C3 - Contextual Theories of Motivation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the first theory surrounding contextual motivation?
Reinforcement Theory (Operant Learning) By Skinner
Identify the four quadrants of the reinforcement theory.
Top left:
Pleasant Events + Stimulus Applied = Positive Reinforcement
Bottom left:
Pleasant Events + Stimulus Withdrawn = Extinction
Top right:
Unpleasant Event + Stimulus Applied = Punishment
Bottom right:
Unpleasant Event + Stimulus Withdrawn = Negative Reinforcement
What is positive reinforcement?
Top left, occurs when there is Pleasant Events + Stimulus Applied.
The stimulus is considered positive if the action is more likely to be repeated again.
Ex. Praise, increased pay, etc...
What is extinction?
Bottom left, occurs when there is Pleasant Events + Stimulus Withdrawn.
The withdrawal of a pleasant stimulus resulting in the behaviour being less likely to occur. Extinguishing a previous level of accepted behaviour.
Ex. Employee not being praised for a Q1 goal being reached in Q2, because standards have shifted.
What is punishment?
Top right, occurs when there is Unpleasant Stimulus + Stimulus Applied.
It makes the behaviour less likely to occur again.
Ex. Reprimand, deduction in pay, etc...
What is negative reinforcement?
Bottom right, occurs when there is Unpleasant Stimulus + Stimulus Withdrawn.
The removal of a positive consequence after negative behaviour.
Ex. Learning to remove negative stimuli in a job setting
Three examples of organizational learning programs include...
1) OB-Mod (Organizational-Behaviour Modification)
2) Employee Recognition Programs
3) Training and Development Programs
Explain OB-Mod
One of the three organizational learning programs.
A managerial technique designed to change employee behaviour on the job using reinforcement principles.
- Thermostat analogy
Define target behaviour --> Set reasonable performance goals --> Measure frequency of behaviour --> Monitor behaviour --> Administer rewards
Explain employee recognition programs.
One of the three organizational learning programs.
Anything that is an award for behaviour.
Ex. Announcements, publications, innovation awards, attendance awards, etc...
Explain training and development programs.
One of the three organizational learning programs.
Training and development can be administered (1) within the workplace, and (2) externally.
Ex. In office courses, or paying for further education.
What is the second theory surrounding contextual motivation?
Job Design Theory
a) Define Job Design.
The structure, content, and configuration of a person's job/ role and associated tasks. How is this job set up? What are the tasks?
a) Define Job Scope.
Breadth depth, the number of different tasks on the job.
High breadth + High GNS = MATCH
Depth is the degree of discretion (decision making power, or autonomy) or control a worker has on how he does his job.
a) Define Job Involvement.
A cognitive state where one identifies with their job and the importance of that work. how much do you identify with your work, and believe it is important?
a) Compare job enlargement versus job enrichment.
Job Enrichment - The design or redesign of a job that enhances (1) Intrinsic Motivation within a job, (2) the quality of working life, and (3) increased job involvement. Providing jobs that aim for personal growth and skill development.
Job Enlargement - Expanding the scope of a job by adding more tasks of a similar level or responsibility.
b) Explain the Job Characteristics Model
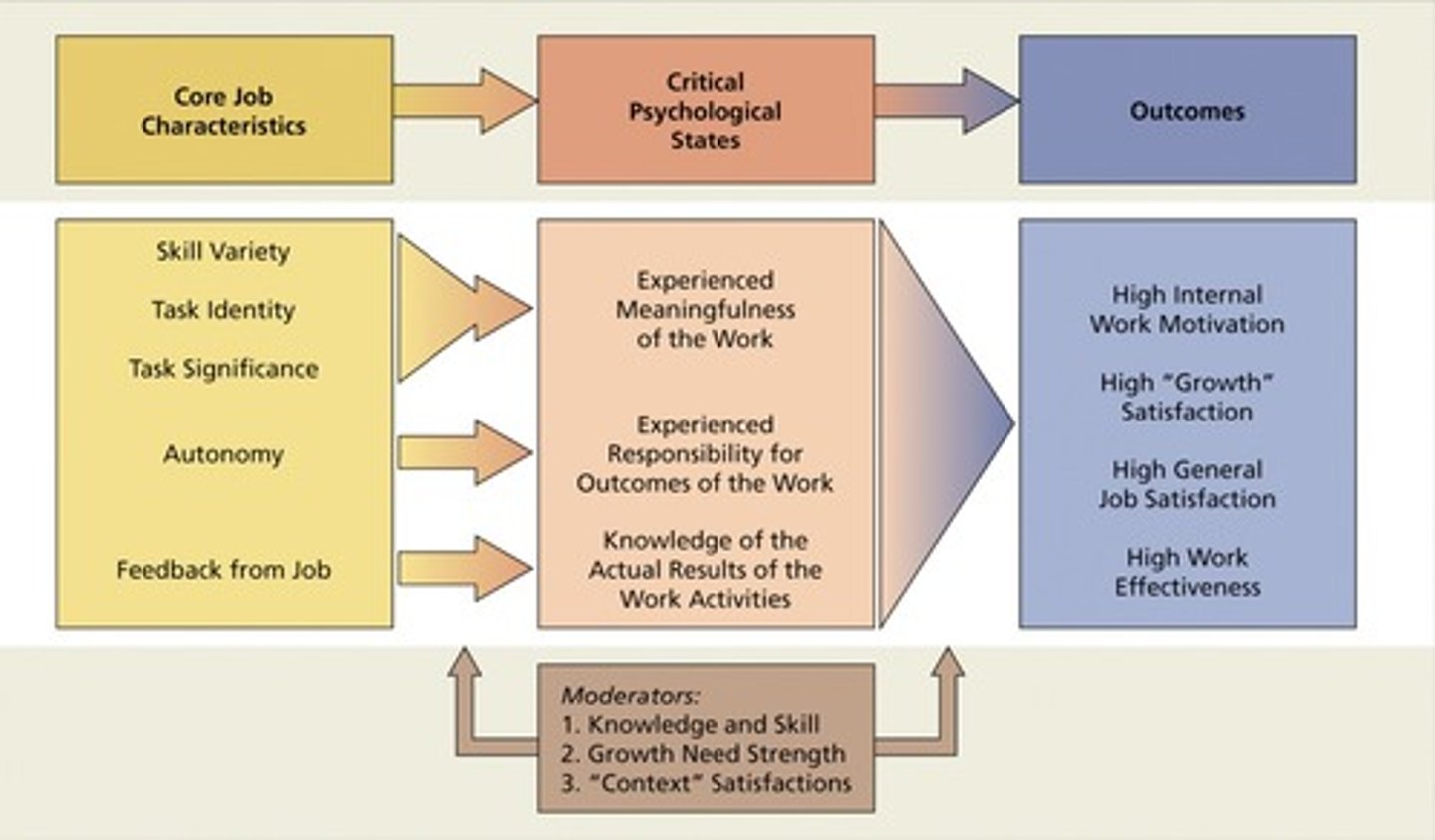
What are the five core job characteristics?
1. Skill Variety
2. Task Identity
3. Task Significance
4. Autonomy
5. Feedback
Define skill variety.
Extent to which a job requires a variety of activities.
Define task identity.
Extent to which a job requires completion of a whole and identifiable piece of work.
Define task significance.
Extent to which you perceive the job to be important, and has a significant impact on other people. Larger scope that TI.
Define autonomy.
Extent to which a job allows a worker to determine how he does his work
Define feedback from job.
The extent to which performing a job results in a worker receiving clear information regarding his level of performance.
What is a moderator?
Not all ind, respond the same way to a given job design- how a job's characteristics impact an employee can vary depending on:
1) Evaluate knowledge ad skills with T&D programs.
2) Don't do anything before measuing GNS
3) External satisfactions
c) Define Relational Job Design.
Companies are deliberately manipulating jobs so that humans can connect more.
d) Define Job Crafting.
Allowing your people to make self-initiated changes to make the job a better fit.
(1) Increasing social resources
(2) Increasing structural job resources (changing parts of the five core job characteristics)
(3) Increasing challenging job demands
Define organizational citizenship behaviours.
Going above and beyond in the workplace.
What are pay for performance or merit pay plans?
PRODUCTION JOBS: "Piece rate pay system" workers are paid a certain sum of money for each item produced. AKA "Wage incentive plan/ system" base hourly wage, plus a piece rate differential.
WHITE COLLAR:
Bonuses or commission.
What are four ways money can motivate teamwork?
(1) Profit sharing
(2) Gain sharing
(3) ESOP's employee stock ownership plans
(4) Skill Based pay
Define profit sharing.
The return of some company profit to employees in the form of a bonus or supplement (always formula based).
A TOPHAT plan is only for exec's.
Define gain sharing.
A pay incentive plan based on productivity and performance improvements, the workforce has some control (always formula based).
Define ESOP's.
Employee stock ownership plans allow a person to own shares.
Define skill-based pay.
A system in which people are paid according to the number of job skills they acquire.
What are two alternate motivation methods?
Alternative work schedules.
(1) Flextime
(2) Compressed work week
(3) Two part-time employees split the workload of a full-time job
(4) Work sharing- reducing the # of hours to avoid layoffs
(5) Telecommuting - Finding a balance between you and the employer commuting
More non-monetary incentives:
- Company car or paid gas
- Company discount
- Discounted uni
What do alternate motivation methods do?
1) Brings people in
2) Makes people stay