Pharmacology MCQ Practice
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
During which phase are animals used in testing?
pre-clinical phase
Which phase of drug evaluation tries informed patients?
Phase II, can be combined with phase I for rare diseases
Which phase of drug evaluation is done after the drug is released on the market?
Phase IV, can lead to drugs being taken off the market if serious long-term side effects are found
Which phase of drug evaluation tests the drug in the clinical market?
Phase III
Which of the following is the definition of absorption?
the movement of drug from site of administration into blood supply
What is the bioavailability of a drug administered IV?
100% (direct)
How do PK profiles help you choose between drugs?
Different drugs can be needed depending on the urgency of the indication, drug can have distinct PK depending on route of administration
How do PK profiles help you choose how frequently to administer drug?
We can see the time it takes to get to the critical concentration
What is the definition of drug distribution in PK?
the movement of drugs throughout the body (from plasma to tissue)
What is the major organ involved in drug metabolism?
liver
What is the definition of metabolism
the enzymatic alteration of drug structure (conversion/modification/biotransformation)
Which of the following organs is involved in excretion
kidney
what is excretion
removal of drug from the body
what is the time it takes for Cmax to be reduced by half
half-life
If we gave a drug of half-life 6, after 12 hours, what’s the concentration?
25%, half after half amount of time, quarter after same amount of time after

which of the following is first-order kinetics?
constant fraction of drug being removed per unit time
which of the following is zero-order kinetics?
constant amount of drug removed per unit time
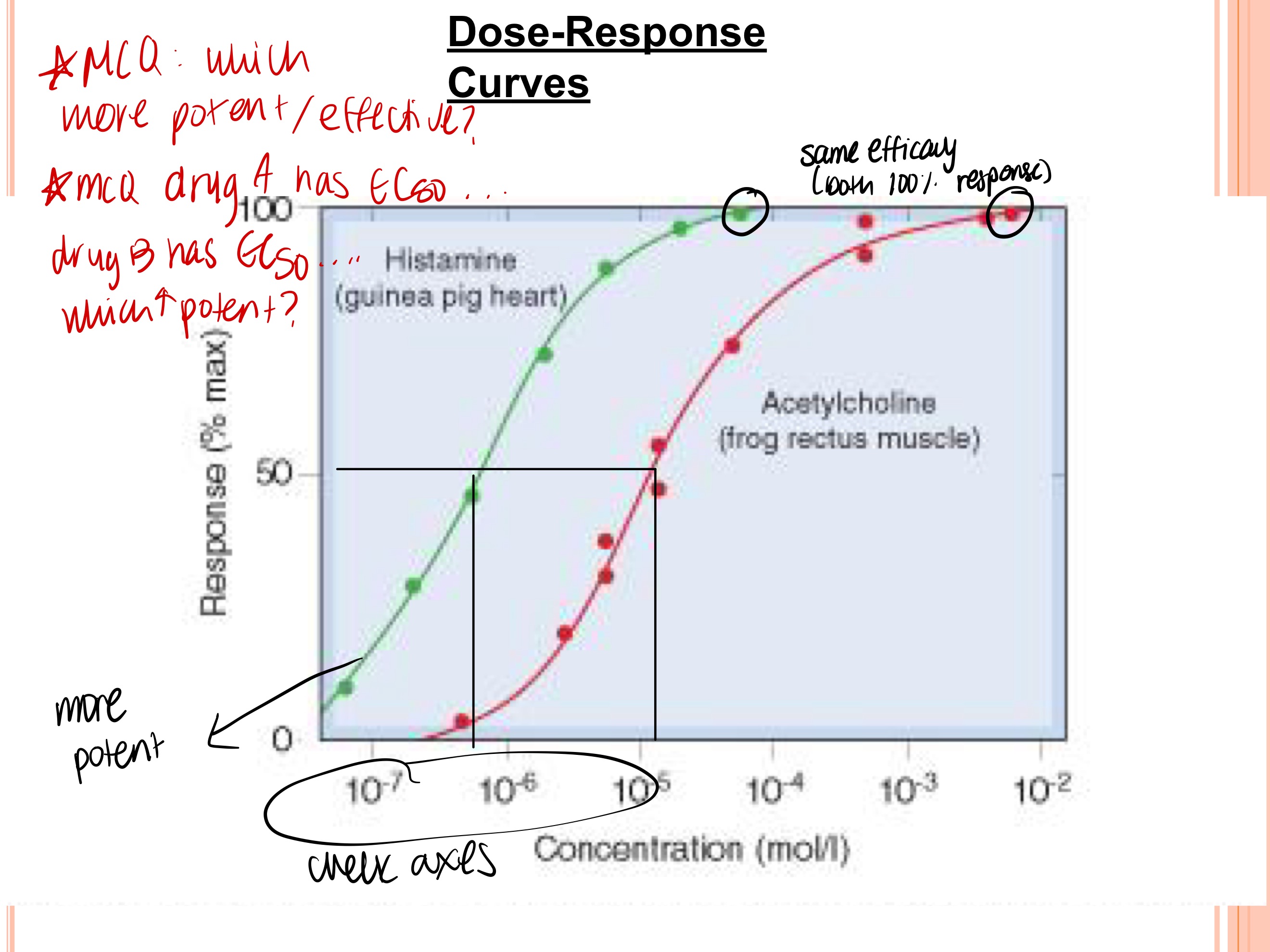
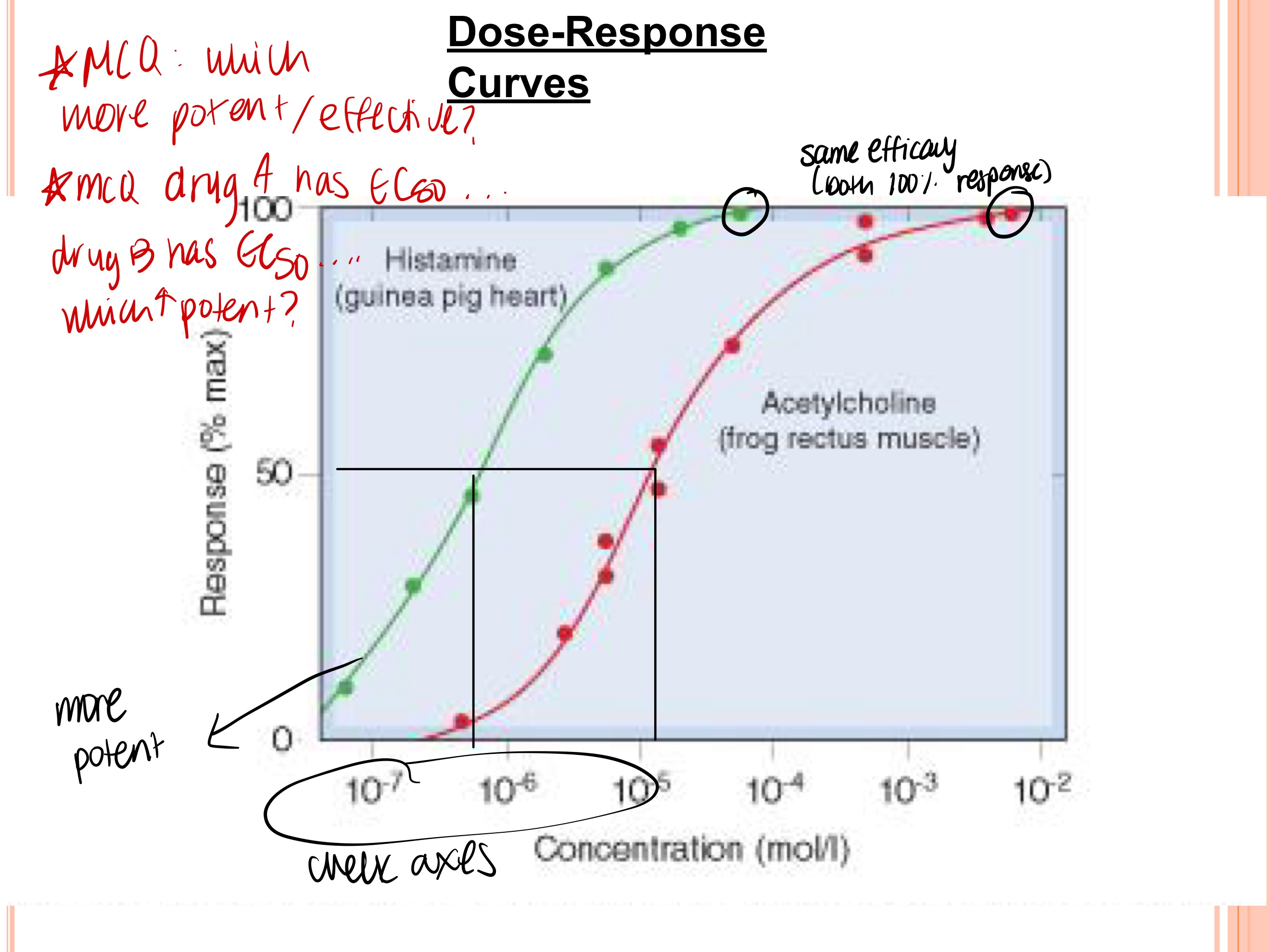
Which drug is more potent? Which drug is more effective?
green, both same effectiveness
Which of the following is an agonist?
one that has affinity and intrinsic activity, stimulates a response, binds and activates
which of the following is an antagonist?
has affinity but no intrinsic ability, prevents agonist action
How many domains do nuclear receptors have?
none, they’re intracellular
what are the specialized domains of GPCR?
G-protein
what are the specialized domains of LGIC?
channel pores
what are the specialized domains of KLR
enzymatic/catalytic domain, usually with phosphorylation
how many subunits and transmembrane receptors do LGIC have?
4-5, 4
how many subunits and transmembrane receptors do GPCR have?
7, 1
how many subunits and transmembrane receptors do KLR have?
1,1
how many subunits and transmembrane receptors do NR have?
0,1
True or false: G-protein bound by GTP is inactive
false, GDP is inactive
True or false: G-protein bound by GDP is inactive
true, GDP is inactive
Pharmacokinetics is best defined as which of the following?
I. the action of drugs on the body
II. The interaction of a drug with its receptor
III. The process of drug absorption
IV. The action of body on drugs
V. The duration of action of a drug
the action of body on drugs
Which of the following is the major site of drug metabolism?
I. Kidney
II. Liver
III. Brain
IV. Lung
V. Skin
Liver
What is the removal of a drug referred to as?
excretion
Which effect refers to the process occurs when an oral medication is processed through the liver before reaching the tissues?
first-pass effect
what is the amount of time it takes for a drug level to decrease to one-half its peak level in the blood?
half-life
drug excretion primarily occurs through which organ?
the kidney
60 mg of drug Z was administered and 6 mg reached the plasma. What is the bioavailability of drug Z?
10%
T/F: coronary flow is blood supply to heart muscle
true
T/F: nitrates stimulate both arterial and venous SMC contraction and contract coronary arteries
false, only vascular
T/F: statins are administered orally and decrease hepatic cholesterol synthesis
true
Which of the following is true about aspirin
irreversible cox-1 inhibitor
which is true about statin MoA
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
T/F: thrombin cleaves plasminogen to plasmin
false, fibrinogen to fibrin
T/F thrombus is a solid mass consisting of only platelets
False, also have white/red blood cells
T/F: coagulation cascade can be activated by contact with damaged tissue or tissue factor release
true
T/F: natriuresis is exceptionally salty urine
true
Which is false about loop diuretics
Increase aldosterone production in collecting duct
Which is true about warfarin
Warfarin is a vit k antagonist
What’s true about statins
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
What is false about CCB
Increase intracellular ca2+
What is false abt beta blockers
Exert effect by blocking sodium movement
Where do thiazide diuretics work
Distal convoluted tubule
Which receptor is found on the presynaptic terminal
Alpha 2
Which one of the following is a class of receptors targeted for heart failure treatment
Beta1
A medication that non-selectively blocks both beta1 and beta2 adrenergic receptors is prescribed to a patient. Which of the following is a potential side effect
Increased bronchial constriction
What are cholinergic drugs
Drugs that act on the same pathway as acetylcholine (often called parasympathomimetic drugs), not limited to a certain site of action, associated with undesirable systemic effects
Which ONE of the following is not a class of anti-depressant drug?
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Which ONE of the following is TRUE regarding opioid drugs?
are associated with withdrawal symptoms
Which of the following is not a feature of a neurotransmitter synapse?
Nuclear Receptor
Which ONE of the following is FALSE regarding excitatory cholinergic neurotransmission in the CNS?
A localised hyperpolarisation occurs in the post-synaptic neuron
Which ONE of the following is FALSE regarding Inhibitory GABA neurotransmission in the CNS?
GABA agonists will decrease receptor activation
If a patient is taking MAO inhibitors and ingests tyramine (red wine, aged cheese),which of the following acute responses is most likely?
Stimulation of NA release
Which ONE of the following statements is TRUE regarding testosterone?
Is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by 5α-reductase
Which one of the following hormones is not produced by the adrenal gland
estrogen
In the diagnosis of Addison’s disease (primary adrenal insufficiency), which ONE of the following is the expected response to corticotropin?
High Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Which one of the following laboratory results would be expected in hypothyroidism
Low T3-Low T4- High TSH
Which gland is primarily responsible for regulating metabolism through hormone secretion
thyroid
Corticosteroids are often used in the management of which ONE of the following
asthma
Which ONE of the following is NOT a mechanism of HIV/AIDS therapy
promotion of reverse transcriptase activity
Which ONE of the following mechanisms is a common target for antibacterial chemotherapeutic agents?
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Which ONE of the following drug types does NOT inhibit cell cycle progression?
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
Which ONE of the following is a FALSE statement about targeted therapies?
They are never targeted to the PD-1 molecule
Which ONE of the following statements about angiotensin II receptor antagonists is TRUE?
they selectively block angiotensin II AT1 receptors
Which ONE of the following is the most appropriate treatment for anaphylaxis?
adrenaline/epinephrine
Which ONE of the following statements regarding aspirin is TRUE?
Aspirin inhibits cyclooxygernase-1 (COX-1)
Which ONE of the following molecules is the target of an immune
checkpoint inhibitor monoclonal antibody?
B. Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1), which is located on the surface of many
cancer cell-types
Imatinib is a groundbreaking small-molecule (tyrosine kinase) inhibitor used primarily in
the treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
Which ONE of the following is the primary molecular target of Imatinib, which drives the
proliferation of CML cells?
B. BCR-ABL fusion protein (a constitutively active tyrosine kinase), resulting from the
Philadelphia chromosome translocation (9;22)
Trastuzumab (herceptin) is useful in treating BCa because of its ability to bind
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
aromatase inhibitors such as anastrozole are used in treating advanced BCa because of their ability to
block estrogen receptors
which one is NOT a mechanism by which antimetabolites inhibit DNA synthesis
stimulate dihydrofolate reductase
which of the following is true
oncogene function is amplified in cancer
which is not a hallmark of cancer cells
promotion of apoptosis
Which ONE of the following is NOT a division of the central nervous
system?
a) Cranial Nerves
b) Autonomic Nervous System
c) Brain
d) Spinal Cord
e) None of the above
cranial nerves
Which ONE of the following is NOT a feature of a neurotransmitter
synapse?
a) Post-synaptic neuron
b) Neurotransmitter
c) Pre-synaptic neuron
d) Kinase-linked receptor
e) Inactivating enzymes
kinase-linked receptor
Which one of the following is FALSE for pathology in Parkinsons
disease?
a) Dopamine levels are reduced
b) Anticholinergic drugs can provide relief
c) Dopamine precursor therapy is effective for 2-5 years
d) Acetylcholine levels are reduced
e) Cause can be a blow to the head
d) Acetylcholine levels are reduced
Which ONE of the following is NOT a treatment strategy for
Parkinson’s disease?
a) Dopamine precursor
b) Cholinergic receptor antagonists
c) Dopamine receptor agonists
d) Inhibition of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
e) Activation of dopa-decarboxylase
e) Activation of dopa-decarboxylase
Which of the following is NOT a mechanism of action for drugs used
in Parkinsons disease?
a) Metabolise dopamine
b) Activate dopamine receptors
c) Reduces dopamine precursor metabolism in gastrointestinal tract
d) Block acetylcholine receptors
e) Increase transport of dopamine precursors into central nervous
system
a) Metabolise dopamine
Which ONE of the following is FALSE regarding opioid drugs?
a) Represents a class of analgesic drugs
b) Reduce synaptic neurotransmitter release at the presynaptic
terminal
c) Hyperpolarise the postsynaptic terminal
d) Act as GABA receptor agonists
e) Are associated with withdrawal symptom
d) Act as GABA receptor agonists
1. Which ONE of the following is not a class of anti-depressant drug?
a) Tricyclic Anti-depressants
b) Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors
c) COMT inhibitors
d) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
e) Serotonin-Noradrenaline re-uptake inhibitors
COMT inhibitors
Which of the following is not a feature of MAO-i?
a) used as anti-depressants
b) reduce re-uptake of serotonin (5-HT) and NA
c) contraindicated during pregnancy
d) metabolized in the liver
e) increase synaptic levels of NA
c) contraindicated during pregnancy
Which ONE of the following types of signalling involves hormones
being
released into the bloodstream to affect distant target cells?
a) Autocrine signalling
b) Synaptic signalling
c) Juxtacrine signalling
d) Endocrine signalling
e) Paracrine signalling
d) Endocrine signalling
Which ONE of the following hormones is secreted by the anterior pituitary
gland?
a) Anti-diuretic hormone/vasopressin (ADH/AVP)
b) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
c) Testosterone
d) Calcitonin
e) Adrenaline
b) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Which one of the following statements regarding human growth hormone is
CORRECT?
a) It is synthesized in the hypothalamus
b) It stimulates production of somatomedins (i.e. IGF-1) by the liver
c) Its release is stimulated by somatostatin
d) It causes a decrease in lipolysis
e) It is a steroid hormon
b) It stimulates production of somatomedins (i.e. IGF-1) by the liver
Drugs that mimic ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) are used in the
diagnosis of Addison’s disease for the measurement of which ONE of
the following?
a) The measurement of blood glucose levels
b) The measurement of thyroid function
c) The measurement of adrenal gland function
d) The measurement of insulin sensitivity
e) The measurement of serum K⁺ concentration
The measurement of adrenal gland function
Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the release of which hormone from
the anterior pituitary?
a) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone(ACTH)
b) Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
c) Luteinising hormone(LH)
d) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
e) Growth Hormone
c) Luteinising hormone(LH)
Which one of the following classes of drug is routinely used in the treatment of prostate
cancer?
a) Androgen receptor antagonist
b) Anabolic androgens
c) 5-alpha reductase inhibitor
d) Aromatase inhibitor
e) Dihydrotestosterone
Androgen receptor antagonist
The estrogen-progesterone combined pill primarily exerts its contraceptive
effect by which ONE of the following mechanisms?
a) Increasing the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
b) Stimulating the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone
(FSH)
c) Providing negative feedback to suppress the release of GnRH, LH, and FSH
d) Enhancing the production of androgens in the ovaries
e) Promoting the secretion of prolacti
Providing negative feedback to suppress the release of GnRH, LH, and FSH
Which ONE of the following drug classes is
NOT used in the treatment of hypertension?
a) diuretics
b) β blockers
c) ACE inhibitors
d) α receptor agonists
e) calcium (Ca++) channel blockers
d) α receptor agonists
Thiazide diuretics mediate their action in which
ONE of the following regions of the nephron?
a) Glomerulus
b) Proximal tubule
c) Loop of Henle
d) Distal convoluted tubule
e) Collecting duct
d) Distal convoluted tubule
Regarding warfarin which ONE of the following
statements is TRUE ?
(a) Warfarin induces Vitamin K reductase
(b) Warfarin is an antithrombin III inhibitor
(c) Warfarin is a Vitamin K agonist
(d) Warfarin is a Vitamin K reductase inhibitor
(e) Warfarin is a cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor
(d) Warfarin is a Vitamin K reductase inhibitor.