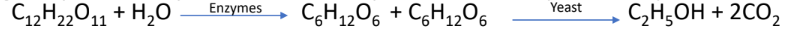industrial chemistry:- Ethanol
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
uses of ethanol
synthesis of acetaldehyde and ethylene
used as a solvent
important reactor for ether synthesis
important gasoline additive (ethanol blending: current target in india is 10%)
carbon source for single cell protein
worldwide production stats
Synthetic production in 1998: 2.6*106 tonnes per year
By fermentation of agricultural products (sugarcane molasses and corn starch) in 1997: 24.1*106 tonnes per year.
production by synthetic methods
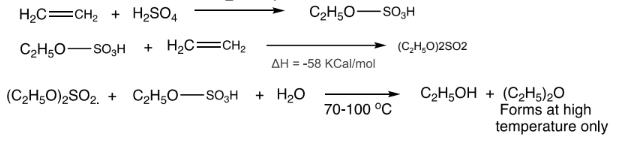
by indirect hydration, addition of H2SO4 and subsequent saponification of sulfuric acid ester
by direct catalytic hydration
indirect hydration
synthesis of ethanol requires conc H2SO4 (94-98% purity) for that purpose submerged burners are used to evaporate water form commercially available dil. H2SO4
Disadvantage: -
corrosion problems
concentrating H2SO4 is an expensive process
submerged burner produces SO2 as a side product
catalytic direct hydration
addition of water is carried out in gas phase and acid catalyst used is H3PO4
/SiO2
the synthesized ethanol is isolated from dilute aqueous solution
H2O azeotrope distillation
H2O removal by adding entraining agent like benzene: - increases volatility of water
disadvantages
C2H4 conversion is low (abt 4%)
high purity ethene required
continuous loss of H3PO4
high energy consumption
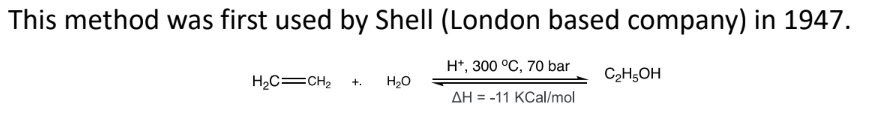
production of ethanol from sugarcane
procuring the grain or the plant
converting this to sugar
fermentation
distillation
industrial scale production of ethanol
fermentation of molasses
molasses is the mother liquor left after crystallization of sugarcane juice
dark colored viscous fluid
contains abt 60% fermentable sugar
process of industrial scale production of ethanol
dilution of molasses: molasses is first diluted with water in 1:5 molasses: water ratio by volume
ammonium sulphate: if nitrogen content of the molasses is less, it is fortified with ammonium sulphate to provide adequate supply of nitrogen to yeast
addition of sulfuric acid: fortified solution of molasses is then acidified with small quantity of sulfuric acid. addition of acid favors growth of yeast but unfavors growth of useless bacteria
Fermentation The resulting solution is received in a large tank and yeast is added to it at 35°C and kept for 2
to 3 days. During this period, enzymes sucrose and zymase which are present in yeast, convert sugar into ethyl alcohol
Fractional distillation: Alcohol obtained by fermentation is called wash which is about 15-18% pure. by using fractional distillation, it is converted to 92% pure alcohol, known as rectified spirit or commercial alcohol.