human anatomy unit 1-2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
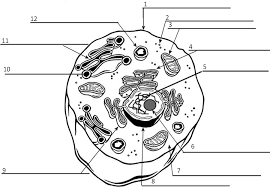
cytosol and organelles
what cytoplasm contains
2
New cards
plasma membrane
1
3
New cards
central dogma
DNA to RNA to protein
4
New cards
step one
nucleus stores DNA, making RNA copies and RNA moves to cytoplasm
5
New cards
step two
RNA read by ribosomes and makes protein
6
New cards
step three
golgi body modifies the protein and gives it a location to go to in the body
7
New cards
vesicles
storage for proteins that arent needed yet
8
New cards
lysosomes
break down protein into raw materials
9
New cards
where DNA is stored
Nucleus
10
New cards
what covers nucleus
nuclear membrane
11
New cards
nucleus
makes RNA copies
12
New cards
ribosomes
reads RNA and makes proteins
13
New cards
golgi body
modifies proteins and gives it a location to go to
14
New cards
peroxisome
removes toxins from cell
15
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes lipids (fat)
16
New cards
mitochondria
makes ATP
17
New cards
centriole
makes microtubules
18
New cards
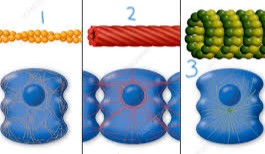
microtubules
pathway for organelles
19
New cards
microtubules
3
20
New cards
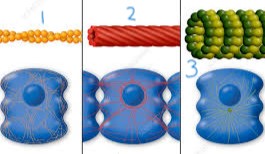
microfilament
gives cell its shape
21
New cards
microfilament
1
22
New cards
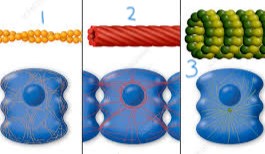
intermediate filament
has an anchoring point
23
New cards
intermediate filament
2
24
New cards
cilia
made of microtubules
25
New cards
phosphate head
hydrophilic
26
New cards
fatty tails
hydrophobic
27
New cards
phosphate head
a
28
New cards
peripheral proteins
messengers and anchoring points
29
New cards
integral proteins
acts as tunnel to let polar molecules pass
30
New cards
presence of glycocalyx molecules
help identify a cells self so it doesnt attack itself
31
New cards
glycocalyx
carbohydrate
32
New cards
cholestrol
keeps plasma membrane flexible
33
New cards
gradient
difference in concentration
34
New cards
passive transport
any movement in and out of the cell that doesnt require energy
35
New cards
simple diffusion
when O2 is higher in concentration on outside, it moves inward, passing the phospholipid bilayer, lowering the concentration outside
36
New cards
facilitated diffusion
needs channel protein to allow for polar molecules to pass through phospholipid bilayer
37
New cards
integrated protein+facilitated diffusion=
channel protein
38
New cards
osmosis
movement of water
39
New cards
low H2O=
more stuff
40
New cards
more H2O=
less stuff
41
New cards
carrier mediated active transport
integral protein takes ATP energy to move concentration from low to high
42
New cards
phagocytosis
bringing in solids
43
New cards
pinocytosis
bringing in liquids
44
New cards
tight junctions
creates seal between cells
45
New cards
desmosomes
prevents cells from ripping; helps cells move as a unit
46
New cards
gap junctions
molecules can pass from one cell to the next; quick communication