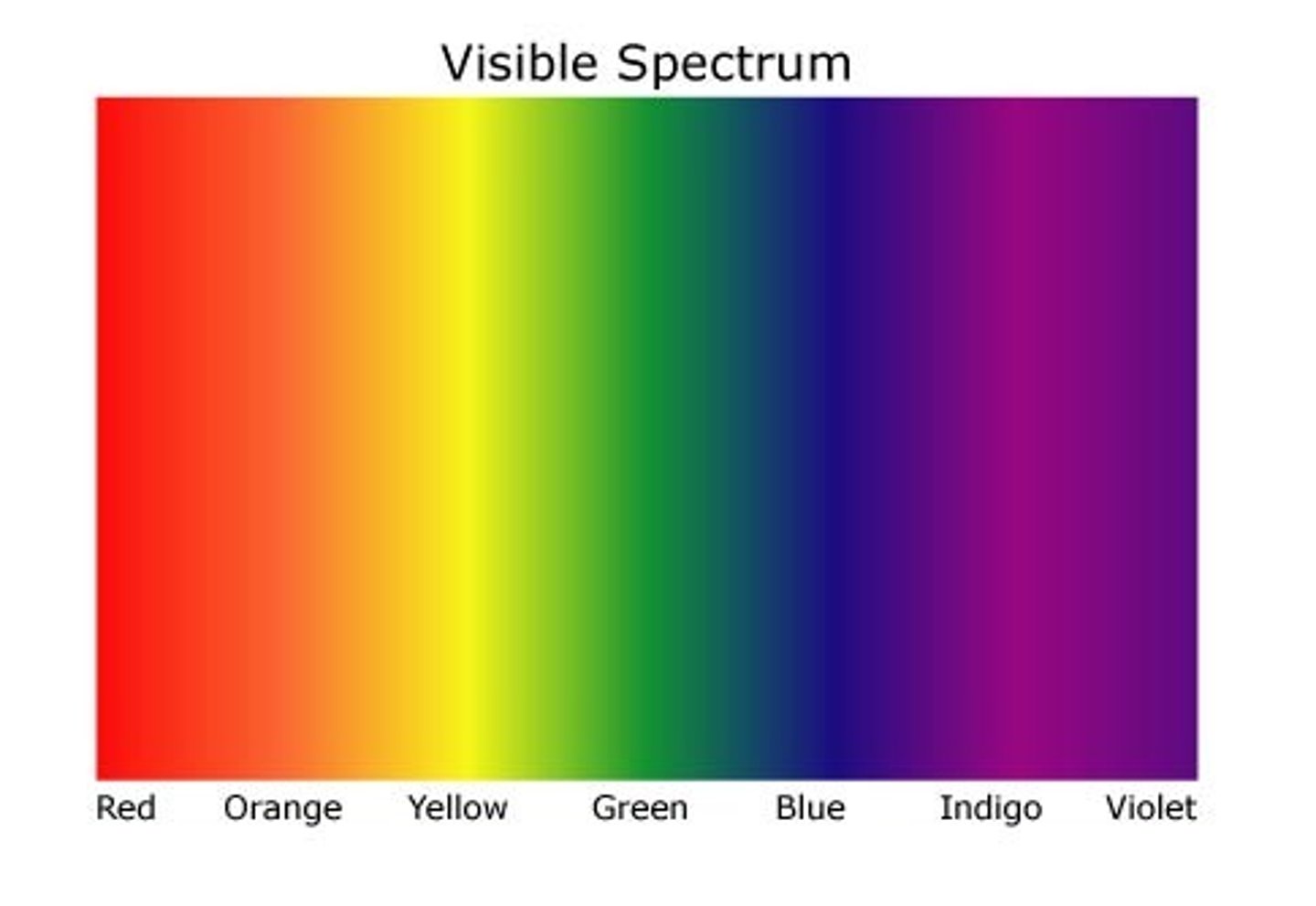
Visible Light
A portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye.
White
Reflects all the colours and the radiant heat.

Black
Absorbs all the colours and the radiant heat.

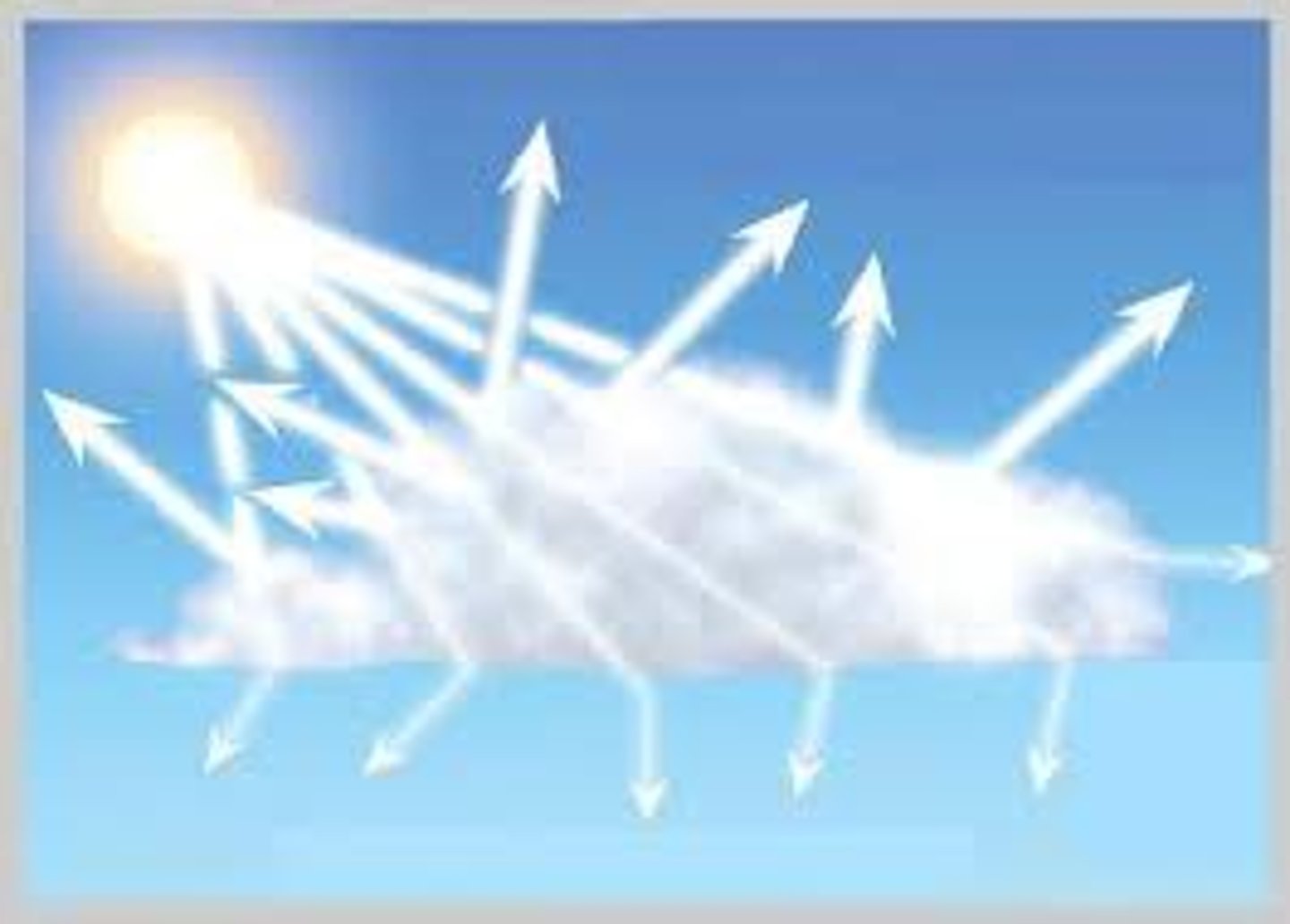
Scattering
When a beam of light is redirected in many different directions as it interacts with a particle of matter.

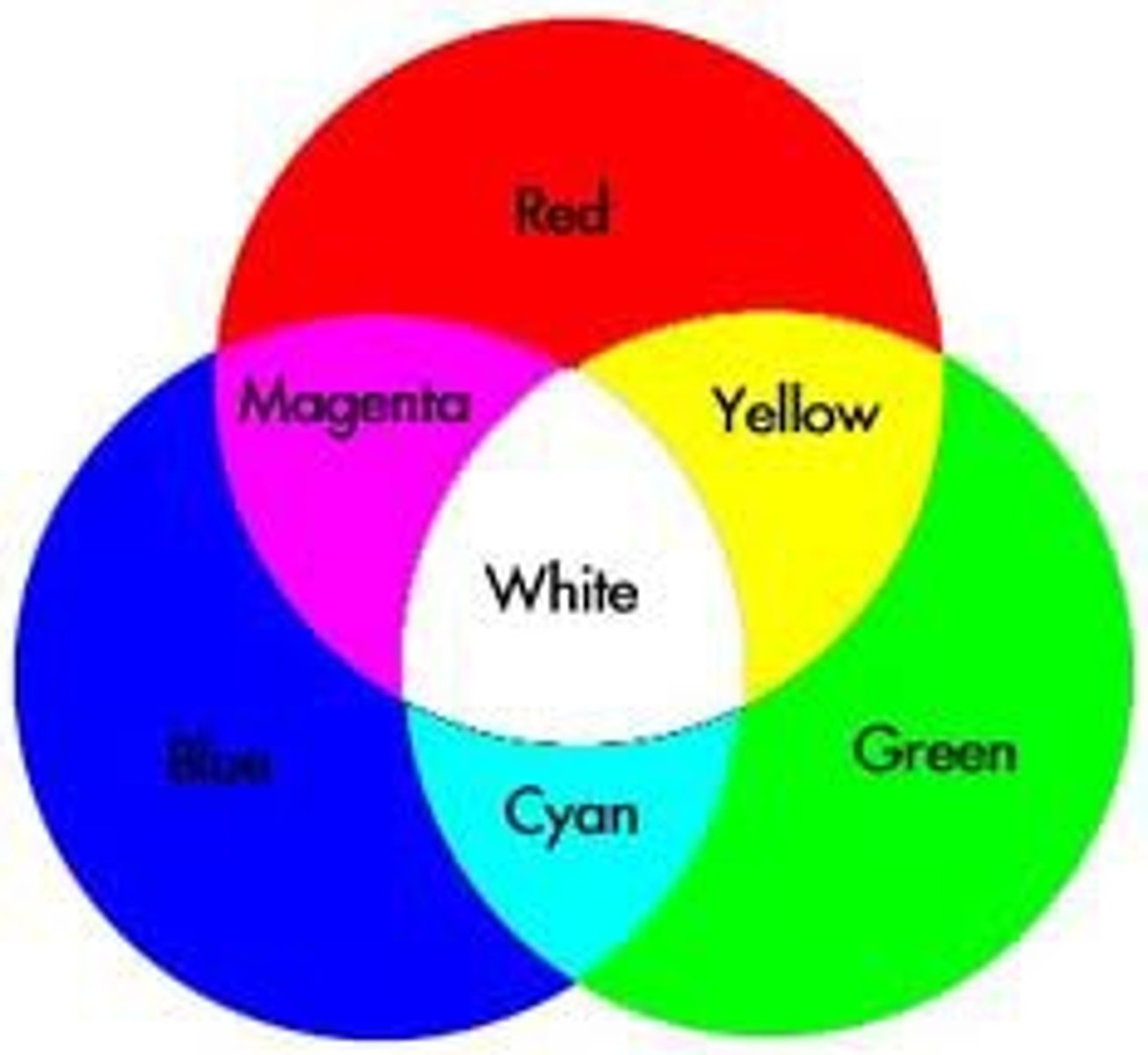
Additive colour
Filters red, green & blue of light.
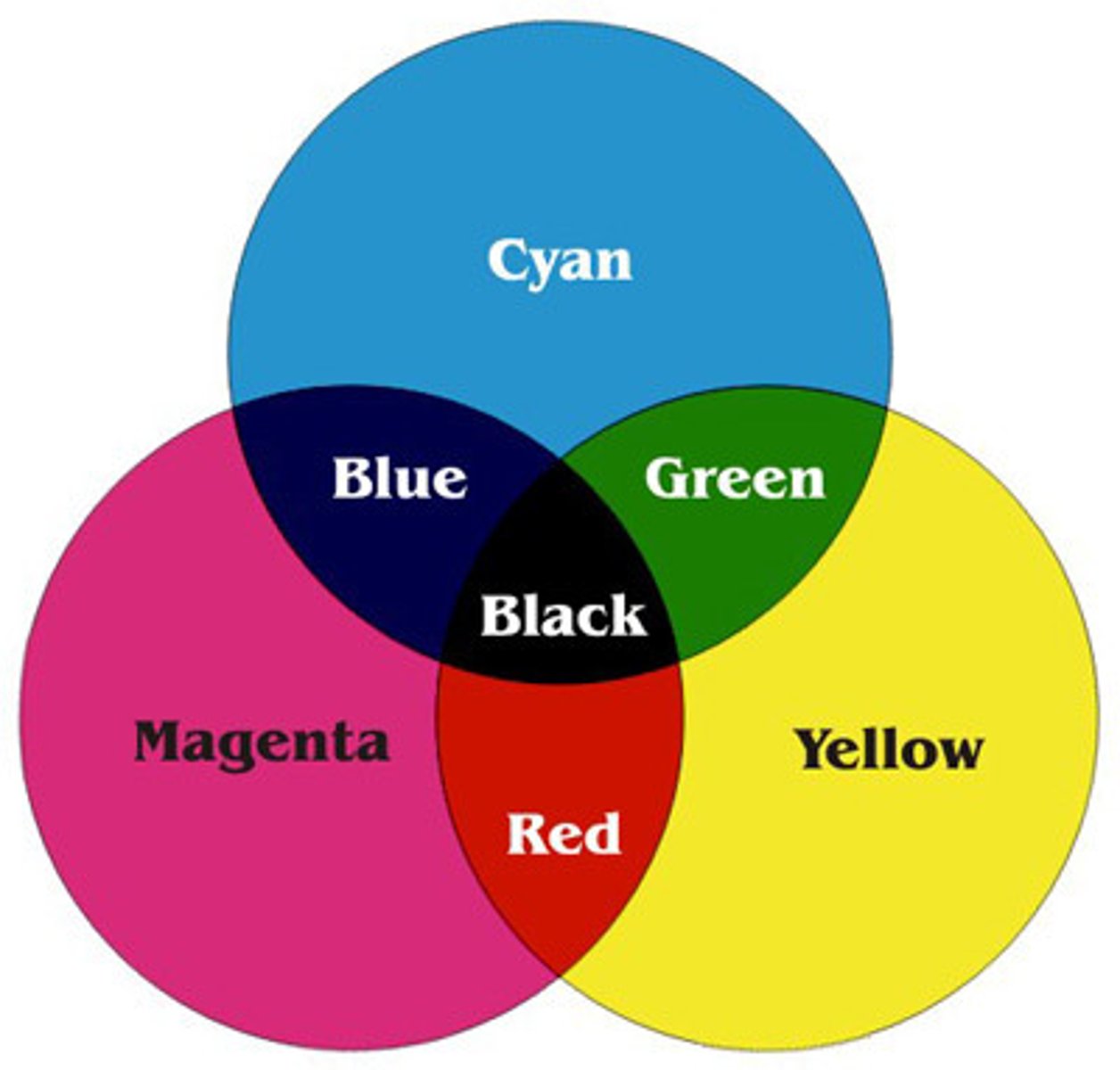
Subtractive colour
Pigments red, yellow & blue of paint.
Filter
Transparent materials that only allow light of a particular colour to be transmitted.
Radio Wave
Electromagnetic waves with the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies
Visible light
Electromagnetic radiation that can be seen with the unaided eye
Ultraviolet radiation
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths that are shorter than visible light but longer than X-rays.
Gamma rays
Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies.
Uses for radiowaves
Transport information through the atmosphere without wires.
Uses for infrared radiation
Night vision goggles, thermal imaging and remote controls.
Uses for ultraviolet radiation
UV lasers, fluorescent lamps and disinfecting waste water, identifying fraudulent bank notes. Too much exposure can cause sunburn.
Uses for gamma rays
Kills living cells, such as cancer, but can provoke DNA alteration by interfering with genetic material.
Violet
Shortest wavelength of visible light
frequency
the number of waves per second
Hertz
The unit used to measure frequency
wave
the transfer of energy without the transfer of matter
longitudinal wave
a wave that moves back and forth parallel to the direction that it is traveling