Week 0-2 (Aquatic Physiotherapy)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Temperature of hydrotherapy pools
33-35 degrees (thermoneutral)
No change in core body temperature when in water
Relative density of water
RD of water is 1
RD greater than 1=SINK
RD less than 1=FLOAT
RD of human body=0.86-0.97
How do different structures in the body differ in relative density?
High: bone & muscle (reduced with osteoporosis & muscle atrophy)
Low: lungs, air & fat (increases with inactivity)
Hydrostatic pressure
weight/compressive force of water
Linear increase of hydrostatic pressure with depth of water (increased pressure, deeper)
Effect of hydrostatic pressure on body
- Increased proprioception at depth?
- Increased resistance to chest expansion making respiration difficult at depth
- Oedema shifts from interstitial region to blood plasma
Buoyancy
when a body is partially or completely immersed in a fluid, it experiences an apparent loss in weight that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the immersed part of the body
Always experienced as an upthrust (opposite direction to the force of gravity). The magnitude/size is equivalent to the size/weight/volume that is under water
Buoyancy and relative weightbearing at different depths
C7: 8% WB
Xiphisternum: 30% WB
ASIS: 50% WB
Note ↑ peak WB with impact activities
Respiratory effects of immersion
- Due to relative central hypervolemia & pressure on abdomen (and hence upward pressure on diaphragm)
- Reduces TLC, FRC and vital capacity
- Increases airway closure & resistance
Cardiovascular effects of immersion
- Shift of fluids from interstitial spaces to blood plasma, causing a reduction in swelling
- Increased fluid/blood return from distal limbs
- Leading to increased SV & hence CO due to increased central circulation
Renal effects of immersion
- Diuresis due to ↓ vasopressin, ADH, renal sympathetic nervous activity, & renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activity
- Natriuresis & Kaliuresis
Effects of immersion in warm water on pain
- Large, myelinated fibres from thermal & mechanoreceptors close the gate to smaller nociceptive activity
- ↑ circulation
- ↑ collagen flexibility & extensibility
Effect of buoyancy on pain
- Reduces stress & compression & mechanical stress on tissues
- ↑ROM, causing more synovial fluid movement and improving nutrition
Effect of hydrostatic pressure on pain
- ↓ Oedema
- ↑ sense of well being
- ↓ sympathetic activity due to reflex ↓ HR
Effect of immersion on exercise
- Increased core temperature due to reduced heat dissipation in warm pools
- Increased RPE and reduced HR at submaximal VO2
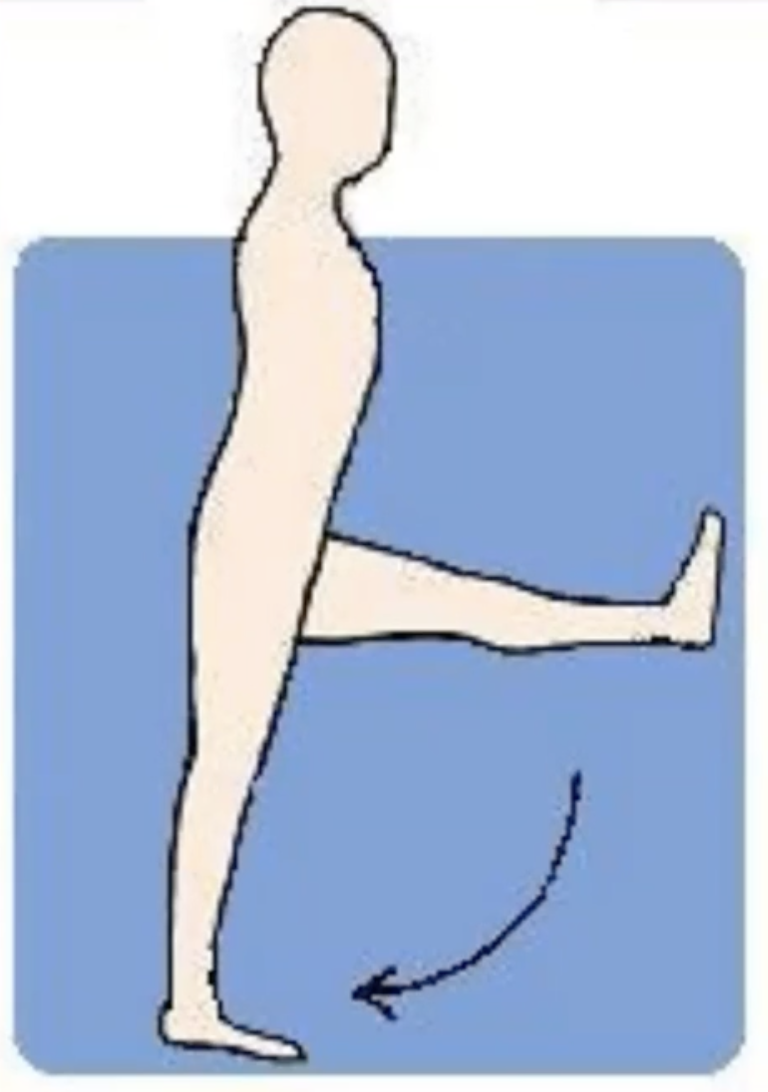
Buoyancy assisted
movement in upward direction (for very weak muscles Grade I-II, or mobilisation and stretching)
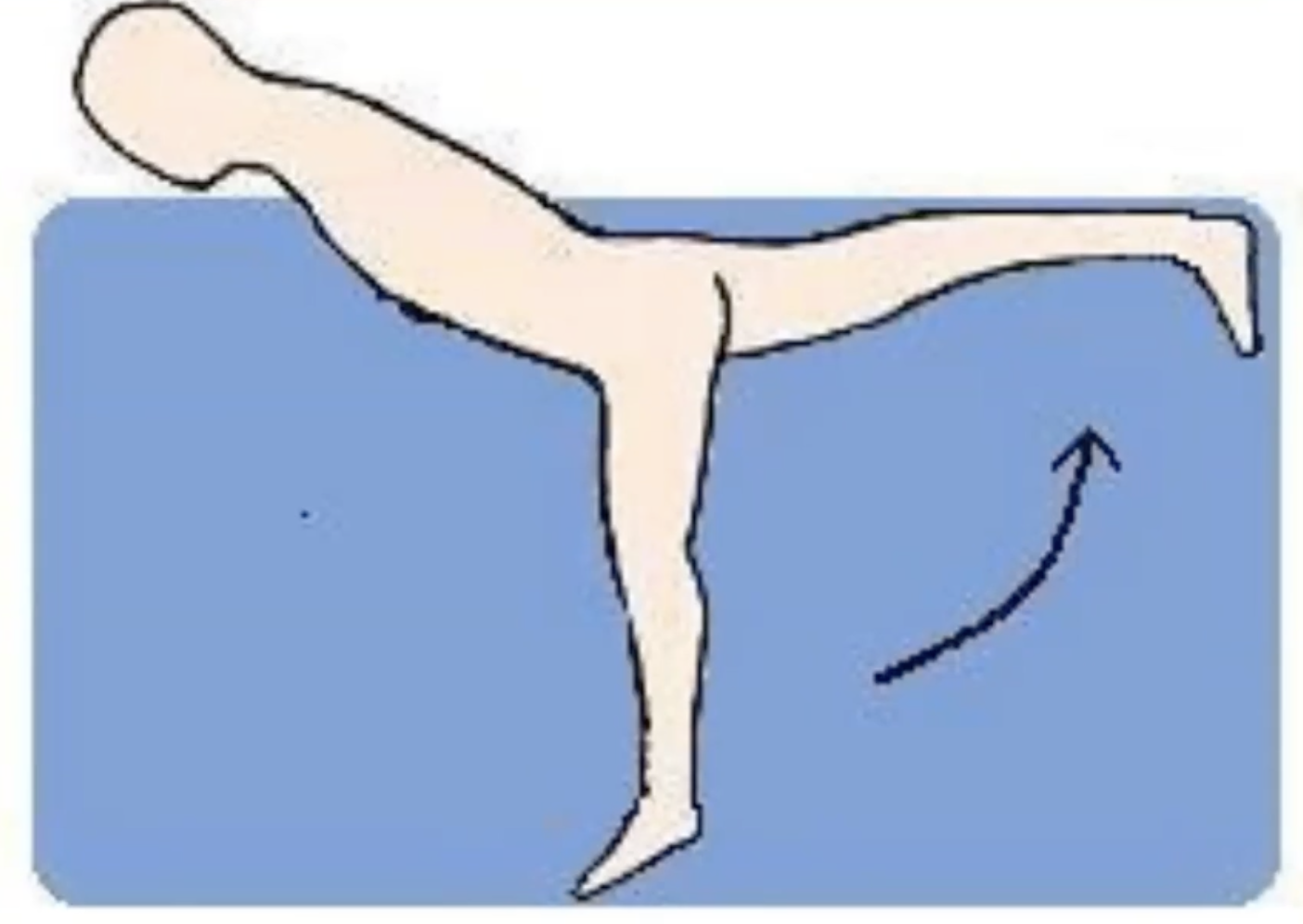
Buoyancy counter balanced or across buoyancy
progression from buoyancy assisted by changing amount of load, typically in sidelying (not favourable for water as head must be kept up), usually Grade I-II strength
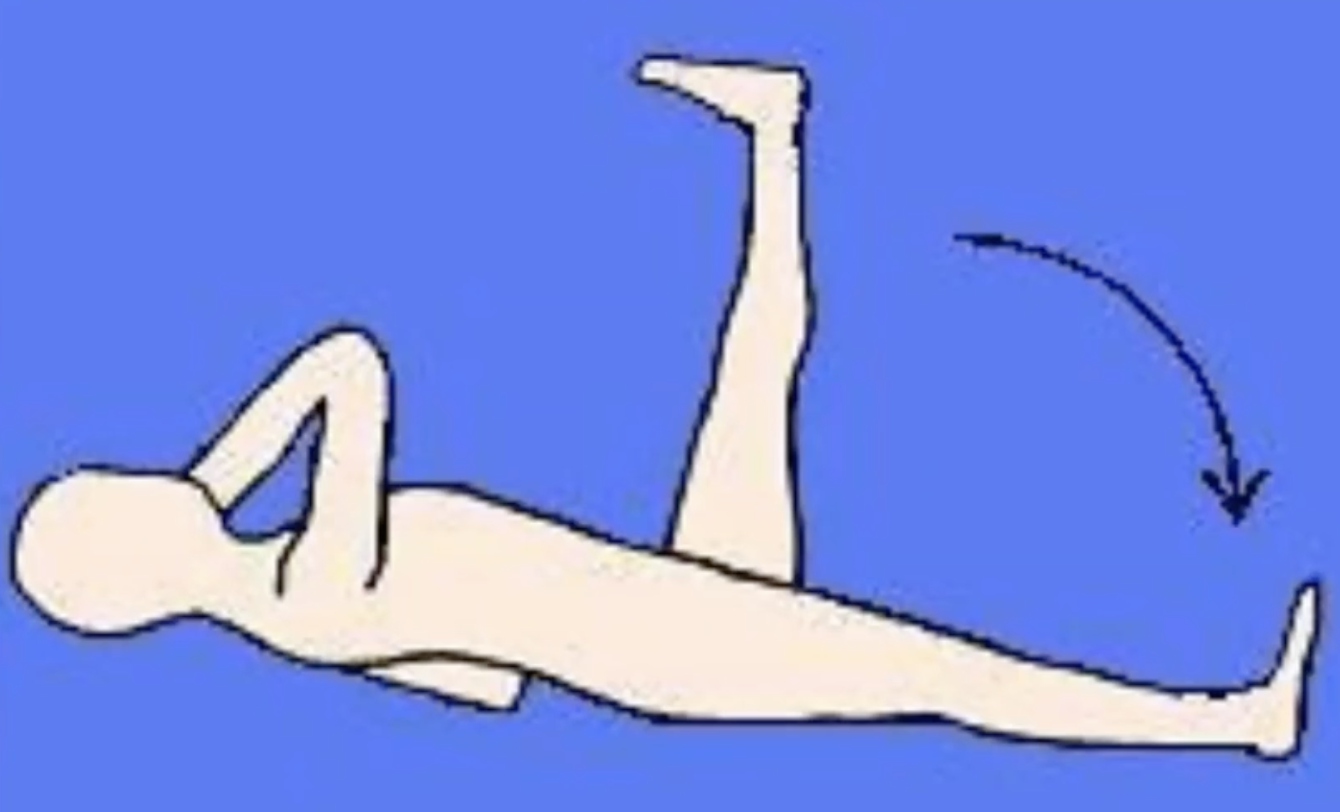
Buoyancy resisted
usually for Grade III strength
Centre of buoyancy
The point in a submerged body where buoyant forces act, helping to stabilize the body in water
If centre of buoyancy is in alignment with centre of gravity, there is no rotation force
If they are not in alignment, this causes rotation. Typically occurs when we are an asymmetrical shape underwater. To do with the amount of water displaced.
How would you change your centre of buoyancy, and why?
- Changing it by bringing a limb e.g. hand / arm out of the water while in box squat / supine
- Using it to challenge core stability
Drag
viscosity + turbulence
What influences drag?
- Created by pressure gradient behind moving objects in fluids
- With surface area and velocity of movements
Practical applications of drag
- To assist or resist movements
- Maintain posture against turbulence (isometric muscle activity & balance)
- Modifying surface area to increase drag
Differences between buoyancy and drag
Buoyancy:
- Upthrust force
- Dominant at lower speeds
Drag:
- In all directions
- Dominant at higher speeds
Screening for aquatic physio
- Cardiorespiratory conditions (no AMI within past 6/52)
Check with GP or respective specialist for stability of conditions:
- Respiratory
- Neurological
- Infections (no open wounds, gastroenteritis or faecal incontinence)
- Heat sensitive conditions (MS & chronic fatigue)
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Cancer / Immunocompromised
- Obesity (↑WOB from abdominal contents)
Examples of conditions referred to aquatic physiotherapy
- Musculoskeletal conditions e.g. hip/knee OA, LBP / postoperatively (orthopaedic surgery)
- Neurological conditions e.g. MS, PD, strokes, SCI, adult CP, GBS, post-polio syndrome
- Cardiorespiratory conditions e.g. COPD / heart failure
- Mental health e.g. depression & dementia
- Autism, breast cancer, muscular dystrophy or CRPS
- Labour related pain / obesity / post menopause
Halliwick style aquatic physiotherapy
- Initially, retraining breath holding underwater (may be lost in e.g. strokes)
- Progress to moving in single planes (e.g. weight shifts in box squat position)
- Progress to gliding in water (prone, supine or side-lying) to and from box squats
- Progress to gliding in multiple planes (note side-lying not terminal due to instability)