Unit 4 AP Psych
What is the psychoanalytic theory of personality?
-Developed by Sigmund Freud
-your childhood, your unconscious, sexual and aggressive impulses, and anxiety driven defense mechanisms determine personality
What is the psychodynamic theory of personality?
Psychodynamic personality was influenced by Carl Jung, Alfred Alder, and Karen Horney
-your childhood, unconscious, and anxiety-driven defense mechanisms influence human personality
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the psychoanalytic theory of personality?
-Developed by Sigmund Freud
-your childhood, your unconscious, sexual and aggressive impulses, and anxiety driven defense mechanisms determine personality
What is the psychodynamic theory of personality?
Psychodynamic personality was influenced by Carl Jung, Alfred Alder, and Karen Horney
-your childhood, unconscious, and anxiety-driven defense mechanisms influence human personality
What’s the id?
-entirely unconscious mind
-operates on the pleasure principal
-strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives
What’s the ego?
-mostly in the unconscious mind
-operates on the reality principal
-mediator of the id-superego, and reality. Wants to realistically bring pleasure over pain.
What’s the superego?
-present in both the unconscious and conscious mind
-driven by our moral compass, (our conscious)
-focuses on how we ought to behave
What is reaction formation?
unacceptable impulses are replaced with their opposites
Difference between Carl Rodgers and Abraham Maslow?
Abraham Maslow: wants us to ask ourselves how we got about reaching our full potential
Carl Rodgers: Wanted us to live up to our ideal self and understand we are basically good
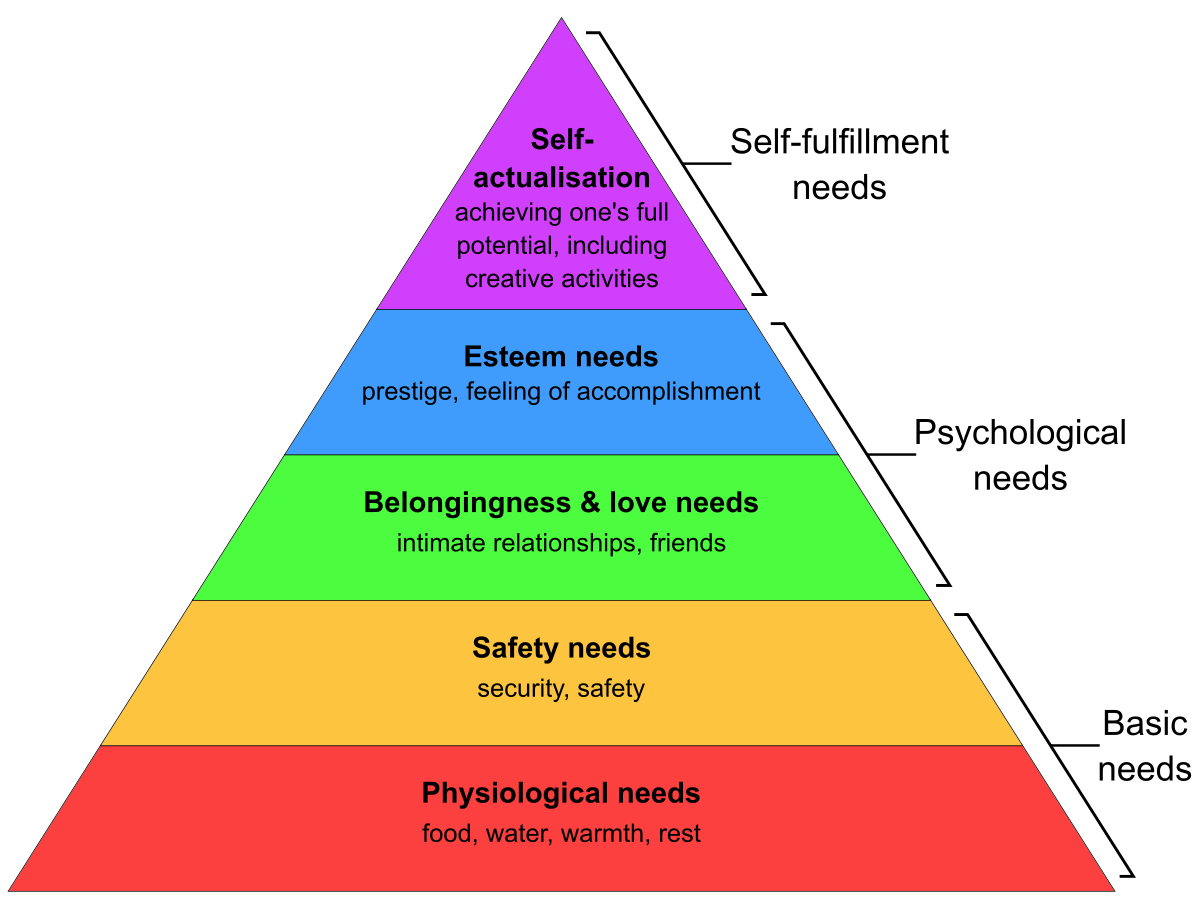
Maslow and self-actualization
-we continue to grow into the person we want to become
-we want to reach our full potential
-this takes time
-maslow developed this idea by studying those who are living a meaningful life who could easily answer the question who am I.
Rodgers and Unconditional Positive Regard
-we look for unconditional positive regard in trusted relationships
-when we have gained unconditional positive regard from a person we can’t let our guard down and be true to oneself.
Unconditional positive regard
a core concept in person-centered therapy popularized by Carl Rogers, refers to accepting and valuing a person without judgment or conditions, regardless of their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
What is humanistic theory centered around?
Growth and potential
Alfred Bandura’s influence on Social-Cognitive Theory
-Bobo Doll Experiment
-Much of what we learn is through watching and imitating others
-But how we think about things also influences our behavior
-social and cognitive factors play off another in our expressions, self-esteem, and self-concept.
reciprocal determinism
a core concept in Albert Bandura's social cognitive theory, proposes that behavior, personal factors, and environment interact and influence each other in a dynamic, continuous cycle.
Gordon Allport
Determined personality could be determined in 7 or fewer terms and were organized into cardinal traits, central traits, and secondary traits
Factor Analysis
use of statistic procedure to clusters similar traits into one overreaching trait
Hans Eyesenk
-Used factor analysis to establish two pairs for traits
Paul Costa and Robert McRae
With the help of factor analysis, they developed The Big 5.
These dimensions appear in all cultures and are considered the most current.
Facial Feedback Hypothesis
individuals' emotional experiences are influenced by their facial expressions. For example, smiling should typically make individuals feel happier, and frowning should make them feel sadder.
Broaden and Build Theory
Barbara Frederick-positive pscyhology’s influence on understand emotion
Cognitive appraisal
is an assessment of an emotional situation wherein a person evaluates how the event will affect them, interprets the various aspects of the event, and arrives at a response based on that interpretation.
Experiencing versus Expression
Experiencing
-always a stimulus
-always some sort of physiological arousal connected to the Autononmic Nervous System
-sometimes a cognitive appraisal
-which leads to experiencing emotion
Expressing
-gestures, facial expressions, and tones of voice help us express
-there are some universal facial expressions
-your culture teaches you how how to express emotions
-your culture teaches you how much emotion to express
Universal Facial Expressions
-Paul Eckman and Wallace Freismen travelled to a remote village in New Guiena to research if facial expressions were learned or universal
-tribe members were asked to identify the facial expression that matched the story being told
-Ekman and Freisman concluded that facial expressions were universal-at least the 6 they tested
What are the 6 universal expressions?
Fear, Happiness, Anger, Disgust, Surprise, Sadness
How can culture influence emotional expression?
-individualistic cultures display emotion more vividly
-collectivist cultures tend to rely more on context to identify emotions and are less expressive
Display rules
culturally learned norms that guide how people express emotions in specific social contexts, influencing their communication and interactions. They dictate when, where, and how it's appropriate to display or suppress emotions.