3019PSY Module 8 Video Games
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Green & Bavelier (2003)
examine the influence of video games on visual attention
RQs for Green & Bavelier (2003)
are there differences in visual attention skills between VGPs and NVGPs?
can NVGPs be trained in their visual attention skills by playing video games?
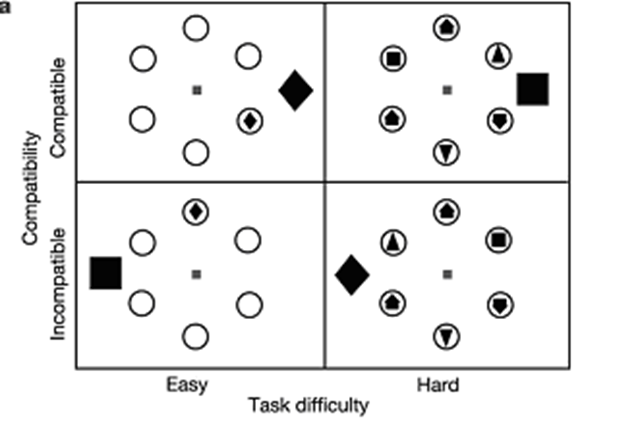
flanker compatability task
measures information processing when distractors are present; difficulty is manipulated by compatability and difficulty
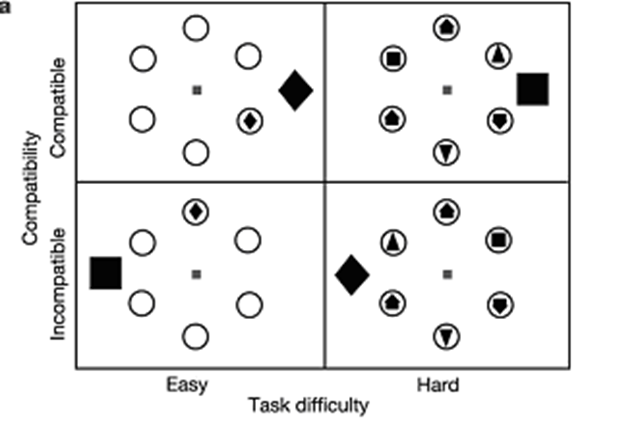
compatability (flanker task)
how similar the distractors are to the target

difficulty (flanker task)
the number of rings that are filled
distractor effect (flanker task)
the difference in reaction time between targets with incompatable and compatable distractors (incompatable RT - compatable RT)
Green & Bavelier results (flanker task)
VGPs had a more stable distractor effect regardless of task difficulty, while NVGPs distractor effect dropped significantly from easy to harder tasks
enumeration task
measures how many items a person can take in at once; flashes 1-12 squared on screen for 50ms
substitizing range (enumeration task)
the number of items apprehended (3-4 for adults)
Green & Baviler results (enumeration task)
VGPs had a much larger subsitizing range (about 5 compared to 3-4) and made less errors for all numbers of squares
useful field of views task
measures how wide/ broad someone can make their attention field; presents 8 intersecting spokes with a target on it; researchers manipulate demand by altering the degree the target is from the centre of the visual field
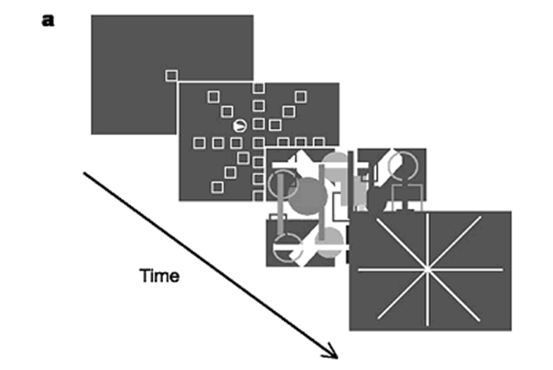
eccentricity (useful field of views task)
how far out from the centre of the visual field the target was presented
Green & Bavelier results (useful field of views task)
VGPs were much more often correct for all eccentricities
attentional blink task
measures temporal attention; participants are presented sequentially with 2 target letters
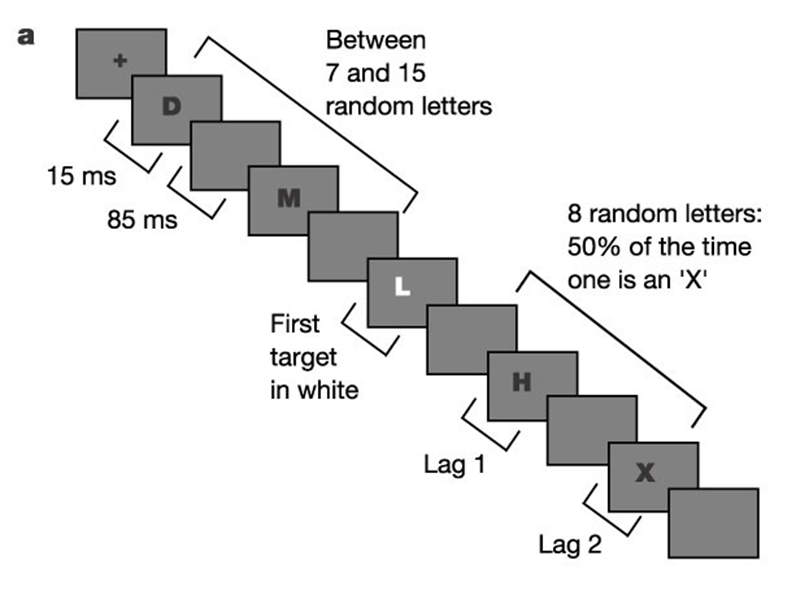
attentional blink (attentional blink task)
when 2 targets follow eachother closely in time, attentional resources are taken up processing target 1 whilst target 2 is shown, so that target 2 isnt processed
Green & Bavelier results (attentional blink task)
VGPs were better at detecting target 2 at all intervals, but the difference got lesser as the number of interviening items got larger
Fransceschini et al (2013)
examined the influence of video game training on attention and reading skills in children with dyslexia
RQ for Fransceschini et al
would visual attention training (through video games) improve reading in children with dyslexia?
Franscechini et al participants
20 Italian children with dyslexia without video gaming experience, split into AVG and NAVG groups
focused attention task
participants are presented with a focus point and a cue which indicates where they need to focus attention to in the stimulus display
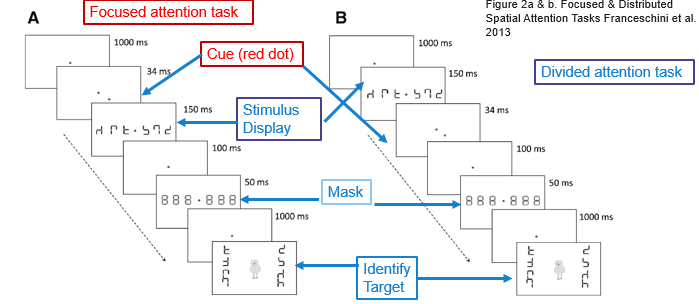
divided attention task
participants are presented with a focus point and then the stimulus display before the cue, so they need to divide their attention across the entire display before they know where they are supposed to look
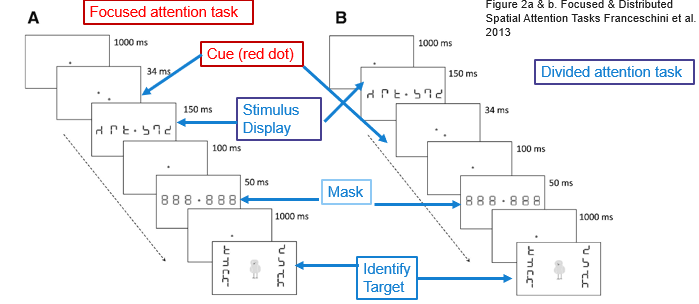
Fransceschini et al results (focused/divided attention task)
AVG group made significantly greater improvements in both tasks
cross-modal attention task
participants are presented with verbal cues as to which side of the screen the target will appear
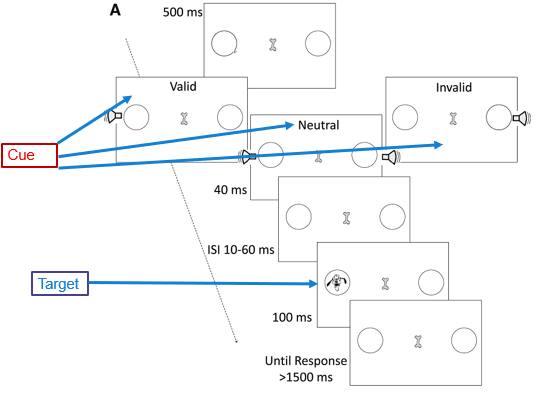
Fransceschini et al results (cross-modal attention task)
AVG made significant improvements pre- to post-test
Fransceschini et al results (word reading)
AVG improved performance more than participants in a 12-month reading program and improvements maintained at 2 months follow-up
Bavelier et al (2012)
examined the link between playing action video games and neural processing
aims of Bavelier et al
examine the role of top-down attention in the dorso-fronto patietal networds for VGPs and NVGPs
compare VGPs and NVGPs on a visual search task and how this affects processing of irrelevant motion information
Bavelier et al participants
26 young adult males who either played action video games often (5 hours / week) or did not
flanker task (Bavelier et al)
participants decide if a square or a diamond was present at low and high levels of difficulty (types of distractors) and distraction location (peripheral or central)
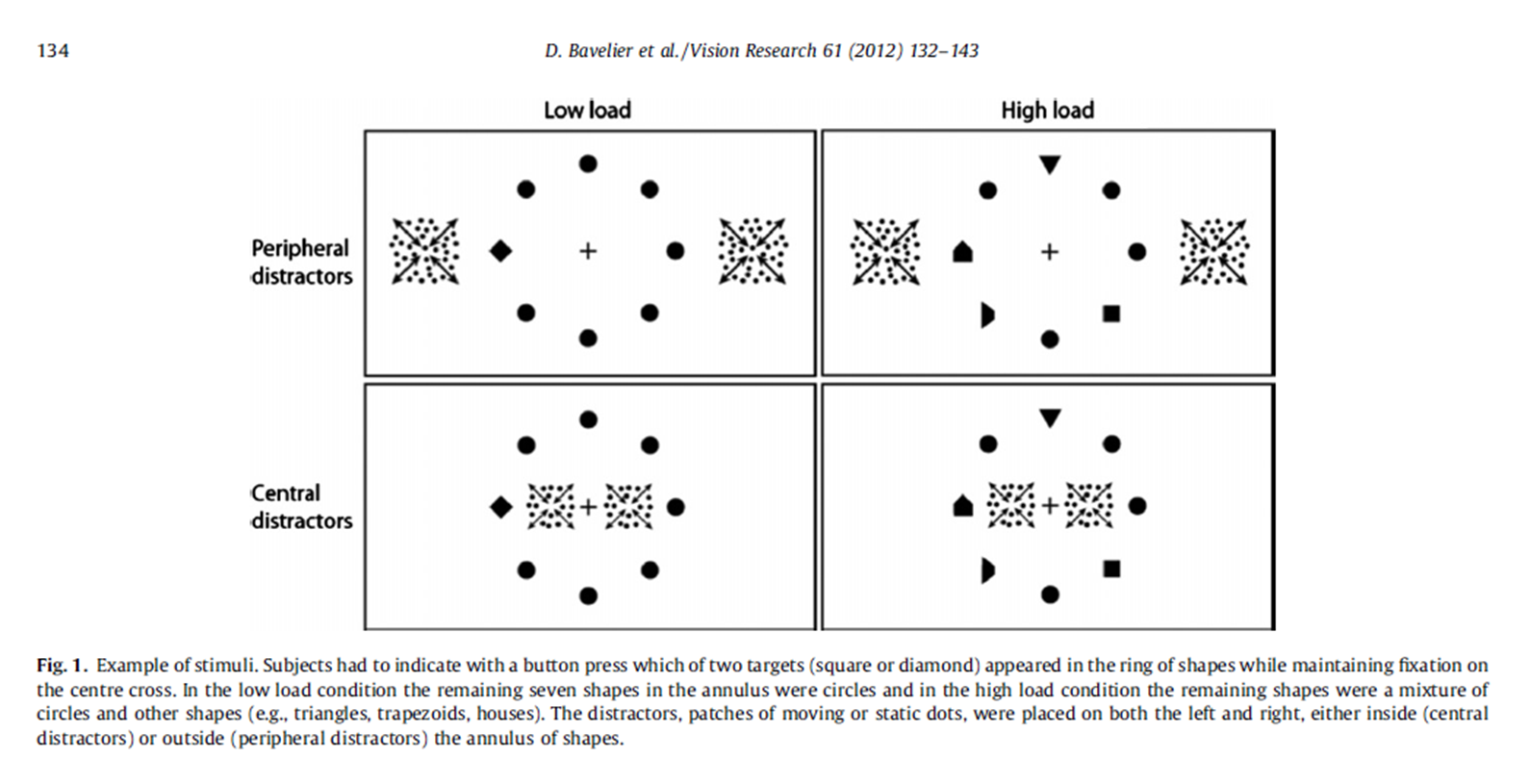
Bavelier et al results (flanker task)
VGPs were equally good at peripheral and central distractor trials; peripheral, irrelevant movement was more distracting for NVGPs; VGPs had a shorter RT but were still affected by task difficulty
Bavelier et al results (fMRI)
NVGPs had greater activation of frontal, parital, and visual areas
Kahn et al (2014)
examined the relationship between playing video games and cortical thickness
aim of Kahn et al
to examine the association between spontaneous video game playing and cortical thickness in adolescents
participants of Kahn et al
152 male and female adolescents (either VGPs or NVGPs)
Kahn et al results
there is a positive correlation between self-reported weekly VGing and thickness of the left dorsalateral PFC and left frontal eye fields
role of the left dorsolateral PFC
executive control (including working memory and decision making)
role of the left frontal eye fields
perceptual decision making, visuo-motor integration, attentional control